Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Communicable Diseases
Uploaded by
Wendy EscalanteCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Communicable Diseases
Uploaded by
Wendy EscalanteCopyright:
Available Formats
1 COMMUNICABLE DISEASE (ESCALANTE-SAAC)
COMMUNICABLE DISEASES
Con-communicable disease
HIV, Malaria, TB. Measles,
Diarrhea, Acute respi infection
Diarrhea, bronchitis, pneumonia,
influenza, HPN, TB, Malaria, Heart
disease, Cancer, Accidents, COPD
and other respi diseases
1. prevention of disease
2. prevention of disability and
death from infection
3. prevention through
immunization
Communicable disease
Direct
3 feet
Indirect, vehicle-borne, vector
borne and break into the
skin integrity
Vehicle-borne
Vector-borne
Break into the skin integrity
through inoculation
Infectious disease
Contagious disease
infectious
Communicable
Contagious
Infection
Host
Carrier
Contact
Isolation
Quarantine
Primary cause of mortality gap between rich and poor countries.
Account 50% of all the deaths worldwide estimated from 28million in 1990 to 50million in
2020
About 60% of deaths caused by communicable disease can be attributed to:
10 leading causes of morbidity and mortality:
Goals of WHO:
Disease caused by pathogenic microorganisms w/c can be transmitted from an infected
person to susceptible person by direct or indirect means or break in the skin.
Meaning it comes in contact with infected person or person-person transmission.
Droplets where microorganisms remain in the surface with limitation of its distance of at least
_ feet; face to face encounter with an individual.
Meaning from the source of infection to a new host with intermediary object through_
Non-living things such as water and fomites
Living things but non-human such as insects
Example: sharp needle and blood transfusions
Invasion of host from disease producing organism
Invasion an multiplication of microorganisms
Disease that easily spreads directly from one person to another
All communicable disease are_ because they are caused by microorganisms (MO) but not all
are contagious because not all of them are easily transmitted.
All infectious diseases are_ butt NOT all are contagious
All_ diseases are both communicable and infectious
Is the implantation and successful replication of an organism in the tissue of the host resulting
to signs and symptoms as well as immunologic responses
Is a person, animal or plant on which a parasite for its survival
Is an individual who harbors the organism and is capable of transmitting it to a susceptible
host without showing manifestation of the disease.
Is any person or animal who is in dose association with an infected person, animal or freshly
soiled material
Is the separation from other persons of an individual suffering from communicable disease
Is the limitation of freedom of movement of persons or animal which have been exposed to
communicable disease for a period of time equivalent to the longest incubation period of that
disease
Time interval between initial infection and 1srt appearance of s/sx
The production of microorganisms affects the patient wither by:
Incubation period
1. competing with hosts
metabolism
2. cellular damage produced by
the microbes
3.intracellular multiplication
1. some bacteria develop
Why microbes that cause infectious disease are so difficult to overcome?
resistance to antibiotics
2. some microbes such as
influenza have so many different
strains that a single vaccine
cannot protect against them
3. most viruses resist antiviral
drugs.
4.new infectious agents
occasionally arise such as HIV
and corona virus
5.some microbes localize in areas
of the body that make treatment
difficult
6.opportunistic organism can
cause infection in
immunocompromised patients
7.most people have not received
immunization
8.increased air travel can cause
the spread of the virulent
organism to a heavily populated
area in hours
9.use of biologic warfare and
bioterrorism with organisms such
as Anthrax and plague
10.the expanded use of
immunosuppressive agents and
invasive procedures increases
rick of infection
CLASSIFICATION OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES
A. Based of Occurrence of Disease
1.Sporadic Disease
Disease that occurs only occasionally and irregularly with no specific pattern ex. Botulism,
tetanus
2. Endemic Disease
Constantly present in a population, country or community usually involves few people during
specific periods. ex. PTB, Malaria, Schisto
2 COMMUNICABLE DISEASE (ESCALANTE-SAAC)
3. Epidemic Disease
Pt. acquire the disease in short period of time :diseases that occur in a grater number than
what is expected in a specific area over a specific time
4. Pandemic Diseases
