Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Parkinsons Nurse Care Plan
Uploaded by
shaleahOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Parkinsons Nurse Care Plan
Uploaded by
shaleahCopyright:
Available Formats
HOWARD COMMUNITY COLLEGE
NURSING EDUCATION PROGRAM
NURSING CARE PLAN
Student Name: Shaleah McQueen
12/2/16_____________________
Patient Initials: C.B
Age/Sex
Date Submitted:
74
Medical Diagnosis
Parkinsons Disease
Complete using your nursing textbooks (cite references used). Underline the etiologies and clinical
manifestations that relate to your client.
I.
Pathophysiology:
The pathologic process of PD involves degeneration of the dopamine producing neurons in the
substanstia nigra of the midbrain, that interrupts the normal balance between DA and
Acetylcholine in the basal ganglia. PD manifestations occurs when 80% of neurons in the
substantia nigra are lost.
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter essential for normal functioning of the extrapyramidal motor
system. Including control of posture, support, and voluntary motion.
(Lewis, 2011) pg.1432
II.
Etiology:
The exact cause of PD is unknown, a complex interplay of environmental and genetic factors is
involved. 10%-15% of PD patients have a family history of the disease. Many autosomal
dominant and recessive genes have been linked to familial PD.
(Lewis, 2011) pg.1432
III.
Clinical Manifestations (Signs & Symptoms):
Gradual/insidious onset
Tremor
1st Year Nursing\339544741.doc
IV.
Rigidity
Bradykinesia
Slight limp
Decreased arm swing
Dysphagia
Treatment and Nursing Management:
V.
Antiparkinsonian Drugs (Drug Therapy)- correcting the imbalance of neurotransmitters
within the CNS
Deep brain stimulation
Ablation surgery
Diagnostic Studies
VI.
There is no specific diagnostic test for PD
Diagnosis is based on clinical features
When at least two of the three signs of the triad (tremor, rigidity, and bradykinesia) are
present
PD is ultimately confirmed when the patient has a positive response to antiparkinsonian
drugs
MRI
Rule out the side effects of phenothiazine, reserpine, benzodiazepines, haloperidol.
Plan ample time for eating to avoid frustration( foods that are easily swallowed and
chewed/ fruits/ adequate roughage)
Discharge Planning and Client Teaching
Teaching and nursing care directed toward maintenance of health
Promote/teach about physical exercise that can limit the consequences of decreased motility
Consult a physical therapist
Consult an occupational therapist to assist patient with self-care strategies
Assist the patient by listening, providing coping strategies, challenging distorted thoughts, and
encouraging social interactions.
Encourage environmental changes such as removing rugs, excess furniture, and wearing easy slip on
shoes.
1st Year Nursing\339544741.doc
VIII.
Growth & Development
According to Erikson: Stage: Late Adulthood______________ Crisis:
_Despair vs. Integrity_______________________
Tasks:
A.
Describe your patients ability to achieve their growth and developmental tasks.
How is this ability affected by the underlying disease process and/or the current
admission?
The patient has the ability to achieve their growth and developmental tasks. The past makes
engineering jokes referring to his old career and is in good spirits even when in pain. The patient
has accepted both of his diseases, but seems like he could be struggling to cope with both at the
same time.
B.
IX.
List nursing actions to assist your client in meeting their growth and
developmental needs.
Encourage the patient to join a support group with people going through similar things
Encourage the patient to do as much self-care as he can
Promote exercising to exercise
List in priority order all relevant nursing diagnoses for your patient. Include
NANDA diagnosis, etiology and supporting data.
Impaired physical mobility related to rigidity, bradykinesia, and akinesia and the patients
slowness of moment.
Imbalanced nutrition: less than body requirements related to inability to ingest food, the
patient having trouble swallowing (the patient stated a pill was stuck in his throat for 6
hours)
Impaired swallowing related to neuromuscular impairment (decreased gag reflex), the
patient being NPO with sips.
1st Year Nursing\339544741.doc
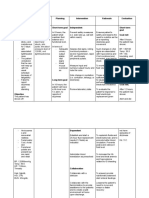
Assessment Data
Nursing Diagnosis
Nursing Actions
Rationale
Evaluation
Identify all data that support the
priority nursing diagnosis.
According to NANDA
List in order of priority. Label
aspect of care.
