Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DRUG STUDY - Calcium Gluconate
Uploaded by
Siergs Smith GervacioCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DRUG STUDY - Calcium Gluconate
Uploaded by
Siergs Smith GervacioCopyright:
Available Formats
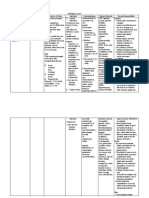
Patients Name:
Sex:
Name of Drug
Generic Name:
Calcium Gluconate
Brand Name:
Apo-Cal
Calci-Chew
Calcarb
Patients Dose:
1000 mg PO
Classification
Pharmacologic:
Mineral Supplements
Therapeutic:
Mineral and Electrolyte
Replacements
Diagnosis:
Age:
Date of Admission:
Height/Weight:
Mechanism of Action
Action:
Essential for nervous, muscular, and skeletal
systems. Maintain cell membrane and
capillary permeability. Act as an activator in
the transmission of nerve impulses and
contraction of cardiac, skeletal, and smooth
muscle. Essential for bone formation and
blood coagulation.
Pharmacokinetics:
ROUTE
PO
IV
ONSET
Unknown
Immediate
PEAK
Unknown
Immediate
DURATION
Unknown
0.5-2 hr
Indication
General:
Treatment and
prevention of
hypocalcemia.
Adjunct in the
prevention of
postmenopausal
osteoporosis.
Patients Indication:
Treatment and
prevention of
hypocalcemia.
Maximum Dose:
2000 mg PO
Absorption: Absorption in the GI tract
requires vitamin D.
Minimum Dose:
500 mg PO
Distribution: Readily enters extracellular
fluid. Crosses the placenta and enters breast
milk.
Metabolism & Excretion: Excreted mostly in
the feces; 20% eliminated by the kidneys.
Availability:
Tablets
Injection
Pregnancy Category:
Category C
Source:
Deglin, J. (2011) Daviss
Drug Guide for Nurses (12th
ed.) Philadelphia, FA Davis
Company pp.265-269
Half-life: Unknown.
Source:
Deglin, J. (2011) Daviss Drug Guide for
Nurses (12th ed.) Philadelphia, FA Davis
Company pp.265-269
Side Effects
CNS: syncope (IV only),
tingling.
CV: CARDIAC ARREST
(IV only), arrhythmias,
bradycardia.
F and E: hypercalcemia.
Precautions:
Patients receiving
digitalis glycosides;
Severe respiratory
insufficiency; Renal
disease;
Cardiac disease; OB:
Hypercalcemia mayqrisk
of maternal and fetal
complications; Lactation:
Breast
feeding not expected to
harm infant provided that
serum
calcium levels monitored.
GI: constipation, diarrhea
(oral solution
only), nausea, vomiting.
Source:
Deglin, J. (2011)
Daviss Drug Guide for
Nurses (12th ed.)
Philadelphia, FA Davis
Company pp.265-269
Source:
Deglin, J. (2011) Daviss
Drug Guide for Nurses
(12th ed.) Philadelphia, FA
Davis Company pp.265269
Nursing Responsibilities
Before:
Local: phlebitis (IV only).
After:
Source:
Deglin, J. (2011) Daviss
Drug Guide for Nurses
(12th ed.) Philadelphia, FA
Davis Company pp.265269
Verify doctors order
Ask for drug allergies
Assess for apical pulse for 1 full
minute before administering.
Observe the 10Rs of drug
administration
Administer the prescribed dosage
During:
GU: calculi,
hypercalciuria.
Drug Interactions:
Hypercalcemiaqthe risk
of digoxin
toxicity. Chronic use with
antacids in renal
insufficiency
may lead to milk-alkali
syndrome. Calcium
supplements, including
calcium-containing
antacids,
mayqrisk of
hypercalcemia
Route:
PO
IV
Source:
Deglin, J. (2011)
Daviss Drug Guide
for Nurses (12th ed.)
Philadelphia, FA
Davis Company
pp.265-269
Contraindication
Hypercalcemia; Renal
calculi;
Ventricular fibrillation;
Concurrent use of
calcium
supplements (calcium
acetate).
Follow oral doses with a full glass
of water
Tablets can be crushed
Do not administer concurrently
with foods containing large
amounts of oxalic acid (spinach,
rhubarb), phytic acid (brans,
cereals), or phosphorus (milk or
dairy products)
Administer on an empty stomach
before meals to optimize
effectiveness
Do not take within 12 hr of other
medications if possible.
Advise patient that calcium
carbonate may cause constipation.
