Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DEVELOPMENT OF PIG EMBRYO
Uploaded by
Astrid AmadorOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DEVELOPMENT OF PIG EMBRYO
Uploaded by
Astrid AmadorCopyright:
Available Formats
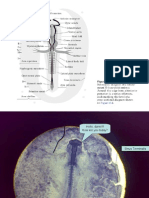
[DEVELOPMENT OF PIG EMBRYO: POSTERIOR]
STRUCTURES
DESCRIPTION
LEVEL OF THE LUNG BUDS (STEM BROCHI) AND FORELEG BUDS
Paired posterior cardinal
Most dorsal vein lying in the place occupied
veins
by the common cardinal veins.
syn: postcardinal vein
Pair of bud-like tissue masses from the
dorsolateral sides of the body
Level of the heart
Foreleg bud
Outer layer ectoderm
Apical ridge at the apex of ectoderm
Core mesoderm
interconnections of the ventral rami of the
cervical & thoracic spinal nerves
Brachial plexus
where the nerves of the forelimb branch out
innervates the limbs
small middle hole beneath the pair of dorsal
Esophagus
aorta
pair of vesicles that appear on both sides of
Lung buds
the trachea
thick partition of mesenchyme enclosing the
Mediastinum
trachea and the lung
pair of coelomic cavities on each side of
Pleural cavity
mediastinum where lung buds developed
Parietal pleura
lining of the lateral wall of the pleural cavity
medial epithelial lining of the pleural cavity
Visceral pleura
which will cover the lungs
mesenchymal partition extending across
Septum transversum
the body
blood vessel embedded on the right sie of
Posterior vena cava
the septum transversum
syn: inferior vena cava
occupies a dorsal position in the substance
thick-walled mass below septum
Ventricle
transversum
LEVEL OF THE LIVER AND THE STOMACH
Spinal nerve
arise from the spinal cord by the roots
contains spinal ganglion and sensory
Dorsal root
neurons that differentiate form the ganglion
syn: afferent / sensory root
cells
Ventral root
made up of motor fibers from motor
syn: efferent / motor root
neurons of the basal plate of the spinal cord
THREE (3) BRANCHES OF SPINAL NERVE TRUNK
carries fibers associated with the drsal
parts of the body
Dorsal ramus
skin, deep muscles of the back,
spinal column
carries fibers associated with the ventral
Ventral ramus
and lateral body wall
Ramus communicans
branch from ventral ramus
carries fibers to the viscera by means of
FATE
[DEVELOPMENT OF PIG EMBRYO: POSTERIOR]
Dorsal root ganglion
Mammary ridges
Descending aorta
Sympathetic ganglion
Mesonephric duct
Glomerulus
Mesonephros
Bowmans capsule
syn: glomerular capsule
Malpigian corpuscle
syn: renal corpuscle
glomerulus + bowmans capsule
coiled tubules at the outer lateral portion of
each mesonephros
connected at the corpuscles
horizontally enlarged segment of the
foregut which replaces the esophagus (series)
large mass with strands of cells hepatic
cord and spaces between strands hepatic
sinusoids
divided into: dorsal and ventral lobes
large blood vessels embedded in the liver
drains blood from: subcardinal sinus
sinus venosus
receives blood from: ductus venosus
lies on the right side of the stomach
supported by caval mesentery
Liver
Posterior vena cava
Ductus venosus
Dorsal mesogaster
Omental bursa
Epiploic foramen
pair of ganglion immediately dorsal to the
descending aorta
functional kidney at this stage
retroperitoneal & posterior to the liver
large oval canal along the ventral margin of
mesonephros
knots of blood capillaries at the medial side
of each kidney
very flat epthelium which surrounds the
glomerulus
Mesonephric tubules
Stomach
prevertebral sympathetic chain
medioventral to sympathetic ganglion
darkly nucleated body on both sides of the
spinal cord
fibers leads to the dorsolateral wall of spinal
cord
pair of elevations on the dorsolateral part of
the body
fused dorsal aorta
paired in the branchial region
Hepatogastric ligament
embedded in the septum transversum
holds the stomach in place
mesenchymal cells within it will form the
spleen
closed cavity to the right of the stomach
opens to peritoneal cavity
opening at the omental bursa
mesentery connecting the liver and
stomach
+ + + + + hepatoduodenal ligament
metanephros
Metanephric duct
Female: degenerate?
