Professional Documents
Culture Documents
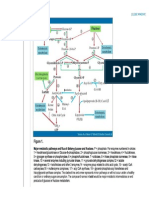
ANS Pharmacology Big Map
Uploaded by
LeeMinhoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ANS Pharmacology Big Map
Uploaded by
LeeMinhoCopyright:
Available Formats
Hypotensive
emergency
Phenylephrine
Mitodrine
Clonidine
Apraclonidine
Brimonidine
More prominent
inotropic (FOC) then
chronotropic (HR)
effect on heart
For cardiogenic
shock
For patient with Low
CO
Methacholine
Carbachol
2 agonist
Direct Acting
Dobutamine
1 agonist
Bethanecol
Selective
Pilocarpine
Xamoterol
Bronchial Asthma Salbutamol
Terbutaline
Salmeterol 2 agonist
Formoterol
Ritodrine
Bromocriptine D2 agonist
oxymetazoline 1 and 2
Isoprenaline
Bronchial Asthma
1 & 2
(Isoproterenol)
Acute anaphylactic
Shock
Adjunct with local
anaesthetics
Haemostatic agent
control superficial
beeding
Provide inotrophic
Adrenaline (given
support (influence
1 2 1 2
IM/SC)
force of muscular
contractions)
Epistaxis nasal
packs
(vasoconstriction)
Bronchial Asthma
Treat CARDIAC
ARREST
In vivo Reflex
bradycardia
In vitro
tachycardia
Restore BP in acute
hypotensive states
In states whr thr is
severe hypotension
and vasodilation of
peripheral blood
vessels
Cannot use clinically
coz very short
acting
Acetylcholine
1 agonist
Direct Acting
Reversible ACHe
Inhibitor (3-4 Hr)
Sympathomimetic
Non-Selective
postoperative
abdominal
distension ; gastric
atony and retention;
gastroparesis
Urinary retention;
gastroparesis
Xerostomia
Opthalmological
diseases, eg
glaucomaa
Parasympathomime
tic
Indirect Acting
(inhibit ACHe)
Noradrenaline
Can pass BBB Has CNS Effect
Treat Atropine
poisoning
(parenterally)
Eye drops; produce
Physostigmine
Miosis; contract
ciliary muscle;
reduce IOP
Antidote to
competitive NMBA
Cannot pass BBB
Act on NMJ nd GIT
treat Myasthenia
Gravis
Neostigmine
Stimulate bowels
and bladders after
surgery
Antidote to
competitive NMBA
Diagnosse
Myasthenia Gravis;
Treat myasthenic
Edrophonium (5
crisis (weakness
min)
due to inadequate
anticholinesterase
treatment
Ecothiophate
Highly lipid soluble
(except
echothiophate)
3 phases: acute
choinergic
phase>>
intermediate
syndrome>>
organophosphate-i
nduced
polyneuropathy
1 2 1
Dopamine D
Amphetamine
Methamphetamine
Releasing agent
Ephedrine
Tyramine
Indirect Acting
Cocaine
Uptake inhibitor
Tricyclic
antidepressants
Pargyline
MAO/ COMT
inhibitor
Entacapone
Ephedrine MIxed Acting
Pupil dilation; IOP
increase; HR, BP
increase;
vasoconstriction;
skeletal muscle
Effects
vessels
vasodilation;
ejaculation; increase
blood glucose,
bronchodilation (2)
Prazosin
Terazosin
Doxazoxin
1 Selective
antagonist
Trimazosin
Tamsulosin
(uroselective)
Tolazoline
Non Selective
Phentolamine
Blocker (1, 2)
Phenoxybenzamine
Systemic
Hypertension
Congestive heart
failure
Therapeutic uses
Pheochromocytoma
Raynauds disease
Benign prostatic
hyperplasia
Propranolol
Non Selective
Timolol
Blocker (1st Gen)
Nadolol
Acebutolol
Atenolol
1 selective (2nd
Bisoprolol
Gen)
Esmolol
Metoprolol
Non Selective
Carteolol
blockers with
Carvedilol
additional actions
Labetalol
(3rd Gen)
1 selective blocker
Betaxolol
with additional
Celiprolol
actions (4th Gen)
Arrhythmia
Angina
Hypertension
Myocardial
infarction
Hyperthyroidism
Anxiety
Alcohol/ Opioid
Therapeutic uses
withdrawal
symptoms
Glaucoma
Benign essential
tremor
Pheochromocytoma
Hepatic portal
hypertension
Irreversible ACHe
Inhibitor (form
covalent bond with
enzyme)
Organophosphorous
compounds cause
poisoning
Trearment:
Cholinesterase
regenerators:
Pralidoxime
reactivate
phosphorylated
enzymes (within first
few hours of
