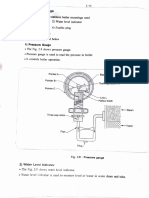
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1 Matter and Measurement
Uploaded by
notyouravguplo876Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1 Matter and Measurement
Uploaded by
notyouravguplo876Copyright:
Available Formats
South Pasadena AP Chemistry
[Keep for Reference]
1 Matter and Measurement
BLUFFERS
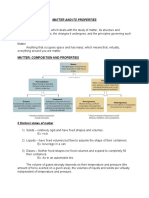
1. Matter
Normally exists in 3 physical states:
LiquidFixed volume, Fluid; Takes on the shape of
lower part of container; well-defined surface
Solid
Rigid Shape; very little volume change as
temperature and pressure change
Gas
Volume expands to fill the container; volume
varies according to temperature and pressure
Kinetic Molecular Theory
The idea that matter consists of molecules or
atoms that are in constant, random motion.
Kinetic Energy = Energy of motion; higher
temperature = more motion
Macroscopic seen with the eyes.
Microscopic seen with a microscope
Particulate or Submicroscopic Structures
at the atomic level (what we think about)
Mixtures
Heterogeneous Mixture A mixture where
the properties of the mixture vary
throughout. (Like an Oatmeal cookie, the
different components are visible)
Homogeneous Mixture Also called a
solution, where the components mix at a
molecular level; different properties of the
mixtures are unnoticeable.
Purification The separation of a mixture
into its components. (techniques: distillation,
filtration, & chromatography)
2. Elements
GUIDE
3. Physical Properties
Properties of a lone sample (ex. mass, volume,
boiling temp, melting temp, conductivity, etc.)
Density is the physical property that relates the
mass of an object to its volume
Mass
Density =
/Volume
Extensive Property Properties, like mass and
volume, that depend on the amount of substance
Intensive Properties Properties like color and
density; independent of the amount of substance
Temperature -- how hot a substance is;
physical properties (like density) vary with temp
Celsius 0C for freezing point of water and
100C for melting point of water.
Kelvin same scale as Celsius; 0C = -273 K;
0 K = no motion; Celsius o + 273 = Kelvin
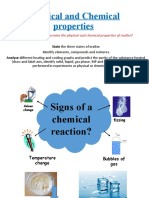
4. Chemical Properties
How substance interacts with other substances.
Ex. forms gas with acid; burns in air, etc.
5. Physical and Chemical Change
Physical Change where the identity of all the
substances remain unchanged (melting, boiling,
grinding, pounding into sheets, etc.)
Chemical Change (Reaction) atoms
rearrange to convert one substance into another
Chemical Equation A representation of the
chemical reaction taking place
Example: P4 + 6Cl2 4PCl3
6. Measurements/Calculations
Accuracy how close to a true value;
quantified by percent error.
A substance that cannot be decomposed
further by chemical means
Precision how close measurements are to
each other. Measured by significant figures or
notation. [I assume you know metric system.]
Names given by symbols: Example: Helium
= He, Gold = Au, Aluminum = Al
Dimensional Analysis use of a conversion
factor to change units (ex: metric conversions,
mass & volume, time units, etc.)
You might also like
- Chemistry 101 MatterDocument3 pagesChemistry 101 MatterTroy SaguinNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Changes PowerpointDocument34 pagesPhysical and Chemical Changes Powerpointapi-294483847100% (1)
- "Matter and Change": Charles Page High School Pre-AP Chemistry Stephen L. CottonDocument47 pages"Matter and Change": Charles Page High School Pre-AP Chemistry Stephen L. CottonSmita SahooNo ratings yet
- S4 Chem Ch.1 Fundamentals of ChemistryDocument5 pagesS4 Chem Ch.1 Fundamentals of Chemistry羅絲雷朵No ratings yet
- CHEMDocument40 pagesCHEMAK FortySevenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Matter and Its PropertiesDocument29 pagesChapter 1 Matter and Its PropertiesLexter CastilloNo ratings yet
- Chapter I Composition of Matter Marilou ELBODocument5 pagesChapter I Composition of Matter Marilou ELBOTn F'dzNo ratings yet
- Chemistry PDFDocument74 pagesChemistry PDFVed JoshiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.3. LEARNING tIMEDocument4 pagesLesson 1.3. LEARNING tIMECruella MajoNo ratings yet
- Fu-Yin Hsu Chapter 1Document58 pagesFu-Yin Hsu Chapter 1Nermeen ElmelegaeNo ratings yet