State the rationale for each
nursing action. Cite reference
and page number.
Evaluate the patient response to
each nursing action providing
objective & subjective data.
Revise nursing actions as
necessary.
Subjective:
The patient stated last
night a pill was stuck in
his throat for 6 hours
The patient stated he had
a difficult time taking his
medication.
Objective:
NPO with sips with
medication, and hard
candy
Calcium- 7.9(decreased)
Magnesium
1.5(decreased)
HCT- 32.9%
Constipation: prescribed
laxatives and constipation
drugs
Imbalanced
nutrition: less than
body requirements
related to inability
to ingest food, the
patient having
trouble swallowing
(the patient stated a
pill was stuck in his
throat for 6 hours)
Expected Outcome:
Short Term Goal (STG):
The patient will
understand and explain
an adequate diet plan to
maintain nutrition at the
end of the shift/
Long Term Goal (LTG):
The patients IV therapy
will fix the electrolyte
imbalance and his I and
Os will be maintained by
discharge.
1st Year Nursing\NURS-133 Accelerated\339544741.doc
Nutritional: Teach the
patient about eating
several small meals a day
that contain roughage
and fruit.
Pharmacological: The
nurse will administer
constipation medication
Rehabilitation: The nurse
will promote exercising
and a well-balanced diet
Physiological: The nurse
will measure the patients
Is and Os to maintain
an equal balances of fluid
going in and come out.
1. The diet should
contain roughage
and fruit to avoid
constipation.
Eating 6 small
meals a day may
be less exhausting
than eating three
large meals a day
(Lewis,2011, pg.
1436)
2. Exercise can limit
the consequences
of decreased
mobility such as
muscle atrophy,
contractures, and
constipation.
(lewis,2011
pg.1437)
3.
Evaluate each expected
outcome:
Short Term Goal (STG):
Long Term Goal (LTG):
1st Year Nursing\NURS-133 Accelerated\339544741.doc
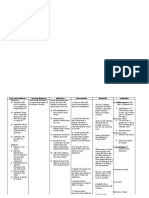
Assessment Data
Nursing Diagnosis
Nursing Actions
Rationale
Evaluation
Identify all data that support the
priority nursing diagnosis.
According to NANDA
List in order of priority. Label
aspect of care.
State the rationale for each
nursing action. Cite reference
and page number.
Evaluate the patient response to
each nursing action providing
objective & subjective data.
Revise nursing actions as
necessary.
Expected Outcome:
Short Term Goal (STG):
Long Term Goal (LTG):
Evaluate each expected
outcome:
Short Term Goal (STG):
Long Term Goal (LTG):
1st Year Nursing\NURS-133 Accelerated\339544741.doc
MEDICATION PREPARATION SHEET
Allergies:
No known allergies
Med as per MAR: acetaminophen
MD Order: Acetaminophen(Tylenol) tablet 650 mg
Time(s) Due: 1000
Generic/Trade Name: Tylenol
Normal Dosage: 325-650mg
Classification/Action: Inhibits synthesis of prostaglandins that may serve as mediators of
pain and fever, primarily in the CNS
Indication for Patient: Treatment of mild pain
Major Side Effects: anxiety, headache, fatigue
Parameters Checked: Pain level:2
Med as per MAR: calcium gluconate 1 g in sodium chloride 0.9% 100ml iVPB
MD Order: calcium gluconate 1 g in sodium chloride 0.9% 100ml iVPB
Time(s) Due: 845
Generic/Trade Name: Kalcinate
Normal Dosage: 0.5g-2g
Classification/Action: essential for nervous, muscular, and skeletal systems. Maintain cell
membrane and capillary permeability
Indication for Patient: Treatment and prevention of hypocalcemia
Major Side Effects: headache, tingling, syncope, Cardiac arrest
Parameters Checked: no parameters
Med as per MAR: docusate sodium(COLACE) capsule 100 mg
MD Order: docusate sodium(COLACE) capsule 100 mg
Time(s) Due: 1000
Generic/Trade Name: COLACE
Normal Dosage: 50-400mg
Classification/Action: promotes incorporation of water into stools
Indication for Patient: prevention of constipation
Major Side Effects: throat irritation, mild cramps, diarrhea
Parameters Checked: no parameters
