Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Concept of Service Marketing
Uploaded by
rajendrakumar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
35 views2 pagesOriginal Title
CONCEPT OF SERVICE MARKETING.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
35 views2 pagesConcept of Service Marketing
Uploaded by
rajendrakumarCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
1.
CONCEPT OF SERVICE MARKETING
Service marketing is the marketing of processes, deeds and performances, i.e. anything
which is essentially intangible in nature. Service marketing addresses the concerns and
needs of any business in which service is an integral part of offering. Service marketing is
not a self-enclosed task but is integral to service organizations as a whole and the object of
the activity is people, who are reactive, not passive as compared to products.
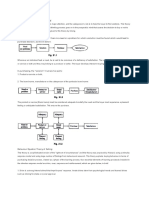
Service: A service is a set of one time consumable and perishable benefits:
Delivered from accountable service provider, mostly in close coactions with his internal
and external service suppliers.
Effectuated by distinct functions of technical systems and by distinct activities of
individuals, respectively.
Commissioned according to the needs of his service consumers by the service customer
from accountable service provider.
Rendered individually to an authorized service consumer at his/her dedicated trigger.
Consumed and utilized by the triggering service consumer for executing his/her
upcoming business activity or private activity.
According to Philip Kotler, service is any act or performance that one party can offer to
another that is essentially intangible and does not result in the ownership of anything.
Stanton proposed a definition in 1974 and defined service as Separately identifiable,
intangible activities which provide want satisfaction when marketed to consumers and/or
industrial users and which are not necessarily tied to the sale of a product or another
service.
The classic four Ps (product, price, place, and promotion) marketing approach works well for
physical goods, but service companies need to pay attention to additional elements.
Marketing gurus Boon and Bitner identify 3 additional Ps for service marketing:
People: People refer to anyone directly or indirectly involved in the production of a service.
People are those who come into contact with customers and have a profound effect- positive
or negative- on customer satisfaction. The reputation of companys brand rests in its
peoples hand. Customers make judgments about service provision and delivery based on
the people representing organisation. They must, therefore, be appropriately trained, well
motivated and have the right attitude. This is because people are one of the few elements of
the service that customers can see and interact with.
For example, employees in McDonalds have a standard uniform and McDonalds specially
focuses on friendly and prompt services to its customers from their employees.
Physical Evidence: Physical evidence is about where the service is being delivered from.
Physical evidence refers to the environment in which the service is assembled and in which
the seller and customer interact, combined with tangible commodities that facilitate
performance or communication of the service. Physical evidence serves as a visual
metaphor of what the company stands for, and facilitates the activities of customers and
employees. For example, many hair salons invest in comfortable and stylish sitting areas
with magazines and plush sofas for patrons to read and relax while they wait.
Process: Process is the delivery and operating systems of procedures, mechanisms and
flow of activities which services are consumed. Because services are performances or
actions done for or with the customers, they typically involve a sequence of steps and
activities. The combination of these steps constitutes a service process which is evaluated
by the customers.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Unit 2 External Environmental Analysis & Forecasting: Components of Remote EnvironmentDocument4 pagesUnit 2 External Environmental Analysis & Forecasting: Components of Remote EnvironmentrajendrakumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Strategic Management: MeaningDocument4 pagesUnit 1 Strategic Management: MeaningrajendrakumarNo ratings yet
- Meaning of EdDocument1 pageMeaning of EdrajendrakumarNo ratings yet
- What Is Strategy?: Foresight VisionDocument1 pageWhat Is Strategy?: Foresight VisionrajendrakumarNo ratings yet
- BBA 8 Sem Business Strategy Tribhuvan UniversityDocument1 pageBBA 8 Sem Business Strategy Tribhuvan Universityrajendrakumar100% (2)
- Strategic Thinking: T 8 Hours. If V Is 50 MPH in Clear Conditions and 30 MPH When It Rains, Then TheDocument1 pageStrategic Thinking: T 8 Hours. If V Is 50 MPH in Clear Conditions and 30 MPH When It Rains, Then TherajendrakumarNo ratings yet
- Wto Tfa 2018 Tu Exam BeDocument1 pageWto Tfa 2018 Tu Exam BerajendrakumarNo ratings yet
- Designing Your Marketing Program: ProductDocument5 pagesDesigning Your Marketing Program: ProductrajendrakumarNo ratings yet
- Marketing Information System in NepalDocument1 pageMarketing Information System in NepalrajendrakumarNo ratings yet
- Using The Systematic - Constructive ApproachDocument1 pageUsing The Systematic - Constructive ApproachrajendrakumarNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behavior: Course ObjectivesDocument1 pageOrganizational Behavior: Course ObjectivesrajendrakumarNo ratings yet
- Production and OperationsDocument1 pageProduction and OperationsrajendrakumarNo ratings yet
- Marketing ControlDocument3 pagesMarketing ControlrajendrakumarNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Background of The Study: VolatilityDocument10 pages1.1 Background of The Study: VolatilityrajendrakumarNo ratings yet
- Subprocesses of PerceptionDocument1 pageSubprocesses of Perceptionrajendrakumar100% (1)
- New Features of Organisational BehaviourDocument2 pagesNew Features of Organisational Behaviourrajendrakumar100% (3)
- Unit 4: Personality and Attitudes LH 9Document1 pageUnit 4: Personality and Attitudes LH 9rajendrakumarNo ratings yet
- Relation Between Occupational Stress and Organizational Commitment: Evidences From Nurses of NepalDocument1 pageRelation Between Occupational Stress and Organizational Commitment: Evidences From Nurses of NepalrajendrakumarNo ratings yet
- New Features of Organisational BehaviourDocument2 pagesNew Features of Organisational Behaviourrajendrakumar100% (3)
- Types of BanksDocument3 pagesTypes of BanksrajendrakumarNo ratings yet
- Buying Formula TheoryDocument3 pagesBuying Formula TheoryrajendrakumarNo ratings yet
- The Marketing ControlDocument3 pagesThe Marketing ControlrajendrakumarNo ratings yet
- Marketing SpecializationDocument10 pagesMarketing SpecializationrajendrakumarNo ratings yet
- Industrial Management ModelDocument2 pagesIndustrial Management Modelrajendrakumar100% (1)
- Nature and CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesNature and CharacteristicsrajendrakumarNo ratings yet
- Models in Service MarketingDocument4 pagesModels in Service Marketingrajendrakumar33% (3)