Professional Documents
Culture Documents
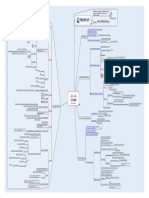
Routings - Mind Map
Uploaded by
Saptarshi GhoshCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Routings - Mind Map
Uploaded by
Saptarshi GhoshCopyright:
Available Formats
p packet
address
4maincomponentsofaroute:
DestinationValue,Mask,Gatewayor
InterfaceAddress,andRoutecostor
metric
Arouterdirectsmessageto
correctdestinationby
a Lookingformatchingrouteinrouting
table
Dest.valuesinroutingtable=
Destinationnetworkaddresses
Resultingnetworkaddresscompared
tonetworkaddressofrouteintable
p Routrpowersup,configuredinterfaces
areenabled
Matchisfound=Packetsforwarded
outcorrectinterface/appropriate
gateway
Routerlooksupsubnetmask
assignedtoeachpotentialroute
table
Applieseachsubnetmaskto
destinationIPaddressinpacket
Netwkaddrmatch>1rt.=Routruses
routew/speciforlongst,netwkaddr.
matchfromtable
Asinterfacesbeomeopertionl=Routr
a storesdirectlyattachloc.netwkaddr's
asconnectdroutsinroutngtble
DirectlyConnectedRoutes
Automat.updtdwhenintisreconfiged
orshutdwn
NoRouterentriesmatch=Routrdirects
messagetogatewayspecifbydefault
routeifconfigured
Ident.inroutingtblewithprefix'C'
Adminmanuallyconfiguresstaticroute
toaspecif.netwk
Doesn'tchangeuntilAdminmanually
reconfigsit
Def.route=typeofstaticroutspecif
gatewaytousewhenrutingtble
doesn'tcontainpathtousetoreach
destinanetwk
StaticRoutes
DynamicallyUpdatedRoutes
(DynamicRoutes)
Ident.withprefix'S'
Commonfordefaultroutestopointto
nextrouterinpathtoISP
Subnethasonlyonerouter=that
routerautomaticallybecomesdefault
gateway
Router1(config)#iproute192.168.16.0
255.255.255.0192.168.15.1
becauseallnetworktraffictoandfrom
thatlocalnetworkhasnooptionbutto
travelthroughthatrouter
ConfiguringStaticRoute
largernetworksgenerallyusedynamic
routingratherthanstaticroutes
Routingprotocols
Learnsallavailableroutes
Dynamicallymanageinformation
receivedfromowninterfacesandother
routers
Canbeconfiguredtomanagemanually
enteredroutes
Placesbestroutesintoroutingtable
Dynamicroutingprotocol
Removesrouteswhentheyareno
longervalid
Methodroutingprotocolusesto
determinebestroutetodestinnetwk=
routingalgorithm
Sends
periodiccopiesofaroutingtable
fromroutertorouter
/communicatetopologychanges
Twomainclasses:1.DistanceVector
2.LinkState
Numberofhops,Administrative
cost,Bandwidth,Transmission
speed,Likelihoodof
delays,Reliability
DistanceHowfarawayisnetwork
fromthisrouter?
Addressofthenexthopalongthepath
tothenetworknamedintheroute
VectorInwhatdirectionshouldpacket
besenttoreachthisnetwork?
Topologyofnetworkchangesdueto
reconfigurationorfailure,routing
tablesinallroutersmustchangeto
reflectaccurateviewofnewtopology
p RoutingAlgorithm
Allroutersinanetwkhaveupdated
theirtablestoreflectthenewroute
=Routersconverged
Fortworouterstoexchangeroutes,
mustbeusingsameroutingprotocol
andsameroutingalgorithm
Interfaceleadingtoeachdirectly
connectednetworkhasadistanceof0
Neighborroutersshareadirectly
connectednetwork
Eachofnetworkentriesintherouting
tablehasanaccumulateddistance
vectortoshowhowfarawaythat
networkisinagivendirection
Eachrouterreceivesaroutingtable
fromdirectlyconnectedneighbor
routers.
a DistanceVector
DistanceVector
Eachroutercommunicatesrouting
informationtoitsneighbors
Useshopcountasmetricforpath
selection
Asdistancevectordiscoveryprocess
proceeds,routersdiscoverthebest
pathtodestinationnetworksbasedon
informationreceivedfromeach
neighbor
Defineshopcountgreaterthan15as
unreachableroute
Sendsroutingtablecontentsevery30
seconds,bydefault
Bestpath=Pathwith
shortestdistanceorsmallestmetric.
