Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Polycystic Kidney Disease Flashcards - Quizlet
Uploaded by
Dery MourtziOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Polycystic Kidney Disease Flashcards - Quizlet
Uploaded by
Dery MourtziCopyright:
Available Formats
9/1/2016
PolycystickidneydiseaseFlashcards|Quizlet
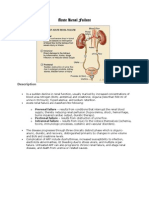
Polycystic kidney disease
21 terms by Bonecrawler
Overview
Growth of multiple, bilateral, grapelike
clusters of fluid-lled cysts in the kidneys
May progress slowly even after symptoms
of renal insuciency appear
Adult form, which has an insidious onset but
usually becomes obvious between ages 30
and 50, has autosomal dominant
inheritance
Usually fatal within 4 years of uremic
symptom onset, unless dialysis begins
Carries a widely varying prognosis in adults
Also known as PKD and autosomal
dominant polycystic kidney disease
(ADPKD)
Overview-Pathophysiology
Cysts enlarge the kidneys, leading to
thickening of the basement membranes in
the tubules, macrophage inltration,
neovascularization, brosis, and cystic
dilation of the renal tubules, and ultimately
resulting in the compression and eventual
replacement of functioning renal tissue.
(See Polycystic kidney.)
Renal deterioration results.
The condition progresses relentlessly to
fatal uremia.
Overview-Causes
Autosomal dominant form inherited as an
autosomal dominant trait (ADPKD),
aecting the short arm of chromosome 16
and the long arm of chromosome 4
Acquired (more than one-half of patients
receiving dialysis for more than 3 years)
https://quizlet.com/21767410/polycystickidneydiseaseflashcards/
1/7
9/1/2016
PolycystickidneydiseaseFlashcards|Quizlet
Overview-Incidence
The disease aects both sexes equally, with
a slight increase in severity of the disease in
men.
Autosomal dominant form accounts for 6%
to 10% of all cases of end-stage renal
disease in the United States.
The usual age of onset for the autosomal
form typically ranges from age 20 to 40.
Overview-Complications
Cyst rupture
Hepatic failure
Cerebral aneurysm, subarachnoid
hemorrhage
Diverticula
Mitral valve prolapse
Metabolic abnormalities
Renal calculi
Renal failure
Respiratory failure
Heart failure
Recurrent hematuria
Life-threatening retroperitoneal bleeding
Assessment-History
Family history
Polyuria
Urinary tract infections
Headaches
Pain in back or flank area
Gross hematuria
Abdominal pain, usually worsened on
exertion and eased by lying down
Assessment-Physical Findings
Hypertension
Microscopic or gross hematuria
Increased abdominal girth
Signs of an enlarging kidney mass
Grossly enlarged kidneys (in advanced
stages)
Uremic fetor
Pallor
https://quizlet.com/21767410/polycystickidneydiseaseflashcards/
2/7
9/1/2016
PolycystickidneydiseaseFlashcards|Quizlet
Diagnostic Test Results-Laboratory
Urinalysis may show hematuria, bacteriuria,
or proteinuria.
Creatinine clearance test results may show
renal insuciency or failure.
Hematocrit may be elevated.
Serum albumin levels may be decreased.
Serum electrolyte levels may reveal
hyponatremia, hyperkalemia,
hyperphosphatemia, or hypocalcemia.
Diagnostic Test Results-Imaging
Excretory or retrograde urography reveals
enlarged kidneys, with pelvic elongation,
flattening of the calyces, and indentations
caused by cysts.
Magnetic resonance imaging (preferred
test) shows multiple areas of cystic
damage.
Treatment-General
Monitoring of renal function
Dialysis; renal replacement therapy
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
(TENS) and hypnotherapy for chronic pain
Treatment-Diet
Low-sodium
Fluid management based on degree of
renal dysfunction
Treatment-Activity
As tolerated in early stages
Avoidance of contact sports with advanced
disease
Exercise to manage hypertension
https://quizlet.com/21767410/polycystickidneydiseaseflashcards/
3/7
9/1/2016
PolycystickidneydiseaseFlashcards|Quizlet
Treatment-Medications
Analgesics, such as opioids, transcutaneous
opioid patches, or perinephric injection of
local anesthetics, for pain relief
Antibiotics, such as ciprofloxacin
hydrochloride, levofloxacin, or
trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for urinary
tract infection
Antihypertensive agents, such as
angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE)
inhibitors (captopril, enalapril, or lisinopril)
or angiotensin receptor blockers (losartan
potassium, irbesartan, or candesartan
cilexetil), for hypertension
Diuretics, such as furosemide, to treat
hypertension and renal calculi
Electrolyte replacements, such as calcium
carbonate, and phosphate binders to
reduce phosphorus load in renal failure.
