Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Knowledge Will Pertain To The Understanding or Learnings Taken From Evident
Uploaded by
Ronilyn Mae AlvarezOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Knowledge Will Pertain To The Understanding or Learnings Taken From Evident
Uploaded by
Ronilyn Mae AlvarezCopyright:
Available Formats
Knowledge will pertain to the understanding or learnings taken from evident.
Skills the
researchers are pertaining to are the ways (???) on how a nurse educator practices EBP,
attitude would refer to the response, reaction, or way of thinking of a nurse educator in
using EBP. Barriers would refer to the obstacles, circumstances that prevents the nurse
educators in utilizing the best recent research findings into practice.
Refer to page 7 According to Mackey 2016 Utilizing nursing best practice guidelines,
reviewing and implementing applicable research evidence, and taking advantage of
technological advances are all ways in which nursing can move forward as a well-informed
discipline.
If a particular university refuses to be part of the study, the researchers would respect the
universitys decision and will ask the reason (if they are willing) on why they refuse to take
part in the study. The refusal of the university would be included in the studys limitation.
So far, studies we have found of evidence-based nursing have focused on clinical nurses
and limited studies are focused on nurse educators. Also another one is findings from
studies that says nurse educators have a positive attitudes towards EBP; however lack of
knowledge, poor skills, limited time and lack of resources were perceived as major
obstacles to implement EBP.
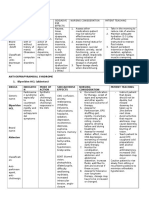
The theory presents a cyclical model of learning, consisting of four stages which includes
CONCRETE EXPERIENCE (OR DO) - The first stage, concrete experience (CE), is where the
learner actively experiences an activity such as a lab session or field work. This is where
the Nurse Educator has an experience in using EBP.
REFLECTIVE OBSERVATION (OR OBSERVE)
The second stage, reflective observation (RO), is when the learner consciously reflects
back on that experience. This is where the Nurse Educator reflects on what the EBP has
proved.
ABSTRACT CONCEPTUALIZATION (OR THINK)
The third stage, abstract conceptualization (AC), is where the learner attempts to
conceptualize a theory or model of what is observed. In this stage, the Nurse educator
conceptualizes the EBP learning in the clinical area, and in the classroom setting.
ACTIVE EXPERIMENTATION (OR PLAN)
The fourth stage, active experimentation (AE), is where the learner is trying to plan how to
test a model or theory or plan for a forthcoming experience. This is the stage where the
Nurse Educator checks the skills of the student nurses and sees if they are effective (??)
For the Rogers theory of Diffusion of Innovations. It is stated there that the elements
included in theory is the main elements are innovation, communication channels, time,
and the social system. According to Rogers, 2003 the theory also argues that certain
characteristics of the innovation (research findings) itself may facilitate its adoption. The
theory may provide valuable insights into why some practices change and others do not,
as well as guiding those who try to effect adoption of best-evidence practice.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Capillary Blood Glucose Monitoring or CBG MonitoringDocument5 pagesCapillary Blood Glucose Monitoring or CBG MonitoringRonilyn Mae Alvarez100% (1)
- Mussel Shells As Alternative Chicken FeedsDocument2 pagesMussel Shells As Alternative Chicken FeedsRonilyn Mae AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Fodor - Reply To Steven PinkerDocument8 pagesFodor - Reply To Steven PinkerflipindoreNo ratings yet
- Anti-Depressants 1. Sertraline (Zoloft)Document5 pagesAnti-Depressants 1. Sertraline (Zoloft)Ronilyn Mae AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Results From The University LibrariesDocument3 pagesResults From The University LibrariesRonilyn Mae AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Teaching PlanDocument6 pagesTeaching PlanRonilyn Mae AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Be It Enacted by The Senate and House of Representatives of The Philippines in Congress AssembledDocument3 pagesBe It Enacted by The Senate and House of Representatives of The Philippines in Congress AssembledRonilyn Mae AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Ballroom DancesDocument4 pagesBallroom DancesRonilyn Mae AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Operating Room TeamDocument3 pagesOperating Room TeamRonilyn Mae AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Anti-Depressants 1. Sertraline (Zoloft)Document5 pagesAnti-Depressants 1. Sertraline (Zoloft)Ronilyn Mae AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Operating Room TeamDocument3 pagesOperating Room TeamRonilyn Mae AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Popularly Known As PlaridelDocument1 pagePopularly Known As PlaridelRonilyn Mae AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Main Elements of a Community in 40 CharactersDocument3 pagesMain Elements of a Community in 40 CharactersRonilyn Mae AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Different UlcersDocument1 pageDifferent UlcersRonilyn Mae AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Phil HistDocument3 pagesPhil HistRonilyn Mae AlvarezNo ratings yet
- OBRDocument3 pagesOBRRonilyn Mae AlvarezNo ratings yet
- BGHMC Med 5 NCPDocument2 pagesBGHMC Med 5 NCPRonilyn Mae AlvarezNo ratings yet
