Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Outline - Script Lesson Plan For Bacteria - Field I
Uploaded by
api-328213101Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Outline - Script Lesson Plan For Bacteria - Field I
Uploaded by
api-328213101Copyright:
Available Formats
OUTLINE OF THE LESSON:
Activate prior knowledge!!!!
HOW DO YOU THINK BACTERIA AFFECT OUR DAILY LIVES? Good ways?
Bad ways?
o Remind them about graphic organizer
o Take 4 examples of good ways and 4 of bad ways.
write them on the board
o Good ways include: food production (cheese, yogurt, wine, beer),
antibiotics (penicillin), live on/in us (in gut to help digestion,
prevent some infections), help us purify waste water, etc.
o Bad ways include: contaminate our food and water, food
poisoning, cause disease, lead to mold, etc.
WHAT IS A BACTERIA?
o Go to powerpoint
What is bacteria?
Prokaryotic microorganism that is too small to be seen without an
unaided eye
Bacteria are found everywhere from hot springs to on your own skin.
HOW BIG DO YOU THINK BACTERIA ARE?
o They range in size from 0.2 2.0 micrometers
That is super small because there are 1,000,000
micrometers in 1 meter!
What is a prokaryote?
A prokaryote is a unicellular organism
o Has a single circular chromosome of DNA
DNA NOT enclosed within a membrane
o Does NOT have membrane-enclosed organelles.
HOW DO WE IDENTIFY BACTERIA?
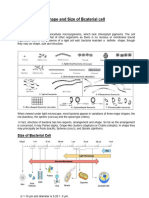
Bacterial cell morphology
Bacterial cell arrangement
What is a morphology?
The form and structure of a particular organism, organ, tissue or cell.
o This includes the shape and other externally visible
characteristics of the cell or colony of bacteria.
5 Types of Morphologies *** Remind them of the graphic organizer,
prompt them to tell something it looks like.
1.)
2.)
3.)
4.)
5.)
Bacillus = rod/cigar shaped
Coccus = spherical shaped
Coccobacilli = potato/ cigar butt shaped
Spirilla = spiral shaped
Vibrios = slightly curved rod
What is a Cell Arrangement mean?
Determined by the number of planes in which the division occurs and
on whether the cells separate after the division
WHY DO BACTERIA DIVIDE?
o They divide because that is how they reproduce
This is called binary fission
So, Which morphologies undergo multicellular associations?
Cocci and Bacilli
Division Patterns Among Cocci *** Remind them of graphic
organizer, prompt them to tell you something it looks like
When cocci divide to reproduce, the cells may remain attached to one
another
The arrangement of the coccus can be helpful when identifying the
bacteria you are looking at
1.) When they divide and stay attached in pairs, they are called
diplococcus
o An easy way to remember is that the prefix di- means two
2.) Those that divide and remain in chainlike patterns are called
streptococcus
o A good way to remember this is that the prefix strepto- is
Greek for twisted chain
3.) Those that divide into two planes and remain in groups of 4 are
called tetrad
o Tetra = 4
4.) Those that divide into 3 planes and remain in cubelike groups of 8
are called sarcina
o Sarcina is latin for pack
5.) Lastly, those that divide into multiple planes and form grapelike
clusters or sheets are called staphylococcus
o Staphylo is Greek for grape
Division patterns Among Bacilli
Different divisions of bacillus can only produce streptobacillus or
diplobacillus
o Bacilli do NOT exhibit tetrads or sarcina
o WHY DO YOU THINK THEY CAN ONLY DO THESE TYPES OF
DIVISIONS think of their shape
They are longer and therefore they typically only divide
across their short axis so there are fewer groupings of
bacilli than cocci
What determines the shape or arrangement of a bacteria?
It is determined by heredity!
