Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biochemistry Review Sheet
Uploaded by
api-299996815Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biochemistry Review Sheet
Uploaded by
api-299996815Copyright:
Available Formats
Name: _____________________________________________
Date: __________________________________
Biochemistry Review Sheet
Organic v Inorganic
Inorganic molecules not containing carbon and hydrogen
Examples: water (H2O), salt (NaCl)
Organic anything that contains a carbon bonded to a
hydrogen (C-H)
Four groups of Organic Molecules:
Lipids
Fats and oils
Made by combining 1 glycerol and 3
fatty acids
Contain C-H-O
Hydrophobic tail and Hydrophilic head
cell membrane
looks like a letter E
more energy than carbohydrates b/c they have more bonds (bonds=energy, so more bonds=
more energy)
saturated fats (solid at room temp, animal) contain all C-C single bonds, and have a straight
shape
unsaturated fats (liquid at room temp, from plants) have some C=C double bonds and have
a crooked shape
Carbohydrates
Sugars and Starches
Ex: Glucose (C6H12 O6), Starch, Cellulose, Sucrose
End in OSE typically (except for the polysaccharides)
Made by combining simple sugars (monosaccharides)
o Example: Glucose
o each simple sugar/monosaccharide looks like a ring
2 rings/sugars/glucose put together = disaccharide
o ex: fructose (in fruit), sucrose (in candy, table sugar), maltose
3 or more rings/sugars/glucose put together = polysaccharide
o ex: starch (how plants store extra carbohydrates), glycogen (how animals store extra
carbohydrates, cellulose (makes up cell walls)
Contains C-H-O in a specific ratio of 1:2:1
Proteins
Found in meat
make up your hair, nails, skin
Made by linking amino acids together
o amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds
20 different amino acids: all have a center C surrounded by 4 groups. Every single
amino acid has these three groups: amino group, carboxyl (acid) group, and a H. The
one thing that is different on each amino acid is the R side-chain group.
You will be able to tell which one this is by looking for the amino group,
carboxyl group, and H around the central C. The only group left is the
R/side chain group.
Contain C-H-O-N
The specific amino acids that make up a protein have different properties such as
hydrophilic or hydrophobic
o these properties determine how the protein folds (its shape!)
THE SHAPE (aka. form) OF THE PROTEIN DETERMINES HOW IT FUNCTIONS!!
If the amino acids are wrong or if the protein folds wrong, it wont
have the shape its supposed to and wont be able to do its job
proteins have very specific pH (acidity) and temperature that they work best
at (their optimal temperature/pH). If they exceed these, they will unfold, or
denature and wont be able to perform their job.
Enzymes are proteins
o Enzymes are a catalyst (speed up chemical reactions)
o name typically end in ASE
o have a very specific shape that only fits a certain substrate, like a lock and key
wont work on anything that doesnt fit their shape
Nucleic Acids
Enzyme activity is affected by 3 things:
-Temperature
-Substrate concentration
-pH
DNA and RNA
Contains C-H-O-N-P
Building block = nucleotides
Nucleotides are made up of a sugar (looks like a house), phosphate (looks like a circular
pool), and a nitrogen base (looks like a garage)
o in DNA, sugar is deoxyribose and the possible bases are ATGC
o in RNA, sugar is ribose and the possible bases are AUGC
DNA has two strands and is in the shape of a double helix
RNA only has one strand
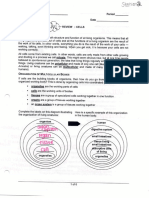
