Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cardiovascular Activities
Uploaded by
Juan RuizOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cardiovascular Activities
Uploaded by
Juan RuizCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 3 Cardiovascular system -
______________________________________
3 E.S.O.
1) What are the 3 types of blood vessels?
2) What is the main difference between arteries and veins?
3) Complete the table:
ARTERIES
VEINS
Type of blood
Direction
Valves
Elastic wall
4) Mark which ones of these are Functions of Circulatory System
A. Transports nutrients
B. Transports gases
C. Transports wastes
D. Transports hormones
E. Maintain balance of fluids
F. Protection from disease
G. Regulate body temperature
H. Blood clotting
5) Find the word:
A. ________________from the heart out, large to small, flexible, collect cholesterol
B. ______________into the heart, small to large, valves to prevent backflow
C. ______________from arteries to veins, one cell wide, responsible for the exchange of
blood gases
6) What is the difference between the right and the left parts of our heart?
7) Choose terms from the list to complete the sentences below.
atria; right hand side; vena cava; ventricles; atrioventricular valves; pacemaker;
pulmonary artery; veins; arteries; left hand side; aorta, coronary artery;
The top two chambers of the heart are called......................
These structures stop blood flowing backwards into the atria.
This side of the heart receives oxygenated blood.
This is the largest artery in the body.
These are blood vessels that carry blood towards the heart.
This structure sets the speed of the heart beats.
This blood vessel supplies the heart muscle with oxygenated blood.
Unit 3 Cardiovascular system -
8) Find the word:
______________________________________
3 E.S.O.
blood cells which help with blood clotting.
a substance that attracts and holds onto oxygen molecules; it contains iron and
is found in the red blood cells
an area of the heart that regulates or signals the beating of the heart
yellowish fluid that makes up more than 50% the volume of blood; it contains
nutrients, hormones, and minerals and is about 90% water
one of two lower chambers of the heart
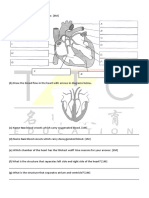
9) Label
the
structures
that
you
recognize
in
the
diagram
below.
On the diagram of the heart shown above indicate the direction of blood flow through
the heart. Use red to show the pathway of oxygen-rich blood and blue the pathway of
oxygen-poor blood.
10) Complete
Pulmonary Circuit
The pulmonary circuit pumps blood from the heart to the ___________ and back to the
heart.
What heart chamber pumps blood in this circuit?
Into what artery?
What chamber receives blood from the pulmonary circuit?
Through what vein(s)?
Unit 3 Cardiovascular system -
______________________________________
3 E.S.O.
11) Systemic Circuit
Answer the same questions as in the previous activity but related to the Systemic circuit.
12)
Which diagram shows the human double circulatory system?
13) The bar chart compares the percentage of oxygen carried by red blood cells entering
and leaving a relaxed muscle. On the bar chart, 100% is the amount of oxygen carried by
red blood cells as they leave the lungs.
How much oxygen would red blood cells be likely to carry when leaving the same muscle
aftercontraction?
A 40 % B 60 % C 90 % D 100 %
Unit 3 Cardiovascular system -
14)
______________________________________
The diagram shows the heart as seen from the front.
3 E.S.O.
Which section shows the heart cut through line P-Q?
15)
Which blood vessel, if it becomes blocked, could lead directly to a heart attack?
(a) coronary artery
(b) pulmonary artery
(c) pulmonary vein
(d) vena cava
16)
Which substances are dissolved in human blood plasma?
A. carbon dioxide, haemoglobin and glucose
B. carbon dioxide, oxygen and haemoglobin
C. glucose, hormones and urea
4
Unit 3 Cardiovascular system -
______________________________________
3 E.S.O.
D. oxygen, urea and starch
17)
What is the characteristic feature of a double circulation?
A In each circuit, blood passes from the gut to the liver before going back to the heart.
B In each circuit, blood passes from the heart to the lungs and then back to the heart before
going to other parts of the body.
