Professional Documents
Culture Documents
V+X DV DX X VX) X (VX) : Marking Scheme Math T p2
Uploaded by
Amier AbdullahOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
V+X DV DX X VX) X (VX) : Marking Scheme Math T p2
Uploaded by
Amier AbdullahCopyright:
Available Formats
Marking scheme math T p2
2
2
dv x +( vx)
v+x =
dx
x (vx) .
dv 1+ v 2
=
v
dx
v
1
dv 1
x = .
dx v
1
1
v . dv= x . dx
v2
=ln x+ c .
2
(0)
=ln 2+c .
2
1
c=ln 2
.
1
y
( )
x
=ln x+ ln2
2
2
2 x =e
2
y
2
2x
t
2
sin 2 2 sin cos
1. (a) If tan
2t 1 t 2
sin 2 2
1 t 2 1 t 2
4t (1 t 2 )
sin 2
(shown)
1 2t 2 t 4
Trigo
1
1
Marking scheme math T p2
(b) If tan
1 sin 2 cos cos 2 sin 4 sin cos (sin cos )
,
sin cos
2 4
sin cos
4
2(2 sin cos )
2 sin 2
2(
4t (1 t 2 )
)
1 2t 2 t 4
2
1
1
4 (1 )
4
4
2(
)
2
4
1
1
1 2
4
4
15
16
2(
)
32
1
1
256 256
15 256
2(
)
16 289
240
2(
)
289
480
289
1
1
t
4
1 t 2 1
cos
2 1 t 2 3
1 t 2 1
1 t 2 3
3 3t 2 1 t 2
(c) Let tan
4t 2 2
1
t2
2
t
tan
4
2
1
2
Marking scheme math T p2
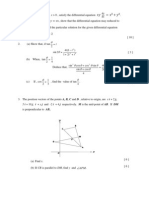
AB OB OA 5i 10 j - ( xi 2 j) (5 x)i 8 j
OM
(5 x) (10 2)
(5 x)
i
j
i 6j
2
2
2
Since M is the mid-point of AB,
(5 x)
(9 x)
DM OM OD
i 6 j (2i 4 j)
i 2j
2
2
1
1
DM AB 0
Since AB is perpendicular to DM,
(9 x )
i 2 j (5 x)i 8 j 0
2
(9 x )
(5 x ) 16 0
2
x 2 4 x 77 0
( x 11)( x 7) 0
1
1
x7
(b) CB OB OC 5i 10 j (i yj) 4i (10 y ) j
Since CB is parallel to DM,
CB DM
4i (10 y ) j (8i 2 j)
Equating the coefficient of i ,
8 4
1
2
1
Marking scheme math T p2
Equating the coefficient of j ,
1
2( ) 10 y
2
2 10 y
y 9
1
OC i 9 j
CA OA OC 7i 2 j (i 9 j) 6i 7 j
since DM 8i 2 j
cos APM
DM CA
DM CA
8i 2 j 6i 7 j
8 2 2 2 6 2 (7) 2
48 14
68 85
cos APM 0.447
APM 63.4
1
(a) PQR is a straight and BP parallel to CR.
Marking scheme math T p2
CRQ APQ (alternate angles)
QCR QAP (alternate angles)
AQ QC (given)
APQ and CRQ are congruen t.( AAS )
1
1
i.e. PQ QR and AP RC
But AP PB (given)
RC PB
BCRP is a parallelog ram
Hence, BC PQ QR 2 PQ (proved)
1
1
(b)
From (a) BC 2 PQ
1
Using the same method as (a)
we have BC 2 MN
2 PQ 2 MN
PQ MN (proved)
Marking scheme math T p2
(a) since KL//AD , ABK BAD x(alternate angles )
since ABCE is a cyclic quadrilate ral, BAD DCE x (cyclic quad. theorem)
ABK ACB x (alternate segment th eorem)
ACB DCE (proved)
1
1
1
(b) HBC BAC y (alternate segment th eorem)
since AB//CH , BAC HCL y (alternate angles )
BCL and CHL are similar.
1
1
LB BC LC
LC CH LH
LB LC
LC LH
LC 2 LH LB
1
1
1
a)
X = number of misprints per page
X P0 (3)
P (X = 0) =
e3 30
0!