Building and Breaking Apart Molecules
Building: Dehydration synthesis- losing water, putting smaller building blocks together to make a larger
molecule
Breaking apart/digesting: Hydrolysis- adding water and breaking apart a larger molecule into its smaller
component building blocks
You might also like
- Organic Molecules Lab (OM LabDocument10 pagesOrganic Molecules Lab (OM Labbassoon11No ratings yet
- Topic I: Introduction To AnatomyDocument3 pagesTopic I: Introduction To AnatomyCristenNo ratings yet
- Introduction 12Document4 pagesIntroduction 12Abdulrahman AhmadNo ratings yet
- Macromolecules BiologyDocument37 pagesMacromolecules Biologyjulia067No ratings yet
- F334 Notes (The Thread of Life)Document15 pagesF334 Notes (The Thread of Life)Becky TenneyNo ratings yet
- Macromolecules PacketDocument13 pagesMacromolecules Packetapi-267079239100% (1)
- CBI4 Structure and Function of BiomoleculesDocument6 pagesCBI4 Structure and Function of BiomoleculesRianna NNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument143 pagesCarbohydratesCharles Darren QuiambaoNo ratings yet
- 6 ChoDocument257 pages6 Chochristianjoygallos9No ratings yet
- Carbohydrate: CarbonDocument6 pagesCarbohydrate: CarbonTrexie JaymeNo ratings yet
- AP Review Organic CompoundsDocument72 pagesAP Review Organic Compounds둡챙브로No ratings yet
- H2 Biology - Notes On BiomoleculesDocument9 pagesH2 Biology - Notes On BiomoleculesSefLRho100% (1)
- Carbohydrates: CO + H O C H O + ODocument10 pagesCarbohydrates: CO + H O C H O + OMini BossNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates (Monosaccharides)Document56 pagesCarbohydrates (Monosaccharides)khadija100% (2)
- Chapter 02 Winter 2020Document53 pagesChapter 02 Winter 2020LESLI RODRIGUEZ BENDEZUNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry (3 Class) : Chapter Two Carbohydrates DR: Zeyan A. AliDocument37 pagesBiochemistry (3 Class) : Chapter Two Carbohydrates DR: Zeyan A. AlizeyanNo ratings yet
- Biological MacromoleculesDocument171 pagesBiological MacromoleculesLev SidorenkoNo ratings yet
- BIO 22 MODULE 1 - Chemical Basis of LifeDocument14 pagesBIO 22 MODULE 1 - Chemical Basis of LifeBryan DGNo ratings yet
- CH3 Alcohols, Carboxylic Acids and EstersDocument8 pagesCH3 Alcohols, Carboxylic Acids and EstersDoc CrocNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Practice QuestionsDocument9 pagesBiochemistry Practice QuestionsJenny AnchetaNo ratings yet
- Lipids: Non-Polar Membrane Lipids AmphipathicDocument12 pagesLipids: Non-Polar Membrane Lipids AmphipathicJoed FelipeNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate NomenclatureDocument8 pagesCarbohydrate NomenclatureAwais Naseer100% (3)
- Untitled DocumentDocument2 pagesUntitled Documentapi-338687135No ratings yet
- Topic2 Biomolecule PPDocument28 pagesTopic2 Biomolecule PPismail aeryNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4, 5: Chemical Reactions Acids, Bases & SaltsDocument13 pagesLecture 4, 5: Chemical Reactions Acids, Bases & Saltstenzin bhutiNo ratings yet
- Casimiro A. Ynares Sr. Memorial National High School: MM MM MMM MM MM MDocument7 pagesCasimiro A. Ynares Sr. Memorial National High School: MM MM MMM MM MM MIrah PradoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (First Part)Document9 pagesChapter 3 (First Part)Georges SarkisNo ratings yet
- Drawing General Amino Acid Structure at pH 7Document38 pagesDrawing General Amino Acid Structure at pH 7Katie CraneNo ratings yet
- The Chemical Constituents of Cells1Document14 pagesThe Chemical Constituents of Cells1ArnelBautistaNo ratings yet