- Study Guide For Ch.1: Science SkillsDocument49 pagesStudy Guide For Ch.1: Science Skillsapi-30718309No ratings yet
- Properties and Changes of MatterDocument21 pagesProperties and Changes of MatterMiraNo ratings yet
- 60a03722666006fe5f0d1003 - SS Gen Chem 1Document43 pages60a03722666006fe5f0d1003 - SS Gen Chem 1Sunnia WilliamNo ratings yet
- Matter Classification and Properties With Pen 1106Document41 pagesMatter Classification and Properties With Pen 1106JOHN DAVE MOISES BALDRIASNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer MATTERDocument3 pagesScience Reviewer MATTERRACHELL SATSATINNo ratings yet
- Chem 112 Final Exam NotesDocument32 pagesChem 112 Final Exam NotesZeba N. Siddiqui100% (2)
- Particle Nature of MatterDocument22 pagesParticle Nature of MatterEve JoyceNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: The Study of The Composition, Structure & Properties of Materials & The Changes They UndergoDocument31 pagesChemistry: The Study of The Composition, Structure & Properties of Materials & The Changes They UndergoSrikar PydaNo ratings yet
- Lessons Chemistry 11Document282 pagesLessons Chemistry 11imosarchitectureNo ratings yet
- Week - q1 State of MatterDocument21 pagesWeek - q1 State of Matterjustine alinaNo ratings yet
- Chem ReviewerDocument16 pagesChem Revieweryxcz.rzNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometric Relationships Chapter 1Document9 pagesStoichiometric Relationships Chapter 1api-392847673No ratings yet
- Note ChemDocument28 pagesNote ChemHoàng Kim LongNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 Measurement and Density Spring 2015Document17 pagesExperiment 1 Measurement and Density Spring 2015Uzo Paul NwabuisiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 CHEM 151 Lecture SlidesDocument82 pagesChapter 1 CHEM 151 Lecture SlidesjohnNo ratings yet
- Properties of Matter and Changes in MatterDocument55 pagesProperties of Matter and Changes in MatterPrinces April ArrezaNo ratings yet
- Qca 1bDocument48 pagesQca 1bAlfredo Salamanca :No ratings yet
- Chapter 1, PPT, NewDocument14 pagesChapter 1, PPT, Newyonatanteshome48No ratings yet
- Matter and Its PropertiesDocument32 pagesMatter and Its Propertiesahmad batataNo ratings yet
- Reviwer 3RD QuarterDocument19 pagesReviwer 3RD QuartermoraledazoesophiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To ChemistryDocument3 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To ChemistryMicaela DNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Chem IDocument11 pagesChapter 1 Chem IStudy LionNo ratings yet
- Basic of ChemistryDocument22 pagesBasic of ChemistryTikie TokieNo ratings yet
- Module 1 (The Atom)Document18 pagesModule 1 (The Atom)renNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ReviewDocument43 pagesChemistry ReviewGreg Smith97% (31)
- Chem01 - General and InorganicDocument15 pagesChem01 - General and InorganicJetz Hontimara RegioNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Matter, Definition and ClassificationDocument41 pagesChapter 1 Matter, Definition and ClassificationMohammed AllamNo ratings yet
- 01 Lecture KMDocument44 pages01 Lecture KMUday Prakash SahuNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Concepts of ChemistryDocument12 pagesSome Basic Concepts of ChemistryS. LakshanyaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 5070 NotesDocument191 pagesChemistry 5070 NotesmwansaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Bascic Chemistry Concepts - 2Document37 pagesIntroduction To Bascic Chemistry Concepts - 2Malak RabieNo ratings yet
- Q3L1 GenSci8Document5 pagesQ3L1 GenSci8yurudumpaccNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Concepts Classification and States of MatterDocument40 pagesUnit 2 Concepts Classification and States of Matterapi-327076063No ratings yet
- Matter - Physical Material of The Universe (With Mass and Occupy Space) Property - Characteristics of The Matter (Distinguishable To Others)Document3 pagesMatter - Physical Material of The Universe (With Mass and Occupy Space) Property - Characteristics of The Matter (Distinguishable To Others)Davinci LegaspiNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document19 pagesModule 1Romel AlojadoNo ratings yet
- General ChemistryDocument45 pagesGeneral Chemistryrieann leonNo ratings yet