Is an epidemic that affects several countries or continents, based on severity suration of
disease ex. HIV, SARS, Influenza
B. Based on severity or Duration of disease
1. Acute Disorder
Develops rapidly but lasts only a short tome ex. ,measles, mumps, influenza
2. Chronic Disease
Develops more slowly(insidious onset) disease likely to be continued ofr recurrent for long
periods ex. TTB, leprosy
3.Subacute Disease
Intermediate between acute and chronic ex. Baxterial endocarditis
4.Latent disease
Causative agent remains inactive for a time but then becomes active to produce symptoms of
the disease ex. Chicken pox-shingles(zoster), amoebaiasis
C. Based on state of host resistance
1. Primary Infection
Acute infection that causes the initial illness
2. Secondary Infection
One caused by opportunistic pathogen after primary infection has weakened the bodys
defenses
3. Subclinical (inapparent
Does not cause noticeable illness
Infection)
MICROBES against HUMAN
Symptoms
Subjective evidence of disease that is experienced or perceived subjective changes in the
body function noted by patient but not apparent to an observer
Signs
Objective evidence of a disease the physician can observe and measure
Syndrome
A specific group of signs and symptoms that accompany a particular disease
Incidence
The number of people in a population who develop a disease during a particular time period
Prevalence
The number of people in a population who develop a disease, regardless of when it appeared,
refers to both old and new cases
EPIDEMIOLOGIC TRIAD OF A DISEASE
Epidemiologic triad of a disease
Is a model that scientists have developed for studying health problems
1.Host
2.Agent
3.Environment
Host
A man or an animal where is susceptible (degree of resistance) is constructed
Patient, carrier, suspect, contact
4 types of hosts
Age, heredity, level of stress,
Host factors that increase risk of infection
nutritional status, current medical
therapy, pre-existing disease
process, immunization status
Agent
Cause of disease, pertains to MO that causes greatest but cant be seen to naked eye
1.Bacteria
Agents
2.Virus
3.Fungi
Bacteria
Single-celled organisms with double cll membranes that protect from harm. They reproduce
rapidly and are considered as the most cause of fatal infectious disease
Virus
Self-limiting, have time frame if not treated, complication ensues
Fungi
Like plants, made up of many cells, they thrive inside or outside the body and may be harmful
of and beneficial, cannot produce their ow food
Environment
Virulence
Strength and power of the MO to cause infection
Pathogenicity
Capable of the MO to cause infection
Infection
Virulence + pathogenicity=?
Environment
Should be conducive and favorable to growth and multiplication of MO
CHAIN OF INFECTION
1. Pathogenic MO
-the chain begins with the existence of a specific pathogenic microorganism
2. Reservoir
-2nd link, an environment where the pathogen can survive
3. Portal of escape
-3rd link
4. MOT
-4th link, from the reservoir to the host
5. Portal of entry
-5th link, into the host
6 Host Susceptibility
-last link
1. Pathogen or causative agent
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Degenerative Joint DiseaseDocument35 pagesDegenerative Joint DiseaseWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals in NursingDocument9 pagesFundamentals in NursingWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Nclex TipsDocument93 pagesNclex TipsAmiel Francisco Reyes86% (7)
- DR Jaban Moore How Do I Know If I Have ParasitesDocument9 pagesDR Jaban Moore How Do I Know If I Have ParasitesViolet VioletNo ratings yet
- NCP 2 MiDocument16 pagesNCP 2 MiWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
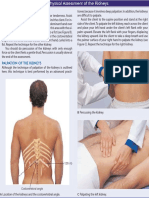
- Assessment of Kidneys PDFDocument1 pageAssessment of Kidneys PDFWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Nasogastric Tube Management and CareDocument21 pagesNasogastric Tube Management and CareWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Caring For The Bedridden PatientDocument1 pageCaring For The Bedridden PatientWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- PATHODocument2 pagesPATHOWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Acid-Ash DietDocument10 pagesAcid-Ash DietWendy Escalante0% (1)
- Modifiable Risk Factors Non - Modifiable Risk Factors: LegendDocument2 pagesModifiable Risk Factors Non - Modifiable Risk Factors: LegendWendy Escalante100% (1)
- Concept Map of Carotid Artery DiseaseDocument2 pagesConcept Map of Carotid Artery DiseaseWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Brat DietDocument8 pagesBrat DietWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
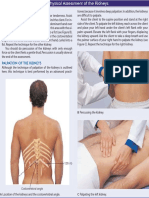
