Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Plant Tissue
Uploaded by
shaardesh84Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Plant Tissue
Uploaded by
shaardesh84Copyright:
Available Formats
Plant Tissue
A cellular organization between a single cell and a complete organism is controlled by the tissue. They
are the collection of similar cells, with specific function. A collection of tissue gives rise to an organ. A
tissue is a simple, which may be single celled type or a complex cell type.
Definition of Plant Tissue
A plant tissue can be defined as a cell or a group of cells dividing, to give rise to large number of cell,
which is collectively referred as tissues. They are structurally and functionally similar to these cells.
Plant Tissue Systems
Plants do have a higher level of structure called plant tissue systems. A plant tissue system can be
defined as a functional unit, which connects all organs of a plant. Like animal tissue system, plant
tissue system is also grouped into various tissues based on their functions.
Types of Plant Tissue Systems
There are three types of tissue systems.
Dermal Tissue
They are the tissues, which covers the external part of the herbaceous plants.
They are composed of epidermal cells, which secrete the waxy cuticle.
Waxy cuticles are responsible for protecting plants against water loss.
Dermal tissue consists of Epidermis and periderm.
Epidermis
They are the outermost layer of the primary plant body, which covers roots, stems, leaves,
floral parts, fruits and seeds.
They are one layer thick with cuticle.
They are composed mostly of unspecialized cells- parenchyma and sclerenchyma.
They include trichomes, stomata, buIIiform ceIIs, etc.
Periderm
They are the outermost layer of stems and roots of woody plants such as trees. They are also
called as barks.
They replace epidermis in plants that undergo secondary growth.
They are multi layered structures.
They include cork cells, which are non-living cells that cover the outside of stems and roots.
The periderm protects the plant from injuries, pathogens and also from excessive water loss.
Ground Tissue
They synthesize the organic compounds and support the plants by storing the
produced products.
They are composed of parenchyma cells and also include collenchyma and sclerenchyma
cells.
Parenchyma
They are the general cells of plants, which are circular in shape and have very thin wall.
They are present in all plant cells.
They have very large vacuoles and are frequently found in all roots, stem, leaves and in fruits
Parenchyma cells help in synthesizing and storage of synthesized food products.
Parenchyma cells also controls plant's metabolism like photosynthesis, respiration, protein
synthesis.
They also play a vital role in wound healing and regeneration of plants.
Collenchyma
Collenchymas are a specialized parenchyma tissue, which are found in all green parts.
Collenchyma cells are elongated with unevenly thickened walls.
They are alive during the cell maturity.
Collenchyma cells controls the functions of young plants.
A collenchyma cell provides a support to plants by not restraining growth, which is caused
due to their absence of secondary walls and hardening agent in their primary walls.
Sclerenchyma
They are rigid, non-living cells.
They have thick, lignified secondary walls and lack protoplasts at maturity.
They provide strength
A sclerenchyma cell also provides a support to plants with the help of hardening agent
present in their cells.
Sclerenchyma cells are of two types:
Sclereids: They are short, irregular in shape and have thick, lignified secondary walls
Fibers: They are long, slender and are arranged in threads.
Vascular Tissues
They are specialized cells with transport of water, hormone and minerals throughout the plant.
They contain transfer cells, fibers in addition to xylem, phloem, parenchyma, cambium and
other conducting cells.
They are located in the veins of the Leaves.
Xylem
The term Xylem is derived from the Greek word meaning Wood.
They are dead with hollow cells, which consist of only cell wall.
They play a vital role in transporting water and dissolved nutrients from the roots to all parts of
a plant.
They transport the nutrients in the upward direction .i.e. from the root to the stem, leaves and
flower.
Xylem is also called as water-conducting cells.
Phloem
The term phloem is derived from the Greek word meaning Bark.
They are live cells, which lack nucleus and other organelles.
They transports dissolved organic food materials (sugars) from the leaves to all parts of a
plant.
They transport the nutrients in the downward direction .i.e. from the leaves to the different
parts of the plant.
Phloem is also called as sugar-conducting cells.
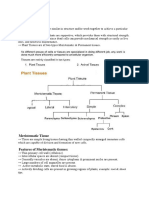
Types of Plant Tissue
There are two types of tissue systems.
Meristematic Tissues
Meristematic tissues are group of cells, which have the ability to divide. This tissue consists of small,
cubodial densely packed cells, which keeps on dividing to form new cells. These tissues are capable
of stretching, enlarging and differentiate into other types of tissues as they mature. Meristematic
tissues give rise to permanent tissues.