Whenrouterreceivesroutingupdate=
Hopcountvalueisincreasedbyoneon
eachrouter
Topologychangeupdatesproceed
stepbystepbysendingcopiesof
routingtablesfromroutertorouter.
Routeruseslocalnetwkaddressof
directlyconnectedrouterwhichsent
updateasnexthopaddress
Developedtoaddresssomelimitations
ofotherdistancevectorrouting
protocolssuchasRIP
Limitationsincludeuseofhopcount
metricandmaxnetwksizeof15hops
Afterupdatingroutingtable,router
immediatelybeginstransmittngroutng
updtestoinformothernetwkroutersof
thechange
Ciscoproprietaryenhanceddistance
vectorroutingprotocol
RIPissimple,easytoimplement,and
availablefreeofcostwithmostrouters
RIPRoutingInformation
Protocol(RFC1058)
AdvantagesofEIGRP:
These"triggeredupdates"aresent
independentlyofregularlyscheduled
updatesthatRIProutersforward.
DisadvantagesofRIP:
p Usesavarietyofmetricstocalculate
costofaroute
Allowsamaximumof15hopscan
p onlybeusedfornetworksthatconnect
Combinesnexthopandmetricfeatures
nomorethan16routersinseries
a ofdistancevectorprotocols,with
additionaldatabaseandupdate
features
Periodicllysendscompletecopiesof
entireroutngtbletodirectlyconncted
a neighbors.Inlargenetwk,thiscan
s Hasmaximumhopcountof224hops
causesignific.amtofnetwktrafficfor
ea.updt
UnlikeRIP,doesnotrelyonlyon
routingtableinroutertoholdall
informationitneedstooperate.EIGRP
createstwoadditionaldatabasetables:
theneighbortableandthe
topologytable
s Convergesslowlyonlargernetworks,
whennetworkchanges
Neighbortable
Includesinformationlike
interfaceIPaddresses,
interfacetype,andbandwidth
Topologytablecontainsallroutes
advertisedbytheneighborrouters
Mostimp.diff.btwRIPv1andRIPv2
RIPv2cansupportclasslessrouting
,becauseit
includesthesubnetmask
informationinroutingupdates
.
EIGRPEnhancedInterior
GatewayRoutingProtocol
Storesdataaboutneighboringrouters
ondirectlyconnectedlocalnetworks.
RIPv1reliesonclassfulldefaultsubnet
masks
Buildstopologytablefromeach
advertisementsofitsneighbors
Routersuseingdistancevectorrouting
algorithmhavelittleinformationabout
distantnetworksandnoneabout
distantrouters
Dependsonroutingalgorithmcalled
DiffusedUpdateAlgorithm(DUAL)to:
Linkstateroutingalgorithmmaintainsa
fulldatabaseofdistantroutersandhow
theyinterconnect
Calculateshortestpathtoadestination
p withinanetworkandtoinstallthisroute
intoroutingtable
Linkstateroutinghasfollowing
features:
Topologytableenablesarouterrunning
EIGRPtofindbestalternatepath
quicklywhennetworkchangeoccurs
RoutingtableListoftheknown
pathsandinterfaces
Ifnoalternaterouteexistsintopology
table,EIGRPqueriesitsneighborsto
findanewpathtodestination
EIGRPisidealforlarger,more
complexnetworksupto224hopsin
sizethatrequirefastconvergence
Linkstateadvertisement(LSA)
Smallpacketofroutinginformationthat
issentbetweenrouters
LinkStateRouting
LSAsdescribestateofinterfaces
(links)ofarouter,andotherinfolikeIP
addressofeachlink
TopologicaldatabaseCollectionof
informationgatheredfromallLSAs
receivedbyrouter
AdvantagesofOSPF:
Routing
Sendsroutingupdatesonlywhen
topologychanges
doesn'tsendperiodicupdatesof
entireroutingtable.