= 0.05
b)
Y = number of pages without misprint
n = 200 , p = 0.05 = np = 10
P ( Y 3 ) = 1 P (Y < 3)
=1[P(Y= 0)+ P(Y=1)+ P(Y= 2)]
0
101 102
10 10
e
+
+
=1
0! 1! 2!
N (100 , 25) and Y
1
1
1
= 0.9972
N (80 , 20)
Marking scheme math T p2
a)
( 2X Y )
N (120 , 120)
P (2X Y > 110) = P
( z < 110120
120 )
1
1
1
= 0.81935
b)
(X+Y)
N (180 , 45)
P (X + Y < a) = 0.2085
a180
z<
P(
= 0.2085
45
a180
45
= 0.812
1
1
1
1
a = 174.55
8
(a) Let A = Nasir takes tuition
B = Nasir passes mathematics paper
B{A
P ( B ) =P
1+1
1
= ( 0.8 ) ( 0.4 ) + ( 0.3 ) (0.6)
= 0.62
P( A B' )
P ( A )=
P(B ' )
(b)
=
9
a)
1+ 1
( 0.4 ) (0.2)
( 0.4 ) ( 0.2 )+ ( 0.6 ) (0.7)
4
25
0.16
p + q + 2p + 2q + 2p = 1
5p + 3q = 1
15 p
q=
3
[
1
1
Marking scheme math T p2
b)
E (X) = 2p q + 0 +2q + 4p
= 2p + q
15 p
= 2p +
3
=
c)
p+1
3
E (Y) = E ( X1 + X2 + X3 )
= 3 E (X)
p+1
3
=
3
( )
=p+1
d)
1
1
1
1
1
P (X1 + X2 = 3) = P (X1 = 1).P(X2 = 2) + P (X1 = 2).P(X2 = 1)
= (2q) (2p) + (2p) (2q)
= 8pq
1 1
8
=
10 6
( )( )
=
10
a)
2
15
1
( 10 k k 2 )= 1 ( 20+k 2 4 k )
20
20
k2 7k + 10 = 0
(k2)(k5)=0
k=2,5
Therefore k = 2
b)
P(2<X<3)
= F (3) F (2)
1
1
2
2
20+3 4 (3) ] [ 10 ( 2 )2 ]
= 20 [
20
=
1
20
1
1
1
1
Marking scheme math T p2
c)
f(x)=
d)
11
100
200
125
200
E (X) =
1
(5x ) 0 x< 2
10
1
(x2) 2 x <4
10
0
otherwise
5 xx 2
4
1
()dx+ ( x 22 x )dx
10 2
2
10 0
3 2
1 5x x
10 2
3
7
5
] [
1 x
2
+
x
0 10 3
100
or ( 125 )
1
4
5
(b)
100
[ 200
75
200
160
200
or
125
200
] qualified for 1 mark
2
75
or ( 160 )
15
32
75
[ 200
or
160
200
] qualified for 1 mark
12
Months
Mid point
Frequency
Cumulative
fx
Marking scheme math T p2
m<10
9
x
9.5
f
16
frequency
16
152
10 m<11
10.5
44
60
462
11 m<12
11.5
66
126
759
12 m<13
12.5
50
176
625
13 m<14
13.5
18
194
243
14 m<15
14.5
198
58
15 m<16
15.5
200
31
2330
200
Mean =
= 11.65
Median =
11+
1
10060
(1)
66
= 11.61
Mode = 11 +
22
(1)
22+16
1
1
= 11.58
(b) since : mean > median > mode , the distribution is skewed.