- OriginsDocument15 pagesOriginsRonilyn Mae AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Rose Colored GlassesDocument1 pageRose Colored GlassesRonilyn Mae AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Journal MM NNDocument3 pagesJournal MM NNRonilyn Mae AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Ielab ObsDocument7 pagesIelab ObsRonilyn Mae AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Phospho Something ChemistryDocument3 pagesPhospho Something ChemistryRonilyn Mae AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Cause of Morbidity For August 2016: Toothache Runny NoseDocument6 pagesCause of Morbidity For August 2016: Toothache Runny NoseRonilyn Mae AlvarezNo ratings yet
- 1st Level AssessmentDocument2 pages1st Level AssessmentRonilyn Mae AlvarezNo ratings yet
- DiagnosticsDocument26 pagesDiagnosticsRonilyn Mae AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Nutrition TeachingDocument5 pagesNutrition TeachingRonilyn Mae AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Handout 2Document5 pagesHandout 2Ronilyn Mae AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument18 pagesChapter TwoRonilyn Mae AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Types of ArrhythmiaDocument10 pagesTypes of ArrhythmiaRonilyn Mae AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Inductive and Deductive ReasoningDocument5 pagesInductive and Deductive ReasoningRonilyn Mae AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Repetition in Language Teaching and LearningDocument17 pagesRepetition in Language Teaching and LearningRodrigo López Escobedo100% (1)
- Introduction To Cognitive and Physiological Psychology Week1v2Document33 pagesIntroduction To Cognitive and Physiological Psychology Week1v2Odaine BennettNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Processes and Expert SystemsDocument12 pagesCognitive Processes and Expert Systemsjohnmauro alapagNo ratings yet
- Economic Education ProposalDocument7 pagesEconomic Education Proposalyuliaarya sastiNo ratings yet
- What Is Mother TongueDocument2 pagesWhat Is Mother TongueJulius CabinganNo ratings yet
- Methods of Philosophizing: Logical Analysis and Conceptual AnalysisDocument13 pagesMethods of Philosophizing: Logical Analysis and Conceptual AnalysisZaldy Belo100% (1)
- Quiz in Social Dimension of EducationDocument2 pagesQuiz in Social Dimension of EducationDavid Renz Pila Bonifacio100% (14)
- Crime RP PDFDocument20 pagesCrime RP PDFprincess sanaNo ratings yet
- Mba Project SynopsisDocument4 pagesMba Project SynopsisAnudeep Sasikumar KuriyangaraNo ratings yet
- Research PresentationDocument29 pagesResearch PresentationSam SmithzNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument3 pagesScienceKezia SantosidadNo ratings yet
- There S No Testimonial Justice Why Pursuit of A Virtue Is Not The Solution To Epistemic Injustice PDFDocument23 pagesThere S No Testimonial Justice Why Pursuit of A Virtue Is Not The Solution To Epistemic Injustice PDFana lauraNo ratings yet
- Bibliography: FallDocument6 pagesBibliography: FallThalita BorgesNo ratings yet
- Context Is Fundamental To Discourse AnalysisDocument3 pagesContext Is Fundamental To Discourse AnalysisBahawalpur 24/7No ratings yet
- (Thought in The Act) David Lapoujade - William James - Empiricism and Pragmatism-Duke University Press Books (2019) PDFDocument162 pages(Thought in The Act) David Lapoujade - William James - Empiricism and Pragmatism-Duke University Press Books (2019) PDFXyrile Joy Siongco100% (1)
- What Is Research MethodologyDocument16 pagesWhat Is Research Methodologysanu8182% (22)
- Philosophy of Science Issues and Perspective SGKulkarni-mergedDocument59 pagesPhilosophy of Science Issues and Perspective SGKulkarni-mergedJaswanth SuggulaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bu Heni Jurnal Ratu Khoirotun Nisa FormatifDocument21 pagesTugas Bu Heni Jurnal Ratu Khoirotun Nisa FormatifRatu nisaNo ratings yet
- William James Theory of EmotionDocument174 pagesWilliam James Theory of EmotionLeo Souza100% (1)
- Introduction to Validity, Reliability and Their EstimationDocument6 pagesIntroduction to Validity, Reliability and Their EstimationWinifridaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Practice Is Based and Provides The Foundation For Understanding Theory As One Type of Nursing KnowledgeDocument32 pagesNursing Practice Is Based and Provides The Foundation For Understanding Theory As One Type of Nursing Knowledgeyousuf pogiNo ratings yet
- Problem Statement ChecklistDocument3 pagesProblem Statement ChecklistPrem Raj AdhikariNo ratings yet
- The Scientific MethodDocument215 pagesThe Scientific MethodMelanie Tagudin TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Nature of Inquiry and ResearchDocument2 pagesChapter 1 Nature of Inquiry and ResearchCelyn Gahol100% (4)
- Trenton Merricks - Objects and Persons 2001 PDFDocument216 pagesTrenton Merricks - Objects and Persons 2001 PDFHisham AliNo ratings yet
- Lev VygotskyDocument2 pagesLev VygotskyMai NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Scientific and PhilosophicalDocument9 pagesLesson 2 Scientific and PhilosophicalMikee MarceloNo ratings yet
- Qualitaive Research The Attitude of Grade 12 Students Towards Learning Parctical Research 2Document9 pagesQualitaive Research The Attitude of Grade 12 Students Towards Learning Parctical Research 2Charles Emmanuel NielesNo ratings yet
- Penology - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia PDFDocument3 pagesPenology - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia PDFAbdul GhaffarNo ratings yet