Review methods of preventing
constipation (increasing bulk in
diet, increasing fluid intake,
increasing mobility) and using
laxatives. Encourage patients to
maintain a diet adequate in
vitamin D
Advise patient to notify health
care professional promptly if
signs and symptoms of
hypercalcemia (constipation,
anorexia, nausea, vomiting,
confusion, stupor) occur.
Documentation
Source:
Deglin, J. (2011) Daviss Drug Guide for
Nurses (12th ed.) Philadelphia, FA Davis
Company pp.265-269
You might also like
- Calcium GluconateDocument2 pagesCalcium GluconateMae Ann Bueno Castillon100% (1)
- Calcium Gluconate Drug StudyDocument1 pageCalcium Gluconate Drug StudyKrissy Java79% (14)
- Calcium Gluconate Drug SummDocument1 pageCalcium Gluconate Drug SummWarren100% (2)
- MisoprostolDocument5 pagesMisoprostolkristenerika100% (2)
- Promethazine HCLDocument2 pagesPromethazine HCLIvanne Hisoler100% (8)
- LabetalolDocument3 pagesLabetalolTri Purma Sari50% (2)
- Chlorthalidone HygrotonDocument2 pagesChlorthalidone HygrotonLIEZEL GRACE VELAYONo ratings yet
- NifedipineDocument1 pageNifedipinetaekado50% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument15 pagesDrug StudyLene Derlene Gerona100% (2)
- Drug Study On CARBOPROSTDocument4 pagesDrug Study On CARBOPROSTshadow gonzalez100% (1)
- Calcium Gluconate Drug StudyDocument2 pagesCalcium Gluconate Drug StudyErika ManubayNo ratings yet
- Ferrous Sulfate: o o o o o o oDocument5 pagesFerrous Sulfate: o o o o o o oLelanie Japitana100% (1)
- Magnesium SulfateDocument1 pageMagnesium SulfateTrixie Anne Gamotin100% (1)
- Fentanyl Citrate Drug StudyDocument1 pageFentanyl Citrate Drug StudyArthur Christopher CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyGladz Talla-ReyesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studysnowyfingers100% (2)
- Vitamin DDocument2 pagesVitamin DAdrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Methergine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMethergine Drug StudycuakialyannaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - DobutamineDocument3 pagesDRUG STUDY - DobutamineAjon Veloso75% (4)
- FurosemideDocument2 pagesFurosemideIvanne HisolerNo ratings yet
- Nifedipine Drug StudyDocument3 pagesNifedipine Drug StudyCrystal Queen MarquezNo ratings yet
- Hydralazine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesHydralazine Drug StudyErika Robella100% (1)
- Calcium Gluconate Drug StudyDocument1 pageCalcium Gluconate Drug StudyMichael Baylon DueñasNo ratings yet
- Patient M. G Drug 1 - Ob MaxDocument5 pagesPatient M. G Drug 1 - Ob MaxGrace MellaineNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Calcium GluconateDocument1 pageDrug Study - Calcium GluconatemikErlhNo ratings yet
- Atenolol Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComDocument3 pagesAtenolol Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComYuuki Chitose (tai-kun)No ratings yet
- DR Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDR Drug Studyslashmortred100% (5)
- Drug Study OxytocinDocument1 pageDrug Study OxytocinGil GanibanNo ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconate Drug StudyDocument1 pageCalcium Gluconate Drug StudyChaepmunk Cy75% (4)
- EsmololDocument3 pagesEsmololTri Purma SariNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AmpicillinDocument6 pagesDrug Study AmpicillinDgjj Compuiter100% (1)
- ErythromycinDocument6 pagesErythromycinkitsilcNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyAbie Jewel Joy Roque100% (1)
- Drug Study (Ferrous Sulfate)Document5 pagesDrug Study (Ferrous Sulfate)JM80% (10)
- Drug Study 1 Ferrous SulfateDocument2 pagesDrug Study 1 Ferrous SulfateKrizzia Mae ColladoNo ratings yet
- Vitamin KDocument7 pagesVitamin KYou know whoNo ratings yet
- Methyldopa Drug StudyDocument1 pageMethyldopa Drug Studychinchin ramosNo ratings yet
- NitroglycerinDocument3 pagesNitroglycerinFreisanChenMandumotanNo ratings yet
- 11111a - CarbetocinDocument3 pages11111a - Carbetocinhahahahaaaaaaa0% (2)