Treatment-Surgery
Kidney transplantation
Surgical drainage for cystic abscess or
retroperitoneal bleeding
Nursing Considerations-Nursing Diagnoses
Acute pain
Chronic pain
Decient fluid volume
Fatigue
Impaired urinary elimination
Ineective coping
Risk for ineective renal perfusion
Risk for infection
Risk for injury
Nursing Considerations-Expected
Outcomes
report feelings of increased comfort
identify measures to address chronic pain
maintain fluid balance
verbalize the importance of balancing
activity with adequate rest periods
demonstrate skill in managing the urinary
elimination problem
demonstrate adaptive coping behaviors
exhibit adequate renal function
remain free from signs and symptoms of
infection
avoid or minimize complications.
https://quizlet.com/21767410/polycystickidneydiseaseflashcards/
4/7
9/1/2016
PolycystickidneydiseaseFlashcards|Quizlet
Nursing Considerations-Nursing
Interventions
Give prescribed drugs, including ACE
inhibitors to control hypertension; if giving
diuretics, obtain specimens for serum
electrolyte levels, especially potassium,
which may be decreased.
Provide comfort measures, including opioid
analgesics; assist the patient with relaxation
techniques and the use of TENS.
Provide fluids and foods based on the
patient's condition, encourage increased
fluids if the patient has a urinary tract
infection, and restrict fluids if the patient
has renal failure.
Provide supportive care to minimize
symptoms.
Obtain specimens for urinalysis and culture
and sensitivity as ordered to evaluate for
hematuria, proteinuria, and infection; obtain
specimens for laboratory tests, such as
electrolyte levels, as ordered.
Individualize patient care, as appropriate
Allow the patient to verbalize his feelings
and concerns, especially related to
possible progression of the disease and
renal failure; provide support and
guidance.
Prepare the patient for dialysis or renal
replacement therapy as indicated.
Encourage the parents of a child with the
infantile form to obtain genetic counseling.
Prepare the patient and his family for
possible renal transplant or surgery.
Nursing Considerations-Monitoring
Renal function
Urinary elimination, including urine color
and characteristics
Fluid balance and hydration
Electrolyte balance
Vital signs, especially blood pressure
Pain level and relief
Laboratory test results (urine and blood
specimens)
Access site for dialysis if appropriate
Eectiveness of therapy and dialysis
https://quizlet.com/21767410/polycystickidneydiseaseflashcards/
5/7
9/1/2016
PolycystickidneydiseaseFlashcards|Quizlet
Nursing Considerations-Associated Nursing
Procedures
https://quizlet.com/21767410/polycystickidneydiseaseflashcards/
Blood pressure assessment
Clean-catch (midstream) urine collection,
female
Clean-catch (midstream) urine collection,
male
Continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis
(CAPD)
Continuous renal replacement therapy
(CRRT)
Health history interview and physical
assessment
Hemodialysis, arteriovenous access
Hemodialysis, double-lumen catheter
Intake and output assessment
Nutritional screening
Oral drug administration
Postoperative care
Preoperative care
Preparing a patient for urologic surgery, OR
Pulse assessment
Venipuncture
Weight measurement
6/7
9/1/2016
PolycystickidneydiseaseFlashcards|Quizlet
Patient Teaching-General
disorder, underlying cause, diagnosis, and
treatment, including medication therapy
and possible dialysis or transplantation
prescribed drug therapy, including the drug
name(s), dosage(s), frequency of
administration, and duration of therapy
possible adverse eects of therapy, such as
hypokalemia with diuretic therapy and GI
upset with ACE inhibitors
follow-up with the practitioner for severe
or recurring headaches
signs and symptoms of urinary tract
infection and renal calculi and the need to
notify the practitioner immediately if any
occur
signs and symptoms of electrolyte
imbalances and the need to notify the
practitioner if any occur
importance of blood pressure control and
adhering to medication therapy
use of analgesics and possible sedative
eects if opioid agents are used and how
to use opioid patches if prescribed
how to use TENS or hypnotherapy for
chronic pain control
that disorder is slowly progressive, and that
dialysis or transplantation may be needed
dialysis procedure, technique, and
frequency, if indicated, and care of the
access site.
ongoing need for follow-up and laboratory
testing to evaluate disease progress,
including ultrasonography every 1 to 2
years.
