Professional Documents
Culture Documents
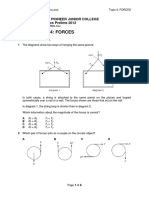
Mass of Block B Is 50 Kg. The Surfaces Are Smooth. If The Blocks Are in Equilibrium, What Is The Force F?
Uploaded by
Wilson Ferley Aguilar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageejercicio resuelto
Original Title
fisica
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentejercicio resuelto
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageMass of Block B Is 50 Kg. The Surfaces Are Smooth. If The Blocks Are in Equilibrium, What Is The Force F?
Uploaded by
Wilson Ferley Aguilarejercicio resuelto
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
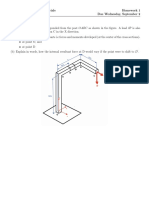
Problem 3.
102 The mass of block A is 42 kg, and the
mass of block B is 50 kg. The surfaces are smooth. If
the blocks are in equilibrium, what is the force F?
B
F
45
A
20
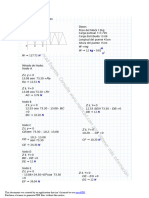
Solution: Isolate the top block. Solve the equilibrium equations.
The weight is. The angle between the normal force N1 and the positive x axis is. The normal force is. The force N2 is. The equilibrium
conditions are
"
from which
"
"
Solve:
B
N2
F D N1 C N2 C W D 0
N1
Fx D (0.7071jN1 j % jN2 j'i D 0
Fy D (0.7071jN1 j % 490.5'j D 0.
N1 D 693.7 N,
N1
jN2 j D 490.5 N
Isolate the bottom block. The weight is
W D 0i % jWjj D 0i % (42'(9.81'j D 0i % 412.02j (N).
The angle between the normal force N1 and the positive x axis is
(270 % 45 ' D 225 .
N3
x
W
The normal force:
N1 D jN1 j(i cos 225 C j sin 225 ' D jN1 j(%0.7071i % 0.7071j'.
The angle between the normal force N3 and the positive x-axis is
(90 % 20 ' D 70 .
The normal force is
N1 D jN3 j(i cos 70 C j sin 70 ' D jN3 j(0.3420i C 0.9397j'.
The force is . . . F D jFji C 0j. The equilibrium conditions are
"
F D W C N1 C N3 C F D 0,
from which:
"
"
Fx D (%0.7071jN1 j C 0.3420jN3 j C jFj'i D 0
Fy D (%0.7071jN1 j C 0.9397jN3 j % 412'j D 0
For jN1 j D 693.7 N from above:
jFj D 162 N
c 2005 Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. This material is protected under all copyright laws as they
#
currently exist. No portion of this material may be reproduced, in any form or by any means, without permission in writing from the publisher.
You might also like
- Problem 3.72: F D T DDDocument3 pagesProblem 3.72: F D T DDYELTSIN DRASKOVIS FRANCO GOMEZNo ratings yet
- Components or Resolved ForcesDocument16 pagesComponents or Resolved ForcesNagarajSitaramNo ratings yet
- Statics OF Rigid Bodies ModuleDocument47 pagesStatics OF Rigid Bodies ModuleCj Llemos67% (3)
- SMA 4v2Document43 pagesSMA 4v2Min Rot MonNo ratings yet
- 4 Forces 2012 - H1 Physics - 21S08Document8 pages4 Forces 2012 - H1 Physics - 21S08Selvi FatimaNo ratings yet
- Surface Waves in Magnetoelastic SolidsDocument35 pagesSurface Waves in Magnetoelastic SolidspsaxenaNo ratings yet
- Roof Truss ProblemDocument6 pagesRoof Truss ProblemKatyayini NelliNo ratings yet
- ECE 305 Homework Solutions for Week 8Document8 pagesECE 305 Homework Solutions for Week 8jiosNo ratings yet
- 7 Damage Mechanics: Anisotropy Have Been Formulated in Detail. This Chapter Is Concerned WithDocument20 pages7 Damage Mechanics: Anisotropy Have Been Formulated in Detail. This Chapter Is Concerned WithmaheshNo ratings yet
- 2D Separation of Variables in Cylindrical Coordinates: QZ T R KDocument11 pages2D Separation of Variables in Cylindrical Coordinates: QZ T R KAB DevilierNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Analysis of Pin Jointed FramesDocument19 pagesChapter 3 Analysis of Pin Jointed Framesghodghod123No ratings yet
- Strain Energy Part 1Document20 pagesStrain Energy Part 1aalijanaabNo ratings yet
- JLD 4.0 - (L3) - Vectors - 22nd JuneDocument58 pagesJLD 4.0 - (L3) - Vectors - 22nd Junepranjal mishraNo ratings yet
- Engineering Electromagnetics Lecture 4 - Chapter 2 Key ConceptsDocument62 pagesEngineering Electromagnetics Lecture 4 - Chapter 2 Key ConceptsSabit ShaihollaNo ratings yet
- Partition Function and Density of StatesDocument1 pagePartition Function and Density of StatesbhpliaoNo ratings yet
- Torsion: 7.1 Overview of The TheoryDocument18 pagesTorsion: 7.1 Overview of The TheoryJuan SilvaNo ratings yet
- Stress States in Octahedral PlanesDocument1 pageStress States in Octahedral Planesahmed shakerNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics: StaticsDocument22 pagesEngineering Mechanics: StaticsNordiana IdrisNo ratings yet
- 3 BalanceDocument7 pages3 BalanceSebastiao SilvaNo ratings yet
- Apphysics Lec 12Document25 pagesApphysics Lec 12Vijay KumarNo ratings yet