(c) Let A = Nasir takes tuition
B = Nasir passes mathematics paper
B{A
P ( B ) =P
1+1
1+1
1
= ( 0.8 ) ( 0.4 ) + ( 0.3 ) (0.6)
(d)
= 0.62
'
P( A B )
P ( A )=
P(B ' )
1+ 1
Marking scheme math T p2
( 0.4 ) (0.2)
( 0.4 ) ( 0.2 )+ ( 0.6 ) (0.7)
4
25
0.16
You might also like
- Mathematics T 2 - SchemeDocument9 pagesMathematics T 2 - SchemeSyafiq JamilNo ratings yet
- IIT-JEE Mathematics Objective Questions with Solutions (Chapter 23 - Straight LinesDocument10 pagesIIT-JEE Mathematics Objective Questions with Solutions (Chapter 23 - Straight LinesPremNo ratings yet
- K J I K J I OQ OPDocument4 pagesK J I K J I OQ OPapi-108235015No ratings yet
- 2013 SMCHMath T1 TrialDocument7 pages2013 SMCHMath T1 TrialchimbiNo ratings yet
- Trajectory Education: Jam-2016 Maths-SolutionsDocument25 pagesTrajectory Education: Jam-2016 Maths-SolutionsBhimesh JettiNo ratings yet
- This File Contains Match The Columns (Collection # 2) : Very Important Guessing QuestionsDocument9 pagesThis File Contains Match The Columns (Collection # 2) : Very Important Guessing QuestionsHNGHNo ratings yet
- Probability Concepts: 1.1 The Given Sets AreDocument21 pagesProbability Concepts: 1.1 The Given Sets AreSudipta GhoshNo ratings yet
- Signal Detection and Estimation - Solution ManualDocument169 pagesSignal Detection and Estimation - Solution ManualSolidstate Raman64% (14)
- Aieee Paper 2008Document30 pagesAieee Paper 2008Ravi LorventNo ratings yet
- Solving Quadratic Equations and Graphing FunctionsDocument9 pagesSolving Quadratic Equations and Graphing FunctionsNatalie Yeung100% (1)
- Narayana Grand Test - 8Document12 pagesNarayana Grand Test - 8Meet ShahNo ratings yet
- LogarithmsDocument9 pagesLogarithmsthinkiitNo ratings yet
- Target Iit-Jee: All India Test SeriesDocument12 pagesTarget Iit-Jee: All India Test SeriesasuhassNo ratings yet
- Answer Key: Paper-2Document18 pagesAnswer Key: Paper-2vishal110085No ratings yet
- RT Solutions-22!01!2012 XIII VXY Paper II Code A SolDocument16 pagesRT Solutions-22!01!2012 XIII VXY Paper II Code A Solvishal110085No ratings yet
- 07-09-201412th Solution P-1Document8 pages07-09-201412th Solution P-1asuhassNo ratings yet
- Final Test Xiii (Xyz) Solutions Paper-1Document22 pagesFinal Test Xiii (Xyz) Solutions Paper-1Shreyans JainNo ratings yet
- AIEEE Mock Solved: Sol. (A) Sol. (B)Document7 pagesAIEEE Mock Solved: Sol. (A) Sol. (B)kishangopi123No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 of 11 (Chap 5, Matrices)Document37 pagesLecture 2 of 11 (Chap 5, Matrices)ABC_Ais Batu CampurNo ratings yet
- IIT JEE Maths SolutionsDocument7 pagesIIT JEE Maths SolutionsVishal GaudNo ratings yet
- Vectors Addition and SubtractionDocument14 pagesVectors Addition and SubtractionSe Khor LahNo ratings yet
- IIT-JEE Mathematics Ellipse SolutionsDocument10 pagesIIT-JEE Mathematics Ellipse SolutionsPremNo ratings yet
- Ath em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm ADocument12 pagesAth em Ati CS: L.K .SH Arm APremNo ratings yet
- 04 03 2012 XIII VXY Paper I Final Test Code A SolDocument19 pages04 03 2012 XIII VXY Paper I Final Test Code A Solvishal110085No ratings yet
- KVPY 2013 Stream SB SX Solved PaperDocument39 pagesKVPY 2013 Stream SB SX Solved PaperSoumya DansanaNo ratings yet
- Model Soalan Matematik PMRDocument13 pagesModel Soalan Matematik PMRchai65No ratings yet
- Solutions to 2014 SH2 H2 Mathematics Preliminary ExaminationDocument13 pagesSolutions to 2014 SH2 H2 Mathematics Preliminary Examinationcherylhzy0% (4)