- Physchem Props and Changes NotesDocument11 pagesPhyschem Props and Changes Notessansary554No ratings yet
- Ch. 1-4 Chemistry: Scientific MethodDocument12 pagesCh. 1-4 Chemistry: Scientific Methodamedawg3No ratings yet
- MatterDocument5 pagesMattererikaNo ratings yet
- Matter and Its PropertiesDocument7 pagesMatter and Its PropertiesAndrei Mae MercadoNo ratings yet
- The Difference Between A Chemical Property and A Physical PropertyDocument12 pagesThe Difference Between A Chemical Property and A Physical PropertyAnthony Jay CombateNo ratings yet
- Separating Mixtures: Chemical ChangesDocument1 pageSeparating Mixtures: Chemical ChangesQuinie Rose OngcoyNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Properties Year 10Document13 pagesPhysical and Chemical Properties Year 10SIRRVET BUKHARINo ratings yet
- GROUP 3 - Physical vs. ChemicalDocument7 pagesGROUP 3 - Physical vs. ChemicalMichael EvanNo ratings yet
- The Study of ChemistryDocument27 pagesThe Study of Chemistryel tetraNo ratings yet
- Oral Presentation PPDocument71 pagesOral Presentation PPSaubie AslamiahNo ratings yet
- Matter and Its PropertiesDocument10 pagesMatter and Its PropertiesGerald CatiponNo ratings yet
- Keməstrē/: Learn To PronounceDocument26 pagesKeməstrē/: Learn To PronounceahgaseX JJpsNo ratings yet
- Category Scoring Criteria Total Points Score Organization (15 Points)Document1 pageCategory Scoring Criteria Total Points Score Organization (15 Points)notyouravguplo876No ratings yet
- 4 Chemical Equations and StoichiometryDocument1 page4 Chemical Equations and Stoichiometrynotyouravguplo876No ratings yet
- 6 - Energy and Chemical Reactions: Study List Driving Forces Chemical Work Expanding GasesDocument1 page6 - Energy and Chemical Reactions: Study List Driving Forces Chemical Work Expanding Gasesnotyouravguplo876No ratings yet
- NH + H O: 5 Reactions in Aqueous SolutionDocument2 pagesNH + H O: 5 Reactions in Aqueous Solutionnotyouravguplo876No ratings yet
- Apch02 Studylist08Document1 pageApch02 Studylist08notyouravguplo876No ratings yet
- B Word Poblems Solutions v02Document9 pagesB Word Poblems Solutions v02notyouravguplo876No ratings yet
- A Geometry Solutions v02Document13 pagesA Geometry Solutions v02notyouravguplo876No ratings yet
- AP Chemistry MemorizationDocument7 pagesAP Chemistry Memorizationnotyouravguplo876No ratings yet
- Study Ndeg1Document2 pagesStudy Ndeg1notyouravguplo876No ratings yet
- AP Common Ions: CATIONS (+ve) ANIONS (-Ve)Document2 pagesAP Common Ions: CATIONS (+ve) ANIONS (-Ve)notyouravguplo876No ratings yet
- Ignite Dec23Document10 pagesIgnite Dec23notyouravguplo876No ratings yet
- Cryolite JM File 2011Document5 pagesCryolite JM File 2011mutemuNo ratings yet
- Epoxy CureDocument5 pagesEpoxy CureElias Kapa100% (1)
- Experiment 8 - The Preparation of AcetanlideDocument12 pagesExperiment 8 - The Preparation of AcetanlideMark Ryan Tripole92% (13)
- Prestressed Concrete Structures: Prepared By: Dr. Amlan K. Sengupta Dr. Devdas MenonDocument11 pagesPrestressed Concrete Structures: Prepared By: Dr. Amlan K. Sengupta Dr. Devdas MenonJeffrey Carlo Viduya AgliamNo ratings yet
- Science of The Total Environment: Farhad Misaghi, Fatemeh Delgosha, Mostafa Razzaghmanesh, Baden MyersDocument10 pagesScience of The Total Environment: Farhad Misaghi, Fatemeh Delgosha, Mostafa Razzaghmanesh, Baden Myersmahdi najafzadehNo ratings yet
- គីមីអាហារ Food ChemistryDocument27 pagesគីមីអាហារ Food Chemistrysokrachemistry100% (1)
- Mechanics of Structure (CE3G) - Simple Stress & StrainDocument40 pagesMechanics of Structure (CE3G) - Simple Stress & StrainMuhammad Muzammil EjazNo ratings yet
- Waled M. El-Senousy Nagwa M. Sidkey Amel S.M. Abu Senna Nermine N. Abed Seham F. HasanDocument8 pagesWaled M. El-Senousy Nagwa M. Sidkey Amel S.M. Abu Senna Nermine N. Abed Seham F. Hasanseham.f. hasanNo ratings yet
- BUFFERS For SEM Fixative Preparation (Karnovsky Fixative Adaptation)Document7 pagesBUFFERS For SEM Fixative Preparation (Karnovsky Fixative Adaptation)Salustiano JurandiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction Practice TestDocument9 pagesChemical Reaction Practice TestMarivic Bernardo GalvezNo ratings yet
- Design and Characterization of Electroconductive GDocument21 pagesDesign and Characterization of Electroconductive GarunkumarshaktivelNo ratings yet