WhenLSAsarereceivedfromother
routersSPFalgorithmanalyzes
informationindatabasetoconstruct
SPFtree
Providesfastconvergence
SupportsVLSManddiscontiguous
subnets
Providesrouteauthentication
BasedonSPFtree,SPFalgorithmthen
calculatesshortestpathstoother
networks
EachtimeanewLSApacketcausesa
changetolinkstatedatabaseSPF
recalculatesbestpathsandupdates
routingtable
OSPFOpenShortestPathFirst
(RFC2328)
Smallnetworkswithonly
onegatewaytoInternetcanuse
staticroutes
Ex:Anewneighborisadded,alink
fails,oralinkisrestored
Networktopologychanges,=routers
affectedbychangesendupdateLSAs
torestofthenetwork.
SPFtreeisamapofnetworkasseen
frompointofviewoftherouter.
Informationinthistreeisusedtobuild
theroutingtable
SPF(ShortestPathFirst)algorithm
Calculationperformedondatabase
thatresultsinSPFtree.
UsesSPFalgorithmtocalculate
lowestcosttodestination
Asorganizationgrows,RIPv2canbe
used.Easytoconfiginsmallnetworks.
Netwkexceed15routers,=RIPno
longergoodchoice.
Routerssendlinkstateadvertisements
toeachotherwhenachangeoccurs
Forlargernetworks,EIGRPandOSPF
arecommon
Allroutersupdatetheirtopology
databasesaccordingly,regenerate
theirSPFtreestofindnewshortest
pathstoeachnetwork,andupdate
theirroutingtableswithchangedroutes
3maincriteriasforchoosingprotocol:
RoutingwithinanOrganization
EaseofmanagementWhat
p informationdoesprotocolkeepabout
itself?Whatshowcommandsare
BeforeconfiguringRIP:
available?
AssignanIPaddressandenableall
thephysicalinterfacesthatwill
participateinrouting.
EaseofconfigurationHowmany
a commandswillaverageconfigrequire?
Isitpossibletoconfigseveralroutersin
yournetworkwithsameconfig?
Onseriallinks,setclockrateon
masterrouter.
EfficiencyHowmuchbandwidth
doesroutngprotocoltakeupwhilein
s steadystate,andhowmuchcouldit
takeup,whenconverginginresponse
toamajornetwkevent?
p Router(config)#routerrip
a Router(configrouter)#version2
s
BasicRIPconfiguration:
ASisasetofnetworkscontrolledbya
singleadministrativeauthorityusing
sameinternalroutingpolicythroughou
Router(configrouter)#network
[networknumber]
EachASisidentifiedbyauniqueAS
number(ASN)
AfterconfiguringRIPCompare
runningconfigwithanaccurate
topologydiagramtoverifynetwk
numbersandinterfaceIPaddresses
MostcommonexampleofanASisthe
ISP
Onewaytoverifythatroutingis
workingproperlyistopingdeviceson
remotenetworks.
ConfigureandVerifyRIP
AutonomousSystems(AS)
showipprotocolscommandverifies
thatRIProutingisconfigured,tcorrect
interfacesaresendingandreceiving
RIPupdates,androuterisadvertising
correctnetworks
SameASNappliestoallnetwork
deviceswithintheASroutingdomain
AprivateASnumberisrequiredwhen
connectingtomultipleISPs
showiproutecommandshows
routingtable,whichverifiesthatroutes
receivedbyRIPneighborsareinstalled
inroutingtable
Exteriorgatewayprotocolsare
designedtoexchangerouting
informationbetweendifferent
AutonomousSystems
Featuresofdebugipripcommand:
Canbeusedtoobservenetworks
advertisedintheroutingupdatesas
theyaresentandreceived
EachASismanagedbyadifferent
administrationandmayusedifferent
interiorprotocols,networksmustusea
protocolthatcancommunicate
betweendiversesystems.
Displaysrouteractivityinrealtime
Usesrouterprocessorresources,
whichcanaffectnetworkoperation
EGPservesasatranslatorforensuring
thatexternalroutinginformationgets
successfulinterpretedinsideeachAS
network
Usedtoexchangeroutinginformation
withinanautonomoussystemor
individualorganization
Purposeofaninteriorroutingprotocol
istofindbestpaththroughinternal
network
ASisadministeredbyISPand
thereforenotonlyincludesitsown
netwkroutes,butalsomanagesroutes
toallbusinessandothercustomer
netwksthatareconnectedtoit
EGPExteriorGateway
Protocols
EGPprotocolsrunonthe
exteriorrouters,theroutersthatare
locatedattheborderofanAS
Exteriorroutersarealsocalled
bordergateways
IGPInteriorGatewayProtocols
IGPsrunontheinteriorrouters,thatis,
theroutersinsideanorganizationand
exchangeindividualroutes
Exteriorroutersexchangeinformation
abouthowtoreachvariousnetworks
usingexteriorprotocols
Examplesofinteriorgatewayprotocols
areRIP,EIGRPandOSPF
Exteriorroutingprotocolsseektofind
bestpaththroughInternetasa
sequenceofAutonomousSystems
EGPallowtraffictoberoutedacross
theInternettoremotedestinations
Themostcommonexteriorrouting
protocolonInternettodayis
BorderGatewayProtocol(BGP)
ISPSprovidebackuproutesand
routersincasetheregularroutefails
ISPadvertisesregularroutetoother
AutonomousSystems.