General characteristics of Meristematic tissues
They have very small cells with thin cell walls.
Their cells have large nuclei.
Their cells have very small vacuoles and they lack intercellular spaces.
They remain young forever and divide actively throughout the life of the plant.
In plants, these tissues are found in the -Tips of roots, stems, nodes of stems, buds, in
between the xylem and phloem, under the epidermis of dicotyledonous plants and also
producing branch roots.
Kinds of Meristematic tissues
Apical meristems : They are found at the tip of stems and roots. During the cell division, this
meristem helps in cellularenlargement and also it influence the shapes of the mature plants.
Lateral meristems : They are found along the sides of roots and stems .They play a vital role
in increasing the width or diameter of stems and roots.
Intercallary meristems : They are found at the bases of young leaves and internodes. They
are mainly responsible for further lengthening of stems and leaves.
Permanent Tissues
The tissues, which are derived from the Meristematic tissues, are called as permanent tissues. They
are the tissues, which have lost their ability to divide as they have attained their mature form.
Kinds of Permanent Tissues
Simple permanent tissue: They are the tissues, which are similar in function and are called as
simple because they are composed of similar types of cells, which have common origin and
function.
Complex permanent tissue: They are the tissues, which are composed of two or more types
of cells but contribute to a common function are called complex tissues.
Plant Tissue Functions
Different types of plant tissue have their own respective functions.
The plant tissue helps in providing mechanical strength to both the internal and external
organs.
They also help in rendering the elasticity and flexibility to the organs.
The tissue also helps in easy bending in various parts of a plant like- leaf, stem and branches
without causing any damages to main plant.
The tissue also helps transportation of materials thorough out the plants and prevents water
loss.
They divide to produce new growth and build the mass of the plants.
They are involved in various cellular metabolisms like photosynthesis, regeneration,
respiration, etc.
You might also like
- Tissues: Chapter - 6Document17 pagesTissues: Chapter - 6Aditya Jha100% (1)
- Plant Tissue SystemsDocument2 pagesPlant Tissue SystemsJohn0% (1)
- A Group of Closely Associated Cells That Perform Related Functions and Are Similar in StructureDocument25 pagesA Group of Closely Associated Cells That Perform Related Functions and Are Similar in StructureMichael Pradhan100% (2)
- Miedy Corazon Tabang Sta. Monica High School PhilippinesDocument68 pagesMiedy Corazon Tabang Sta. Monica High School PhilippinesArman Austria100% (1)
- Plant Tissues and The Multicellular Plant BodyDocument4 pagesPlant Tissues and The Multicellular Plant BodyAnonymous HXLczq3100% (1)
- Different Types of TissuesDocument24 pagesDifferent Types of Tissuesneha_asNo ratings yet
- The Plant CellDocument35 pagesThe Plant Cellzalifah74No ratings yet
- Flowers:: Sexual Reproductive Organs of AngiospermsDocument106 pagesFlowers:: Sexual Reproductive Organs of AngiospermsAlfonso PlantillaNo ratings yet
- Tissues, Roots, Stems, LeavesDocument128 pagesTissues, Roots, Stems, LeavesAlfonso PlantillaNo ratings yet
- General BotanyDocument4 pagesGeneral BotanyAngela ParaynoNo ratings yet
- 8384 ST PDFDocument20 pages8384 ST PDFJohn Dave Francisco100% (1)
- Tissues - Comprehensive NotesDocument4 pagesTissues - Comprehensive NotesRatheesh HrishikeshNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts To BotanyDocument6 pagesBasic Concepts To BotanyPrincess De LeonNo ratings yet
- Microscope LabDocument3 pagesMicroscope Labpepotera100% (1)
- Topic 1 Chemistry of LifeDocument31 pagesTopic 1 Chemistry of LifeHapsah Muhammad100% (1)