Most bacteria are monomorphic
o This means that they typically maintain a single shape or
arrangement
However, some bacteria are pleomorphic
o This means that they might have several different shapes
DO YOU THINK IT IS EASIER TO IDENTIFY BACTERIA THAT ARE
PLEOMORPHIC OR MONOMORPHIC ? WHY?
o Monomorphic
RECAP
Morphology refers to the shape of the bacterial cell
Arrangement describes the different types of divisions that may occur
Ask if they have any questions
Answers to the assessment at the end of the PPT: A, C, B, A,
Left, Right, Left, Right, Left, Left, Left, Left, Left, Right
You might also like
- Outlines of Dairy Bacteriology, 8th edition A Concise Manual for the Use of Students in DairyingFrom EverandOutlines of Dairy Bacteriology, 8th edition A Concise Manual for the Use of Students in DairyingNo ratings yet
- BacteriaDocument11 pagesBacteriaBhanu AcademyNo ratings yet
- Different Size, Shape and Arrangement of Bacterial CellsDocument17 pagesDifferent Size, Shape and Arrangement of Bacterial CellsRatan YadavNo ratings yet
- Bacteria Lesson PlanDocument11 pagesBacteria Lesson PlanFrancis Kevin Mag-usaraNo ratings yet
- Are All Bacteria Dangerous? Biology Book for Kids | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandAre All Bacteria Dangerous? Biology Book for Kids | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Universidad Estatal Amazonica Departamento de Ciencias de La Vida Carrera de Ingenieria AmbientalDocument11 pagesUniversidad Estatal Amazonica Departamento de Ciencias de La Vida Carrera de Ingenieria AmbientalMishelita KatrinNo ratings yet
- Outlines of dairy bacteriology A concise manual for the use of students in dairyingFrom EverandOutlines of dairy bacteriology A concise manual for the use of students in dairyingNo ratings yet
- Bacterial MorphologyDocument5 pagesBacterial MorphologyRakia PillayNo ratings yet
- Bacteria Classification and Characteristics in 40 CharactersDocument2 pagesBacteria Classification and Characteristics in 40 CharactersyashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- MicroDocument13 pagesMicroArsalan KhanNo ratings yet
- Bacteria ShapesDocument14 pagesBacteria Shapessai kiranNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology (English Language)Document12 pagesBacteriology (English Language)Sely BoysalaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER - 4 "Virus, Bacteria and Cyano Bacteria": Micro-OrganismsDocument7 pagesCHAPTER - 4 "Virus, Bacteria and Cyano Bacteria": Micro-OrganismsdikpalakNo ratings yet
- Bacteria Morphology IDocument19 pagesBacteria Morphology ISourav SumanNo ratings yet
- Result Sample Characteristics of Bacteria Image Shape: Arrangement: Staphylococci Size: 0.5-2.0 M Gram's Type: Gram-PositiveDocument2 pagesResult Sample Characteristics of Bacteria Image Shape: Arrangement: Staphylococci Size: 0.5-2.0 M Gram's Type: Gram-PositiveAshNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology 1Document11 pagesBacteriology 1catherinemukami98No ratings yet
- 8th Biological Science EM L2 WS 15-60Document92 pages8th Biological Science EM L2 WS 15-60PRESIDENT OF INDIANo ratings yet
- CH 4-Virus, Bacteria and Cyano BacteriaDocument5 pagesCH 4-Virus, Bacteria and Cyano BacteriaMushtaqAnsariNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Science Chapter 1 PDFDocument20 pagesForm 5 Science Chapter 1 PDFfrez_kingdom100% (1)
- Bacteria: Maya Fadhillah 140410090024 Biology FMIPA UnpadDocument32 pagesBacteria: Maya Fadhillah 140410090024 Biology FMIPA UnpadMaya FadhillahNo ratings yet
- Basic Dairy TechnologyDocument13 pagesBasic Dairy TechnologylaviniakartikaNo ratings yet
- Bacteria: The Microcosmos of Yogur TDocument24 pagesBacteria: The Microcosmos of Yogur TLuifran Espinoza100% (1)
