Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Applications of Ohm's Law: Calculating Voltage, Current, Resistance & Power
Uploaded by
cuambyahoo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
70 views1 pageohms law
Original Title
Applications of Ohm
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentohms law
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
70 views1 pageApplications of Ohm's Law: Calculating Voltage, Current, Resistance & Power
Uploaded by
cuambyahooohms law
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Applications of Ohms Law
The applications of ohms law are that it helps us in
determining either voltage, current or resistance of a linear circuit
when the other two quantities are known to us. Apart from that,
it makes power calculation a lot simpler, like when we know the
value of the resistance for a particular circuit, we need not know
both the current and the voltage to calculate the power
dissipation since P =
VI. Rather we can use Ohms
Law. To replace either
the voltage or current in the
above expression to produce the result
These are the
applications of Ohms law as we can see from the results, that
the rate of energy loss varies with the square of the voltage or
current. When we double the voltage applied to a circuit, obeying
Ohms law, the rate at which energy is supplied (or power) gets
four times bigger. This phenomena occurs because increasing the
voltage also makes the current rise by the same amount as it has
been explained above.
Limitation of Ohms Law
The limitations of Ohms law are explained as follows:
1. This law cannot be applied to unilateral networks. A
unilateral network has unilateral elements like diode,
transistors, etc., which do not have same voltage current
relation for both directions of current.
2. Ohms law is also not applicable for non linear elements.
Non-linear elements are those which do not give current through
it, is not exactly proportional to the voltage applied, that means
the resistance value of those elements changes for different
values of voltage and current. Examples of non linear elements
are thyristor, electric arc, etc.
You might also like
- Ohm S Law TutorialDocument17 pagesOhm S Law Tutorialchristopher pazmiño panchanaNo ratings yet
- Ohms LawDocument25 pagesOhms LawLui PorrasNo ratings yet
- Basic Elec Ohms LawDocument16 pagesBasic Elec Ohms Lawrashmiame0% (1)
- Ohms Law Formula WheelDocument2 pagesOhms Law Formula WheelTesda SfistNo ratings yet
- WWW Electrical4u ComDocument6 pagesWWW Electrical4u ComNh Chuminda YapaNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument2 pagesOhm's LawHossain BabuNo ratings yet
- Document 43Document20 pagesDocument 43bumbadiyaviralNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law and Its ApplicationsDocument16 pagesOhm's Law and Its ApplicationsJasmitha Shree.RNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument11 pagesOhm's LawMarifer RamirezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Ohms LawDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Ohms LawJoshteKunNo ratings yet
- Principles and Definition of Ohms LawDocument36 pagesPrinciples and Definition of Ohms LawIrfanNo ratings yet
- Ohm S Law TutorialDocument17 pagesOhm S Law Tutorialchristopher pazmiño panchanaNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law: This Article Is About The Law Related To Electricity. For Other Uses, SeeDocument10 pagesOhm's Law: This Article Is About The Law Related To Electricity. For Other Uses, SeeAditya Singh BaisNo ratings yet
- 1.Dr - Said Ebiad Physics (I)Document20 pages1.Dr - Said Ebiad Physics (I)Khaled AhmedNo ratings yet
- Basic Circuit Laws: Georg Ohm Kirchhoff's LawsDocument4 pagesBasic Circuit Laws: Georg Ohm Kirchhoff's LawsrezhabloNo ratings yet
- برزنتيشن طرق قياس اكوادDocument13 pagesبرزنتيشن طرق قياس اكوادMomen SalahNo ratings yet
- Potential Energy: Current Conductor Proportional Voltage ResistanceDocument2 pagesPotential Energy: Current Conductor Proportional Voltage Resistanceschauhan12No ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument32 pagesOhm's LawDezz Balleta-BonaNo ratings yet