SometimesanISPmaywantrouterto
beincludedinitsautonomoussystem
andtoparticipateinBGP.,sorouter
mustbeconfigedtoenableBGP
EGPPovidemethodbywhichISPscan
setandenforcepoliciesandlocal
preferencessothattrafficflowthrough
ISPisefficientandnoneoftheinternal
routesareoverloadedwithtransit
traffic
Cancauserouterstooverloadandfail,
ifthoseroutersdonothavethe
capacitytohandlelargeamountsof
traffic.
ManyAutonomousSystemsarenot
willingtocarrytransittraffic
p ThefirststepinenablingBGPona
routeristoconfiguretheASnumber
a neighborwithwhichtheCustomer
PremiseEquipment(CPE)router
FlowoftrafficbetweenAutonomous
Systemsiscarefullycontrolled.
Itisimportanttobeabletolimitoreven
prohibitcertaintypesofmessagesfrom
goingtoorfromanAS,forsecurity
reasonsortopreventoverloading.
neighbor[IPAddress]remoteas[AS
number]
exchangesinformation
WhenanISPcustomerhasitsown
registeredIPaddressblock,maywant
ConfiguringandVerifyingBGP
routerbgp[ASnumber]
IdentifyISProuterthatistheBGP
ExteriorRoutingProtocolsand
ISP
LocalTrafficTrafficcarriedwithinan
ASthateitheroriginatedinthatsame
AS,orisintendedtobedeliveredwithin
thatAS.Thisislikelocaltrafficona
street.
TransitTraffic Trafficthatwas
generatedoutsidethatASandcan
travelthroughinternalASnetworkin
routetobedeliveredtodestinations
outsideAS.Thisislikethroughtraffic
onastreet.
MostcurrentversionofBGPisversion
4(BGP4)inRFC4271
WhenanISPputsaborderrouterata
customerlocation,theyusually
configureitwithadefaultstaticrouteto
theISP
Regularroutefails,thenISPsendsan
exteriorprotocolupdatemessageto
advertisebackuprouteinstead
Flowofmessagesintheinternet=
TRAFFIC.Twotypesoftraffic:
95%ofAutonomousSystemsuseBGP
s routestosomeofitsinternalnetworks
tobeknownonInternet.TouseBGP
network[networkaddress]
toadvertiseaninternalroute,a
networkcommandisneeded.
Onceallofcustomerpremise
equipmentisinstalledandtrouting
protocolsconfigured,customerhas
bothlocalandInternetconnectivity.