- CalciumDocument1 pageCalciumRhika Mae Flores ValdezNo ratings yet
- Brand Name: Dilzem Generic Name: Diltiazem Indications: Angina Pectoris IncludingDocument3 pagesBrand Name: Dilzem Generic Name: Diltiazem Indications: Angina Pectoris Includingianecunar0% (1)
- MethergineDocument2 pagesMethergineKureaa Oh100% (1)
- Mindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology Student: Section: 263Document2 pagesMindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology Student: Section: 263AkiraMamo100% (1)
- Vit K Drug StudyDocument2 pagesVit K Drug StudyTrina Joy Domantay100% (1)
- HydralazineDocument2 pagesHydralazineShermayne Mallapre HernandezNo ratings yet
- OxytocinDocument1 pageOxytocinIvanne Hisoler100% (7)
- Ferrous Sulfate Drug StudyDocument1 pageFerrous Sulfate Drug StudyAgeededin HartNo ratings yet
- Nitroglycerin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesNitroglycerin Drug StudyNasrah N. Musa100% (6)
- Labetalol Hydro ChlorideDocument3 pagesLabetalol Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941100% (1)
- Calcium CarbonateDocument1 pageCalcium CarbonateRye AnchNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - DigoxinDocument1 pageDrug Study - DigoxinSiergs Smith Gervacio100% (2)
- Drug Study (Paracetamol, Lactulose, Ascorbic Acid)Document6 pagesDrug Study (Paracetamol, Lactulose, Ascorbic Acid)Roland Mark Rodel LagosNo ratings yet
- Capstone Final Justin IsnerDocument21 pagesCapstone Final Justin Isnerapi-312746225No ratings yet
- Na HCO3Document2 pagesNa HCO3Niño Karol Zamora100% (1)
- Oral Rehydration Solution: A Drug Study OnDocument7 pagesOral Rehydration Solution: A Drug Study OnRaijenne VersolaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 51 - Diuretic AgentsDocument11 pagesChapter 51 - Diuretic AgentsJonathon100% (2)
- MV + FeSO4 Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMV + FeSO4 Drug Studymilkv71% (7)
- Drugs & DialysisDocument34 pagesDrugs & DialysisZulfkar Latief QadrieNo ratings yet
- Major Case StudyDocument26 pagesMajor Case StudyVin Mamuric Meneses100% (1)
- Hepatic FailureDocument37 pagesHepatic FailureWinston Dela FuenteNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - TramadolDocument1 pageDrug Study - TramadolSiergs Smith GervacioNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - DigoxinDocument1 pageDrug Study - DigoxinSiergs Smith Gervacio100% (2)
- DRUG STUDY - MetoprololDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY - MetoprololSiergs Smith Gervacio100% (2)
- DRUG STUDY - Vit B ComplexDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY - Vit B ComplexSiergs Smith Gervacio78% (9)
- DRUG STUDY - Ferrous SulfateDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY - Ferrous SulfateSiergs Smith GervacioNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - CelecoxibDocument1 pageDrug Study - CelecoxibSiergs Smith GervacioNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - CefoxitinDocument1 pageDrug Study - CefoxitinSiergs Smith Gervacio100% (6)
- Drug Study - CefuroximeDocument2 pagesDrug Study - CefuroximeSiergs Smith GervacioNo ratings yet
- Professional Adjustment Practice QuestionDocument41 pagesProfessional Adjustment Practice QuestionSiergs Smith GervacioNo ratings yet
- Placenta Previa Case StudyDocument59 pagesPlacenta Previa Case StudySiergs Smith GervacioNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions NLEDocument418 pagesPractice Questions NLESiergs Smith Gervacio100% (2)
- Surgical EquipmentsDocument6 pagesSurgical EquipmentsSiergs Smith GervacioNo ratings yet
- Acute GastroenteritisDocument28 pagesAcute GastroenteritisSiergs Smith GervacioNo ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument26 pagesEmergency DrugsSiergs Smith GervacioNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions NLEDocument418 pagesPractice Questions NLESiergs Smith Gervacio100% (2)
- NCP - Risk For InfectionDocument3 pagesNCP - Risk For InfectionSiergs Smith Gervacio100% (3)