- What Is Ohm's Law Definition, Formula, Graph & LimitationsDocument10 pagesWhat Is Ohm's Law Definition, Formula, Graph & LimitationsjackNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Electricity - Part 6Document11 pagesUnit 2 Electricity - Part 6Maurya AdeshraNo ratings yet
- كرار جاهرDocument4 pagesكرار جاهرkararalzide2005No ratings yet
- Fundamental Activity 2 - Ifes 2016711 - CeDocument7 pagesFundamental Activity 2 - Ifes 2016711 - CeFernanda EsparzaNo ratings yet
- الفطاحلةDocument6 pagesالفطاحلةyr44grf94kNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Electrical Theory PDFDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Electrical Theory PDFVilcu IonNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law: Parallel CircuitDocument2 pagesOhm's Law: Parallel Circuitnhie_quh29No ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument2 pagesOhm's LawDon't Know EverythingNo ratings yet
- Advance Physics For Grade 10 STE StudentsDocument5 pagesAdvance Physics For Grade 10 STE StudentsJoshua AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document7 pagesUnit 5NurFajrina MuthmainnahNo ratings yet
- المستند (wDocument3 pagesالمستند (wyr44grf94kNo ratings yet
- Voltage and Current Sources RepresentationDocument46 pagesVoltage and Current Sources RepresentationMiran SolankiNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law: Presented By: Shantell Limjoco Tonet Sy Viana AngDocument12 pagesOhm's Law: Presented By: Shantell Limjoco Tonet Sy Viana AngViana Celina AngNo ratings yet
- DOT - ZacDocument12 pagesDOT - ZacZac BismonteNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law ExplainedDocument2 pagesOhm's Law ExplainedKatrina Zoi ApostolNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument27 pagesUnit IPratap VeerNo ratings yet
- Understanding Ohms Law A Beginners GuideDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Ohms Law A Beginners GuideMomen SalahNo ratings yet
- Electronic CircuitsDocument13 pagesElectronic CircuitsAbhisek PagadNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument15 pagesOhm's Lawpaancute8982No ratings yet
- His Article Is About The Law Related To ElectricityDocument22 pagesHis Article Is About The Law Related To ElectricitySandeep GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ohmic and Non-OhmicDocument4 pagesOhmic and Non-Ohmicjustnothing010100No ratings yet
- Famusudo Catharine OluwaseunfunmiDocument15 pagesFamusudo Catharine OluwaseunfunmiAkinola AyomideNo ratings yet
- IntroDocument1 pageIntroMARREN JEIRELLE PENAFLORNo ratings yet
- Tugas 1. Bahasa Inggris Vazil Naufal FarasDocument3 pagesTugas 1. Bahasa Inggris Vazil Naufal FarasVazil NaufalNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document4 pagesLab 2api-3720469No ratings yet
- RLJDMC Dav Public SchoolDocument9 pagesRLJDMC Dav Public SchoolVikrant SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument23 pagesOhm's Lawmini2268100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Elctricity and Electronics Week 3Document13 pagesFundamentals of Elctricity and Electronics Week 3richie cuizonNo ratings yet
- Lab 20 Report Ohms LawnewDocument5 pagesLab 20 Report Ohms Lawnewapi-270816603No ratings yet
- OhmssDocument2 pagesOhmssMark SantillanNo ratings yet
- Electrical Terms Summary DefinationsDocument9 pagesElectrical Terms Summary Definationsemmanuel akaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Introduction To Basics ElectronicsDocument50 pagesLesson 2 - Introduction To Basics ElectronicsMark SalvañaNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Acoustic LawDocument1 pageOhm's Acoustic LawBenjamin Duallo FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument1 pageOhm's Lawsyedshehzd_9No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electricity and ElectronicsDocument26 pagesFundamentals of Electricity and ElectronicsBryan AremadoNo ratings yet
- Electric CurrentDocument4 pagesElectric CurrentFelix De Los ReyesNo ratings yet