C In each circuit, blood passes through atria and ventricles before going to other parts of the
body.
D In each circuit, blood passes through the arteries and the capillaries before returning to the
heart in veins.
18)
(a) Fig. 2.1 shows a section through the heart.
(i) Table 2.1 lists functions of parts of the heart and associated blood vessels. Complete the
table by identifying which structure, A to H, carries out each of the following functions.
(ii) Describe the function of structure V
(b) A persons pulse rate rises as they run a race.
(i) Explain why the pulse rate rises during the race
(ii) Describe how you could measure the pulse rate of a person
Unit 3 Cardiovascular system -
19)
______________________________________
3 E.S.O.
- Fig. 8.1 shows a section through the heart.
(a) (i) Name the two blood vessels, shown on Fig. 8.1, that carry oxygenated blood.
(ii) State the letter that identifies the tricuspid valve. [1]
(iii) State a letter that identifies a semilunar valve. [1]
(b) Describe how the heart forces blood into the aorta.
(b) (i) Name the blood vessel that delivers blood to the muscles of the walls
20)
Fig. 3.1 shows an external view of the heart.
(a) A blood clot is stuck at X. Explain what will happen to the heart muscle cells in the
shaded area on Fig. 3.1.
(b) List three actions people can take to reduce the risk of having a blood clot in the
coronary arteries.
Unit 3 Cardiovascular system -
21)
______________________________________
3 E.S.O.
Fig. 7.1 shows a section through the heart.
(a)
Fig 7.1
(i) Identify the blood vessels X and Y.
X
Y
(ii) What is the function of the valves within the heart?
(iii) Explain why the wall of the left ventricle is thicker than the wall of the right ventricle.
Unit 3 Cardiovascular system -
______________________________________
3 E.S.O.
Find the circulatory
system words below
in the grid to the left.
1
2
3
6
7
10
11
12
13
14
15
Across
Down
3. The place where nutrients enter the blood.
1. The heart ___________ blood.
7. The pump in the circulatory system.
2. The heart, blood, and vessels.
8. A small vessel that connects veins and
arteries.
4. Blood in arteries is ____________ red
because it is rich in oxygen.
10. The circulatory system ___________
nutrients, gases, liquids, and heat around the
body.
5. The largest artery in the body.
11. The circulatory system transports this,
which helps regulate temperature.
12. The liquid in the circulatory system.
6. A waste gas that is transported in veins
from the body to the lungs via the heart.
9. A vessel that moves blood away from the
heart.
13. The place where oxygen enters the blood
and carbon dioxide leaves the blood.
14. A vessel that moves blood to the heart.
15. A gas that is transported in arteries from
the lungs to the rest of the body via the heart.
2006 www.bogglesworldesl.com
You might also like
- How The Brain Works - DK PDFDocument224 pagesHow The Brain Works - DK PDFHai Quang Ha95% (38)
- Introduction to the Circulatory SystemDocument27 pagesIntroduction to the Circulatory SystemPapiNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System Revision WorksheetDocument4 pagesCirculatory System Revision WorksheetPoulomi Sengupta100% (1)
- Medical Terms PDFDocument204 pagesMedical Terms PDFrengachen89% (9)
- Disease and DefenceDocument5 pagesDisease and DefenceNabindra Ruwali100% (1)
- Fundamental Principles of Human Anatomy & Physiology: July 2016Document41 pagesFundamental Principles of Human Anatomy & Physiology: July 2016mabel yapuraNo ratings yet