- Elements, Macromolecules & Organic Compounds in Living ThingsDocument13 pagesElements, Macromolecules & Organic Compounds in Living ThingsmagiclcjNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Lecture NotesDocument237 pagesBiochemistry Lecture NotesKenneth DizonNo ratings yet
- G07-2019 Carbohydrates IDocument12 pagesG07-2019 Carbohydrates INirajNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 IiDocument26 pagesChap 1 IiChong HyenNo ratings yet
- CHO For PKK 5203Document51 pagesCHO For PKK 5203serang87No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Chemistry: Ionization, DissociationDocument4 pagesChapter 2 - Chemistry: Ionization, Dissociationtomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayNo ratings yet
- Intro to Carbohydrates: Monosaccharides, Cyclization, and IsomerismDocument36 pagesIntro to Carbohydrates: Monosaccharides, Cyclization, and IsomerismMelinda Pham100% (1)
- Macromolecules: Self-Preparation Biology Assessment TestDocument36 pagesMacromolecules: Self-Preparation Biology Assessment Testmay ann dimaanoNo ratings yet
- Notes CarbohydratesDocument21 pagesNotes CarbohydratesChris_Barber09100% (1)
- Elements Found in Living Things2Document6 pagesElements Found in Living Things2Maevrick HaleyNo ratings yet
- Particle Properties and Bonding TypesDocument61 pagesParticle Properties and Bonding Typesalathena alathenaNo ratings yet
- Structures and Functions of Biomolecules PDFDocument23 pagesStructures and Functions of Biomolecules PDFMark Bryan TolentinoNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 - Overview of Organic Chemistry (20200810)Document22 pagesMODULE 1 - Overview of Organic Chemistry (20200810)Mark SeverinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 The Molecules of CellsDocument5 pagesChapter 3 The Molecules of Cellsmzunl25476No ratings yet
- Biomolecules: Proteins, Nucleic Acids, Carbs & LipidsDocument9 pagesBiomolecules: Proteins, Nucleic Acids, Carbs & LipidsYash Singh 11th BNo ratings yet
- BIOMACROMOLECULESDocument25 pagesBIOMACROMOLECULESAina Mira PalouNo ratings yet
- Sbi4u1 - BiochemistryDocument60 pagesSbi4u1 - BiochemistryRory Collins-GreenNo ratings yet
- Tabaco National High School Students Learn About BiomoleculesDocument9 pagesTabaco National High School Students Learn About BiomoleculesElla Mae Red BarbadilloNo ratings yet
- Monosaccharide Disaccharide PolysaccharideDocument3 pagesMonosaccharide Disaccharide PolysaccharideRhissan Bongalosa AcebucheNo ratings yet
- Natural Phenomena Often Require An ExplanationDocument7 pagesNatural Phenomena Often Require An Explanationpmm23d177No ratings yet
- Notes LipidsDocument15 pagesNotes LipidsletapvihsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: The Building Blocks of LifeDocument64 pagesChapter 2: The Building Blocks of LifeFeven SiumNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology Water Carbs LipidsDocument33 pagesMolecular Biology Water Carbs LipidsШунаси ХалиловNo ratings yet
- Mcromolecules HandoutsDocument5 pagesMcromolecules HandoutsJ-heart Basabas MalpalNo ratings yet
- Chemsitry of CarbohydratesDocument120 pagesChemsitry of CarbohydratesShafaqat Ghani Shafaqat GhaniNo ratings yet
- Chem Lec Homework 020714Document18 pagesChem Lec Homework 020714Almarie PasaoaNo ratings yet
- Biology 12 Biological Molecules Review KEYDocument5 pagesBiology 12 Biological Molecules Review KEYFeras TarawnehNo ratings yet
- 5 Natural PolymersDocument10 pages5 Natural PolymersakeemNo ratings yet
- BCH 201 Lecture Notes by DR ApiamuDocument17 pagesBCH 201 Lecture Notes by DR Apiamuprudylove03No ratings yet
- Schaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionFrom EverandSchaum's Easy Outline of Organic Chemistry, Second EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- HC Measurements Calculations Quiz TopicsDocument1 pageHC Measurements Calculations Quiz Topicsapi-299996815No ratings yet
- RC Measurements Calculations Quiz TopicsDocument1 pageRC Measurements Calculations Quiz Topicsapi-299996815No ratings yet
- Le Must Know Facts1Document12 pagesLe Must Know Facts1api-299996815No ratings yet
- Reproduction Worksheet Review SheetDocument6 pagesReproduction Worksheet Review Sheetapi-299996815No ratings yet
- Organic Review Study GuideDocument11 pagesOrganic Review Study Guideapi-299996815No ratings yet
- 200 Ways To Pass The Chemistry Physical Setting Regents ExamDocument12 pages200 Ways To Pass The Chemistry Physical Setting Regents ExamCharliegirl108No ratings yet
- Measurements in Chemistry KeyDocument6 pagesMeasurements in Chemistry Keyapi-299996815No ratings yet
- LebootcampDocument21 pagesLebootcampapi-265621022No ratings yet
- Organic Practice Test KeyDocument5 pagesOrganic Practice Test Keyapi-299996815No ratings yet
- Reproduction Worksheet KeyDocument6 pagesReproduction Worksheet Keyapi-299996815No ratings yet
- How Does The Embryo Develop After ImplantationDocument31 pagesHow Does The Embryo Develop After Implantationapi-299996815No ratings yet
- Organic Practice TestDocument5 pagesOrganic Practice Testapi-299996815No ratings yet
- Dihybrid Cross Questions KeyDocument4 pagesDihybrid Cross Questions Keyapi-299996815No ratings yet
- Chemistry Reference Table TipsDocument16 pagesChemistry Reference Table Tipsapi-299996815No ratings yet
- Human Reproduction Crossword Puzzle 1Document2 pagesHuman Reproduction Crossword Puzzle 1api-299996815No ratings yet
- Male Reproductive System Functions KeyDocument1 pageMale Reproductive System Functions Keyapi-299996815No ratings yet
- Development and Menstrual CycleDocument10 pagesDevelopment and Menstrual Cycleapi-299996815No ratings yet
- Human Reproduction Crossword KeyDocument2 pagesHuman Reproduction Crossword Keyapi-299996815No ratings yet
- Internal Vs External DevelopmentDocument13 pagesInternal Vs External Developmentapi-299996815No ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System KeyDocument1 pageFemale Reproductive System Keyapi-299996815No ratings yet
- Male Reproductive System Diagram KeyDocument1 pageMale Reproductive System Diagram Keyapi-299996815No ratings yet
- Asexual Reproduction PPT 1Document15 pagesAsexual Reproduction PPT 1api-299996815No ratings yet
- Female Reproductive System Functions KeyDocument1 pageFemale Reproductive System Functions Keyapi-299996815No ratings yet
- Station 3 KeyDocument3 pagesStation 3 Keyapi-299996815No ratings yet
- Cells Review KeyDocument6 pagesCells Review Keyapi-299996815No ratings yet
- Balancing Chemical Equations WorksheetDocument3 pagesBalancing Chemical Equations Worksheetapi-299996815No ratings yet
- Balancing Equations Worksheet KeyDocument2 pagesBalancing Equations Worksheet Keyapi-299996815No ratings yet
- Station 1 KeyDocument2 pagesStation 1 Keyapi-299996815No ratings yet
- Station 2 KeyDocument2 pagesStation 2 Keyapi-299996815No ratings yet
- Chemistry Xam IdeaDocument9 pagesChemistry Xam Ideagowrimanohar1975No ratings yet
- C.F.A.S. Hba1C: Value Sheet Ver.1 Cobas Integra 800 AnalyzerDocument8 pagesC.F.A.S. Hba1C: Value Sheet Ver.1 Cobas Integra 800 AnalyzertechlabNo ratings yet
- Feasibility Report On Cassava Processing in NigeriaDocument18 pagesFeasibility Report On Cassava Processing in NigeriaOgbesetuyi seun AugustineNo ratings yet
