Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Foreign Body in Respiratory Tract
Uploaded by
Abhishek0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views1 pageFB IN RESPIRATORY TRACT
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentFB IN RESPIRATORY TRACT
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views1 pageForeign Body in Respiratory Tract
Uploaded by
AbhishekFB IN RESPIRATORY TRACT
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
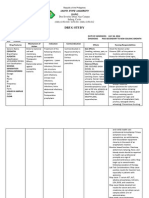
FOREIGN BODY IN RESPIRATORY TRACT
Foreign bodies aspiration is often seen during childhood.
They include TYPES: AGE- Younger than 3 years account for 73% cases.
Non-organic (buttons, metallic
1) Laryngeal Foreign Bodies
objects)
2) Tracheal Foreign Bodies
Foreign bodies may be found in Organic (eatables, peanuts, etc.)
3) Bronchial Foreign Bodies
(1) The Larynx (2) Trachea (3) Bronchi
material
& LARYNGEAL FOREIGN BODIES:TRACHEAL FOREIGN BODIES:BRONCHIAL FOREIGN BODIES:1) Croupy or hoarse cough
1) Cough
1) Cough, Wheeze, Blood-streaked sputum may occur
2) Aphonia
2) Hoarseness
2) With slight obstruction, passage of air in both
3) Haemoptysis
3) Dyspnoea
directions produces only wheezing
4) Dyspnoea
4) Cyanosis
3) With complete obstruction, atelectasis occurs due to
5) Wheezing
5) Wheeze with audible slab &
absorption of air distal to the obstruction
6) Cyanosis
palpable thud produced due to
4) History of choking, gagging, paroxysmal coughing,
momentary expiratory impaction
history of eating substances like groundnuts etc. is vital
at the subglottic level are
in the diagnosis
characteristic.
5) On examination tracheal shift, decreased breath sounds
on side of the FB aspiration occurs.
LARYNGEAL FOREIGN BODIES:TRACHEAL FOREIGN BODIES:BRONCHIAL FOREIGN BODIES:1) X-ray Neck- Lateral view
1) Chest X-ray
1) X-ray Chest
2) Laryngoscopy
2) Bronchoscopy
2) Fluoroscopy
Laryngeal FB needs to be removed by rigid endoscope.
Tracheotomy may be required with severe degree of dyspnoea.
Lobectomy may be required for longstanding vegetal FB.
Chest physiotherapy and bronchodilators should not be given (these may lead to disimpaction & movement of the FB with obstruction of a
more distal airway)
Antibiotics are needed for secondary infections.
BACK BLOWS:CHEST THRUSTS: Hold the infant face down on your forearm, which in turn should Now turn the infant around as a unit to a supine position while firmly
rest on your thigh.
supporting the head and neck. Administer up to five quick chest
Support the head of the child by firmly holding the jaw.
thrusts in the similar method and location used for chest compressions.
Position the infants head lower than the trunk.
The whole process is repeated until the foreign body is expelled out.
Deliver up to five blows with heel of your hand between the
shoulder blades of the infant.
HEIMLICH MANEUVER : (SUB-DIAPHRAGMATIC ABDOMINAL THRUSTS)
The maneuver is used in children older than 1 year. The aim is to increase the intrathoracic pressure and creating an artificial cough, so as to
force the foreign body out of the airway.
Heimlich maneuver is not used in infants for the risk of liver injuries.
It is carried out differently for conscious and unconscious children.
HEIMLICH MANEUVER : CONSCIOUS CHILD
HEIMLICH MANEUVER : UNCONSCIOUS CHILD
Stand behind the child and encircle his torso but putting both arms directly Position the child in a supine position and kneel at the
under his axillae.
childs feet.
Place the thumb side of one fist against the childs abdomen in midline slightly Place the heel of hand on the childs abdomen in the
above navel and well below the xiphoid.
midline slightly above navel and well below rib cage.
With other hand, grasp this fist and exert quick upward thrusts taking care not Place the second hand on top of the first and press into
to touch the xiphoid process or lower rib margins.
abdomen with quick upward thrust.
Each thrust should be forceful enough and intended to relieve the obstruction.
Prevention is of utmost importance with small objects being placed beyond the reach of young children.
Nuts, small toys with lose parts, coins should never be given to young children.