- Microorganisms: Tiny Living Organisms That Surround UsDocument18 pagesMicroorganisms: Tiny Living Organisms That Surround UsBiology 9 ModulesNo ratings yet
- BIOL 324 Introduction To MicroBDocument5 pagesBIOL 324 Introduction To MicroBKargboNo ratings yet
- Pink Blob Organic Stationary A4 Document 2Document5 pagesPink Blob Organic Stationary A4 Document 2IyaNo ratings yet
- GATE Sample Material - MicrobiologyDocument0 pagesGATE Sample Material - MicrobiologyAnkur BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Organisms of The Microbial WorldDocument32 pagesOrganisms of The Microbial WorldChristiel John MagtibayNo ratings yet
- LO: Describe Basic Bacterial Classification and Some Important Representatives For Each Group of Bacteria Bacterial ClassificationDocument5 pagesLO: Describe Basic Bacterial Classification and Some Important Representatives For Each Group of Bacteria Bacterial ClassificationTan SinCosNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Monera: Bacteria Structure, Growth, Reproduction & ClassificationDocument5 pagesKingdom Monera: Bacteria Structure, Growth, Reproduction & ClassificationMSNo ratings yet
- Commonly Used Microbes in BiotechnologyDocument30 pagesCommonly Used Microbes in BiotechnologyNILA MAZON100% (1)
- Bacteria Domain Hierarchy ClassificationDocument51 pagesBacteria Domain Hierarchy ClassificationleyluuuuuhNo ratings yet
- Module I MycologyDocument30 pagesModule I Mycologyashermilez95No ratings yet
- Prokaryotic Cell Shapes, Sizes and ArrangementsDocument4 pagesProkaryotic Cell Shapes, Sizes and ArrangementsAmit GodaraNo ratings yet
- Characterization of Microorganisms: Lecture-13Document20 pagesCharacterization of Microorganisms: Lecture-13ShamaNo ratings yet
- Basic Medical Microbiology: SECTION I IntroductionDocument2 pagesBasic Medical Microbiology: SECTION I IntroductionYanyan BalitungNo ratings yet
- BacteriaDocument12 pagesBacteriaamora eliNo ratings yet
- MorphologyDocument6 pagesMorphologyBảo ĐoànNo ratings yet
- MICROORGANISMSDocument20 pagesMICROORGANISMSHezil Mae MancaoNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology and Virology by KaziDocument35 pagesBacteriology and Virology by KaziMohibNo ratings yet
- Environment MicrobiologyDocument16 pagesEnvironment Microbiologymohamed ishaqNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Science (Chapter 1)Document20 pagesForm 5 Science (Chapter 1)Sensei J-dai95% (42)
- Eubacteria and Archaebacteria ComparisonDocument9 pagesEubacteria and Archaebacteria Comparison相原浩No ratings yet
- Bacteria - General CharacteristicsDocument12 pagesBacteria - General Characteristicsvasundhara ayyagariNo ratings yet
- PP1 Diversity Change and Continuity Micro-OrganismsDocument62 pagesPP1 Diversity Change and Continuity Micro-OrganismsmmabaneconnieNo ratings yet
- Materi Kelompok 10 BacteriaDocument7 pagesMateri Kelompok 10 BacteriarisalNo ratings yet
- Lesson 35Document16 pagesLesson 35Abdelraouf ElmanamaNo ratings yet
- Shape and Size of Bacterial CellDocument8 pagesShape and Size of Bacterial Cellkmr260210No ratings yet
- Lab Report 9Document14 pagesLab Report 9Jhon Patrick DelmonteNo ratings yet
- BIOC17 NotesDocument56 pagesBIOC17 NotesIqbalNo ratings yet
- BacteriaDocument2 pagesBacteriaKomet BudiNo ratings yet
- Kinds of BacteriaDocument2 pagesKinds of BacteriaMystery 95No ratings yet
- BacteriaDocument2 pagesBacteriaAileen GalichaNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity of Micro-OrganismsDocument58 pagesBiodiversity of Micro-Organismsowethugwama09No ratings yet
- Microbio Lec Midterms ReviewerDocument4 pagesMicrobio Lec Midterms Reviewernicole juanicoNo ratings yet
- Cell Morphology of MicrobesDocument26 pagesCell Morphology of MicrobesWajiha FatimaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 MergedDocument62 pagesChapter 6 Mergedamsal200416No ratings yet