poisoning)
Sympathetic
ANS
Pharmacology
Diazepam: control
convulsion
Pupil constriction
(miosis); IOP, HR,
BP decrease;
vasodilation;
Effects
bronchoconsriction;
GI motility increase;
uterine contraction;
erection
Ganglion Blocking
Acting at
Agent
Nicotinic
Neuromuscular
Receptor
Blocking Agent
Parasympathetic
adrenoceptor
antagonist
Acting at Muscarinic
Receptor
Sympatholytic
adrenoceptor
antagonist
D-tubocurarine
Non- Depolarizing (
Gallamine
competitive)
Atracurium
Succinylcholin
Depolarizing
Metabolised by
e
(Non-competitive;
pseudocholine
(Suxamethoni
Depolarize plasma
esterase in plasma
um)
membrane of
skeletal m. fiber)
Decamethonium
Competitive: by
neostigmine,
physostigmine
Termination of
Non-competitive
Action
(depolarizing):
Cannot be reversed
by
anticholinesterase
Parasympatholytic
(competitive
antagonist of Ach)
NMBA
Treatment: Atropine
in high doses until
signs of atropine
poisoning appear
Hexamethonium
D- Tubocurarine
Succinylcholine
Dilate Pupil
Anaesthetic
premedication dry
secretions
Decrease
pancreatic
Atropine
secretions in acute
pancreatitis
Organophosphorous
poisoning treatment
Natural
(block muscarinic
action)
Antiemetic (prevent
motion sickness)
Anaesthetic
Hyoscine
premedication dry
(scopolamine)
secretions
Relax GI smooth m.
fascilitate
endoscopy
Semi-synthetic Homatropine Dilate Pupil
Bronchial asthma
Ipratopium Bromide
COPD
Oxyphencyclimine
Cyclopentolate Eye drops
Synthetic
Eye drops
Tropicamide
Congeners
mydriasis
Antispasmodic in
Dicyclomine
irritable bowel
syndrome
Benztropine
Effects:
Mydriasis;IOP
increase; MODEST
Tachycardia; block
all secretions
excepet milk; Inhibit
GI motility; relax
bronchial, biliary,
urinary tract smooth
m; CNS effect: mild
restlessness,
hallucination;
antiemetic action
Dry mouth; blurred
vision; dizziness;
fatigue; urinary
retention in old men;
coonstipation;
cyclopegia;
increased IOP
Toxicity: Hot as a
Adverse Effects hare, Blind as a Bat,
Dry as a bone, Red
as Beet, Mad as
Hatter
Gastric lavage, Ice
bags,
Physostigmine, dark
comfortable
room, gastric lavage
You might also like
- Neurology Study Guide Oral Board Exam ReviewDocument1 pageNeurology Study Guide Oral Board Exam Reviewxmc5505No ratings yet
- Cholinergic DrugsDocument15 pagesCholinergic DrugsChris Girgis100% (1)
- Anatomy MCQDocument3 pagesAnatomy MCQSrinivasa Rao BollaNo ratings yet
- PHM - Endocrine DrugsDocument3 pagesPHM - Endocrine DrugsJeanne RodiñoNo ratings yet
- Skitchy MicroDocument190 pagesSkitchy MicrohaneenNo ratings yet
- Saeed Sentence Relation and Truth (Summary)Document11 pagesSaeed Sentence Relation and Truth (Summary)Mohammad Hassan100% (1)
- Porifera and CnidariaDocument16 pagesPorifera and CnidariaMichaelNo ratings yet
- Oxygenation - NCPDocument5 pagesOxygenation - NCPCazze SunioNo ratings yet
- Antiadrenergic DrugsDocument44 pagesAntiadrenergic DrugsHUZAIFA YAMAANNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The Adrenergic Nervous SystemDocument37 pagesDrugs Affecting The Adrenergic Nervous SystemJah SuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 (Adrenergic Antagonists)Document64 pagesChapter 7 (Adrenergic Antagonists)Aneeza AhmadNo ratings yet
- Ascending Tracts (Somatosensory Axis)Document94 pagesAscending Tracts (Somatosensory Axis)Gks100% (1)
- 1 Practise Questions Keith Moore 5th Edition Should ReadDocument113 pages1 Practise Questions Keith Moore 5th Edition Should ReadNasan Shehada100% (1)
- BOARD REVIEW NEUROPHYSIOLOGY DGS For March PLEDocument293 pagesBOARD REVIEW NEUROPHYSIOLOGY DGS For March PLEKaye Nee100% (2)