INTRODUCTION
SIGN
SYMPTOMS
DIAGNOSIS
TREATMENT
PREVENTION
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Ankle SprainDocument4 pagesAnkle SprainLaurencia LenyNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Pediatric Quick NotesDocument178 pagesPediatric Quick NotesCharlotte McDonald100% (5)
- Spotters in Pediatrics PDFDocument269 pagesSpotters in Pediatrics PDFAbhishekNo ratings yet
- Review of Inguinal Hernia ManagementDocument10 pagesReview of Inguinal Hernia ManagementNining Rhyanie TampubolonNo ratings yet
- CefoxitinDocument3 pagesCefoxitinAngelica Cassandra VillenaNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Critical Care MedicineDocument107 pagesPediatric Critical Care Medicinerahmawatusayu100% (1)
- Patient Identification PolicyDocument26 pagesPatient Identification PolicyrenalgoodNo ratings yet
- Toxic Ingestions Pediatric EmergencyDocument24 pagesToxic Ingestions Pediatric EmergencyXimenaEspinaNo ratings yet
- Better Vision Class: Eyesight Improvement Through AwarenessDocument22 pagesBetter Vision Class: Eyesight Improvement Through Awarenesssmilinkovic_4No ratings yet
- Practice in Clinical BiochemistryDocument112 pagesPractice in Clinical BiochemistryMohamed Magdi100% (1)
- Standardization of Ayurvedic Clinical TermsDocument242 pagesStandardization of Ayurvedic Clinical TermsAbhishek100% (1)
- Dhanvantari SahastranamaDocument38 pagesDhanvantari SahastranamaAbhishekNo ratings yet
- Balrog Visheshank October 2010 PDFDocument12 pagesBalrog Visheshank October 2010 PDFSanjeev AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Physiology Pactical (2013) PDFDocument220 pagesPhysiology Pactical (2013) PDFsudeepkmNo ratings yet
- Breath Holding SpellDocument19 pagesBreath Holding SpellAbhishekNo ratings yet
- Intellectual Disability and Psychotic Disorders of Adult EpilepsyDocument0 pagesIntellectual Disability and Psychotic Disorders of Adult EpilepsyRevathi SelvapandianNo ratings yet
- Margo Lynch, Ppa Dennis Lynch, Dennis Lynch and Margaret Lynch v. Merrell-National Laboratories, Division of Richardson-Merrell, Inc., 830 F.2d 1190, 1st Cir. (1987)Document11 pagesMargo Lynch, Ppa Dennis Lynch, Dennis Lynch and Margaret Lynch v. Merrell-National Laboratories, Division of Richardson-Merrell, Inc., 830 F.2d 1190, 1st Cir. (1987)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Jewish Standard Readers' Choice 2016Document80 pagesJewish Standard Readers' Choice 2016New Jersey Jewish StandardNo ratings yet
- Epilepsy in African-RegionDocument56 pagesEpilepsy in African-RegionJaiye WeissNo ratings yet
- Total Knee Replacement Rehabilitation Protocol: General ConsiderationsDocument1 pageTotal Knee Replacement Rehabilitation Protocol: General ConsiderationsukissirrorrNo ratings yet
- Patient Evaluation and Wound Assessment: Key Practice PointsDocument6 pagesPatient Evaluation and Wound Assessment: Key Practice PointsFofiuNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Hidung Dan Sinus Paranasal 2Document54 pagesAnatomi Hidung Dan Sinus Paranasal 2anditri weningtyas0% (1)
- Hearing Related Quality of Life Outcomes For 2016 European Annals of OtorhiDocument6 pagesHearing Related Quality of Life Outcomes For 2016 European Annals of OtorhiElmoPranauskasNo ratings yet
- Recent Developments in The Management of Neonatal HyperbilirubinemiaDocument8 pagesRecent Developments in The Management of Neonatal HyperbilirubinemiaMyrtle SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Fixation of The Distal Tibiofibular Bone-Bridge in Transtibial Amputation PDFDocument4 pagesFixation of The Distal Tibiofibular Bone-Bridge in Transtibial Amputation PDFThomas BowersNo ratings yet
- Infrared Thermometer PDFDocument18 pagesInfrared Thermometer PDFDadang SyarieffidayatNo ratings yet
- Naturopathic Treatment For Ear Pain in ChildrenDocument8 pagesNaturopathic Treatment For Ear Pain in ChildrenDr Siddharth SP YadavNo ratings yet
- Infant Formula and Early Childhood CariesDocument5 pagesInfant Formula and Early Childhood Cariesmutiara hapkaNo ratings yet
- The 13th ATR Memorial Lecture ProgrammeDocument5 pagesThe 13th ATR Memorial Lecture ProgrammePGH Department of SurgeryNo ratings yet
- Effective materials procurementDocument5 pagesEffective materials procurementAkua Henaku-LarbiNo ratings yet
- Claude H. Organ, JRDocument3 pagesClaude H. Organ, JRgassun2999No ratings yet
- Salbutamol Sulphate Inhaler for Asthma ReliefDocument5 pagesSalbutamol Sulphate Inhaler for Asthma ReliefRajib MandalNo ratings yet
- DAFTAR PUSTAKA Acute Symptomatic SeizureDocument3 pagesDAFTAR PUSTAKA Acute Symptomatic SeizureApidha KartinasariNo ratings yet
- Fischer Esterification of p-Aminobenzoic Acid: Synthesis of BenzocaineDocument3 pagesFischer Esterification of p-Aminobenzoic Acid: Synthesis of BenzocaineKariEspinoza100% (1)
- 3 - ALR Main - DoigtsDocument62 pages3 - ALR Main - DoigtsProfesseur Christian Dumontier100% (1)
- Hospital Interior Designing Services PDFDocument6 pagesHospital Interior Designing Services PDFreddi.demullu007No ratings yet
- Rotary EndodonticsDocument12 pagesRotary EndodonticsEkta KhobragadeNo ratings yet
- INTRODUCTIONDocument3 pagesINTRODUCTIONSoumya Suguna TripathyNo ratings yet