- Bacillus: Bacillus Includes Both Free-Living and PathogenicDocument4 pagesBacillus: Bacillus Includes Both Free-Living and PathogenicSartika SalehNo ratings yet
- Roughly Bacteria Are Divided Into Three Shapes, That Is:: Coccus Bacillus SpiralDocument10 pagesRoughly Bacteria Are Divided Into Three Shapes, That Is:: Coccus Bacillus Spiraltozwa_essyNo ratings yet
- Education - Physical DisabilitiesDocument17 pagesEducation - Physical Disabilitiesapi-328213101No ratings yet
- Mini Unit Vocabulary - All 3 DaysDocument1 pageMini Unit Vocabulary - All 3 Daysapi-328213101No ratings yet
- Tbi PresentationDocument11 pagesTbi Presentationapi-328213101No ratings yet
- Learning Disabilities PresentationDocument14 pagesLearning Disabilities Presentationapi-328213101No ratings yet
- Day 2 - Cooperative Learning - Food Webs Field II Spring 2017Document4 pagesDay 2 - Cooperative Learning - Food Webs Field II Spring 2017api-328213101No ratings yet
- Collaboration and Communication Between Parent Teacher and StudentDocument2 pagesCollaboration and Communication Between Parent Teacher and Studentapi-328213101No ratings yet
- Communication Disorders PresentationDocument15 pagesCommunication Disorders Presentationapi-328213101No ratings yet
- DeafnessDocument10 pagesDeafnessapi-328213101No ratings yet
- Erikas Ebd PresentationDocument12 pagesErikas Ebd Presentationapi-328213101No ratings yet
- Fieldii TechniquepresentationreflectionDocument1 pageFieldii Techniquepresentationreflectionapi-328213101No ratings yet
- Blindness Low VisionDocument11 pagesBlindness Low Visionapi-328213101No ratings yet
- Day 1 - Direct Instruction Lesson Plan Food WebsDocument5 pagesDay 1 - Direct Instruction Lesson Plan Food Websapi-328213101No ratings yet
- Learning From Lived Experience 1Document8 pagesLearning From Lived Experience 1api-328213101No ratings yet
- Personal Theory of Teaching Learning and Assessment Part II - Field II Spring 2017Document3 pagesPersonal Theory of Teaching Learning and Assessment Part II - Field II Spring 2017api-328213101No ratings yet
- Virtual Lab - Ecosystems Inquiry Based Lesson Instructions and Worksheets - Field II Spring 2017Document7 pagesVirtual Lab - Ecosystems Inquiry Based Lesson Instructions and Worksheets - Field II Spring 2017api-328213101No ratings yet
- Mini Unit Vocabulary - All 3 DaysDocument1 pageMini Unit Vocabulary - All 3 Daysapi-328213101No ratings yet
- Apr 24 2c 2017 2c 1341Document2 pagesApr 24 2c 2017 2c 1341api-328213101No ratings yet
- Day 3 - Discovery or Inquiry Based Lesson - Food Webs - Field II Spring 2017Document4 pagesDay 3 - Discovery or Inquiry Based Lesson - Food Webs - Field II Spring 2017api-328213101No ratings yet
- Mary - Live Lesson WorksheetsDocument2 pagesMary - Live Lesson Worksheetsapi-328213101No ratings yet
- Field II - Trade BooksDocument13 pagesField II - Trade Booksapi-328213101100% (1)
- Food Webs - Field II Unit Plan PowerpointDocument22 pagesFood Webs - Field II Unit Plan Powerpointapi-328213101No ratings yet
- Mini Unit Vocabulary - All 3 DaysDocument1 pageMini Unit Vocabulary - All 3 Daysapi-328213101No ratings yet
- Day 1 - Direct Instruction Food Web HomeworkDocument2 pagesDay 1 - Direct Instruction Food Web Homeworkapi-328213101No ratings yet
- Live Lesson - Field II Spring 2017Document6 pagesLive Lesson - Field II Spring 2017api-328213101No ratings yet
- Anticipation Guide - Battle of GettysburgDocument1 pageAnticipation Guide - Battle of Gettysburgapi-328213101No ratings yet
- The Battle of Gettysburg Graphic OrganizerDocument2 pagesThe Battle of Gettysburg Graphic Organizerapi-328213101No ratings yet
- Battle of GettysburgDocument9 pagesBattle of Gettysburgapi-328213101No ratings yet