Nowthecustomeris
abletofullyparticipateinother
servicestheISPmayoffer
TheIPaddressesusedforBGPare
normallyregistered,routable
addresseswhichidentifyunique
organizations
Inverylargeorganizationsprivate
addressesmaybeusedintheBGP
OntheInternet,BGPshould
neverbeusedtoadvertiseaprivate
networkaddress
Create a Mind Map
Like 4
Tweet
You might also like
- Client Server Architecture A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionFrom EverandClient Server Architecture A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionNo ratings yet
- Mapping the Evolving Telecoms Industry: Uses and Limitations of the Layer ModelDocument15 pagesMapping the Evolving Telecoms Industry: Uses and Limitations of the Layer ModelRodrigo PontesNo ratings yet
- Powershell Cheat Sheet: Setting Security PolicyDocument2 pagesPowershell Cheat Sheet: Setting Security Policybf10l2No ratings yet
- Linux Mind MapDocument4 pagesLinux Mind MapMuhsin MahamoodNo ratings yet
- HpingDocument6 pagesHpingjosej.castilla.exts3183No ratings yet
- MindCert Wireshark MindMapDocument1 pageMindCert Wireshark MindMapacehussainNo ratings yet
- Computer Network AttacksDocument15 pagesComputer Network AttacksRadhey RajNo ratings yet
- List of Useful Windows 10 HotkeysDocument2 pagesList of Useful Windows 10 HotkeysYose FratamaNo ratings yet
- ITIL V3 Continual Service Improvement MindmapDocument1 pageITIL V3 Continual Service Improvement MindmapIgor100% (6)
- Event Log Analysis: Introduction ToDocument12 pagesEvent Log Analysis: Introduction ToKAliNo ratings yet
- Essential PowerShell Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesEssential PowerShell Cheat SheetFederico MarzulloNo ratings yet
- TCP/IP Troubleshooting ToolsDocument41 pagesTCP/IP Troubleshooting ToolsShivakumar S KadakalNo ratings yet
- Mind MapDocument1 pageMind MapShu ShengNo ratings yet
- Network descriptionDocument5 pagesNetwork descriptionketavmodiNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 Personnel Security and Risk Management ConceptsDocument4 pagesCHAPTER 2 Personnel Security and Risk Management ConceptsJerome MamauagNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Computer SecurityDocument16 pagesFundamental Computer Securitykakyo29433No ratings yet
- Presented By: Intrusion Detection SysytemDocument15 pagesPresented By: Intrusion Detection SysytemRagala VishwatejaNo ratings yet
- Web Application Security Standard PDFDocument5 pagesWeb Application Security Standard PDFyshprasdNo ratings yet
- Installing Squid Web ProxyDocument14 pagesInstalling Squid Web Proxystiyke100% (1)
- HCIA SECURITY Searchable PDFDocument294 pagesHCIA SECURITY Searchable PDFgurungeNo ratings yet
- TCPIP Protocol SuiteDocument27 pagesTCPIP Protocol SuiteVedant AggrawalNo ratings yet
- Submitted By-Anurag Deyasi Information Technology SSEC, BhilaiDocument39 pagesSubmitted By-Anurag Deyasi Information Technology SSEC, BhilaiAnonymous kbmKQLe0JNo ratings yet
- Enable TLS 1.2Document7 pagesEnable TLS 1.2Manuela KuczynskaNo ratings yet
- ADSVS v1Document98 pagesADSVS v1valerabn01100% (1)
- Data Leakage DetectionDocument15 pagesData Leakage DetectionJanardhan Daasari100% (1)
- SOC 2 Audit Scoping Questionnaire 2021Document4 pagesSOC 2 Audit Scoping Questionnaire 2021RSA ArcherNo ratings yet
- Network Management Paper SNMP Vs WMIDocument13 pagesNetwork Management Paper SNMP Vs WMIBerry Hoekstra100% (2)
- Title of Assignment: Security Vulnerabilities and Countermeasures inDocument19 pagesTitle of Assignment: Security Vulnerabilities and Countermeasures inErwinFunaNo ratings yet
- Secret Server Installation Windows 5Document24 pagesSecret Server Installation Windows 5smart_eagle44No ratings yet
- Gao It AuditDocument601 pagesGao It AuditbenjaminbofNo ratings yet
- 9 Rules For Evaluating Web TWAIN Components: Presents..Document8 pages9 Rules For Evaluating Web TWAIN Components: Presents..Santosh MahatoNo ratings yet
- EBIT Miner Network Operation GuideDocument9 pagesEBIT Miner Network Operation GuideLuis AcostaNo ratings yet