Patient Teaching-Discharge Planning
Refer the patient and his family to
community and social services for support.
https://quizlet.com/21767410/polycystickidneydiseaseflashcards/
7/7
You might also like
- Fulminant Hepatic FailureDocument10 pagesFulminant Hepatic FailureAira Anne Tonee VillaminNo ratings yet
- Renal Biopsy of Dogs and CatsDocument12 pagesRenal Biopsy of Dogs and CatsfrankyNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Kidney FailureDocument7 pagesResearch Paper Kidney Failurexfeivdsif100% (3)
- Research Paper On Acute Renal FailureDocument4 pagesResearch Paper On Acute Renal FailureafeartslfNo ratings yet
- Hydronephrosis and HydroureterDocument4 pagesHydronephrosis and HydroureterChiki CacaNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal FailureDocument5 pagesAcute Renal FailureJean De Vera MelendezNo ratings yet
- Case Report On CRF PrtatikDocument7 pagesCase Report On CRF PrtatikOm PalekarNo ratings yet
- Department of Faculty SurgeryDocument40 pagesDepartment of Faculty SurgeryMandar GokhaleNo ratings yet
- Essential Update: FDA Approves First Test To Predict AKI in Critically Ill PatientsDocument5 pagesEssential Update: FDA Approves First Test To Predict AKI in Critically Ill PatientsRika Ariyanti SaputriNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis: Etiology, Complications, TreatmentDocument5 pagesCirrhosis: Etiology, Complications, TreatmentNahanNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Tests and Nursing Care for Renal DisordersDocument47 pagesDiagnostic Tests and Nursing Care for Renal DisordersJAN KRISTIAN JIMENEA TULIBASNo ratings yet
- Nursing Patho CardsDocument195 pagesNursing Patho Cardsgiogmail100% (1)
- Nursing Management of AKI/CKD Patients in ICUDocument24 pagesNursing Management of AKI/CKD Patients in ICUheenamaharjanNo ratings yet
- CKD Management and ProgressionDocument23 pagesCKD Management and ProgressionENOCK BENDERENo ratings yet
- Aetiology: Save Time & Improve Your PDP On Patient - Co.ukDocument9 pagesAetiology: Save Time & Improve Your PDP On Patient - Co.ukBaihaqi SaharunNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract DisordersDocument54 pagesUrinary Tract Disorderssharon ocharaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Profile and Outcome of Pelvi-Ureteric Junction Obstruction (PUJO) in Children Presenting Above 1 YearDocument48 pagesClinical Profile and Outcome of Pelvi-Ureteric Junction Obstruction (PUJO) in Children Presenting Above 1 YearWai GyiNo ratings yet
- Pathology Polycystic Kidney DiseaseDocument4 pagesPathology Polycystic Kidney DiseaseOnyedika EgbujoNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Evaluation of Kidney StonesDocument15 pagesMetabolic Evaluation of Kidney StonesKaizer JhapzNo ratings yet
- Primary Care Approach To Proteinuria: Amir Said Alizadeh Naderi, MD, and Robert F. Reilly, MDDocument6 pagesPrimary Care Approach To Proteinuria: Amir Said Alizadeh Naderi, MD, and Robert F. Reilly, MDraviibtNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal Failure & Chronic Renal FailureDocument38 pagesAcute Renal Failure & Chronic Renal FailureArti GondNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Accesssory Organs in GI SystemDocument29 pagesDisorders of Accesssory Organs in GI SystemY. Beatrice AbigailNo ratings yet
- Oftal Case StudyDocument11 pagesOftal Case StudyMohamad RaisNo ratings yet
- Polycystic Kidney DiseaseDocument9 pagesPolycystic Kidney DiseaseCésar Aguilar ContrerasNo ratings yet
- HydronephrosisDocument7 pagesHydronephrosisNaqash NobleNo ratings yet
- Urology MCQsDocument13 pagesUrology MCQsRahmah Shah Bahai83% (6)