- Answer Key: 13 VXY (Date: 04-09-2011) Review Test-2 Paper-2Document16 pagesAnswer Key: 13 VXY (Date: 04-09-2011) Review Test-2 Paper-2vishal110085No ratings yet
- Modul 7 PDF July 13 2009 9 39 PM 129kDocument15 pagesModul 7 PDF July 13 2009 9 39 PM 129kSin YeeNo ratings yet
- RT Solutions-17!07!2011 XII ABCD Paper II Code BDocument15 pagesRT Solutions-17!07!2011 XII ABCD Paper II Code Bvishal110085No ratings yet
- Answer Key: Paper-1Document16 pagesAnswer Key: Paper-1vishal110085No ratings yet
- Uts Rivan 54545Document26 pagesUts Rivan 54545multimediaNo ratings yet
- Vectors Introduction To The Basic Concepts of Vectors (Week 1)Document19 pagesVectors Introduction To The Basic Concepts of Vectors (Week 1)Anandraj GovindarajNo ratings yet
- GATE Electrical by Kanodia PDFDocument422 pagesGATE Electrical by Kanodia PDFsreekantha2013100% (4)
- 04 09 2011 Xiii Vxy Paper II Code AooooooooooooooooooooooooooDocument16 pages04 09 2011 Xiii Vxy Paper II Code Aoooooooooooooooooooooooooovishal110085No ratings yet
- MODULE 7-The Straight LinesDocument15 pagesMODULE 7-The Straight Lineskkwei93No ratings yet
- CALCULATING DIRECTED NUMBERS, FRACTIONS AND OTHER ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONSDocument31 pagesCALCULATING DIRECTED NUMBERS, FRACTIONS AND OTHER ALGEBRAIC EXPRESSIONSAmu KevinNo ratings yet
- GATE Electrical - R K KanodiaDocument422 pagesGATE Electrical - R K KanodiaNavajyoth Kumar90% (10)
- Skema p2Document12 pagesSkema p2fnbaNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument35 pagesTrigonometryShantanu AryaNo ratings yet
- DPP (37-38) 11th J-Batch MathsDocument5 pagesDPP (37-38) 11th J-Batch MathsRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Skema Jawapan Kertas 1 2016 Set 8 Sub Marks Full Marks 1 (A) 8 6 4 2Document6 pagesSkema Jawapan Kertas 1 2016 Set 8 Sub Marks Full Marks 1 (A) 8 6 4 2Anonymous x0kzb3UNo ratings yet
- Math Stats Booklet 1Document20 pagesMath Stats Booklet 1Koh Boon HaoNo ratings yet
- IZHO2018Document9 pagesIZHO2018đoàn đăngNo ratings yet
- Set 3 MawarDocument36 pagesSet 3 MawarAmu KevinNo ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Ten-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesFrom EverandTen-Decimal Tables of the Logarithms of Complex Numbers and for the Transformation from Cartesian to Polar Coordinates: Volume 33 in Mathematical Tables SeriesNo ratings yet
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Test Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsFrom EverandTest Bank for Precalculus: Functions & GraphsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Solving Differential Equations and Finding Probabilities of Random VariablesDocument8 pagesSolving Differential Equations and Finding Probabilities of Random VariablesSyafiq JamilNo ratings yet
- Solving Differential Equations and Finding Probabilities of Random VariablesDocument8 pagesSolving Differential Equations and Finding Probabilities of Random VariablesSyafiq JamilNo ratings yet
- RPH WK 1Document4 pagesRPH WK 1Amier AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan EnglishDocument7 pagesLesson Plan Englishkarishma10No ratings yet
- RPH Bahasa Inggeris Tahun 2 KSSRDocument10 pagesRPH Bahasa Inggeris Tahun 2 KSSRsyazalina8383% (6)
- English - Daily Lesson Plan Year 2Document7 pagesEnglish - Daily Lesson Plan Year 2Paklong Cikgu67% (9)
- A New High Drive Class-AB FVF Based Second Generation Voltage ConveyorDocument5 pagesA New High Drive Class-AB FVF Based Second Generation Voltage ConveyorShwetaGautamNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing and Service TechnologiesDocument18 pagesManufacturing and Service Technologiesajit123ajitNo ratings yet