- # Prefix, Root, Suffix Examples (Generic Names) Drug Class or Drug CategoryDocument3 pages# Prefix, Root, Suffix Examples (Generic Names) Drug Class or Drug CategorySharon TanveerNo ratings yet
- Anti EmeticsDocument29 pagesAnti EmeticsBezawit TsigeNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic AntagonistsDocument6 pagesAdrenergic Antagonistsfiena92100% (2)
- Drugs Acting On Peripheral Nervous SystemDocument72 pagesDrugs Acting On Peripheral Nervous SystemاسيرالاحزانNo ratings yet
- Antiviral Agents: Unit - 2 Pharmaceutical Chemistry - I (Advanced Medicinal Chemistry) Topic: Antiviral AgentsDocument20 pagesAntiviral Agents: Unit - 2 Pharmaceutical Chemistry - I (Advanced Medicinal Chemistry) Topic: Antiviral AgentsGunjan Kalyani100% (1)
- Anti FungalsDocument5 pagesAnti FungalskakuNo ratings yet
- ANTIVIRAL DRUGS AssignmentDocument9 pagesANTIVIRAL DRUGS AssignmentRAMSHA RAMSHANo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument120 pagesPharmacologyFluffy_iceNo ratings yet
- SAQ in EmbryologyDocument14 pagesSAQ in EmbryologyDr Md Abedur Rahman100% (3)
- Assignment - Anti Viral DrugsDocument5 pagesAssignment - Anti Viral DrugsmziabdNo ratings yet
- 6-8 Thrombolitics Antiplatelet AnticoagulantDocument36 pages6-8 Thrombolitics Antiplatelet AnticoagulantFatima ZahraNo ratings yet
- Renal Physiology IDocument16 pagesRenal Physiology IJubilee Christiene AngNo ratings yet
- A Summary of The Chemical Mediators Involve in The Acute Inflammatory Response Is Shown in The Table BelowDocument30 pagesA Summary of The Chemical Mediators Involve in The Acute Inflammatory Response Is Shown in The Table Belowinny100% (1)
- Total Proteins & Albumin AnalysisDocument16 pagesTotal Proteins & Albumin AnalysisMustafa KhandgawiNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Disorders 1234399857677955 1Document130 pagesEndocrine Disorders 1234399857677955 1api-19824701No ratings yet
- Autonomic and Systemic Pharmacology DR DahalDocument119 pagesAutonomic and Systemic Pharmacology DR Dahalअविनाश भाल्टरNo ratings yet
- Approach To Comatose Child: DR G.VenkateshDocument83 pagesApproach To Comatose Child: DR G.VenkateshG VenkateshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Neoplastic Proliferations of White CellsDocument16 pagesChapter 13 Neoplastic Proliferations of White CellsOmar100% (1)
- 3.0 Grand Physiology Finals Compilation - Batch 2017Document89 pages3.0 Grand Physiology Finals Compilation - Batch 2017Sheryl Layne Lao-SebrioNo ratings yet
- Blood Supply of The BrainDocument37 pagesBlood Supply of The BrainueumanaNo ratings yet
- PK Practice Problems KeyDocument4 pagesPK Practice Problems KeyMohamed AmrNo ratings yet
- Pons MedullaDocument32 pagesPons MedullaEnaWahahaNo ratings yet
- Metabolism of XenobioticsDocument5 pagesMetabolism of XenobioticsJanelle Bondad100% (2)
- Renal Physiology PDFDocument24 pagesRenal Physiology PDFMishal IlyasNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument40 pagesCardiovascular SystemDouglas Jacques100% (1)
- MCQ For PharmacologyDocument6 pagesMCQ For PharmacologyTasneem Elwaleed100% (1)
- Normal Microbiota of The BodyDocument20 pagesNormal Microbiota of The BodyeyezakeyeNo ratings yet
- (8!5!13) Cell Injury OutlineDocument9 pages(8!5!13) Cell Injury OutlineBhumiShahNo ratings yet
- PharmacologyDocument74 pagesPharmacologyKiara Denise Tamayo100% (1)
