Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Lymphatic System Handout
Uploaded by
bernachurchCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Lymphatic System Handout
Uploaded by
bernachurchCopyright:
Available Formats
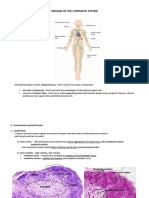
THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
The lymphatic system aids the immune system in
removing and destroying waste, debris, dead
blood cells, pathogens, toxins, and cancer cells.
The lymphatic system absorbs fats and fat-soluble
vitamins from the digestive system and delivers
these nutrients to the cells of the body where
they are used by the cells.
The lymphatic system also removes excess fluid,
and waste products from the interstitial spaces
between the cells.
The lymphatic system is a subset of the circulatory
system and It acts as a highway, transporting
white blood cells to and from the lymph nodes
into the bones, and antigen-presenting cells to
the lymph nodes.
these are superficial capillaries located near, or
just under, the skin. The remaining 30%, which
are known as deep lymphatic capillaries,
surround most of the bodys organs.
Lymphatic capillaries begin as blind-ended tubes
that are only a single cell in thickness. These
cells are arranged in a slightly overlapping
pattern, much like the shingles on a roof. Each of
these individual cells is fastened to nearby
tissues by an anchoring filament.
LYMPHATIC VESSELS
The lymphatic capillaries gradually join together to
form a mesh-like network of tubes that are
located deeper in the body.
As they become larger, and deeper, these structures
become lymphatic vessels.
Deeper within the body the lymphatic vessels
LYMPH
become progressively larger and are located
The remaining 10% of the fluid that stays behind in
near major blood veins.
the tissues as a clear to yellowish fluid known as Like veins, the lymphatic vessels, which are known
lymph.
as lymphangions, have one-way valves to
Unlike blood, which flows throughout the body in a
prevent any backward flow.
continue loop, lymph flows in only one direction
Smooth muscles in the walls of the lymphatic
within its own system. This flow is only upward
vessels cause the angions to contract
toward the neck. Here, it flows into the venous
sequentially to aid the flow of lymph upward
blood stream through the subclavian veins which
toward the thoracic region. Because of their
are located on either sides of the neck near the
shape, these vessels are previously referred to
collarbones.
as a string of pearls.
After plasma has delivered its nutrients and
removed debris, it leaves the cells. 90% of this
LYMPH NODES
fluid returns to the venous circulation through
There are between 600-700 lymph nodes present in
the venules and continues as venous blood.
the average human body. It is the role of these
The remaining 10% of this fluid becomes lymph
nodes to filter the lymph before it can be
which is a watery fluid that contains waste
returned to the circulatory system. Although
products. This waste is protein-rich due to the
these nodes can increase or decrease in size
undigested proteins that were removed from the
throughout life, any nodes that has been
cells.
damaged or destroyed, does not regenerate.
Lymph originates as plasma (the fluid portion of
Afferent lymphatic vessels carry unfiltered lymph
blood). The arterial blood, which flows out of the
into the node. Here waste products, and some of
heart, slows as it moves through a capillary bed.
the fluid, are filtered out.
This slowing allows some plasma to leave the
In another section of the node, lymphocytes, which
arterioles (small arteries) and flow into the
are specialized white blood cells, kill any
tissues where it becomes tissue fluid.
pathogens that may be present. This causes the
Also known as extracellular fluid, this is fluid that
swelling commonly known as swollen glands.
flows between the cells but is not into the cells.
Lymph nodes also trap and destroy cancer cells to
This fluid delivers nutrients, oxygen, and
slow the spread of the cancer until they are
hormones to the cells.
overwhelmed by it.
As this fluid leaves the cells, it takes with it cellular
Efferent lymphatic vessels carry the filtered lymph
waste products and protein cells.
out of the node so that it can continue its return
Approximately 90% of this tissue fluid flows into the
to the circulatory system.
small veins. Here it enters the venous circulation
as plasma and continues in the circulatory
LYMPHATIC ORGANS
system.
The spleen, which is largest lymphatic organ, is
The remaining 10% of the fluid that is left behind is
located on the left side of the body just above
known as lymph.
the kidney. Humans can live without a spleen,
although people who have lost their spleen to
LYMPHATIC CAPILLARIES
disease or injury are more prone to infections.