- Bowel ObstructionDocument10 pagesBowel Obstructionenke.nwekeNo ratings yet
- Acute Liver Failure-1Document40 pagesAcute Liver Failure-1elizabethNo ratings yet
- Dayrit, Zandra Chris S.: What Is Pancreatitis?Document5 pagesDayrit, Zandra Chris S.: What Is Pancreatitis?Nicole Anne TungolNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney Injury: On Completion of This Chapter, The Learner Will Be Able ToDocument9 pagesAcute Kidney Injury: On Completion of This Chapter, The Learner Will Be Able TojhcacbszkjcnNo ratings yet
- CP Acute Renal Failure Chap7Document128 pagesCP Acute Renal Failure Chap7Katherine 'Chingboo' Leonico LaudNo ratings yet
- Renal Disorders 1Document73 pagesRenal Disorders 1Kyla PamaNo ratings yet
- SeminarDocument26 pagesSeminarMinte TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument7 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseLardel Balbiran LafortezaNo ratings yet
- Acute Kidney InjuryDocument17 pagesAcute Kidney InjuryCha-cha UzumakiNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 Study GuideDocument3 pagesExam 1 Study GuideNataraj LoganathanNo ratings yet
- Renal Failure: Symptoms, Causes, Tests & TreatmentDocument7 pagesRenal Failure: Symptoms, Causes, Tests & TreatmentAndrelyn Balangui LumingisNo ratings yet
- Urology NotesDocument8 pagesUrology NotesCzarinah Bacuado67% (3)
- UntitledDocument18 pagesUntitledFun joyNo ratings yet
- Seminar On Cirrhosis of LiverDocument9 pagesSeminar On Cirrhosis of Liverrufusprasanth_rachaproluNo ratings yet
- Inter'Medic CKDDocument31 pagesInter'Medic CKDMAHEJS HD100% (1)
- English Text 2 Dr. FilandyDocument35 pagesEnglish Text 2 Dr. FilandymichaelNo ratings yet
- ACUTE RENAL FAILURE DIAGNOSIS & MANAGEMENTDocument2 pagesACUTE RENAL FAILURE DIAGNOSIS & MANAGEMENTSetiya Dini LarasatiNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal FailureDocument29 pagesAcute Renal Failurelianrose448No ratings yet
- Urinary Incontinence and Chronic Kidney Disease - Important Points (1) - 2Document4 pagesUrinary Incontinence and Chronic Kidney Disease - Important Points (1) - 2barbaraNo ratings yet
- Polycystic Kidney: Formation of Cysts in The Cortex and MedullaDocument6 pagesPolycystic Kidney: Formation of Cysts in The Cortex and MedullaEileen OoiNo ratings yet
- Prominent U wave on EKG indicates HypokalemiaDocument5 pagesProminent U wave on EKG indicates HypokalemiaJwaltzPadlanNo ratings yet
- Acute Renal FailureDocument35 pagesAcute Renal FailureKaelyn Bello Giray100% (1)
- EASL Clinical Guidelines on Nutrition for Chronic Liver DiseaseDocument22 pagesEASL Clinical Guidelines on Nutrition for Chronic Liver Diseasexmobile iasiNo ratings yet
- Gangguan Pada Ginjal Dan UreterDocument127 pagesGangguan Pada Ginjal Dan UreterFebrina TrizaNo ratings yet
- Case Study 10 Renal FailureDocument19 pagesCase Study 10 Renal FailureAriadne Cordelette100% (2)
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument40 pagesChronic Kidney DiseasePaul SinsNo ratings yet
- Atresia Billier 27 Tahun PDFDocument5 pagesAtresia Billier 27 Tahun PDFWiwit ClimberNo ratings yet
- Accesory OrganDocument12 pagesAccesory OrganTrisha SuazoNo ratings yet
- CKD UnsoedDocument42 pagesCKD UnsoedSutan Malik IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Mr. R.E.B. - CKDDocument61 pagesMr. R.E.B. - CKDChristy Rose AgrisNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Kidney DiseaseDocument4 pagesResearch Paper Kidney Diseasesgfdsvbnd100% (1)
- Nephrolithiasis PDFDocument16 pagesNephrolithiasis PDFApriany Cordias Arlita SilalahiNo ratings yet
- Renal Failure: Prepare by Mohammed Sahman Basees Alsharari - 391110030Document31 pagesRenal Failure: Prepare by Mohammed Sahman Basees Alsharari - 391110030jsksNo ratings yet