- Fieldii ObservationquestionsDocument2 pagesFieldii Observationquestionsapi-328213101No ratings yet
- Battle of Gettysburg Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesBattle of Gettysburg Lesson Planapi-328213101No ratings yet
- Personal Theory of Teaching Learning and Assessment - Field II Spring 2017Document2 pagesPersonal Theory of Teaching Learning and Assessment - Field II Spring 2017api-328213101No ratings yet
- Gavrila Eduard 2Document6 pagesGavrila Eduard 2Eduard Gabriel GavrilăNo ratings yet
- A Development of The Test For Mathematical Creative Problem Solving AbilityDocument27 pagesA Development of The Test For Mathematical Creative Problem Solving AbilityanwarNo ratings yet
- Ds 3805Document4 pagesDs 3805sparky2017No ratings yet
- Wargames Illustrated #115Document64 pagesWargames Illustrated #115Анатолий Золотухин100% (1)
- An Improved Ant Colony Algorithm and Its ApplicatiDocument10 pagesAn Improved Ant Colony Algorithm and Its ApplicatiI n T e R e Y eNo ratings yet
- Assessment (L4) : Case Analysis: Managerial EconomicsDocument4 pagesAssessment (L4) : Case Analysis: Managerial EconomicsRocel DomingoNo ratings yet
- p2 - Guerrero Ch13Document40 pagesp2 - Guerrero Ch13JerichoPedragosa88% (17)
- Hilton 5-29 Case SolutionDocument4 pagesHilton 5-29 Case SolutionPebbles RobblesNo ratings yet
- Liu030 Nepal Bans Solo Mountain ClimbersDocument2 pagesLiu030 Nepal Bans Solo Mountain Climberssanti.miranda.parrillaNo ratings yet
- Exercise C: Cocurrent and Countercurrent FlowDocument6 pagesExercise C: Cocurrent and Countercurrent FlowJuniorNo ratings yet
- Buyers FancyFoodDocument6 pagesBuyers FancyFoodvanNo ratings yet
- Capex Vs RescoDocument1 pageCapex Vs Rescosingla.nishant1245No ratings yet
- VISCOSITY CLASSIFICATION GUIDE FOR INDUSTRIAL LUBRICANTSDocument8 pagesVISCOSITY CLASSIFICATION GUIDE FOR INDUSTRIAL LUBRICANTSFrancisco TipanNo ratings yet
- WCM - March 2017-Final Version PDF - 4731677 - 01Document211 pagesWCM - March 2017-Final Version PDF - 4731677 - 01Antonio VargasNo ratings yet
- KG ResearchDocument257 pagesKG ResearchMuhammad HusseinNo ratings yet
- Offshore Wind Turbine 6mw Robust Simple EfficientDocument4 pagesOffshore Wind Turbine 6mw Robust Simple EfficientCristian Jhair PerezNo ratings yet
- Optimum Work Methods in The Nursery Potting ProcessDocument107 pagesOptimum Work Methods in The Nursery Potting ProcessFöldi Béla100% (1)
- Past Paper Booklet - QPDocument506 pagesPast Paper Booklet - QPMukeshNo ratings yet
- Solution of Introduction To Many-Body Quantum Theory in Condensed Matter Physics (H.Bruus & K. Flensberg)Document54 pagesSolution of Introduction To Many-Body Quantum Theory in Condensed Matter Physics (H.Bruus & K. Flensberg)Calamanciuc Mihai MadalinNo ratings yet
- Imp RssDocument8 pagesImp RssPriya SharmaNo ratings yet
- Research of William Wells at HarvardDocument10 pagesResearch of William Wells at HarvardARGHA MANNANo ratings yet
- Module 7 - Assessment of Learning 1 CoursepackDocument7 pagesModule 7 - Assessment of Learning 1 CoursepackZel FerrelNo ratings yet
- Cypress Enable Basic Rer Erence ManualDocument2 pagesCypress Enable Basic Rer Erence ManualCarlos RodasNo ratings yet
- CM Template For Flora and FaunaDocument3 pagesCM Template For Flora and FaunaJonathan Renier Verzosa0% (1)
- Case Study - Help DocumentDocument2 pagesCase Study - Help DocumentRahNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledMOHD JEFRI BIN TAJARINo ratings yet
- APTARE IT Analytics: Presenter NameDocument16 pagesAPTARE IT Analytics: Presenter NameCCIE DetectNo ratings yet
- Trabajo de Investigación FormativaDocument75 pagesTrabajo de Investigación Formativalucio RNo ratings yet
- List of StateDocument5 pagesList of StatedrpauliNo ratings yet
