Professional Documents
Culture Documents
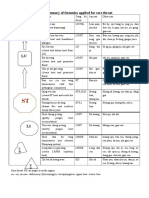
F07-07-Factors Affecting Pulse Volume
Uploaded by
JiayiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
F07-07-Factors Affecting Pulse Volume
Uploaded by
JiayiCopyright:
Available Formats
Yang activity
fever, infection
Body temperature
Metabolic activity
Pregnancy: normal
RBC and plasma
volume
Metabolic activity
Peripheral
vasodilation
Heart rate
Venous return
Stroke volume
Obstruction of urination
Inhibition of sweating
Excessive fluid intake
Kidney
Yang
vacuity
Spleen
dysfunction
Impaired
transformation
and transportation
of fluids
Agitation of Qi and
Blood, causing them
to overfill vessels
Fluid retention
If extracellular fluid
more than 3050%
above normal, fluid
goes into internal
spaces (tissue)
Extracellular fluid
volume
Excess fluid moves
into blood vessels
Blood volume
Cardiac output
Pulse
volume
Compresses
blood vessels
Pulse
volume
Complicated
by damp
Insufficient
blood
production
Cardiac output
Arterial pressure
Sympathetic stimulation of the circulation,
contraction of blood vessels to help
increase blood pressure
Acute
Trauma
GIT bleeding, e.g.
rupture of ulcer
Chronic
GIT inflammatory disease
Heavy periods
Abnormal uterine bleeding
Nosebleeds
Haemoptysis
Blood loss
Circulatory shock due to
Valve problems
Arrhythmias
Myocardial infarction
Fluid loss such as:
Profuse sweating
Vomiting
Diarrhoea
Excessive urination
Renal damage
Inadequate fluid intake
Plasma loss due to
Intestinal blockage
Severe burns
F07-07-F10248
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Ambassador 36 Classic SalesDocument2 pagesAmbassador 36 Classic SalesJiayiNo ratings yet
- Ambassador 41 2013 Classic 1Document2 pagesAmbassador 41 2013 Classic 1JiayiNo ratings yet
- Sydney DomainDocument12 pagesSydney DomainJiayiNo ratings yet
- Radha Thambi Rajah 2018Document2 pagesRadha Thambi Rajah 2018JiayiNo ratings yet
- 2017 Autumn 99657 v2 Standard City 20-1-17Document9 pages2017 Autumn 99657 v2 Standard City 20-1-17JiayiNo ratings yet
- AHPRA Registration Standard English Language Skills 1 July 2015Document6 pagesAHPRA Registration Standard English Language Skills 1 July 2015JiayiNo ratings yet
- Travel Insurance Direct - Quote - JapanDocument10 pagesTravel Insurance Direct - Quote - JapanJiayiNo ratings yet
- Natural Patterns of Sleep - Healthy SleepDocument3 pagesNatural Patterns of Sleep - Healthy SleepJiayiNo ratings yet
- 9aca PDFDocument11 pages9aca PDFJiayiNo ratings yet
- Exploring Chinese History: History: Ancient Chinese History: ComprehensiveDocument10 pagesExploring Chinese History: History: Ancient Chinese History: ComprehensiveJiayiNo ratings yet
- Wen Bing2 PDFDocument9 pagesWen Bing2 PDFJiayiNo ratings yet
- Divergent Meridians: Indications and Pathways According to Ling Shu and Su WenDocument13 pagesDivergent Meridians: Indications and Pathways According to Ling Shu and Su WenNayra GomesNo ratings yet
- Sore Throat Case FormulasDocument1 pageSore Throat Case FormulasJiayiNo ratings yet
- Cocaine Use and Its EffectsDocument2 pagesCocaine Use and Its EffectsJiayiNo ratings yet
- Application Gas Service Line Meter Installation Act NSWDocument2 pagesApplication Gas Service Line Meter Installation Act NSWJiayiNo ratings yet
- Comparative Timeline PDFDocument8 pagesComparative Timeline PDFRodrigo Santibáñez Abraham100% (1)
- The Truth About Solar Panel Performance and TemperatureDocument54 pagesThe Truth About Solar Panel Performance and TemperatureJiayiNo ratings yet
- Sydney DomainDocument13 pagesSydney DomainJiayiNo ratings yet
- China High Speed Rail, Bullet Train Tickets Booking OnlineDocument3 pagesChina High Speed Rail, Bullet Train Tickets Booking OnlineJiayiNo ratings yet
- Beijing Trains Schedule and Tickets BookingDocument3 pagesBeijing Trains Schedule and Tickets BookingJiayiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 22Document40 pagesChapter 22JiayiNo ratings yet
- Beijing - Xi'an Bullet Trains, Duration, Price, and TimetableDocument5 pagesBeijing - Xi'an Bullet Trains, Duration, Price, and TimetableJiayiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document64 pagesChapter 6Jiayi100% (1)
- Beijing - Xian High-Speed Train: Schedule, Duration, Ticket, FareDocument2 pagesBeijing - Xian High-Speed Train: Schedule, Duration, Ticket, FareJiayiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20Document31 pagesChapter 20JiayiNo ratings yet
- Jin Gui Yao Lue Acupuncture PDFDocument2 pagesJin Gui Yao Lue Acupuncture PDFJiayiNo ratings yet
- China - Prepaid Data SIM Card Wiki - FANDOM Powered by WikiaDocument8 pagesChina - Prepaid Data SIM Card Wiki - FANDOM Powered by WikiaJiayiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document28 pagesChapter 7JiayiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document41 pagesChapter 5JiayiNo ratings yet
- Jin Gui Yao Lue - Essential Prescriptions of the Golden Cabinet Chapter 3Document37 pagesJin Gui Yao Lue - Essential Prescriptions of the Golden Cabinet Chapter 3JiayiNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)