- Hypertension and Angina DrugsDocument158 pagesHypertension and Angina DrugsMelissa SalayogNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic DrugsDocument10 pagesAntiarrhythmic DrugsUma MounaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Gland Hormone(s) Secreted Stimulus Effect of Hormone Inhibition PathologyDocument3 pagesEndocrine Gland Hormone(s) Secreted Stimulus Effect of Hormone Inhibition PathologySamuelNo ratings yet
- Em Viva PhysiologyDocument11 pagesEm Viva PhysiologyWaleed Mabood100% (1)
- Cholinergic Anticholinergic DrugsDocument60 pagesCholinergic Anticholinergic DrugsMD. RASEL MAHMUD MIMNo ratings yet
- MOCK QUIZ - Head & Neck EmbryoDocument3 pagesMOCK QUIZ - Head & Neck EmbryoLanz RomuloNo ratings yet
- Slides of Fever 3Document52 pagesSlides of Fever 3Selly SelNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Cranial NervesDocument3 pagesAnatomy Cranial NervesMedShare100% (1)
- ANS ReceptorsDocument14 pagesANS ReceptorsAisha AliNo ratings yet
- Cholinergic Agonists/ Cholinomimetic Agents: Dr. Kyi Kyi Tha Basic Medical Sciences Kulliyyah of Pharmacy IiumDocument21 pagesCholinergic Agonists/ Cholinomimetic Agents: Dr. Kyi Kyi Tha Basic Medical Sciences Kulliyyah of Pharmacy IiumZhuan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Cough and Bronchial AsthmaDocument47 pagesDrugs For Cough and Bronchial AsthmaNavlika DuttaNo ratings yet
- Special NeurologyDocument115 pagesSpecial NeurologyUbaidillah Romadlon AlfairuziNo ratings yet
- Pharma LMRP 2019Document30 pagesPharma LMRP 2019sk100% (1)
- Histamine 5-ht Angiotensin Kinin Endothelins Eicosanoids Interleukins TNF Interferones Growth FCDocument57 pagesHistamine 5-ht Angiotensin Kinin Endothelins Eicosanoids Interleukins TNF Interferones Growth FCFaisal 'arifNo ratings yet
- Problem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyFrom EverandProblem-based Approach to Gastroenterology and HepatologyJohn N. PlevrisNo ratings yet
- The Leukotrienes: Chemistry and BiologyFrom EverandThe Leukotrienes: Chemistry and BiologyLawrence ChakrinNo ratings yet
- Ion Channels in Health and DiseaseFrom EverandIon Channels in Health and DiseaseGeoffrey S. PittNo ratings yet
- Deficiencies of the Urea Cycle - Clinical Significance and TherapyFrom EverandDeficiencies of the Urea Cycle - Clinical Significance and TherapyNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Cholinergic and Adrenergic Transmission: Proceedings of the Second International Pharmacological Meeting, August 20—23, 1963From EverandPharmacology of Cholinergic and Adrenergic Transmission: Proceedings of the Second International Pharmacological Meeting, August 20—23, 1963G. B. KoelleNo ratings yet
- Selected Topics in the History of Biochemistry. Personal Recollections. Part IIIFrom EverandSelected Topics in the History of Biochemistry. Personal Recollections. Part IIIRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Lipid MetabolismDocument1 pageLipid MetabolismLeeMinhoNo ratings yet
- StaphylococciDocument1 pageStaphylococciLeeMinhoNo ratings yet
- Cute Wildlife AnimalsDocument1 pageCute Wildlife AnimalsLeeMinhoNo ratings yet
- Adrenaline in Dental PracticeDocument1 pageAdrenaline in Dental PracticeLeeMinhoNo ratings yet
- Incisors 2.0Document5 pagesIncisors 2.0LeeMinhoNo ratings yet
- Overview of Haematopoeisis FinalDocument39 pagesOverview of Haematopoeisis FinalLeeMinhoNo ratings yet
- Permanent Maxillary Central INCISOR (11, 21) Permanent Maxillary Lateral Incisor (12, 22)Document6 pagesPermanent Maxillary Central INCISOR (11, 21) Permanent Maxillary Lateral Incisor (12, 22)LeeMinhoNo ratings yet
- Axilla and Cubital Fossa (AYY)Document19 pagesAxilla and Cubital Fossa (AYY)LeeMinhoNo ratings yet
- Sensodyne Toothpaste ProductsDocument5 pagesSensodyne Toothpaste ProductsLeeMinhoNo ratings yet