- Amma dedicates 'Green Year' to environmental protection effortsDocument22 pagesAmma dedicates 'Green Year' to environmental protection effortsOlivia WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondFrom EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Mitochondria and the Future of Medicine: The Key to Understanding Disease, Chronic Illness, Aging, and Life ItselfFrom EverandMitochondria and the Future of Medicine: The Key to Understanding Disease, Chronic Illness, Aging, and Life ItselfRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (98)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- This Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyFrom EverandThis Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- The Mind & The Brain: Neuroplasticity and the Power of Mental ForceFrom EverandThe Mind & The Brain: Neuroplasticity and the Power of Mental ForceNo ratings yet
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (396)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindFrom EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (93)
- Gathering Moss: A Natural and Cultural History of MossesFrom EverandGathering Moss: A Natural and Cultural History of MossesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (347)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (515)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Superlative: The Biology of ExtremesFrom EverandSuperlative: The Biology of ExtremesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (51)
- The Confident Mind: A Battle-Tested Guide to Unshakable PerformanceFrom EverandThe Confident Mind: A Battle-Tested Guide to Unshakable PerformanceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (45)
- Why We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsFrom EverandWhy We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2083)
- The Dragons of Eden: Speculations on the Evolution of Human IntelligenceFrom EverandThe Dragons of Eden: Speculations on the Evolution of Human IntelligenceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (632)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- Human Errors: A Panorama of Our Glitches, from Pointless Bones to Broken GenesFrom EverandHuman Errors: A Panorama of Our Glitches, from Pointless Bones to Broken GenesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (56)
- Fearfully and Wonderfully: The Marvel of Bearing God's ImageFrom EverandFearfully and Wonderfully: The Marvel of Bearing God's ImageRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (40)
- Unthinkable: An Extraordinary Journey Through the World's Strangest BrainsFrom EverandUnthinkable: An Extraordinary Journey Through the World's Strangest BrainsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (50)
- Awkward: The Science of Why We're Socially Awkward and Why That's AwesomeFrom EverandAwkward: The Science of Why We're Socially Awkward and Why That's AwesomeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (23)
- Minds Make Societies: How Cognition Explains the World Humans CreateFrom EverandMinds Make Societies: How Cognition Explains the World Humans CreateRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (23)
- Inside of a Dog: What Dogs See, Smell, and KnowFrom EverandInside of a Dog: What Dogs See, Smell, and KnowRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (390)
- The Nature Fix: Why Nature Makes us Happier, Healthier, and More CreativeFrom EverandThe Nature Fix: Why Nature Makes us Happier, Healthier, and More CreativeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (157)
- The Dog Who Couldn't Stop Loving: How Dogs Have Captured Our Hearts for Thousands of YearsFrom EverandThe Dog Who Couldn't Stop Loving: How Dogs Have Captured Our Hearts for Thousands of YearsNo ratings yet