- University of The East - Caloocan College of EngineeringDocument4 pagesUniversity of The East - Caloocan College of EngineeringAkane HitomiNo ratings yet
- Verify Ohms LawDocument3 pagesVerify Ohms Lawhome143No ratings yet
- Ohm's LawDocument2 pagesOhm's LawBelly JoeNo ratings yet
- Electric Current and Circuit FundamentalsDocument24 pagesElectric Current and Circuit FundamentalsJohaina NorNo ratings yet
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsFrom EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Peterdruckers Whatmakesaneffectiveleaderpps 150823134802 Lva1 App6891Document20 pagesPeterdruckers Whatmakesaneffectiveleaderpps 150823134802 Lva1 App6891cuambyahooNo ratings yet
- Immigration To Australia-StepbyStep Guide (Subclass 189&190) V3.0Document5 pagesImmigration To Australia-StepbyStep Guide (Subclass 189&190) V3.0cuambyahooNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Business - Report WritingDocument16 pagesFaculty of Business - Report WritingcuambyahooNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Business - Report WritingDocument16 pagesFaculty of Business - Report WritingcuambyahooNo ratings yet
- Democracy Accountability and RepresentationDocument25 pagesDemocracy Accountability and RepresentationcuambyahooNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy Act 67Document11 pagesPharmacy Act 67Aqeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- PPSC Advt 60-2017 - 48cmx8colDocument1 pagePPSC Advt 60-2017 - 48cmx8colcuambyahooNo ratings yet
- Advt - No - 1-2018Document5 pagesAdvt - No - 1-2018aminaNo ratings yet
- Balance Sheet Format PDFDocument1 pageBalance Sheet Format PDFpraveenyarandoleNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy Act 67Document11 pagesPharmacy Act 67Aqeel AhmedNo ratings yet
- Advt - No - 1-2018Document5 pagesAdvt - No - 1-2018aminaNo ratings yet
- Aleppo massacres and need for justiceDocument28 pagesAleppo massacres and need for justicecuambyahooNo ratings yet
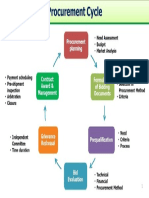
- Procurement Cycle PDFDocument1 pageProcurement Cycle PDFcuambyahoo100% (1)
- Medialeer Engels HsDocument1 pageMedialeer Engels HscuambyahooNo ratings yet
- Schmal - Cdncrimtdy - 2e - ch03 (Compatibility Mode) PDFDocument2 pagesSchmal - Cdncrimtdy - 2e - ch03 (Compatibility Mode) PDFcuambyahooNo ratings yet
- Quetta Attack PDFDocument1 pageQuetta Attack PDFcuambyahooNo ratings yet
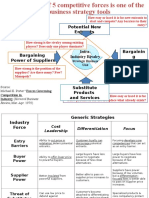
- Potential New Entrants: Strategic Business UnitDocument6 pagesPotential New Entrants: Strategic Business UnitcuambyahooNo ratings yet
- HomeostasisDocument36 pagesHomeostasisUwais AhmedNo ratings yet
- Criminology Reviewer For Licensure Exam And Board ExaminationDocument48 pagesCriminology Reviewer For Licensure Exam And Board ExaminationJona Addatu96% (24)
- Richard Nixon - Resignation Address PDFDocument4 pagesRichard Nixon - Resignation Address PDFcuambyahooNo ratings yet
- Schmal Cdncrimtdy 2e Ch11 (Compatibility Mode)Document2 pagesSchmal Cdncrimtdy 2e Ch11 (Compatibility Mode)cuambyahooNo ratings yet
- Quetta Attack PDFDocument1 pageQuetta Attack PDFcuambyahooNo ratings yet
- Workshop IntroDocument41 pagesWorkshop Introjdpatel28No ratings yet
- Impact of Demographic Changes On Inflation in Pakistan: A A J, F F F MDocument1 pageImpact of Demographic Changes On Inflation in Pakistan: A A J, F F F McuambyahooNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy S&G 06Document13 pagesEnthalpy S&G 06OnSolomonNo ratings yet
- 17 LectureDocument61 pages17 LecturecuambyahooNo ratings yet
- A Kashmir Statement by Ashraf JhangirDocument5 pagesA Kashmir Statement by Ashraf JhangircuambyahooNo ratings yet
- Area Population Density and Urban Rural Proportion, PakistanDocument1 pageArea Population Density and Urban Rural Proportion, PakistanZeibJahangirNo ratings yet
- Minority Report 2016Document70 pagesMinority Report 2016cuambyahooNo ratings yet
- Pakistan 1998 Census Unemployment Rates by Gender and LocationDocument1 pagePakistan 1998 Census Unemployment Rates by Gender and LocationcuambyahooNo ratings yet