- 3j Cuci - The Circulatory System WorksheetDocument6 pages3j Cuci - The Circulatory System Worksheetcharmaine nwankwoNo ratings yet
- I. Attachments Worksheets Worksheet 1 How Does Blood Flow in My Body?Document8 pagesI. Attachments Worksheets Worksheet 1 How Does Blood Flow in My Body?elizalde100% (1)
- The Heart and Circulation ReviewDocument4 pagesThe Heart and Circulation ReviewRona Carta OñateNo ratings yet
- Exploring Anatomy Circulatory System WorksheetDocument4 pagesExploring Anatomy Circulatory System WorksheetBrian MartinezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Transport in Mammals - WorksheetDocument5 pagesChapter 8 Transport in Mammals - Worksheetapi-3728508100% (2)
- 8384 ST PDFDocument20 pages8384 ST PDFJohn Dave Francisco100% (1)
- Science Class 8 Topic: Respiration and Circulation Reinforcement WorksheetDocument7 pagesScience Class 8 Topic: Respiration and Circulation Reinforcement WorksheetNuzhat Ibrahim100% (1)
- Answer Key Circulatory System QuizDocument6 pagesAnswer Key Circulatory System Quizapi-534129744No ratings yet
- Physiology SyllabusDocument11 pagesPhysiology SyllabusBarney Cordova100% (1)
- The Digestive System LabelDocument3 pagesThe Digestive System LabelUSMP FN ARCHIVOSNo ratings yet
- Table e - Liver Anatomy Biliary SystemDocument11 pagesTable e - Liver Anatomy Biliary Systemapi-371971600No ratings yet
- Ib Biology Topic 9 - Plant Biology HL Revision Sheet: © David Faure, InthinkingDocument1 pageIb Biology Topic 9 - Plant Biology HL Revision Sheet: © David Faure, InthinkingMarwan PharaonNo ratings yet
- Dystocia in Mare: - By: Dr. Dhiren BhoiDocument50 pagesDystocia in Mare: - By: Dr. Dhiren BhoidrdhirenvetNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System QuizDocument2 pagesCirculatory System Quizapi-281108263No ratings yet
- Amoebiasis Case PresentationDocument28 pagesAmoebiasis Case Presentationjan micah100% (1)
- Cytopathology of Neuroendocrine Neoplasia - Color Atlas and TextDocument411 pagesCytopathology of Neuroendocrine Neoplasia - Color Atlas and TextIsabella CrăciunNo ratings yet
- Organisation Revision Booklet Part 2Document32 pagesOrganisation Revision Booklet Part 2Elliot KilroyNo ratings yet
- CK-12 Biology Chapter 23 Worksheets[1]Document32 pagesCK-12 Biology Chapter 23 Worksheets[1]maleskunNo ratings yet
- QOch 11 Studyguide QODocument16 pagesQOch 11 Studyguide QOHenry HoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument40 pagesCardiovascular SystemDouglas Jacques100% (1)
- Unlock SGCh13Document10 pagesUnlock SGCh13SilaxNo ratings yet
- The circulatory system in 30 secondsDocument11 pagesThe circulatory system in 30 secondsRentika SiahaanNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System IntroductionDocument3 pagesCardiovascular System IntroductionMartina KlanjcicNo ratings yet
- 6.2 Blood System Exam Styled Formative AssessmentDocument5 pages6.2 Blood System Exam Styled Formative AssessmentYeshake FranceschiNo ratings yet
- HSB Week 12Document2 pagesHSB Week 12edhanassarNo ratings yet
- TRANSPORT IN HUMANS AND ANIMALSDocument9 pagesTRANSPORT IN HUMANS AND ANIMALSBF CLNo ratings yet
- Circulation WorksheetDocument6 pagesCirculation WorksheetKukresh TanveeraNo ratings yet
- Body FluidsDocument39 pagesBody FluidsSANSKRITI 3928No ratings yet
- Transport in AnimalsDocument5 pagesTransport in Animals29seolaiscooltbhNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Lab WorksheetDocument5 pagesCardiovascular System Lab WorksheetJan Russel TevesNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science 6 Lesson 1.1Document4 pagesLesson Plan in Science 6 Lesson 1.1Jean Saberola GarboNo ratings yet
