Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Wish List of An Undergraduate Trainee at CEB and LECO (Complete)
Uploaded by
Nipuna Thushara WijesekaraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Wish List of An Undergraduate Trainee at CEB and LECO (Complete)
Uploaded by
Nipuna Thushara WijesekaraCopyright:
Available Formats
A wish-list of an undergraduate trainee during in-plant training at Ceylon Electricity Board and Lanka
Electricity Company Note: Abbreviations and acronyms have their usual meanings.
1. Ownership and Corporate structure
Who are the owners of CEB and LECO ? Which law(s) passed by parliament (and when) allow
each of them draw their authority and function?
Who are the members of the Boards of Directors of CEB and LECO? What are the power of
Chairman and Board Members? Where does the General Manager stand in the line of authority?
Study the most recent Annual Reports of CEB and LECO.
Are these two institutions making profits or losses?
Study the management structure of CEB and LECO, including the legal basis in which CEB
operates as six different licensees within the same corporate framework.
What are the benefits of operating as separate licensees ?
How is the electricity industry regulated by PUCSL and its strengths and weaknesses ?
What regulatory targets (financial and qualitative) are operational on each licensee within CEB
and on LECO ? Are they meeting the targets?
2. Be familiar with the specific details of Sri Lanka Generating System
Obtain and be familiar with the locations and capacities, fuels used, of the full list of generating
plants, both CEB-owned and privately-owned.
Study the hydro system and the network of reservoirs, Mahaweli irrigation and power
coordination, constraints in operating hydropower plants for power generation alone.
Thermal generation system, fuels, costs, ownership (IPP and CEB)
Types of fuels used in thermal power plants: study the five types of fuels used, why they are
different, their relative costs and prices, delivery mechanisms to power plants
Visit to a hydropower plant, understand its key design features and operation
Visit an oil-fired power plant, study as above
Visit a coal-fired power plant, study as above
What are the plans to add new generating plants ? Where ? What fuel types ?
What is the methodology used to identify generating plants/plant types, and develop plans for the
future ? What are the principal criteria guiding the planning process?
3. Development of Renewable Energy (RE) other than major hydro
The Small Power Producer (SPP) programme- policy, history, prices/pricing policy, SPP
Agreement, achievements, pitfalls
Roles of other agencies in promoting and facilitating RE development
What are the RE resources ? Where are they located ?
What is the share of RE (SPP and major hydro) in terms of capacity and energy?
Small hydro plant: site visit
Wind energy plant: site visit
What are the plans to further develop these resources ? What are the barriers, both technical and
financial?
4. Sri Lanka Transmission System
HV and MV Transmission network + equipment
What are operational voltage levels, nominal voltage, voltage tolerances (in planning as well as in
real time operations), what are the difficult points in the transmission network to manage voltages,
what remedies are available.
Visit to a grid substation, identify various equipment used and their purpose, study the protection
system
Specifically study the safety procedures in substation and line operation and maintenance
Visit System Control Centre, understand how unit commitment and dispatch are decided on, what
methodology is used, software used, problems.
What is meant by merit order dispatch and out-of-merit operation?
What is spinning reserve and how is spinning reserve maintained in the system, and how much ?
What happens when spinning reserve is inadequate ?
What is under-frequency load shedding? Why is it required, what are its capabilities and
limitations?
How does a power system collapse in cascading failures ? Ask and learn the sequence of events
that led to a cascading failure of the Sri Lanka power system.
5. Transmission Lines and Equipment, and Planning
Study different types of lines (single circuit, double circuit, conductor types, conductor names,
special conductors used for specific lines and reasons, tower types)
Be familiar with the entire transmission network, grid substations.
Study/visit a line construction site, safety in construction, safety in operations
Planned transmission lines, substations, higher voltages.
How is the transmission network planned to meet future requirements ? What are the guiding
principals ? What methodology and software is used.
Study the Transmission Plan.
6. Distribution Lines and Equipment, and Planning
Study different types of lines (single circuit, double circuit, conductor types, conductor names,
pole Vs tower lines, LV lines, types of poles used)
Be familiar with the MV distribution network of a CEB Region or of LECO.
Study the planned MV distribution network (planning document) of a CEB Region or of LECO.
How are expansion decision made ? What are the guiding principals ?
How is the distribution network (both MV and LV) planned to meet future requirements ? What are
the guiding principals ? What methodology and software is used for MV planning ? Is any
software used for LV planning ?
7. Distribution Operations and Commercial Management
What procedures are there for maintenance ? What safety procedures are adopted?