Male: epididymis, vas
deferens, seminal vesicle
Dorsal omentum
Lesser omentum
[DEVELOPMENT OF PIG EMBRYO: POSTERIOR]
Falciform ligament
Somites
Common bile duct
remnant of the ventral mesentery
attaches the liver to the ventral body wall
LEVEL OF THE COMMON BILE DUCT
44 paired somites
lumen = myocoel
myotome dorsomedian part of the block
dermatome will migrate under epidermis
sclerotome surround spinal cord and
notochord to form vertebral column
Skeletal muscles
Connective tissue of dermis
Duodenum
Posterior vena cava
Hepatic portal vein
Gonad rudiment
Big left & small right
umbilical veins
LEVEL THROUGH THE GALLBLADDER AND UMBILICAL CORD
Hepatic portal vein
Dorsal pancreas
Ventral pancreas
Gallbladder
Pair of umbilical veins
Cranial and caudal limb
of the intestinal loop
Superior mesenteric vein
and artery
Common vitelline vein
Left and right umbilical
arteries
allantois
Small right umbilical vein
& big left umbilical veins
tail
LEVEL THROUGH THE UROGENITAL SINUS AND UMBILICAL CORD
Subcardinal veins
Mesocolon
Mesonephric duct
Urogenital sinus
Rectum
Umbilical veins
Umbilical arteries
Allantois
Umbilical cord
Whartons jelly
LEVEL OF THE HINDLIMB BUD
Hindleg bud
[DEVELOPMENT OF PIG EMBRYO: POSTERIOR]
Pair of mesonephric duct
Mesocolon
Ureter
Spinal ganglia
Ventral roots of the
spinal nerves
Sclerotome
Myotome
Dermatome
Epidermis
Intersegmental arteries
LEVEL THROUGH THE SPINAL NERVE
You might also like
- Exercise 8 Pig Embryo (Posterior Sections)Document16 pagesExercise 8 Pig Embryo (Posterior Sections)Gail AmuraoNo ratings yet
- 72 HR ReviewerDocument8 pages72 HR ReviewerAstrid AmadorNo ratings yet
- 33-Hour Chick ReviewerDocument5 pages33-Hour Chick ReviewerBeatriceNo ratings yet
- Frog EmbryosDocument43 pagesFrog EmbryosNics Martinez100% (7)
- Pig Embryo Development StagesDocument12 pagesPig Embryo Development StagesKarmina SantosNo ratings yet
- EmbryoLab 10mm FrogDocument13 pagesEmbryoLab 10mm FrogpauNo ratings yet
- 33 Hour Embryo Sections and Labeled DiagramsDocument24 pages33 Hour Embryo Sections and Labeled Diagramsnabilalk100% (1)
- Early Chick Embryo Development StagesDocument74 pagesEarly Chick Embryo Development StagesMinette EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- 72-HR ChickDocument16 pages72-HR Chick411452123100% (1)
- Chick Embryo (Embryology Lab)Document9 pagesChick Embryo (Embryology Lab)humanupgrade100% (1)
- ANIMAL GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT: The Tadpole (External Gill Stage)Document6 pagesANIMAL GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT: The Tadpole (External Gill Stage)Junko TsukudaNo ratings yet
- 33 hour Chick Embryo Development StagesDocument36 pages33 hour Chick Embryo Development StagesSasha GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Chick Embryo 72 HoursDocument48 pagesChick Embryo 72 HoursogheeluvNo ratings yet
- 48 Hour Chick Reviewer PDFDocument5 pages48 Hour Chick Reviewer PDFSheanna May FuriaNo ratings yet
- Ex4.2 Development of Frog EmbryoDocument14 pagesEx4.2 Development of Frog EmbryoNexie100% (1)
- Exercise 17 Serial Transverse Section of A 33 Hour Chick Embryo PDFDocument4 pagesExercise 17 Serial Transverse Section of A 33 Hour Chick Embryo PDFMichaela FayeNo ratings yet