- HeartstructurewsDocument2 pagesHeartstructurewsChaturbhuj AgrawalNo ratings yet
- WS On Circulatory System PDFDocument5 pagesWS On Circulatory System PDFthe lillyNo ratings yet
- F3 C3 Human Blood Circulatory System ExerciseDocument3 pagesF3 C3 Human Blood Circulatory System ExerciseCharvini SreeNo ratings yet
- Ha June 5 2009 Sbi3u - WebDocument4 pagesHa June 5 2009 Sbi3u - Webrico0903No ratings yet
- Tyler Lynch - CirculationDocument2 pagesTyler Lynch - CirculationTyler LynchNo ratings yet
- Exercise Y5 SC SK (Unit 2)Document5 pagesExercise Y5 SC SK (Unit 2)胡佳玲No ratings yet
- CirculationDocument5 pagesCirculationPoonam MishraNo ratings yet
- CSEC Science - Blood Circulatory System WorksheetDocument2 pagesCSEC Science - Blood Circulatory System WorksheetC ROBERTSNo ratings yet
- תרגול עצבים לב ונשימהDocument15 pagesתרגול עצבים לב ונשימהdodbenNo ratings yet
- Transport System in HumanDocument7 pagesTransport System in HumanMSMohanaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesCirculatory System Lesson Planhafeez ahmedNo ratings yet
- Cicrulatory and Immune Workbook KEYDocument32 pagesCicrulatory and Immune Workbook KEYgeorgia robinsonNo ratings yet
- Week 2 In-Video Quiz Questions and AnswersDocument5 pagesWeek 2 In-Video Quiz Questions and AnswersErjus HoxhajNo ratings yet
- Module Question Chapter TransportDocument16 pagesModule Question Chapter TransportMardz ArayusofNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument2 pagesIntroductionEMAXE GAMINGNo ratings yet
- Complete - SLASh - Science9 - Week 1 and 2Document5 pagesComplete - SLASh - Science9 - Week 1 and 2Creative ImpressionsNo ratings yet
- Biology C - Lesson 1 - Circulatory SystemDocument46 pagesBiology C - Lesson 1 - Circulatory SystemMuhammad Azrie0% (1)
- Document 7Document6 pagesDocument 7stelrax21No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Lecture - NotesDocument23 pagesCardiovascular System Lecture - NotesParker KapembwaNo ratings yet
- Ugi-3 (Nut 2101) - F2021Document9 pagesUgi-3 (Nut 2101) - F2021Andrew DarnelNo ratings yet
- Anp2001 Test 1 Questions 2014Document7 pagesAnp2001 Test 1 Questions 2014Jerilee SoCute WattsNo ratings yet
- Chevannese Ellis - Circ Class WorkDocument3 pagesChevannese Ellis - Circ Class WorkChevannese EllisNo ratings yet
- This Question Paper Consists of 3 Sections and Answer All QuestionsDocument12 pagesThis Question Paper Consists of 3 Sections and Answer All QuestionsKhusyairy Daeng Sailendra0% (1)
- Circulatory System WorksheetDocument3 pagesCirculatory System WorksheetMichael KhanNo ratings yet
- Blood Circulatory SystemDocument1 pageBlood Circulatory SystemshakirasweetstuffNo ratings yet
- Biology Mock Paper QuestionsDocument3 pagesBiology Mock Paper QuestionsANo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels: I. Overview of Blood Vessel Structure and FunctionDocument7 pagesThe Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels: I. Overview of Blood Vessel Structure and FunctionAdam ButterworthNo ratings yet
- QP Circulatory SystemDocument9 pagesQP Circulatory SystemelizabethNo ratings yet
- Blood Circulation and AnswersDocument2 pagesBlood Circulation and AnswersAyush SinghNo ratings yet
- Bio Revision Exercise - Answer KeyDocument11 pagesBio Revision Exercise - Answer Keynmhk89100% (1)