What is the customer mix of the country ? What are their relative consumption levels ? What is
the per capita electricity consumption in Sri Lanka?
What documents are available in the public domain describing the electricity sector operations
(study Sri Lanka Energy Balance, CEB Statistical Digest, CEB Data on Sales and Generation,
websites of CEB, LECO, SLSEA and PUCSL)
The problem of network technical and commercial losses. What are the loss targets and
achievements so far? What further potential is there to reduce losses ?
What are the sales growth levels of each category of customers?
What is meant by TOU tariffs ? Why is such a system there ? What is its structure ?
What is Demand-side management ? Why is it required ? What measures have been
implemented by CEB/LECO ? What more can be done?
8. Improvements
Study and propose one specific project or an initiative that can achieve favourable improvements
in one or several of the following at CEB or LECO: (i) cost of electricity generation, (ii)
transmission and/or distribution costs, (iii) customer service, (iv) safety, (v) system operations
including demand management, (vi) power quality including voltage regulation, (vii) losses, both
technical and commercial. The costs and benefits must be quantified.
You might also like
- Master of Energy Management (Mem) : DMX9405 Renewable Energy Technology Academic Year 2020 Assignment 1Document1 pageMaster of Energy Management (Mem) : DMX9405 Renewable Energy Technology Academic Year 2020 Assignment 1Nipuna Thushara WijesekaraNo ratings yet
- DMX9404 Assignment 1 - 520253279Document18 pagesDMX9404 Assignment 1 - 520253279Nipuna Thushara WijesekaraNo ratings yet
- Master of Energy Management (Mem) : DMX9402 Thermal Energy Utilities Academic Year 2020 Assignment 1Document1 pageMaster of Energy Management (Mem) : DMX9402 Thermal Energy Utilities Academic Year 2020 Assignment 1Nipuna Thushara WijesekaraNo ratings yet
- Algebra: Combined Mathematics Revision 2017Document1 pageAlgebra: Combined Mathematics Revision 2017Nipuna Thushara WijesekaraNo ratings yet
- Abx Aby Ab X Y: Ax by BX Ay Ax BX Ay byDocument7 pagesAbx Aby Ab X Y: Ax by BX Ay Ax BX Ay byNipuna Thushara WijesekaraNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 Volume and Capacity/Length and Distance: L ML of PaintDocument3 pagesGrade 5 Volume and Capacity/Length and Distance: L ML of PaintNipuna Thushara WijesekaraNo ratings yet
- Abx Aby Ab X Y: Ax by BX Ay Ax BX Ay byDocument1 pageAbx Aby Ab X Y: Ax by BX Ay Ax BX Ay byNipuna Thushara WijesekaraNo ratings yet
- Good Data SheetDocument20 pagesGood Data SheetNipuna Thushara WijesekaraNo ratings yet
- 2nd Term Test Paper-ICT - KS4Document3 pages2nd Term Test Paper-ICT - KS4Nipuna Thushara Wijesekara100% (1)
- Light BulbsDocument3 pagesLight BulbsNipuna Thushara WijesekaraNo ratings yet
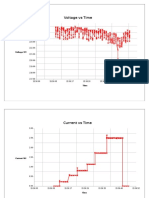
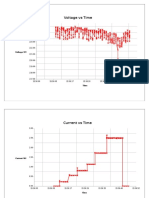
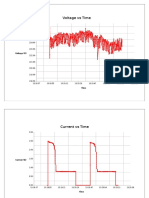
- Voltage Vs TimeDocument6 pagesVoltage Vs TimeNipuna Thushara WijesekaraNo ratings yet
- Small BusinessDocument7 pagesSmall BusinessNipuna Thushara WijesekaraNo ratings yet
- FYP Budget Approval RequestDocument1 pageFYP Budget Approval RequestNipuna Thushara WijesekaraNo ratings yet
- Simulink Model of An Incandescent BulbDocument3 pagesSimulink Model of An Incandescent BulbNipuna Thushara WijesekaraNo ratings yet
- IM 2016 Jun 16 (Recovered)Document39 pagesIM 2016 Jun 16 (Recovered)Nipuna Thushara WijesekaraNo ratings yet
- Earthing CalculationDocument4 pagesEarthing CalculationNipuna Thushara WijesekaraNo ratings yet
- Light BulbsDocument3 pagesLight BulbsNipuna Thushara WijesekaraNo ratings yet