- Biology 453 - Comparative Vert. Anatomy WEEK 1, LAB 2: Embryology of Frog & ChickDocument9 pagesBiology 453 - Comparative Vert. Anatomy WEEK 1, LAB 2: Embryology of Frog & ChickPunk Midget-FairyNo ratings yet
- Chick Embryo WMDocument6 pagesChick Embryo WMdhyan_ajjah67% (3)
- 48hr and 72hr Chick EmbryoDocument28 pages48hr and 72hr Chick EmbryoRichelle IgnacioNo ratings yet
- 10 MM Transverse Section Level of Telencephalon and Olfactory OrgansDocument9 pages10 MM Transverse Section Level of Telencephalon and Olfactory OrgansMarina of The SeaNo ratings yet
- 7 MM Frog EmbryoDocument20 pages7 MM Frog EmbryoCourtneyNo ratings yet
- Development of Frog EmbryoDocument13 pagesDevelopment of Frog EmbryoNexieNo ratings yet
- Embryo Lab: 72 HR Chick ReviwerDocument7 pagesEmbryo Lab: 72 HR Chick ReviwerGail AmuraoNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4 Frog Embryo 4mm 7mm 10mmDocument23 pagesExercise 4 Frog Embryo 4mm 7mm 10mmrexartooz95% (19)
- 10mm Frog Embryo - Embryology LabDocument4 pages10mm Frog Embryo - Embryology LabIvy CruzNo ratings yet
- 4Mm Frog Embryo: Lab Exercise 4 OrganogenesisDocument16 pages4Mm Frog Embryo: Lab Exercise 4 OrganogenesisDimple May Gianne DumaguitNo ratings yet
- 48 96 Hour Chick Embryo Wholoe Mount and Serial Sections EmbryologyDocument34 pages48 96 Hour Chick Embryo Wholoe Mount and Serial Sections EmbryologyChristalie Bea Fernandez100% (2)
- 7 MM Frog DevelopmentDocument28 pages7 MM Frog DevelopmentaemilianneNo ratings yet
- 7 MM FrogDocument28 pages7 MM FrogNiki Reroll04No ratings yet
- Embryo Lab Exercise 4Document17 pagesEmbryo Lab Exercise 4Karmina SantosNo ratings yet
- Chick 33 HRDocument14 pagesChick 33 HRaa628No ratings yet
- Embryo Lab Org 2Document14 pagesEmbryo Lab Org 2pauNo ratings yet
- 72 Hours Chick EmbryoDocument18 pages72 Hours Chick EmbryoZhairra Marie DionsonNo ratings yet
- Chick Embryo ImagesDocument19 pagesChick Embryo ImagesnesyaNo ratings yet
- Development of the pig embryo anterior regionsDocument11 pagesDevelopment of the pig embryo anterior regionsvada_soNo ratings yet
- 48-Hour Chick ReviewerDocument5 pages48-Hour Chick ReviewerBeatrice100% (1)
- 4 MM FrogDocument5 pages4 MM FrogMarina of The SeaNo ratings yet
- Parts of Frog HistologyDocument6 pagesParts of Frog HistologyVanessa RebancosNo ratings yet
- 24-Hr Chick EmbryoDocument8 pages24-Hr Chick EmbryopauNo ratings yet
- Chick 72 HR DDocument35 pagesChick 72 HR Daa628No ratings yet
- 24hr Chick Cross SectionsDocument16 pages24hr Chick Cross Sectionsaa628100% (9)
- Chick Serial SectionsDocument74 pagesChick Serial SectionsKazuki FuchoinNo ratings yet
- 48 Hour Chick Embryo Serial SectionsDocument22 pages48 Hour Chick Embryo Serial SectionsNathan Bantayan100% (1)
- Chick Embryo ReviewerDocument9 pagesChick Embryo ReviewerKeana TapangNo ratings yet
- 10mm Frog TadpoleDocument30 pages10mm Frog TadpoleSarah Margaret Chong33% (3)
- Serial Sections of a 10 mm Pig EmbryoDocument16 pagesSerial Sections of a 10 mm Pig EmbryoMichaela Faye100% (1)