- EMail Security Protocols ComparedDocument20 pagesEMail Security Protocols ComparedAayatKhanNo ratings yet
- XMPP Presentation 160108105545 PDFDocument17 pagesXMPP Presentation 160108105545 PDFRiska AANo ratings yet
- Secured Database Application DevelopmentDocument103 pagesSecured Database Application DevelopmentRameshbabu BandamNo ratings yet
- IT Service DeliveryDocument19 pagesIT Service DeliveryBambang Puji Haryo WicaksonoNo ratings yet
- TCP 3-Way Handshake 3WHS CheatSheet - ATech (Waqas Karim)Document1 pageTCP 3-Way Handshake 3WHS CheatSheet - ATech (Waqas Karim)Waqas KarimNo ratings yet
- ALS Security+ Lab01Document10 pagesALS Security+ Lab01Mishel JiménezNo ratings yet
- SQL Scripts For ProWatchDocument1 pageSQL Scripts For ProWatchAlen KuharićNo ratings yet
- Ccna Presentation TrainingDocument21 pagesCcna Presentation TrainingbikkerNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 CYBER SECURITY (AUC-002)Document49 pagesUnit 1 CYBER SECURITY (AUC-002)PrachiNo ratings yet
- Manage file permissions with IcaclsDocument4 pagesManage file permissions with Icaclsfenix6232No ratings yet
- SCADA Xom 1Document31 pagesSCADA Xom 1jtutokeyNo ratings yet
- Policy Based Forwarding-RevADocument8 pagesPolicy Based Forwarding-RevAPatricio VarelaNo ratings yet
- MindCert Cisco IPsec MindMap PDFDocument1 pageMindCert Cisco IPsec MindMap PDFzinzinNo ratings yet
- Wipro CRS Threat Advisory - WannaCry Ransomware 1.1Document12 pagesWipro CRS Threat Advisory - WannaCry Ransomware 1.1pallavsinhaNo ratings yet
- Lab 4.5.1 Observing TCP and UDP Using Netstat (Instructor Version)Document7 pagesLab 4.5.1 Observing TCP and UDP Using Netstat (Instructor Version)Rifqi Imaduddin IrfanNo ratings yet
- Training Letter DirectorDocument1 pageTraining Letter DirectorArpan MondalNo ratings yet
- Cyber Security PDFDocument189 pagesCyber Security PDFVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- Table of Content OMADocument12 pagesTable of Content OMAkae'sNo ratings yet
- Symantec Network Security Administration GuideDocument432 pagesSymantec Network Security Administration GuideTibor CsizovszkyNo ratings yet
- Biometric US GovDocument20 pagesBiometric US GovreanthalNo ratings yet
- Intro To ITIL WatITis2012Document45 pagesIntro To ITIL WatITis2012Damian AlvarezNo ratings yet
- LogRhythmRuleBuilding CheatSheet 6.1Document11 pagesLogRhythmRuleBuilding CheatSheet 6.1William Pope0% (1)
- Route CommandDocument5 pagesRoute Commandkapil514No ratings yet
- Network Layer: Delivery, Forwarding, and RoutingDocument31 pagesNetwork Layer: Delivery, Forwarding, and Routingyuwee yiiiNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document106 pagesUnit 3sona jainNo ratings yet
- CCENT Chapter 15 Key TopicsDocument3 pagesCCENT Chapter 15 Key Topicshoang nguyen baNo ratings yet
- CCNA II Chapter 2 SummaryDocument3 pagesCCNA II Chapter 2 SummaryAdam Jian YinNo ratings yet
- Brocade Adapters Troubleshooting Guide (Supporting CNA Models 1010 and 1020 and Supporting HBA Models 415, 425, 815, 825)Document116 pagesBrocade Adapters Troubleshooting Guide (Supporting CNA Models 1010 and 1020 and Supporting HBA Models 415, 425, 815, 825)Saptarshi GhoshNo ratings yet
- 150 Vital CCNA Commands PDFDocument60 pages150 Vital CCNA Commands PDFSaptarshi GhoshNo ratings yet
- Converged Enhanced Ethernet - Administrator's Guide (53 - 1001346 - 01 - CEE - AG - v630)Document162 pagesConverged Enhanced Ethernet - Administrator's Guide (53 - 1001346 - 01 - CEE - AG - v630)Saptarshi GhoshNo ratings yet
- v6.3.0 Releasenotes v1.0Document161 pagesv6.3.0 Releasenotes v1.0debshubra100% (1)
- The Five Keys To Success On Cisco Simulator Exam Questions An Exclusive Ebook From The Bryant Advantage Chris Bryant CCIE #12933Document6 pagesThe Five Keys To Success On Cisco Simulator Exam Questions An Exclusive Ebook From The Bryant Advantage Chris Bryant CCIE #12933darkfirexNo ratings yet