- Taxonomy and ClassificationDocument91 pagesTaxonomy and ClassificationshakiraNo ratings yet
- General BotanyDocument5 pagesGeneral BotanyKNo ratings yet
- Kingdom PlantaeDocument12 pagesKingdom PlantaeJohnrey CastilloNo ratings yet
- 05 Plant Structure and FunctionDocument87 pages05 Plant Structure and Functionapi-263663768100% (1)
- Plant BiologyDocument6 pagesPlant Biologypatricia capolaNo ratings yet
- Monocot vs. DicotDocument2 pagesMonocot vs. DicotRonalynNo ratings yet
- Kingdom PlantaeDocument20 pagesKingdom PlantaeJaznMon100% (1)
- Periodic Properties of The Elements: Theodore L. Brown H. Eugene Lemay, Jr. and Bruce E. BurstenDocument48 pagesPeriodic Properties of The Elements: Theodore L. Brown H. Eugene Lemay, Jr. and Bruce E. BurstenCory Perrin100% (1)
- Plant Structure, Growth, and Development: Chapter 35 & 36Document35 pagesPlant Structure, Growth, and Development: Chapter 35 & 36Zarlene SierraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Botany (W1)Document12 pagesIntroduction To Botany (W1)ASHLEY NICOLE JACINTO100% (1)
- (Preferred) Plant and Animal TissuesDocument20 pages(Preferred) Plant and Animal TissuesHannah CenaNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Living OrganismsDocument15 pagesCharacteristics of Living Organismswahab.7803No ratings yet
- Leaves Activity SheetDocument6 pagesLeaves Activity SheetTJ ArciagaNo ratings yet
- Phylum ChordataDocument25 pagesPhylum ChordataNicole100% (1)
- Botany SubdivisionsDocument70 pagesBotany Subdivisionsjackassjoey100% (1)
- Std11 Zoo EMDocument303 pagesStd11 Zoo EMElangovan PalanisamyNo ratings yet
- GENERAL BIOLOGY 4th Quarter - ACTIVITY #1-5Document7 pagesGENERAL BIOLOGY 4th Quarter - ACTIVITY #1-5Kimberly AyusoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BotanyDocument4 pagesIntroduction To BotanyEmanuel LacedaNo ratings yet
- Plant HistologyDocument2 pagesPlant HistologyNurul Rayhana100% (3)
- Network Structure in Root, Stem, and LeafDocument5 pagesNetwork Structure in Root, Stem, and LeafMarwana SuaibNo ratings yet
- CH 7.3 Cell TransportDocument19 pagesCH 7.3 Cell TransportRoen Grace Lapuz CalivosoNo ratings yet
- Course Outline in Botany 101Document4 pagesCourse Outline in Botany 101Anonymous lKxkZ9MNo ratings yet
- NSB BOT 20 Intro Chapter 1A Plant PhysiologyDocument21 pagesNSB BOT 20 Intro Chapter 1A Plant PhysiologyZeldeign ManuelNo ratings yet
- Protists and FungiDocument25 pagesProtists and Fungichasing catNo ratings yet
- History of ZoologyDocument4 pagesHistory of ZoologyBen Gabriel MaghuyopNo ratings yet
- Botany Exam PDFDocument9 pagesBotany Exam PDFanon_262141250No ratings yet
- TaxonomyDocument71 pagesTaxonomyNabeel Uddin100% (1)
- Taxonomy and Systematic and Biology Nomenclature and Some Basic Rules PDFDocument3 pagesTaxonomy and Systematic and Biology Nomenclature and Some Basic Rules PDFjer montillaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Mod 6Document24 pagesGen Bio Mod 6GMusa, Dexie Heart U.No ratings yet
- Botany IntroDocument4 pagesBotany IntroMichi OnozaNo ratings yet
- Chloroplast NotesDocument4 pagesChloroplast NotesAnanda100% (1)
- Plant Growth and Development 2016Document55 pagesPlant Growth and Development 2016Alex Xander100% (1)
- Plant Tissue: Ciar, Diaz, MedenillaDocument35 pagesPlant Tissue: Ciar, Diaz, MedenillaMich DiazNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal TissuesDocument9 pagesPlant and Animal TissuesfranciscocyrilleNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissues and OrgansDocument76 pagesPlant Tissues and Organsaldinette75% (4)
- Plant Tissue: Learning ObjectivesDocument17 pagesPlant Tissue: Learning ObjectivesSri Nagamani ThumuNo ratings yet
- Vascular Basic Shapes in TaxonomyDocument109 pagesVascular Basic Shapes in TaxonomykuldeepdeepikaNo ratings yet
- Engler and Prantel System of ClassificationDocument14 pagesEngler and Prantel System of ClassificationEasha tu RaziaNo ratings yet
- LamarckDocument1 pageLamarckGapmil Noziuc NylevujNo ratings yet