- 10mm Pig Embryo Whole Mount with Labeled StructuresDocument34 pages10mm Pig Embryo Whole Mount with Labeled StructuresVanessa CarinoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System - Comparative Anatomy of VertebratesDocument7 pagesRespiratory System - Comparative Anatomy of VertebratesAlyssa Gail de Vera0% (1)
- PigDocument34 pagesPigaa62893% (14)
- Skin Histology ComparisonDocument7 pagesSkin Histology ComparisonMinamiSapphire BarbosaNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 7 The Frog EmbryoDocument13 pagesActivity No. 7 The Frog EmbryoFerhaeeza KalayakanNo ratings yet
- 18 Hour Chick EmbryoDocument7 pages18 Hour Chick Embryoaa628100% (2)
- Dumaguit (2021)Document12 pagesDumaguit (2021)Dimple May Gianne DumaguitNo ratings yet
- Cestodes 2020Document10 pagesCestodes 2020CDNo ratings yet
- 10mm Frog Lungbud-AnusDocument11 pages10mm Frog Lungbud-Anusaa628100% (2)
- Male Reproductive Tract: Kristel Paulane Fleur Lubrin-Oandasan MD DpogsDocument28 pagesMale Reproductive Tract: Kristel Paulane Fleur Lubrin-Oandasan MD DpogsFaith CarylaineNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Serous Sacs, Features and FunctionsDocument7 pagesLecture 5 Serous Sacs, Features and Functionssomebody_maNo ratings yet
- The AbdomenDocument3 pagesThe AbdomenotaNo ratings yet
- Anterior Abdominal WallDocument47 pagesAnterior Abdominal WallJohn NgumbiNo ratings yet
- Circulatory ShockDocument9 pagesCirculatory ShockTri UtomoNo ratings yet
- As To Number of People Exercising Government Powers: (Type The Document Title)Document2 pagesAs To Number of People Exercising Government Powers: (Type The Document Title)Astrid AmadorNo ratings yet
- Monthly calendar sheetsDocument12 pagesMonthly calendar sheetsAstrid AmadorNo ratings yet
- Embryo QuizDocument2 pagesEmbryo QuizAstrid AmadorNo ratings yet
- DiscussionDocument1 pageDiscussionAstrid AmadorNo ratings yet
- Structures TalagaDocument8 pagesStructures TalagaAstrid AmadorNo ratings yet
- Forms of GovernmentDocument2 pagesForms of GovernmentAstrid AmadorNo ratings yet
- Taxonomic Classification of Phylum Echinodermata PDFDocument1 pageTaxonomic Classification of Phylum Echinodermata PDFAstrid AmadorNo ratings yet
- 24 HRDocument3 pages24 HRAstrid AmadorNo ratings yet
- 48 HR ReviewerDocument7 pages48 HR ReviewerAstrid AmadorNo ratings yet
- Kingdom classification of Cyanobacteria, Euglena, Dinoflagellates, Diatoms and Brown AlgaeDocument2 pagesKingdom classification of Cyanobacteria, Euglena, Dinoflagellates, Diatoms and Brown AlgaeAstrid AmadorNo ratings yet
- Problem Set On Membrane PotentialDocument1 pageProblem Set On Membrane PotentialAstrid AmadorNo ratings yet
- Introduction To InvertebratesDocument1 pageIntroduction To InvertebratesAstrid AmadorNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ProtozoaDocument5 pagesIntroduction To ProtozoaAstrid AmadorNo ratings yet
- Sleep Disorders in Children and Adolescents: Understanding Causes and Treatment OptionsDocument50 pagesSleep Disorders in Children and Adolescents: Understanding Causes and Treatment OptionsCitra Sukri Sugesti100% (1)
- Psychology Prelim Exam 1st Sem 2016-17Document2 pagesPsychology Prelim Exam 1st Sem 2016-17Monroe Ortizano100% (1)
- Cafeine PDFDocument376 pagesCafeine PDFLuis RamosNo ratings yet