In order to leave the tissues, the lymph must enter
the lymphatic system through specialized
lymphatic capillaries. Approximately 70% of
The thymus, which stores immature lymphocytes
and prepares them to become active T cells, is
located in the chest just above the heart.
Tonsils are large clusters of lymphatic cells found in
the pharynx. Although tonsillectomies occur
much less frequently today then they did in the
1950s, it is still among the most common
operations performed and typically follows
frequent throat infections.
Bone marrow contains tissue that produces
lymphocytes. B-lymphocytes (B-cells) mature in
the bone marrow.Other blood cells such as
monocytes and leukocytes are produced in the
bone marrow.
DRAINAGE AREAS
Lymphatic system drainage is organized into two
separate, and very unequal drainage areas. The
right drainage area clears the right arm and
chest. The left drainage area clears all of the
other areas of the body including both legs, the
lower trunk upper left of the chest, and the left
arm.
LYMPHATIC CIRCULATION
The lymph is moved through the body in its own
vessels making a one-way journey from the
interstitial spaces to the subclavian veins at the
base of the neck.
Since the lymphatic system does not have a heart to
pump it, its upward movement depends on the
motions of the muscle and joint pumps.
As it moves upward toward the neck the lymph
passes through lymph nodes which filter it to
remove debris and pathogens.
The cleansed lymph continues to travel in only one
direction, which is upward toward the neck.
At the base of the neck, the cleansed lymph flows
into the subclavian veins on either side of the
neck.
Lymphedema is a chronic swelling of the limbs
caused by the accumulation of lymph fluid that
occurs if the lymphatic system is damaged or not
functioning properly. While the limbs are typically
involved, the face, neck and abdomen may also
be affected. Many develop the disorder following
cancer therapy particularly breast cancer
where the lymph nodes under the arms are
removed recurrent infections, injuries or
vascular surgery.
You might also like
- Lymphatic SystemDocument37 pagesLymphatic SystemDam Lakbao100% (1)
- Lymphatic SystemDocument29 pagesLymphatic SystemlecturioNo ratings yet
- 4 19 Lymphmatic SystemDocument10 pages4 19 Lymphmatic SystemJohn Lawrence Ybanez100% (1)
- Lymphedema: Natthaphong Jirojananukul 4 Year Medical Student Phichit Medical CenterDocument26 pagesLymphedema: Natthaphong Jirojananukul 4 Year Medical Student Phichit Medical CenterPuthiput ChotsutaworakulNo ratings yet
- Cellulitis: Current Insights Into Pathophysiology and Clinical ManagementDocument13 pagesCellulitis: Current Insights Into Pathophysiology and Clinical Managementtucto849915No ratings yet
- Investigations of LymphaticsDocument26 pagesInvestigations of LymphaticsManoj B MyatherNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System DiseasesDocument1 pageLymphatic System DiseasesRJ San JuanNo ratings yet
- "Cancer 101: What You Need to Know About Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention"From Everand"Cancer 101: What You Need to Know About Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention"No ratings yet
- The Lymphatic System and Lymphoid Organs and TissuesDocument46 pagesThe Lymphatic System and Lymphoid Organs and Tissuessanananaa100% (1)
- 2017 FULL LymphedemaSelfCareGuide BlackandwhiteDocument25 pages2017 FULL LymphedemaSelfCareGuide BlackandwhiteVintila LiviuNo ratings yet
- Emily Iker, MD: LymphedemaDocument37 pagesEmily Iker, MD: LymphedemaJustin HarperNo ratings yet
- The Slim Book of Health Pearls: Hormones, Nerves, and StressFrom EverandThe Slim Book of Health Pearls: Hormones, Nerves, and StressNo ratings yet
- 6.10.13 Intervention For LymphedemaDocument85 pages6.10.13 Intervention For LymphedemaAyyappan JayavelNo ratings yet
- Lymphoedema of Upper Limb: DR G Avinash Rao - Fellow Hand and MicrosurgeryDocument93 pagesLymphoedema of Upper Limb: DR G Avinash Rao - Fellow Hand and Microsurgeryavinashrao39No ratings yet
- Lymph DetoxifyDocument5 pagesLymph DetoxifyGeorge Ciuca75% (4)
- The Self-Care Deficit Nursing PPT OriginalDocument15 pagesThe Self-Care Deficit Nursing PPT OriginalApril Joy de LimaNo ratings yet