- B Services Design Guide 5-0-220617Document40 pagesB Services Design Guide 5-0-220617Saptarshi GhoshNo ratings yet
- CCNP Wireless 300-365 Study MaterialDocument66 pagesCCNP Wireless 300-365 Study MaterialSaptarshi Ghosh100% (1)
- Brocade Adapters Administrator's Guide (Brocade - Adapters - Admin - Guide)Document228 pagesBrocade Adapters Administrator's Guide (Brocade - Adapters - Admin - Guide)Saptarshi GhoshNo ratings yet
- En Switch v6 Ch04Document70 pagesEn Switch v6 Ch04ignaciomatte2011No ratings yet
- B Epn Implementguide Smallnetwork E2E SR 5-0-23062017Document24 pagesB Epn Implementguide Smallnetwork E2E SR 5-0-23062017Saptarshi GhoshNo ratings yet
- B EPN Service Orchestration Userguide 5-0-220617Document82 pagesB EPN Service Orchestration Userguide 5-0-220617Saptarshi GhoshNo ratings yet
- 100 CCNA® Exam Gotchas - and How To Avoid Them!Document0 pages100 CCNA® Exam Gotchas - and How To Avoid Them!dibpalNo ratings yet
- B Epn Transport Design Guide 5-0-230617Document36 pagesB Epn Transport Design Guide 5-0-230617Saptarshi GhoshNo ratings yet
- B System Test Topology Reference Guide 21stjune2017Document12 pagesB System Test Topology Reference Guide 21stjune2017Saptarshi GhoshNo ratings yet
- B Epn ImplementGuide LDP SR Interworking 23062017Document48 pagesB Epn ImplementGuide LDP SR Interworking 23062017Saptarshi GhoshNo ratings yet
- B Epn Implementguide Large Network E2E SR 5-0-23062017Document52 pagesB Epn Implementguide Large Network E2E SR 5-0-23062017Saptarshi GhoshNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Robotic Process Automation - A Primer by Institute For Robotic Process Automation in Association With Carnegie Mellon University, June 2015 PDFDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Robotic Process Automation - A Primer by Institute For Robotic Process Automation in Association With Carnegie Mellon University, June 2015 PDFgong688665100% (1)
- B EPN Implementguide E2E Program SR 5-0-23062017Document36 pagesB EPN Implementguide E2E Program SR 5-0-23062017Saptarshi GhoshNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Robotic Process Automation - A Primer by Institute For Robotic Process Automation in Association With Carnegie Mellon University, June 2015 PDFDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Robotic Process Automation - A Primer by Institute For Robotic Process Automation in Association With Carnegie Mellon University, June 2015 PDFgong688665100% (1)
- Robotic Process Automation PDFDocument57 pagesRobotic Process Automation PDFSaptarshi GhoshNo ratings yet
- Transformative Enterprise Architecture Guiding and Governing The Metamorphosis of Organizations and IT Ecosystems PDFDocument356 pagesTransformative Enterprise Architecture Guiding and Governing The Metamorphosis of Organizations and IT Ecosystems PDFSaptarshi GhoshNo ratings yet
- White Paper - Robotic Process Automation PDFDocument22 pagesWhite Paper - Robotic Process Automation PDFSaptarshi GhoshNo ratings yet
- Robotics. Are You Ready For The New World PDFDocument37 pagesRobotics. Are You Ready For The New World PDFSaptarshi GhoshNo ratings yet
- Transformative Enterprise Architecture Guiding and Governing The Metamorphosis of Organizations and IT Ecosystems PDFDocument356 pagesTransformative Enterprise Architecture Guiding and Governing The Metamorphosis of Organizations and IT Ecosystems PDFSaptarshi GhoshNo ratings yet
- White Paper - Robotic Process Automation PDFDocument22 pagesWhite Paper - Robotic Process Automation PDFSaptarshi GhoshNo ratings yet
- Robotics. Are You Ready For The New World PDFDocument37 pagesRobotics. Are You Ready For The New World PDFSaptarshi GhoshNo ratings yet
- Robotic Process Automation PDFDocument57 pagesRobotic Process Automation PDFSaptarshi GhoshNo ratings yet