- Guideline, Management of HypoglycemiaDocument5 pagesGuideline, Management of HypoglycemianellieauthorNo ratings yet
- Lecture (Endocrine System)Document15 pagesLecture (Endocrine System)GerofeNo ratings yet
- RN Thread NclexDocument21 pagesRN Thread NclexMaria Nadia MihalikNo ratings yet
- Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Presenting With Priapism: A Case ReportDocument4 pagesChronic Myeloid Leukemia Presenting With Priapism: A Case ReportJulio LeviNo ratings yet
- DM Type IiDocument5 pagesDM Type IiKay Clarice G. TimosaNo ratings yet
- Sensory Processing and Autism Evidence Research Future Directions DR Roseann Schaaf PDFDocument59 pagesSensory Processing and Autism Evidence Research Future Directions DR Roseann Schaaf PDFKiyorNo ratings yet
- DLaboratory Actiivty 5 - Integumentary System AnswerDocument6 pagesDLaboratory Actiivty 5 - Integumentary System AnswerSYDNEY JILL ACHAINo ratings yet
- ImciDocument3 pagesImciJohn Benzon0% (1)
- Crystalls & Mineralls MeaningsDocument26 pagesCrystalls & Mineralls MeaningsCandice Cogburn100% (1)
- The Speaking ProcessDocument29 pagesThe Speaking ProcessJoshua AbadNo ratings yet
- Iran's General Medicine Degree Program OverviewDocument16 pagesIran's General Medicine Degree Program OverviewMohamad GhafooryNo ratings yet
- Hong Kong LolDocument18 pagesHong Kong Lolpewep2No ratings yet
- An evidence-based approach to undifferentiated shockDocument1 pageAn evidence-based approach to undifferentiated shockHely ICNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 BloodDocument43 pagesChapter 10 Bloodemms meNo ratings yet
- Thesis Reza Salman Roghani PDFDocument76 pagesThesis Reza Salman Roghani PDFscoopyNo ratings yet
- Kasus Farmakoterapi 3Document32 pagesKasus Farmakoterapi 3AnisNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Monod KineticsDocument19 pagesLecture 3 - Monod KineticsZeny Naranjo0% (1)
- Comparing Animal and Plant Cell Structures and FunctionsDocument30 pagesComparing Animal and Plant Cell Structures and FunctionsNetty BontuyanNo ratings yet
- Tetralogy of FallotDocument3 pagesTetralogy of FallotKamal FauzeNo ratings yet
- Genetics - Poster - Sex Determination and Sex LinkageDocument1 pageGenetics - Poster - Sex Determination and Sex LinkageTisha TabhitaNo ratings yet
- ConceptsOfBiology OPDocument638 pagesConceptsOfBiology OPReby Nirupu100% (1)
- A Level Extended Response QuestionsDocument206 pagesA Level Extended Response QuestionsakilNo ratings yet
- Neuropsychoanalysis - The Concious ID Solms PDFDocument16 pagesNeuropsychoanalysis - The Concious ID Solms PDFAndrei PredaNo ratings yet
- Passive to Active Voice ConversionDocument3 pagesPassive to Active Voice ConversionQhaisya Binasanjaya67% (3)
- Contorneo de Hipocamo en RadioterapiaDocument33 pagesContorneo de Hipocamo en RadioterapiaclaudiaNo ratings yet
- Klubsybear Additional Recalls: Hematology A.karyolysisDocument2 pagesKlubsybear Additional Recalls: Hematology A.karyolysisMartin ClydeNo ratings yet
- Full Download Sensation and Perception 9th Edition Goldstein Test BankDocument35 pagesFull Download Sensation and Perception 9th Edition Goldstein Test Bankezrak2martin100% (34)