Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Circles I, II 1
Uploaded by
Shah Ozair0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pageshuuuu
Original Title
Math
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documenthuuuu
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesCircles I, II 1
Uploaded by
Shah Ozairhuuuu
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Circles I, II
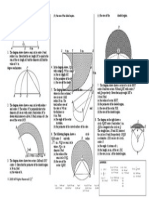
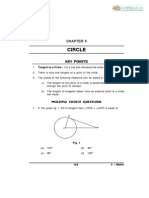
In the diagram, PQRS is a circle with centre O, POR is the diameter and QR = RS.
The value of x is
A.
20
C.
70
B.
50
D.
80
[2004, No.16]
In the diagram, PQRS is a cyclic quadrilateral.
The value of x + y is
A.
150
C.
190
B.
170
D.
210
[2004, No.17]
The diagram shows a circle with centre O.
10
The radius of the circle is
22
7
1
2
cm. Calculate the length, in cm, of the minor arc MN.
1155
8
55
2
A.
(Use =
B. 77/2
C.
D. 1617/8
[2004, No.19]
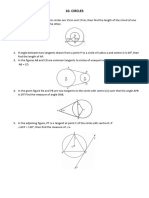
In the diagram, POR is the diameter of circle PQR.
Given that PQ = QR and PR = 14 cm. Calculate the area, in cm2, of the shaded region.
A.
56
C.
105
B.
93
D.
142
(Use =
22
7
[2004, No.20]
5
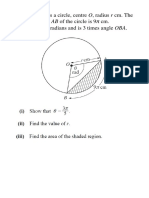
The diagram shows three congruent circles with centre L, M, and R respectively.
Given that PQ = 24 cm and KL = 5 cm, calculate the length, in cm, of KR.
A.
15
C.
31
B.
26
D.
39
[2004, No.21]
In the diagram, PQR is an arc of a circle with centre O and PRO is an equilateral triangle.
The perimeter, in cm, of the whole diagram is
22
7
(Use =
)
A.
42
C.
64
B.
63
D.
85
[2004, No.39]
You might also like
- Chapter 14 I Circles ENRICHDocument16 pagesChapter 14 I Circles ENRICHjuriah binti ibrahim100% (1)
- Module 8A - Circular MeasureDocument11 pagesModule 8A - Circular MeasureHayati Aini Ahmad100% (2)
- SPM Circular Measure QuestionsDocument3 pagesSPM Circular Measure QuestionsRosmizar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Calculating Arc Length, Sector Area & PerimeterDocument21 pagesCalculating Arc Length, Sector Area & PerimeterNorliha JamilNo ratings yet
- Circular Measure QuestionsDocument7 pagesCircular Measure QuestionspopoutNo ratings yet
- Circular Measure@Set 1Document2 pagesCircular Measure@Set 1Hayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 II Arc Length & Area of Sector ENRICHDocument17 pagesChapter 3 II Arc Length & Area of Sector ENRICHjuriah binti ibrahim100% (1)
- Circular Measures: Calculating Areas and Perimeters of Sectors and Circles (40Document4 pagesCircular Measures: Calculating Areas and Perimeters of Sectors and Circles (40SasiKalaRamayahNo ratings yet
- 8 Circular MeasuresDocument12 pages8 Circular MeasuresNor Hanina100% (6)
- Circular Measure CalculationsDocument17 pagesCircular Measure CalculationsRahman AnwarNo ratings yet
- Circular MeasureDocument15 pagesCircular MeasureJoann Ng100% (1)
- Add MathsDocument5 pagesAdd MathsDzul JefriNo ratings yet
- E (I) Circular Measures 1Document8 pagesE (I) Circular Measures 1Wong Jing KaeNo ratings yet
- Done Circular MeasureDocument12 pagesDone Circular MeasureSharvinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Microsoft-Word-F4 c8 Circular Measures NewDocument10 pagesMicrosoft-Word-F4 c8 Circular Measures Newuzai88No ratings yet
- Sector and Arc Length Word Problems with Step-by-Step SolutionsDocument8 pagesSector and Arc Length Word Problems with Step-by-Step SolutionssungoesroundNo ratings yet
- Ethics & Legal Issues in PsychiatryDocument91 pagesEthics & Legal Issues in PsychiatryShah OzairNo ratings yet
- AMATH Circular MeasureDocument21 pagesAMATH Circular MeasureLene100% (1)
- Circular Measures Problems and SolutionsDocument3 pagesCircular Measures Problems and SolutionspizamNo ratings yet
- Quiz: CIRCLE (Form 2)Document4 pagesQuiz: CIRCLE (Form 2)raudatunnur87No ratings yet
- Chapter 8: Circular MeasureDocument9 pagesChapter 8: Circular MeasureHayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- Form 2 Math Chapter 10Document4 pagesForm 2 Math Chapter 10Lywee Neo75% (4)
- Circumference and Area of CirclesDocument6 pagesCircumference and Area of CirclesSashineka SumbulingamNo ratings yet
- Review Exercise 22 Objective)Document9 pagesReview Exercise 22 Objective)Vimalraj MoghanNo ratings yet
- Exercise Chapter 8Document5 pagesExercise Chapter 8Shafiqah SamsuriNo ratings yet
- Circular Measure NADocument26 pagesCircular Measure NAJoann NgNo ratings yet
- CHP 10 BookletDocument28 pagesCHP 10 Booklettommytan1021No ratings yet