- Vit and MineralsDocument12 pagesVit and MineralsSiergs Smith GervacioNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesEctopic Pregnancy PathophysiologySiergs Smith GervacioNo ratings yet
- NCP FormDocument4 pagesNCP FormSiergs Smith GervacioNo ratings yet
- DR PDFDocument252 pagesDR PDFa_ouchar0% (1)
- Plans PDFDocument49 pagesPlans PDFEstevam Gomes de Azevedo85% (34)
- Save Water SpeechDocument4 pagesSave Water SpeechHari Prakash Shukla0% (1)
- Kindergarten Math Problem of The Day December ActivityDocument5 pagesKindergarten Math Problem of The Day December ActivityiammikemillsNo ratings yet
- Catalogo GatesDocument255 pagesCatalogo GatesBenjamin HedoneweNo ratings yet
- AKI in ChildrenDocument43 pagesAKI in ChildrenYonas AwgichewNo ratings yet
- Hydrodynamic Calculation Butterfly Valve (Double Disc)Document31 pagesHydrodynamic Calculation Butterfly Valve (Double Disc)met-calcNo ratings yet
- Shree New Price List 2016-17Document13 pagesShree New Price List 2016-17ontimeNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Engineering Handbook Revised 5 2015Document37 pagesBiomedical Engineering Handbook Revised 5 2015Teja GuttiNo ratings yet
- Malvinas Gas Plant Operator Training: Paragon Engineering Services, Inc. Houston, TexasDocument71 pagesMalvinas Gas Plant Operator Training: Paragon Engineering Services, Inc. Houston, TexasMary Cruz Meza CahuanaNo ratings yet
- NF en Iso 5167-6-2019Document22 pagesNF en Iso 5167-6-2019Rem FgtNo ratings yet
- Oil Whirl and Whip Instabilities - Within Journal BearingsDocument27 pagesOil Whirl and Whip Instabilities - Within Journal BearingsTalha AamirNo ratings yet
- Lecture Planner - Inorganic Chemistry (Legend) - Yakeen NEET 2.0 2024Document1 pageLecture Planner - Inorganic Chemistry (Legend) - Yakeen NEET 2.0 2024Dipendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Goldhofer FTV 850 BrochureDocument2 pagesGoldhofer FTV 850 BrochureMauroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3.c (Centroid by Intergration)Document15 pagesChapter 3.c (Centroid by Intergration)Ariff AziziNo ratings yet
- Cisco 2500 Series RoutersDocument16 pagesCisco 2500 Series RoutersJull Quintero DazaNo ratings yet
- Cargo ManagementDocument45 pagesCargo ManagementShubham Chaurasia75% (8)
- Bulacan Agricultural State College: Lesson Plan in Science 4 Life Cycle of Humans, Animals and PlantsDocument6 pagesBulacan Agricultural State College: Lesson Plan in Science 4 Life Cycle of Humans, Animals and PlantsHarmonica PellazarNo ratings yet
- Douluo Dalu Volume 05 - Star Dou Forest PDFDocument141 pagesDouluo Dalu Volume 05 - Star Dou Forest PDFRay Joseph LealNo ratings yet
- Combined Shear and TensionDocument16 pagesCombined Shear and TensionDAN MARK OPONDANo ratings yet
- Provision of EPCI Services For EPCIC Sidayu Wellhead Platforms and Pipelines Sidayu Field DevelopmentDocument7 pagesProvision of EPCI Services For EPCIC Sidayu Wellhead Platforms and Pipelines Sidayu Field Developmentriandi100% (1)
- Plastics and Polymer EngineeringDocument4 pagesPlastics and Polymer Engineeringsuranjana26No ratings yet
- Syllabus Unit Iv Unit Commitment and Economic DispatchDocument23 pagesSyllabus Unit Iv Unit Commitment and Economic DispatchBALAKRISHNANNo ratings yet
- 2022 Audi e Tron 22Document318 pages2022 Audi e Tron 22Alejandro Alberto Robalino MendezNo ratings yet
- Indor Lighting DesignDocument33 pagesIndor Lighting DesignRajesh MalikNo ratings yet
- Gemh 108Document20 pagesGemh 108YuvrajNo ratings yet
- The Broadband ForumDocument21 pagesThe Broadband ForumAnouar AleyaNo ratings yet
- SambongDocument3 pagesSambongNica Del GallegoNo ratings yet
- Determinants - DPP 01 (Of Lec 02) - Lakshya JEE 2.0 2024Document3 pagesDeterminants - DPP 01 (Of Lec 02) - Lakshya JEE 2.0 2024Apurv ChitranshNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis and Design of Pressure Hulls - The State of The Art and Future TrendsDocument118 pagesStructural Analysis and Design of Pressure Hulls - The State of The Art and Future TrendsRISHABH JAMBHULKARNo ratings yet