- Monocots Vs DicotsDocument3 pagesMonocots Vs Dicotsmonkey luffy100% (1)
- Lab 5 The Cell - Cell StructureDocument5 pagesLab 5 The Cell - Cell StructureDiegoOrtega8No ratings yet
- Definition of Plant TissueDocument3 pagesDefinition of Plant TissueCrash Zerocool67% (3)
- Info Sheets On Plant TissuesDocument6 pagesInfo Sheets On Plant TissuesjasmineecasttNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissues WordDocument5 pagesPlant Tissues WordJeannie de leonNo ratings yet
- Class 9 MT Science Notes TissueDocument12 pagesClass 9 MT Science Notes TissueKhushi Agrawal100% (1)
- 3 3 Cell Organelles PPT 1193949429900273 1Document19 pages3 3 Cell Organelles PPT 1193949429900273 1kikkabuttigieg1466No ratings yet
- Endocytosis ExocytosisDocument5 pagesEndocytosis ExocytosisMiska Fairuz100% (1)
- Cell Structure and Function WorksheetDocument3 pagesCell Structure and Function WorksheetKiersten RobertsNo ratings yet
- Cells and Organisation L4 Specialised Cells PowerPointDocument24 pagesCells and Organisation L4 Specialised Cells PowerPointJhyvril GulacNo ratings yet
- Forward and ReverseDocument11 pagesForward and ReversecyrhenmieNo ratings yet
- Exercises of Reversible InjuriesDocument6 pagesExercises of Reversible InjuriesRamel Yen CerantesNo ratings yet
- Cell TransportDocument7 pagesCell TransportMillenNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Cell SMSTR I 20 Nov 2013Document54 pagesStudy Guide Cell SMSTR I 20 Nov 2013Yuda DiraNo ratings yet
- 4-Hematology Analyzer - Detecting Erroneous Blood CountsDocument23 pages4-Hematology Analyzer - Detecting Erroneous Blood CountsRajeshNo ratings yet
- Experiment 9 (Animal Tissue)Document3 pagesExperiment 9 (Animal Tissue)soniaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsDocument32 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Farm Animalsufaysa gensaNo ratings yet
- PMLS1 Trans L2 Term 1Document6 pagesPMLS1 Trans L2 Term 1Julianne Amber VillalunaNo ratings yet
- Keratinization SeminarDocument38 pagesKeratinization Seminarbands85100% (2)
- Bone TissueDocument46 pagesBone TissueFiraol DiribaNo ratings yet
- Hematology - Leukopoiesis NotesDocument5 pagesHematology - Leukopoiesis NotesVictor Juris Anonuevo0% (1)
- Anaphy Lec (Chapter 3)Document6 pagesAnaphy Lec (Chapter 3)Aya MojicaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Histology PDFDocument43 pagesChapter 2 Histology PDFpizzaNo ratings yet
- HematologyDocument5 pagesHematologyIvy Jan OcateNo ratings yet
- Fixation NotesDocument35 pagesFixation NotesAnya IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Artificial Blood Artificial Blood: Presenter NameDocument26 pagesArtificial Blood Artificial Blood: Presenter NameMelvin AlexNo ratings yet
- Biologi Struktur Jaringan Keras GigiDocument66 pagesBiologi Struktur Jaringan Keras GigiRhena FitriaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1: Bacteria: Course: B.Sc. Biotechnology Semester IiiDocument24 pagesUNIT 1: Bacteria: Course: B.Sc. Biotechnology Semester IiiPriya PankajNo ratings yet
- Cytokeratin: A Review On Current ConceptsDocument6 pagesCytokeratin: A Review On Current ConceptsErick MartinezNo ratings yet
- Ijmds 2014 V 3 N 2 P 484Document6 pagesIjmds 2014 V 3 N 2 P 484Agita Khansa' P. NorinkhaNo ratings yet
- Notes Plant TissuesDocument7 pagesNotes Plant TissuesHariprasanthNo ratings yet
- Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsDocument70 pagesFunctional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsTrixie De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Biomecânica Do Músculo Esquelético PDFDocument24 pagesBiomecânica Do Músculo Esquelético PDFThiago LealNo ratings yet
- CBC LalpathDocument2 pagesCBC Lalpathmoyic39272No ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell Lecture PDFDocument49 pagesEukaryotic Cell Lecture PDFDaezel Deux100% (1)
- MegakaryopoiesisDocument41 pagesMegakaryopoiesisHazel FlorentinoNo ratings yet