- 06 Circular MeasureDocument10 pages06 Circular MeasureVivianne YongNo ratings yet
- Circ MeasureDocument15 pagesCirc MeasureKaren OngNo ratings yet
- Circles II: Properties of Circles and Angles in CirclesDocument11 pagesCircles II: Properties of Circles and Angles in Circlessims363No ratings yet
- ZZ C MeasureDocument1 pageZZ C MeasureAnas FahmiNo ratings yet
- 8 CircularmeasuresDocument8 pages8 CircularmeasuresSyafiqah RedzwanNo ratings yet
- Perimeter and Area CemDocument15 pagesPerimeter and Area CemRafidah RamliNo ratings yet
- Add Maths - Circular Measurement IIIDocument10 pagesAdd Maths - Circular Measurement IIIJohnLimNo ratings yet
- Assign Sheet TrigDocument3 pagesAssign Sheet TrigChirag Hablani100% (1)
- CircleDocument20 pagesCirclejuriah binti ibrahimNo ratings yet
- CircleDocument20 pagesCirclesabummathewNo ratings yet
- Answers (October 2009) : Example 1Document5 pagesAnswers (October 2009) : Example 1robanloiNo ratings yet
- Circle TheoremDocument8 pagesCircle Theoremapi-291428736No ratings yet
- 1 3 1 1 5Document16 pages1 3 1 1 5Himanshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- F3 Math PMR QuestionsDocument2 pagesF3 Math PMR QuestionsGee LengNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About CirclesDocument9 pagesEverything You Need to Know About CirclesLooyee ChenNo ratings yet
- Areas Related To CirclesDocument23 pagesAreas Related To Circlesthinkiit80% (5)
- Set Item Item Tambahan Tingkatan 5Document147 pagesSet Item Item Tambahan Tingkatan 5Amanina Edham Azree EdhamNo ratings yet
- Maths Form 2 Exam P3Document5 pagesMaths Form 2 Exam P3JKNo ratings yet
- Rumus-Rumus Berikut Boleh Membantu Anda Menjawab Soalan. Simbol-Simbol Yang Diberi Adalah Yang Biasa DigunakanDocument31 pagesRumus-Rumus Berikut Boleh Membantu Anda Menjawab Soalan. Simbol-Simbol Yang Diberi Adalah Yang Biasa DigunakanNordiana IdrisNo ratings yet
- 10 Mathematics Impq Sa 2 5 CircleDocument14 pages10 Mathematics Impq Sa 2 5 CircleJesse SandersNo ratings yet
- Circular Measure Problems SolvedDocument11 pagesCircular Measure Problems SolvedTerence RileyNo ratings yet
- IB Questionbank Mathematics Higher Level 3rd Edition 1Document5 pagesIB Questionbank Mathematics Higher Level 3rd Edition 1Ayush MunotNo ratings yet
- Q C1 NER9 Ifs RDvxdeq MWVDocument5 pagesQ C1 NER9 Ifs RDvxdeq MWVtgaryangamerzsNo ratings yet
- ADD MATHS Quiz1 Circular MeasureDocument2 pagesADD MATHS Quiz1 Circular MeasureNor Irwaida Ab KarimNo ratings yet
- PPR Maths NBK: Diagram 1 Shows Two Sector of Circle ORQ and OPS With Centre ODocument17 pagesPPR Maths NBK: Diagram 1 Shows Two Sector of Circle ORQ and OPS With Centre OakuesukaNo ratings yet
- Formative Practice Paper 1Document20 pagesFormative Practice Paper 1Ardiyanti SetyoriniNo ratings yet
- TrignometryDocument12 pagesTrignometryAbdo AbdalatifNo ratings yet
- Hyrdoacoustic Ocean Exploration: Theories and Experimental ApplicationFrom EverandHyrdoacoustic Ocean Exploration: Theories and Experimental ApplicationNo ratings yet
- DebateDocument5 pagesDebateShah OzairNo ratings yet
- Why I dislike doc sharing sitesDocument1 pageWhy I dislike doc sharing sitesShah OzairNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Nets of Geometric Solids SubjectiveDocument2 pagesMathematics Nets of Geometric Solids SubjectiveAmir AimanNo ratings yet
- Exercise Pt3 Science Form 2 N 3Document64 pagesExercise Pt3 Science Form 2 N 3Shah OzairNo ratings yet
- Alumni Contribution ProgramDocument1 pageAlumni Contribution ProgramShah OzairNo ratings yet
- Uyfjygjjvuk KJVJHVKJBKJN Bjkbkjbkjhiin HJVJHVKJBKJNLKNDocument1 pageUyfjygjjvuk KJVJHVKJBKJN Bjkbkjbkjhiin HJVJHVKJBKJNLKNShah OzairNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Transformations Reflection SubjectiveDocument1 pageMathematics Transformations Reflection SubjectiveMuhammad Ammar NaufalNo ratings yet
- Liaison PsychiatryDocument59 pagesLiaison PsychiatryShah OzairNo ratings yet
- Child PsychiatryDocument61 pagesChild PsychiatryShah OzairNo ratings yet
- Tetamu-Tetamu Kehormat: Lampiran ADocument28 pagesTetamu-Tetamu Kehormat: Lampiran AShah OzairNo ratings yet
- JadualDocument1 pageJadualShah OzairNo ratings yet
- 8 Cardiac RemodingDocument2 pages8 Cardiac RemodingShah OzairNo ratings yet
- Case PortfolioDocument2 pagesCase PortfolioShah OzairNo ratings yet
- Circulation 2000 Lorell 470 9Document11 pagesCirculation 2000 Lorell 470 9Shah OzairNo ratings yet