- Assessment of KidneysDocument1 pageAssessment of KidneysWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- 02 Orig Art 02 PDFDocument3 pages02 Orig Art 02 PDFWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- At DietDocument8 pagesAt DietWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FinalDocument8 pagesDrug Study FinalWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Concept Map of CKD Gastrointestinal SymptomsDocument4 pagesConcept Map of CKD Gastrointestinal SymptomsWendy Escalante0% (1)
- Case Presentation: Group 2Document30 pagesCase Presentation: Group 2Wendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Pediatric NursingDocument16 pagesPediatric NursingWendy Escalante100% (1)
- Diabetes MellitusDocument5 pagesDiabetes MellitusWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic DietDocument3 pagesTherapeutic DietWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- FNCP CommunityDocument4 pagesFNCP CommunityWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- DM Report1Document16 pagesDM Report1Wendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care For Patient With Neurological DiseaseDocument8 pagesNursing Care For Patient With Neurological DiseaseWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- Integrated Management of Childhood Illness: Sick Child Age 2 Months Up To 5 YearsDocument78 pagesIntegrated Management of Childhood Illness: Sick Child Age 2 Months Up To 5 YearsWendy EscalanteNo ratings yet
- US Army Medical Course MD0856-200 - BacteriologyDocument267 pagesUS Army Medical Course MD0856-200 - BacteriologyGeorges100% (2)
- Spirochetes and Curved RodsDocument54 pagesSpirochetes and Curved RodsDegee O. GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Nurses Compliance Towards Infection Control Practices at Sulu Sanitarium and General HospitalDocument12 pagesNurses Compliance Towards Infection Control Practices at Sulu Sanitarium and General HospitalJournal of Interdisciplinary PerspectivesNo ratings yet
- Health: Every Human Being Is The Author of His Own Health or Disease. BuddhaDocument18 pagesHealth: Every Human Being Is The Author of His Own Health or Disease. BuddhaAdrian PușcașuNo ratings yet
- H18 A3 PDFDocument52 pagesH18 A3 PDFJenny Rosali0% (1)
- J Annemergmed 2017 01 018Document14 pagesJ Annemergmed 2017 01 018Jorge BarriosNo ratings yet
- Infections of SpineDocument64 pagesInfections of Spineefancoolhand09100% (2)
- Golden Age MIcrobiologyDocument3 pagesGolden Age MIcrobiologyBecca TayNo ratings yet
- Bag Technique: Ms. Gincy JosephDocument23 pagesBag Technique: Ms. Gincy JosephNeethu Vincent67% (3)
- Icha 1Document5 pagesIcha 1kadek ayu ichaNo ratings yet
- April Newsletter 2006Document17 pagesApril Newsletter 2006api-3802004No ratings yet
- Nadja Durbach - Bodily Matters - The Anti-Vaccination Movement in England, 1853-1907 - SeminarDocument294 pagesNadja Durbach - Bodily Matters - The Anti-Vaccination Movement in England, 1853-1907 - SeminarMatthew ParnellNo ratings yet
- Arero Hospital Patient Death ProtocolDocument9 pagesArero Hospital Patient Death Protocolsami ketemaNo ratings yet
- Infection ControlDocument12 pagesInfection ControlJules FillyNo ratings yet
- Remsik 2021Document12 pagesRemsik 2021MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Diseases Parasites and Predators Management and ControlDocument7 pagesDiseases Parasites and Predators Management and ControlGeorge AtaherNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper Mice EventsDocument9 pagesReaction Paper Mice EventsAca DemiceNo ratings yet
- Slide Pediatric TuberculosisDocument112 pagesSlide Pediatric TuberculosisFenny RahmadaniNo ratings yet
- Vax ScriptDocument3 pagesVax ScriptJae Xyrille GarcisoNo ratings yet
- Mumps Frequently Asked Questions - NICDDocument2 pagesMumps Frequently Asked Questions - NICDGreg WrightNo ratings yet
- General Properties of VirusesDocument93 pagesGeneral Properties of VirusesSeena SamNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Microbiology and ParasitologyDocument13 pagesReviewer in Microbiology and ParasitologyCharlot Navarro100% (2)
- Thacker - The Shadows of Atheology - Epidemics, Power and Life After FoucaultDocument19 pagesThacker - The Shadows of Atheology - Epidemics, Power and Life After FoucaultAmbaejo96No ratings yet
- New PMDC Neb Format 2011Document28 pagesNew PMDC Neb Format 2011AliHazratNo ratings yet
- 8 Human Health N Disease-NotesDocument5 pages8 Human Health N Disease-NotesAnanth DharanidharanNo ratings yet
- FUNDA Handouts!Document18 pagesFUNDA Handouts!Anthoinete AlbaNo ratings yet
- AM - ICD-10-AM GuideDocument26 pagesAM - ICD-10-AM GuidedrrskhanNo ratings yet
- Submitted By: Group 6 MT 3BDocument49 pagesSubmitted By: Group 6 MT 3BChristine Joy TanglaoNo ratings yet