- Periodic StructuresDocument37 pagesPeriodic StructuresYarden MazorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Scalar and Vector PDFDocument22 pagesChapter 2 - Scalar and Vector PDFhakimNo ratings yet
- MD 2Document33 pagesMD 2Wilfredo Nieves OsoriaNo ratings yet
- 1718sem2 Ce2155Document8 pages1718sem2 Ce2155calchan79No ratings yet
- A Numerical Example: SolutionDocument6 pagesA Numerical Example: Solutionreza2224No ratings yet
- Notes Prepared by (01) Kıvanç Arslan: y X, Z FDocument4 pagesNotes Prepared by (01) Kıvanç Arslan: y X, Z FanNo ratings yet
- DEE-23106 Fundamentals of Electrical and Power Engineering: Exercise #1Document12 pagesDEE-23106 Fundamentals of Electrical and Power Engineering: Exercise #1shoptodipNo ratings yet
- Mat 115 TheoryDocument1 pageMat 115 Theorymustafa sertNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Formulation of a String Element Using Galerkin ApproachDocument22 pagesFinite Element Formulation of a String Element Using Galerkin ApproachLIU HengxuNo ratings yet
- Other Through Special Points ("Nodes") P P 3 2 1 4 3Document31 pagesOther Through Special Points ("Nodes") P P 3 2 1 4 3m_er100No ratings yet
- Are The Reactions at C in The Two Cases?: Problem 5.49 The Tension in Cable AB Is 2 Kn. WhatDocument5 pagesAre The Reactions at C in The Two Cases?: Problem 5.49 The Tension in Cable AB Is 2 Kn. WhatMahir MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Deflection Buckling LaminatesDocument33 pagesDeflection Buckling LaminatesfayuangNo ratings yet
- 2-1 External Work and Strain Energy 2-2 Principle of Work and Energy 2-3 Principle of Virtual Work 2-4 Method of Virtual Work: TrussesDocument37 pages2-1 External Work and Strain Energy 2-2 Principle of Work and Energy 2-3 Principle of Virtual Work 2-4 Method of Virtual Work: TrussesMary Grace VelitarioNo ratings yet
- Now: Smooth Piece of A CurveDocument9 pagesNow: Smooth Piece of A CurveAmmar AjmalNo ratings yet
- HW01Document4 pagesHW01Potatoes123No ratings yet
- 2012 ENGG317 Midterm SolutionDocument4 pages2012 ENGG317 Midterm SolutionEmmanuel ConstantinidisNo ratings yet
- 2007 IITJEE - Paper2Document37 pages2007 IITJEE - Paper2Shashank PopliNo ratings yet
- PS1 SolutionsDocument6 pagesPS1 SolutionsrickyfavarettoNo ratings yet
- Mat 073 TheoryDocument2 pagesMat 073 Theorymustafa sertNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Steady-State Beam-LoadingDocument2 pages4.2 Steady-State Beam-Loading甘逸凱No ratings yet
- Welcome To My Class!: I'm Sir AaronDocument20 pagesWelcome To My Class!: I'm Sir AaronAaron DayloNo ratings yet
- StressDocument42 pagesStressNauman SuriaNo ratings yet
- Chapter05 - Plane Frame and Grid EqDocument63 pagesChapter05 - Plane Frame and Grid EqAgus BaeNo ratings yet
- Means Are Guided and Given To The Students. However The Answers To TheDocument8 pagesMeans Are Guided and Given To The Students. However The Answers To TheMANAPNo ratings yet
- Rotational DynamicsDocument91 pagesRotational DynamicsYugandhar VeeramachaneniNo ratings yet
- PUENTER1Document2 pagesPUENTER1EdwinNo ratings yet
- Phhysics 1st Paper Chapter 2Document40 pagesPhhysics 1st Paper Chapter 2chipshentaiNo ratings yet
- Volume and Surface IntegralsDocument5 pagesVolume and Surface IntegralsAtirut AlphabetNo ratings yet
- Torsion IV Review LectureDocument9 pagesTorsion IV Review LecturesaratNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Lecture Numerical ExampleDocument4 pagesHeat Transfer Lecture Numerical Examplereza2224No ratings yet
- (Ex) 8 (1) 1Document7 pages(Ex) 8 (1) 1baewonyeong0575No ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion (Applications) : Lecture 11-Part.IDocument10 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion (Applications) : Lecture 11-Part.IRaghda JoudaNo ratings yet
- Intrinsic Point Defects: VacanciesDocument23 pagesIntrinsic Point Defects: VacanciesNitpreet RandhawaNo ratings yet
- MANE 4240 & CIVL 4240 Introduction to Finite ElementsDocument33 pagesMANE 4240 & CIVL 4240 Introduction to Finite ElementsM.Saravana Kumar..M.ENo ratings yet
- Components or Resolved ForcesDocument16 pagesComponents or Resolved ForcesSalil DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- MANE 4240 & CIVL 4240 Introduction To Finite Elements: Constant Strain Triangle (CST)Document33 pagesMANE 4240 & CIVL 4240 Introduction To Finite Elements: Constant Strain Triangle (CST)Jason MillerNo ratings yet
- Solution: Given Data:: 165 Kpa 69 CDocument30 pagesSolution: Given Data:: 165 Kpa 69 Cyogeshkumar3089_8250No ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNo ratings yet