- LymphedemaDocument3 pagesLymphedemaFirtanty Tasya Andriami SyahputriNo ratings yet
- Go Green for Wellness: Smoothies, Juices, Green Recipes: Practical Advice for Achieving Good HealthFrom EverandGo Green for Wellness: Smoothies, Juices, Green Recipes: Practical Advice for Achieving Good HealthNo ratings yet
- Blood Vessels and Lymphatics in Organ SystemsFrom EverandBlood Vessels and Lymphatics in Organ SystemsDavid AbramsonNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument46 pagesHuman Anatomy and PhysiologyBegumHazinNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Blood Clot in Lungs, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Blood Clot in Lungs, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 2nd-U-2 Lymphatic SystemDocument52 pagesAnatomy 2nd-U-2 Lymphatic Systemsinte beyuNo ratings yet
- Ebstein Anomaly, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandEbstein Anomaly, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Blood Vessels and LymphaticsFrom EverandBlood Vessels and LymphaticsDavid I. AbramsonNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemLabDocument7 pagesLymphatic SystemLabMax DelvalleNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic System SummaryDocument3 pagesThe Lymphatic System SummaryVasile100% (1)
- Edema LymphedemaDocument2 pagesEdema LymphedemaAsmat BurhanNo ratings yet
- Analyzing and Defining Medical TermsDocument7 pagesAnalyzing and Defining Medical Termsmarcus colgroveNo ratings yet
- Massage and The Lymphatic SystemDocument9 pagesMassage and The Lymphatic Systemarmanious64No ratings yet
- Killer Diseases, Modern-Day Epidemics: Keys to Stopping Heart Disease, Diabetes, Cancer, and Obesity in Their TracksFrom EverandKiller Diseases, Modern-Day Epidemics: Keys to Stopping Heart Disease, Diabetes, Cancer, and Obesity in Their TracksNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument28 pagesLymphatic SystemChristine Lorne Aborde100% (1)
- Endocrine System Study GuideDocument5 pagesEndocrine System Study GuideClaudia SanchezNo ratings yet
- RenalSystem Part 1 (Spring2020)Document49 pagesRenalSystem Part 1 (Spring2020)Sahil ParikhNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic System in Colorectal Cancer: Basic Concepts, Pathology, Imaging, and Treatment PerspectivesFrom EverandThe Lymphatic System in Colorectal Cancer: Basic Concepts, Pathology, Imaging, and Treatment PerspectivesWim CeelenNo ratings yet
- IBS Diet: A 4-Week Beginner's Guide to Managing IBS Symptoms Through the Low-FODMAP Diet with Selected Recipes and a Meal PlanFrom EverandIBS Diet: A 4-Week Beginner's Guide to Managing IBS Symptoms Through the Low-FODMAP Diet with Selected Recipes and a Meal PlanNo ratings yet
- Chapter25 Urinary SystemDocument9 pagesChapter25 Urinary Systemkikajet23No ratings yet
- Herbal Solutions 2010Document12 pagesHerbal Solutions 2010Manuel Antonio Araujo ChavezNo ratings yet
- Myelofibrosis, (Bone Marrow Fibrosis) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandMyelofibrosis, (Bone Marrow Fibrosis) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide To Anal Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide To Anal Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Small Intestines Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Small Intestines Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Manual Lymphatic DrainageDocument2 pagesManual Lymphatic DrainageTIME-TREVELERNo ratings yet
- Hyper-coagulation, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandHyper-coagulation, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Diabetes WorksheetDocument2 pagesDiabetes WorksheetAstrid TelloNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology: The EssentialsFrom EverandGastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology: The EssentialsJohn F. ReinusNo ratings yet
- Table Vitamins PDFDocument3 pagesTable Vitamins PDFthomasqilNo ratings yet
- Adapting Resiliently: A healing journey to vitality by addressing inflammation mind, body and spiritFrom EverandAdapting Resiliently: A healing journey to vitality by addressing inflammation mind, body and spiritNo ratings yet
- Presented by Rasgas Medical Centre: Lowering Your CholesterolDocument22 pagesPresented by Rasgas Medical Centre: Lowering Your CholesterolNarasimhan PNo ratings yet