- NBDE DownloadDocument4 pagesNBDE DownloadLeeMinho100% (1)
- Fructose Metabolism PathwayDocument1 pageFructose Metabolism PathwayLeeMinhoNo ratings yet
- 1000 Q BankDocument169 pages1000 Q BankRahul Rohal ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Ahu 1997 22 1 95Document15 pagesAhu 1997 22 1 95Pasajera En TranceNo ratings yet
- LG) Pc-Ii Formulation of Waste Management PlansDocument25 pagesLG) Pc-Ii Formulation of Waste Management PlansAhmed ButtNo ratings yet
- English 9 Week 5 Q4Document4 pagesEnglish 9 Week 5 Q4Angel EjeNo ratings yet
- Porsche Dealer Application DataDocument3 pagesPorsche Dealer Application DataEdwin UcheNo ratings yet
- Vishakha BroadbandDocument6 pagesVishakha Broadbandvishakha sonawaneNo ratings yet
- On The Margins - A Study of The Experiences of Transgender College StudentsDocument14 pagesOn The Margins - A Study of The Experiences of Transgender College StudentsRory J. BlankNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Educational Background Certification Major Name of Institute PeriodDocument2 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Educational Background Certification Major Name of Institute PeriodTHEVINESHNo ratings yet
- Film Interpretation and Reference RadiographsDocument7 pagesFilm Interpretation and Reference RadiographsEnrique Tavira67% (3)
- Curry PowderDocument8 pagesCurry PowderMahendar Vanam100% (1)
- Manual ML 1675 PDFDocument70 pagesManual ML 1675 PDFSergio de BedoutNo ratings yet
- P4 Science Topical Questions Term 1Document36 pagesP4 Science Topical Questions Term 1Sean Liam0% (1)
- Grade 8 Science Text Book 61fb9947be91fDocument289 pagesGrade 8 Science Text Book 61fb9947be91fNadarajah PragatheeswarNo ratings yet
- Time-Temperature Charge Function of A High Dynamic Thermal Heat Storage With Phase Change MaterialDocument15 pagesTime-Temperature Charge Function of A High Dynamic Thermal Heat Storage With Phase Change Materialgassoumi walidNo ratings yet
- Reaffirmed 1998Document13 pagesReaffirmed 1998builconsNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Gastrointestinal Organs: Muhammad ImranDocument21 pagesFunctions of The Gastrointestinal Organs: Muhammad ImranSalman KhanNo ratings yet
- PresentationDocument6 pagesPresentationVruchali ThakareNo ratings yet
- Guide For Sustainable Design of NEOM CityDocument76 pagesGuide For Sustainable Design of NEOM Cityxiaowei tuNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER THREE-Teacher's PetDocument3 pagesCHAPTER THREE-Teacher's PetTaylor ComansNo ratings yet
- Pelatihan Dan Workshop Peningkatan Kompetensi GuruDocument6 pagesPelatihan Dan Workshop Peningkatan Kompetensi Guruhenry jakatariNo ratings yet
- Benson Ivor - The Zionist FactorDocument234 pagesBenson Ivor - The Zionist Factorblago simeonov100% (1)
- Specific Instuctions To BiddersDocument37 pagesSpecific Instuctions To BiddersShahed Hussain100% (1)
- Zanussi Parts & Accessories - Search Results3 - 91189203300Document4 pagesZanussi Parts & Accessories - Search Results3 - 91189203300Melissa WilliamsNo ratings yet
- MATLAB For Data VisualizationDocument63 pagesMATLAB For Data Visualizationfahmi fawjiNo ratings yet
- Revised Exam PEDocument3 pagesRevised Exam PEJohn Denver De la Cruz0% (1)
- The Meanings of Goddess PT IIIDocument14 pagesThe Meanings of Goddess PT IIILevonce68No ratings yet
- Fortigate System Admin 40 Mr2Document115 pagesFortigate System Admin 40 Mr2KhaleelNo ratings yet
- Laminar Premixed Flames 6Document78 pagesLaminar Premixed Flames 6rcarpiooNo ratings yet