- Food Analysis by M Theobald Einstein From UNIVERSITY OF RWANDA PHARMACYDocument262 pagesFood Analysis by M Theobald Einstein From UNIVERSITY OF RWANDA PHARMACYMINANI TheobaldNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 BoilerDocument17 pagesUnit 3 BoilerAnonymous R7wV0zbMNo ratings yet
- Zach West's " Electrolyser&Quot - Free-Energy DevicesDocument17 pagesZach West's " Electrolyser&Quot - Free-Energy DevicesCarlos JuniorNo ratings yet
- Test Series For Neet-2020Document23 pagesTest Series For Neet-2020Bandhavi Singhania0% (1)
- Biology Grade 11 Midterm ReviewDocument35 pagesBiology Grade 11 Midterm Review02-11TH2- Trần Ngọc Ngân AnhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Lecture Notes: The Structure of DNADocument9 pagesChapter 11 Lecture Notes: The Structure of DNAKrishna VenkataNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Real Pharmaceutical Wastewater Using Different Processes Based On Ultrasound in Combination With OxidantsDocument9 pagesTreatment of Real Pharmaceutical Wastewater Using Different Processes Based On Ultrasound in Combination With OxidantsVijaya GosuNo ratings yet
- Seibert Annual ReportDocument109 pagesSeibert Annual ReportChien NguyenNo ratings yet
- Pair and Group ExercisesDocument91 pagesPair and Group Exercisesedgaranaya13No ratings yet
- Wave Assisted Propulsion by Lieutenant General SPC Cory A. HofstadDocument6 pagesWave Assisted Propulsion by Lieutenant General SPC Cory A. HofstadCory Andrew HofstadNo ratings yet
- Notes For Chemistry PracticalsDocument32 pagesNotes For Chemistry Practicalsj0ntj2ivjyNo ratings yet
- SPH Bearing Draft (09.06.11)Document38 pagesSPH Bearing Draft (09.06.11)rchandra2473No ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet Modelling 1718Document2 pagesCheat Sheet Modelling 1718Siti MaisarahNo ratings yet
- Introductory Biochemistry: CHEM 160Document31 pagesIntroductory Biochemistry: CHEM 160Gianna Kristen MirandaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3: Structure of The AtomDocument34 pagesChapter - 3: Structure of The AtomFozia ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Daftar Alat, Biaya Pengujian Dan Operator: TMT 3 September 2016 Jenispengujian Biaya Per Sampel (Rupiah) Operator Ket.Document6 pagesDaftar Alat, Biaya Pengujian Dan Operator: TMT 3 September 2016 Jenispengujian Biaya Per Sampel (Rupiah) Operator Ket.Charis Achmad TajuddinNo ratings yet
- Identifying Nutrients Lab ReportDocument4 pagesIdentifying Nutrients Lab ReportKara Mandawe PatelNo ratings yet
- Pec LTD.: Daily Welding Visual Inspection ReportDocument5 pagesPec LTD.: Daily Welding Visual Inspection ReportNatarajan MurugesanNo ratings yet
- ATSP Lecture 01 (Bonding and Types of Solids)Document53 pagesATSP Lecture 01 (Bonding and Types of Solids)Linh DangNo ratings yet
- ICH Quality Guidelines: An Implementation GuideFrom EverandICH Quality Guidelines: An Implementation GuideAndrew TeasdaleNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideFrom EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideNo ratings yet
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (137)
- Lower Secondary Science Workbook: Stage 8From EverandLower Secondary Science Workbook: Stage 8Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsFrom EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsFrom EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- How to Teach Nature Journaling: Curiosity, Wonder, AttentionFrom EverandHow to Teach Nature Journaling: Curiosity, Wonder, AttentionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactFrom EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactFrom EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandChemistry: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- It's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingFrom EverandIt's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- AP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeFrom EverandAP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeNo ratings yet
- AP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeFrom EverandAP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)From EverandMental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)No ratings yet
- Limitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersFrom EverandLimitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)