- Vaman Vyapada: DR .Pournima Rikibe Associate Professor Pancakarma Department C.A.R.C. Akurdi PuneDocument22 pagesVaman Vyapada: DR .Pournima Rikibe Associate Professor Pancakarma Department C.A.R.C. Akurdi PunePournimaNo ratings yet
- D D I 6130.03 M S A, E, I M SDocument49 pagesD D I 6130.03 M S A, E, I M Snour abdallaNo ratings yet
- Stress Ulcer Ditinjau Dari Aspek Patofisiologi Dan TreatmentDocument16 pagesStress Ulcer Ditinjau Dari Aspek Patofisiologi Dan TreatmentJufri NstNo ratings yet
- Detailed Study of NyagrodadiganaDocument33 pagesDetailed Study of NyagrodadiganaAnil Das100% (1)
- Intensive PediaDocument13 pagesIntensive PediaNathaniel VenusNo ratings yet
- Praseno Hadi - ARDS (Malang 2018)Document25 pagesPraseno Hadi - ARDS (Malang 2018)Rian HutabaratNo ratings yet
- Gastric aspirate shake test predicts need for surfactant in preterm infantsDocument9 pagesGastric aspirate shake test predicts need for surfactant in preterm infantsVita DesriantiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Pranic HealingDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Pranic HealingRujuta Kulkarni33% (3)
- Exudative Pleural Effusions - UpToDateDocument2 pagesExudative Pleural Effusions - UpToDateAsif IqbalNo ratings yet
- Study - Guide.to - Accompany.pathophysiology.2nd - Ed Ublog - TKDocument159 pagesStudy - Guide.to - Accompany.pathophysiology.2nd - Ed Ublog - TKhemo04086100% (11)
- PicolDocument663 pagesPicolNico Rey Yamas RANo ratings yet
- Undergraduate Admission Form: Mashal GulraizDocument5 pagesUndergraduate Admission Form: Mashal GulraizMarya KhanNo ratings yet
- WMA Guidelines Against Physician TortureDocument2 pagesWMA Guidelines Against Physician TortureMohammad Fardeen ShihabNo ratings yet
- Safety Tips For Covid-19Document5 pagesSafety Tips For Covid-19Angelo AsoqueNo ratings yet
- HemothoraxDocument27 pagesHemothoraxShreyasi AnkushNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Fetal GrowthDocument41 pagesAssessment of Fetal GrowthmskotNo ratings yet
- Healthcare Information SystemDocument9 pagesHealthcare Information SystemcbjdcbsjdNo ratings yet
- Critical Incident Stress DebriefingDocument7 pagesCritical Incident Stress DebriefingjaneaNo ratings yet
- JK. NOTES - ConsentDocument3 pagesJK. NOTES - ConsentMei DreeNo ratings yet
- CancerDocument4 pagesCancerJan Jamison ZuluetaNo ratings yet
- Systemic Effects of Local Anaesthesia in Hypertensive PatientsDocument6 pagesSystemic Effects of Local Anaesthesia in Hypertensive PatientsKarina HernandezNo ratings yet
- Lakewood Police Department Return To Work Decision MatrixDocument1 pageLakewood Police Department Return To Work Decision MatrixMichael_Roberts2019No ratings yet
- Optometry SeniorDocument8 pagesOptometry Seniorapi-504989033No ratings yet
- Borang HirarcDocument41 pagesBorang Hirarcnailul muna binti ahmad musadadNo ratings yet
- National TLD transition and viral load monitoringDocument18 pagesNational TLD transition and viral load monitoringSemeeeJuniorNo ratings yet
- Self-Assessment of Nursing Standards of PracticeDocument14 pagesSelf-Assessment of Nursing Standards of Practiceapi-236260255100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Ineffective Infant Feeding PatternDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan Ineffective Infant Feeding PatternMarife Lipana Reyes100% (1)
- AlprazolamDocument2 pagesAlprazolamGLen CaniedoNo ratings yet
- The Haunted Self Structural Dissociation and The T PDFDocument7 pagesThe Haunted Self Structural Dissociation and The T PDFKomáromi PéterNo ratings yet
- OHMSFlyerDocument2 pagesOHMSFlyerthe mad king readerNo ratings yet