- Disorders of the Patellofemoral Joint: Diagnosis and ManagementFrom EverandDisorders of the Patellofemoral Joint: Diagnosis and ManagementNo ratings yet
- Ks Module 12Document29 pagesKs Module 12jerinthomasrajanNo ratings yet
- Excursion WorksheetDocument6 pagesExcursion Worksheetapi-348781812No ratings yet
- Quick-Cross Product BrochureDocument2 pagesQuick-Cross Product Brochurebiomedical_com_brNo ratings yet
- AngioplastyDocument10 pagesAngioplastyВлада ХоружийNo ratings yet
- Science: Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsDocument31 pagesScience: Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsEjelmae Olaivar TutorNo ratings yet
- Journal Heptojugular RefluxDocument5 pagesJournal Heptojugular RefluxFarhan RezaNo ratings yet
- MRCP Revision NotesDocument104 pagesMRCP Revision NotesPass MRCP67% (12)
- Nursing Care Plan and Drug StudyDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan and Drug StudyEllaNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary HypertensionDocument1 pagePulmonary HypertensionSa KhunNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic System HistologyDocument14 pagesLymphatic System HistologySilhouette SignNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument22 pagesCirculatory Systemparitosh7_886026No ratings yet
- 2 Evaluation of Role of Family Physicians in Management and Diagnosis of Hypertension in Primary HeaDocument5 pages2 Evaluation of Role of Family Physicians in Management and Diagnosis of Hypertension in Primary HeaVANESSA GLORIA POLIINo ratings yet
- Group 3 Cardiovascular System Complete HandoutDocument65 pagesGroup 3 Cardiovascular System Complete HandoutNicole LantinNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Vascular (PVS) Examination OSCE Station GuideDocument4 pagesPeripheral Vascular (PVS) Examination OSCE Station GuideNikita JacobsNo ratings yet
- Short Answer: Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular SystemDocument23 pagesShort Answer: Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular SystemRafael CastilloNo ratings yet
- PPK IccuDocument27 pagesPPK IccumuhiqbalyunusNo ratings yet
- 2015 Thoracic-Aorta PDFDocument64 pages2015 Thoracic-Aorta PDFAnca Oprea TighiliuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of BVDocument16 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of BVMarivic DianoNo ratings yet
- BP503T Unit 1-3Document432 pagesBP503T Unit 1-3Solomon GyampohNo ratings yet
- Balloon-Assisted Cannulation For Difficult Anterior Cerebral Artery AccessDocument5 pagesBalloon-Assisted Cannulation For Difficult Anterior Cerebral Artery AccessaldyNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Class: Subject: Topic: Submitted byDocument10 pagesLesson Plan: Class: Subject: Topic: Submitted bysimonjosan67% (3)
- Charcot-Bouchard Aneurysm - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument2 pagesCharcot-Bouchard Aneurysm - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaAniket MittalNo ratings yet
- (Kenneth Tan) Pharmacologic Management For Cardiogenic Shock - EBM or Gut FeelDocument21 pages(Kenneth Tan) Pharmacologic Management For Cardiogenic Shock - EBM or Gut FeelAdriana VillarrealNo ratings yet
- Sudden Cardiac Arrest: Introduction & Disease OverviewDocument18 pagesSudden Cardiac Arrest: Introduction & Disease OverviewVivekanandGuptaNo ratings yet
- Dilated Cardiomyopathy Notes AtfDocument15 pagesDilated Cardiomyopathy Notes AtfSingha ChangsiriwatanaNo ratings yet
- Mcat Questions TestDocument14 pagesMcat Questions TestBrandon DeveaultNo ratings yet
- Corazon AnatomiaDocument10 pagesCorazon AnatomiaMariaAndreaRuizVelásquezNo ratings yet
- LV Systolic FunctionDocument36 pagesLV Systolic Functionsruthimeena6891No ratings yet
- The Heart Is Not A Pump - The Blood Moves The Heart, Not Vice VersaDocument14 pagesThe Heart Is Not A Pump - The Blood Moves The Heart, Not Vice VersagiovacaneNo ratings yet
- 1.08 - The Cardiovascular System, The Heart & The Blood VesselsDocument9 pages1.08 - The Cardiovascular System, The Heart & The Blood Vessels13PLAN, SENTH RUEN, ANo ratings yet
- Renal Blood Flow RegulationDocument3 pagesRenal Blood Flow RegulationTawhid ZihadNo ratings yet