- FDA 2020 N 1359 0004 - Attachment - 1Document6 pagesFDA 2020 N 1359 0004 - Attachment - 1zellgatoNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - GenBio1 BIOMOLECULES 1st Term SY 2021-2022Document7 pagesWeek 2 - GenBio1 BIOMOLECULES 1st Term SY 2021-2022JAN PAULINE BABINANo ratings yet
- Gcse Marking Scheme: Science - Biology JANUARY 2011Document16 pagesGcse Marking Scheme: Science - Biology JANUARY 2011sureshthevanNo ratings yet
- 9C End of Unit Test: Name - ClassDocument4 pages9C End of Unit Test: Name - ClassLeena ElNo ratings yet
- Effects of Energy Gel Ingestion On Blood Glucose, Lactate, and Performance Measures During Prolonged CyclingDocument9 pagesEffects of Energy Gel Ingestion On Blood Glucose, Lactate, and Performance Measures During Prolonged Cyclingjose david HerreraNo ratings yet
- BIOMOLECULESDocument2 pagesBIOMOLECULESKeith Chastine MiraballesNo ratings yet
- CarbohydratesDocument50 pagesCarbohydratesEukeen Bancale100% (1)
- Biochemical ConversionDocument38 pagesBiochemical ConversionAlex GechNo ratings yet
- As-Level Biology Notes: By: Bianca HimawanDocument64 pagesAs-Level Biology Notes: By: Bianca HimawanAdham EtmanNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: Combined Science 5129/22 October/November 2021Document14 pagesCambridge O Level: Combined Science 5129/22 October/November 2021For GamingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Notes AP BiologyDocument11 pagesChapter 5 Notes AP BiologyAndrew AltenNo ratings yet
- IJSO 2008 Theory Part 1Document9 pagesIJSO 2008 Theory Part 1Karttikeya Mangalam NemaniNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Physical and Chemical PropertiesDocument44 pagesCarbohydrates Physical and Chemical Propertiesrizal_31No ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration QuizDocument6 pagesCellular Respiration QuizParisa YahyaieNo ratings yet
- Diabetes - Comparison Oftype 1 and Type 2Document1 pageDiabetes - Comparison Oftype 1 and Type 2dervaleeNo ratings yet
- 1-5 Kareem ZainabDocument68 pages1-5 Kareem ZainabBobby SeroNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Assignment GLUCAGONE by IQRA ARIFDocument10 pagesBiochemistry Assignment GLUCAGONE by IQRA ARIFIqra BaigNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Optimization of FermentativDocument13 pagesModeling and Optimization of FermentativThayna Rhomana da Silva CandidoNo ratings yet
- Ameliorative Effects of Syzygium JambolanumDocument9 pagesAmeliorative Effects of Syzygium JambolanumRegiane Godoy de LimaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level Biology Revision GuideDocument201 pagesCambridge O Level Biology Revision GuideAayan S. Abbasi50% (2)
- Biology Lab ReportDocument5 pagesBiology Lab Reportapi-2576094460% (1)
- Biochemistry Quiz OneDocument5 pagesBiochemistry Quiz Onesehrish_salamNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Insulin and It'S AnaloguesDocument31 pagesPharmacology of Insulin and It'S AnaloguesVikas VikiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument114 pagesIntroduction To Organic ChemistryJudy Panguito Aralar100% (1)
- Panacea of SSC General Science English MediumDocument98 pagesPanacea of SSC General Science English MediumSuryakumar BendalamNo ratings yet
- Microbial Alkaline Proteases: Optimization of Production Parameters and Their PropertiesDocument12 pagesMicrobial Alkaline Proteases: Optimization of Production Parameters and Their PropertiesArieNo ratings yet
- MCQsDocument32 pagesMCQsamNo ratings yet