- Keltbray Crude Oil and Gas LTDDocument2 pagesKeltbray Crude Oil and Gas LTDIana LeynoNo ratings yet
- DowerDocument7 pagesDowerabrash111No ratings yet
- House Bill 470Document9 pagesHouse Bill 470Steven DoyleNo ratings yet
- Long-Range FM Transmitter With Variable Power OutputDocument2 pagesLong-Range FM Transmitter With Variable Power OutputHaspreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Case Digests Injunctive Reliefs People Vs Grey (GR No. 180109 July 26, 2010) FactsDocument18 pagesCase Digests Injunctive Reliefs People Vs Grey (GR No. 180109 July 26, 2010) FactsjbjacildoNo ratings yet
- Vim 101 - A Beginner's Guide To VimDocument5 pagesVim 101 - A Beginner's Guide To VimHuy TranNo ratings yet
- ERACS JournalDocument8 pagesERACS Journalmahasiswaprofesi2019No ratings yet
- Valuing Common and Preferred SharesDocument31 pagesValuing Common and Preferred SharesAdam Mo AliNo ratings yet
- Intra Cell HODocument10 pagesIntra Cell HOMostafa Mohammed EladawyNo ratings yet
- Volkswagen Group - Wikipedia PDFDocument115 pagesVolkswagen Group - Wikipedia PDFFayad A ANo ratings yet
- SPIE/COS Photonics Asia Abstract Submission Guidelines: Important DatesDocument1 pageSPIE/COS Photonics Asia Abstract Submission Guidelines: Important Dates李健民No ratings yet
- Export Promoting InstitutesDocument21 pagesExport Promoting InstitutesVikaskundu28100% (1)
- FSK Demodulator With PLLDocument5 pagesFSK Demodulator With PLLHema100% (1)
- Financial Management Toolkit For Recipients of Eu Funds For External ActionsDocument12 pagesFinancial Management Toolkit For Recipients of Eu Funds For External ActionsGeorge BekatorosNo ratings yet
- Lecture No 5Document41 pagesLecture No 5sami ul haqNo ratings yet
- ELEC 121 - Philippine Popular CultureDocument10 pagesELEC 121 - Philippine Popular CultureMARITONI MEDALLANo ratings yet
- Breadtalk AR 2011Document158 pagesBreadtalk AR 2011Wong ZieNo ratings yet
- Self Improvement Books To ReadDocument13 pagesSelf Improvement Books To ReadAnonymous oTtlhP67% (3)
- Presentacion ISA Graphic Febrero 2015Document28 pagesPresentacion ISA Graphic Febrero 2015Ileana ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Cement Lined Piping SpecificationDocument167 pagesCement Lined Piping SpecificationvenkateshwaranNo ratings yet
- Philippine Constitutional Commissions Powers and FunctionsDocument36 pagesPhilippine Constitutional Commissions Powers and Functionssharlica1990No ratings yet
- Delhi Metro Rail Corporation LTD Jr. Engineer Results PDFDocument3 pagesDelhi Metro Rail Corporation LTD Jr. Engineer Results PDFedujobnewsNo ratings yet
- Introducing Global PoliticsDocument8 pagesIntroducing Global PoliticsMeann Joy BaclayonNo ratings yet
- Strict Liability - ProjectDocument7 pagesStrict Liability - ProjectRushabh Lalan100% (1)
- IP Dect AP 8340 R150 DatasheetDocument3 pagesIP Dect AP 8340 R150 DatasheetAsnake TegenawNo ratings yet
- List of Family Outing EpisodesDocument7 pagesList of Family Outing EpisodesFanny KesumaliaNo ratings yet
- MAINTENANCE AND RELIABILITY ENGINEERING - Lecture 1Document24 pagesMAINTENANCE AND RELIABILITY ENGINEERING - Lecture 1K ULAGANATHANNo ratings yet
- 26 27 16 Electrical Cabinets and EnclosuresDocument3 pages26 27 16 Electrical Cabinets and EnclosureskaichosanNo ratings yet





















































![Mathematical Tables: Tables of in G [z] for Complex Argument](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/word_document/282615796/149x198/febb728e8d/1699542561?v=1)