- Transformative Enterprise Architecture Guiding and Governing The Metamorphosis of Organizations and IT Ecosystems PDFDocument356 pagesTransformative Enterprise Architecture Guiding and Governing The Metamorphosis of Organizations and IT Ecosystems PDFSaptarshi GhoshNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Robotic Process Automation - A Primer by Institute For Robotic Process Automation in Association With Carnegie Mellon University, June 2015 PDFDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Robotic Process Automation - A Primer by Institute For Robotic Process Automation in Association With Carnegie Mellon University, June 2015 PDFgong688665100% (1)
- Robotics. Are You Ready For The New World PDFDocument37 pagesRobotics. Are You Ready For The New World PDFSaptarshi GhoshNo ratings yet
- MN AG v. SANOFI - 3:18-cv-14999 - Defendants' Joint Motion To Dismiss - 2019-08-12Document124 pagesMN AG v. SANOFI - 3:18-cv-14999 - Defendants' Joint Motion To Dismiss - 2019-08-12The Type 1 Diabetes Defense FoundationNo ratings yet
- Backup and Recovery ScenariosDocument8 pagesBackup and Recovery ScenariosAmit JhaNo ratings yet
- Organisation Study Report On Star PVC PipesDocument16 pagesOrganisation Study Report On Star PVC PipesViswa Keerthi100% (1)
- Dissolved Oxygen Primary Prod Activity1Document7 pagesDissolved Oxygen Primary Prod Activity1api-235617848No ratings yet
- Craft's Folder StructureDocument2 pagesCraft's Folder StructureWowNo ratings yet
- KSRTC BokingDocument2 pagesKSRTC BokingyogeshNo ratings yet
- Elementary School: Cash Disbursements RegisterDocument1 pageElementary School: Cash Disbursements RegisterRonilo DagumampanNo ratings yet
- Wind EnergyDocument6 pagesWind Energyshadan ameenNo ratings yet
- NEW CREW Fast Start PlannerDocument9 pagesNEW CREW Fast Start PlannerAnonymous oTtlhP100% (3)
- Ayushman BharatDocument20 pagesAyushman BharatPRAGATI RAINo ratings yet
- Bob Wright's Declaration of BeingDocument1 pageBob Wright's Declaration of BeingBZ Riger100% (2)
- 2JA5K2 FullDocument22 pages2JA5K2 FullLina LacorazzaNo ratings yet
- As 1769-1975 Welded Stainless Steel Tubes For Plumbing ApplicationsDocument6 pagesAs 1769-1975 Welded Stainless Steel Tubes For Plumbing ApplicationsSAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- Excavator Loading To Truck TrailerDocument12 pagesExcavator Loading To Truck TrailerThy RonNo ratings yet
- Global Cleantech Innovation Programme IndiaDocument122 pagesGlobal Cleantech Innovation Programme Indiaficisid ficisidNo ratings yet
- DSA NotesDocument87 pagesDSA NotesAtefrachew SeyfuNo ratings yet
- Ten Golden Rules of LobbyingDocument1 pageTen Golden Rules of LobbyingChaibde DeNo ratings yet
- Gps Anti Jammer Gpsdome - Effective Protection Against JammingDocument2 pagesGps Anti Jammer Gpsdome - Effective Protection Against JammingCarlos VillegasNo ratings yet
- WitepsolDocument21 pagesWitepsolAnastasius HendrianNo ratings yet
- CST Jabber 11.0 Lab GuideDocument257 pagesCST Jabber 11.0 Lab GuideHải Nguyễn ThanhNo ratings yet
- Econ Old Test 2Document7 pagesEcon Old Test 2Homer ViningNo ratings yet
- Computers As Components 2nd Edi - Wayne WolfDocument815 pagesComputers As Components 2nd Edi - Wayne WolfShubham RajNo ratings yet
- NAC Case Study AnalysisDocument25 pagesNAC Case Study AnalysisSushma chhetriNo ratings yet
- An4856 Stevalisa172v2 2 KW Fully Digital Ac DC Power Supply Dsmps Evaluation Board StmicroelectronicsDocument74 pagesAn4856 Stevalisa172v2 2 KW Fully Digital Ac DC Power Supply Dsmps Evaluation Board StmicroelectronicsStefano SalaNo ratings yet
- MCDO of Diesel Shed, AndalDocument12 pagesMCDO of Diesel Shed, AndalUpendra ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- APM Terminals Safety Policy SummaryDocument1 pageAPM Terminals Safety Policy SummaryVaviNo ratings yet
- Gary Mole and Glacial Energy FraudDocument18 pagesGary Mole and Glacial Energy Fraudskyy22990% (1)
- Broker Name Address SegmentDocument8 pagesBroker Name Address Segmentsoniya_dps2006No ratings yet
- Competency-Based Learning GuideDocument10 pagesCompetency-Based Learning GuideOliver BC Sanchez100% (2)
- Question Paper Code: 31364Document3 pagesQuestion Paper Code: 31364vinovictory8571No ratings yet