- Circulation Notes I To VIDocument8 pagesCirculation Notes I To VIStacey KwiatkowskiNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument10 pagesCardiovascular SystemDhea BugnaNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System: Assessments for LessonsDocument14 pagesThe Circulatory System: Assessments for LessonsCarolyn D MayugaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Unit Circulatory System AICLEDocument9 pagesTeaching Unit Circulatory System AICLEJuan RuizNo ratings yet
- Sheep Heart DissectionDocument3 pagesSheep Heart DissectionJuan RuizNo ratings yet
- Teaching Unit Circulatory System AICLEDocument5 pagesTeaching Unit Circulatory System AICLEJuan RuizNo ratings yet
- Teaching Unit Circulatory System AICLEDocument5 pagesTeaching Unit Circulatory System AICLEJuan RuizNo ratings yet
- HEART WORKSHEETanswers FernandoDocument10 pagesHEART WORKSHEETanswers FernandoJuan RuizNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System UnitDocument12 pagesCirculatory System UnitJuan RuizNo ratings yet
- Teaching Unit Circulatory System AICLEDocument5 pagesTeaching Unit Circulatory System AICLEJuan RuizNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System UnitDocument12 pagesCirculatory System UnitJuan RuizNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System UnitDocument12 pagesCirculatory System UnitJuan RuizNo ratings yet
- SecretionDocument27 pagesSecretionAlfi Oktafani100% (1)
- DentinDocument89 pagesDentinDr Zadeno kithanNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 - 1st Monthly Exams - ScienceDocument23 pagesGrade 8 - 1st Monthly Exams - ScienceInah MasubayNo ratings yet
- Harrison's Review - Chapter 65 Bleeding and ThrombosisDocument2 pagesHarrison's Review - Chapter 65 Bleeding and ThrombosisJason CentenoNo ratings yet
- Self CareDocument27 pagesSelf CareJessa May RapadasNo ratings yet
- Medical Terminology For Dummies Cheat SheetDocument5 pagesMedical Terminology For Dummies Cheat SheetSir SuneNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound Diagnosis of Pelvic TuberculosisDocument58 pagesUltrasound Diagnosis of Pelvic TuberculosischandranNo ratings yet
- 1999-Identification and Function of The Centrosome CentromatrixDocument10 pages1999-Identification and Function of The Centrosome CentromatrixyicinenNo ratings yet
- Cellulite Types by Location: Superficial Spaces of the Head and NeckDocument30 pagesCellulite Types by Location: Superficial Spaces of the Head and NeckLUNo ratings yet
- Antibody Structure and Function PDFDocument8 pagesAntibody Structure and Function PDFJay JaswaniNo ratings yet
- Immunology Mid-ExamDocument11 pagesImmunology Mid-ExamNgMinhHaiNo ratings yet
- 6 Esr BT CTDocument9 pages6 Esr BT CTdlerNo ratings yet
- Fisiologi Sistem Saraf TepiDocument19 pagesFisiologi Sistem Saraf TepiNata NayottamaNo ratings yet
- Science Chapter 2 Form 4Document16 pagesScience Chapter 2 Form 4Muhammad Akmal Kamaluddin75% (4)
- Year 4 Reading Your Digestive SystemDocument11 pagesYear 4 Reading Your Digestive SystemMa Donabel LopezNo ratings yet
- RADIOLOGY ASPECT OF EXTRA PULMONARY TUBERCULOSISDocument45 pagesRADIOLOGY ASPECT OF EXTRA PULMONARY TUBERCULOSISAndre F SusantioNo ratings yet
- Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology (FNAC) of GISTDocument7 pagesFine Needle Aspiration Cytology (FNAC) of GISTurfriendanshul100% (1)
- Foetal Membrane and Amniotic Fluid FunctionsDocument10 pagesFoetal Membrane and Amniotic Fluid FunctionsN. SivaNo ratings yet























![CK-12 Biology Chapter 23 Worksheets[1]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/722153728/149x198/67101ec154/1712856288?v=1)