- Raven GraphicsDocument1 pageRaven GraphicsNipuna Thushara WijesekaraNo ratings yet
- Temperatue Rise of An Electrical Machine: Instructed By: Dr. Udayanga HemapalaDocument8 pagesTemperatue Rise of An Electrical Machine: Instructed By: Dr. Udayanga HemapalaNipuna Thushara WijesekaraNo ratings yet
- Exhaust FanDocument6 pagesExhaust FanNipuna Thushara WijesekaraNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Illustrating An Experiment, Outcome, Sample Space and EventDocument9 pagesIllustrating An Experiment, Outcome, Sample Space and EventMarielle MunarNo ratings yet
- Speech On Viewing SkillsDocument1 pageSpeech On Viewing SkillsMera Largosa ManlaweNo ratings yet
- YIC Chapter 1 (2) MKTDocument63 pagesYIC Chapter 1 (2) MKTMebre WelduNo ratings yet
- Clark SM 616 Service ManualDocument20 pagesClark SM 616 Service Manualenid100% (55)
- Design of Combinational Circuit For Code ConversionDocument5 pagesDesign of Combinational Circuit For Code ConversionMani BharathiNo ratings yet
- Catedral de SevillaDocument28 pagesCatedral de SevillaAnonymous LkgNmKeNo ratings yet
- Sem4 Complete FileDocument42 pagesSem4 Complete Fileghufra baqiNo ratings yet
- Cloud Comp PPT 1Document12 pagesCloud Comp PPT 1Kanishk MehtaNo ratings yet
- 2022 Mable Parker Mclean Scholarship ApplicationDocument2 pages2022 Mable Parker Mclean Scholarship Applicationapi-444959661No ratings yet
- Hans Belting - The End of The History of Art (1982)Document126 pagesHans Belting - The End of The History of Art (1982)Ross Wolfe100% (7)
- Music CG 2016Document95 pagesMusic CG 2016chesterkevinNo ratings yet
- Evs ProjectDocument19 pagesEvs ProjectSaloni KariyaNo ratings yet
- Health Post - Exploring The Intersection of Work and Well-Being - A Guide To Occupational Health PsychologyDocument3 pagesHealth Post - Exploring The Intersection of Work and Well-Being - A Guide To Occupational Health PsychologyihealthmailboxNo ratings yet
- Science 4 Diagnostic/Achievement TestDocument5 pagesScience 4 Diagnostic/Achievement TestGe PebresNo ratings yet
- SweetenersDocument23 pagesSweetenersNur AfifahNo ratings yet
- 1 in 8.5 60KG PSC Sleepers TurnoutDocument9 pages1 in 8.5 60KG PSC Sleepers Turnoutrailway maintenanceNo ratings yet
- Tesco True Results Casing Running in China Results in Total Depth PDFDocument2 pagesTesco True Results Casing Running in China Results in Total Depth PDF123456ccNo ratings yet
- Progressive Muscle RelaxationDocument4 pagesProgressive Muscle RelaxationEstéphany Rodrigues ZanonatoNo ratings yet
- Thesis PaperDocument53 pagesThesis PaperAnonymous AOOrehGZAS100% (1)
- Quarter 1-Week 2 - Day 2.revisedDocument4 pagesQuarter 1-Week 2 - Day 2.revisedJigz FamulaganNo ratings yet
- Subject Manual Tle 7-8Document11 pagesSubject Manual Tle 7-8Rhayan Dela Cruz DaquizNo ratings yet
- Standard Answers For The MSC ProgrammeDocument17 pagesStandard Answers For The MSC ProgrammeTiwiNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 SolvedDocument3 pagesTutorial 5 SolvedAshutoshKumarNo ratings yet
- Skills Checklist - Gastrostomy Tube FeedingDocument2 pagesSkills Checklist - Gastrostomy Tube Feedingpunam todkar100% (1)
- Toeic: Check Your English Vocabulary ForDocument41 pagesToeic: Check Your English Vocabulary ForEva Ibáñez RamosNo ratings yet
- Leadership Styles-Mckinsey EdDocument14 pagesLeadership Styles-Mckinsey EdcrimsengreenNo ratings yet
- Cisco UCS Adapter TroubleshootingDocument90 pagesCisco UCS Adapter TroubleshootingShahulNo ratings yet
- Head Coverings BookDocument86 pagesHead Coverings BookRichu RosarioNo ratings yet
- 8051 NotesDocument61 pages8051 Notessubramanyam62No ratings yet
- Recitation Math 001 - Term 221 (26166)Document36 pagesRecitation Math 001 - Term 221 (26166)Ma NaNo ratings yet