Med as per MAR: magnesium sulfate 2g in 50 mL IVPB
MD Order: magnesium sulfate 2g in 50 mL IVPB
Time(s) Due: 845
Generic/Trade Name: magnesium sulfate
Normal Dosage: 2 grams
Classification/Action: essential for the activity of many enzymes. Neurotransmission and
muscular excitability
1st Year Nursing\NURS-133 Accelerated\339544741.doc
Indication for Patient: treatment/prevention of hypomagnesemia
Major Side Effects: drowsiness, decreases respiratory rate
Parameters Checked: Low mg lab values(1.5)
Med as per MAR: rasagiline(AZILECT) tablet 1 mg
MD Order: rasagiline(AZILECT) tablet 1 mg
Time(s) Due: 1000
Generic/Trade Name:AZILECT
Normal Dosage:1mg
Classification/Action: inactivates monoamine oxidase by binding to it at type B to increase
dopamine available in CNS
Indication for Patient: History of Parkinsons disease
Major Side Effects: depression, dizziness
Parameters Checked: N/a
Med as per MAR: senna(SENOKOT) tablet 8.6 mg
MD Order: senna(SENOKOT) tablet 8.6 mg
Time(s) Due: 1000
Generic/Trade Name:SENOKOT
Normal Dosage: 2 tablets once daily
Classification/Action: acts as a local irritant on the colon stimulating peristalsis
Indication for Patient: treatment of constipation associated with dry hard stools
Major Side Effects: electrolyte imbalances, dehydration
Parameters Checked: n/a
1st Year Nursing\NURS-133 Accelerated\339544741.doc
You might also like
- Encyclopedia of Energy Engineering and Technology PDFDocument1,708 pagesEncyclopedia of Energy Engineering and Technology PDFPradeep SarodeNo ratings yet
- Care Plan Small Bowel ObstructionDocument9 pagesCare Plan Small Bowel Obstructionshaleah80% (5)
- (1)Document94 pages(1)Luigi TencoNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPAbbie TantengcoNo ratings yet
- Get the Most Out of Your Nutanix Cloud Platform TrainingDocument12 pagesGet the Most Out of Your Nutanix Cloud Platform TrainingJohramoNo ratings yet
- The Brain Fitness Book Activities and Puzzles To Keep Your Mind Active and Healthy (Rita Carter) (Z-Library)Document192 pagesThe Brain Fitness Book Activities and Puzzles To Keep Your Mind Active and Healthy (Rita Carter) (Z-Library)Richard Wokard100% (1)
- GSM BTS Over IP Deployment Troubleshooting GuideDocument27 pagesGSM BTS Over IP Deployment Troubleshooting GuideKeartichai Chomtaku100% (1)
- NCP and Drug Study For Case in SleDocument34 pagesNCP and Drug Study For Case in SlePaolo Vittorio Perdigueros GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Quadrant Grid: Worksheet For Calculating Quadrant Scores On The Sensory PROFILE (Dunn, 1999) For Children Ages 3-10 YearsDocument2 pagesQuadrant Grid: Worksheet For Calculating Quadrant Scores On The Sensory PROFILE (Dunn, 1999) For Children Ages 3-10 YearsLorenzo CastroNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPMarius Clifford BilledoNo ratings yet
- A1 Cp-Self Care DeficitDocument7 pagesA1 Cp-Self Care DeficitCherryjuliejane Rosales CaperidaNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPranee diane0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan for Parkinson's Disease and Nutritional ImbalanceDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan for Parkinson's Disease and Nutritional Imbalancedonnam8689% (9)
- School Learning and Development Plan For Head TeachersDocument3 pagesSchool Learning and Development Plan For Head TeachersLiza Bacudo100% (1)
- Revised NCP (Baiae)Document9 pagesRevised NCP (Baiae)Jennifer BactatNo ratings yet
- Gi-Rle - NCP For Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument2 pagesGi-Rle - NCP For Deficient Fluid VolumeEvangeline Villa de Gracia100% (1)
- Lesson Plan With GAD Integration SampleDocument7 pagesLesson Plan With GAD Integration SampleMae Pugrad67% (3)
- NCP CVDDocument4 pagesNCP CVDNadeene Corpuz SubradoNo ratings yet
- Impaired Tissue IntegrityDocument2 pagesImpaired Tissue IntegrityJacoJone11100% (1)
- Demonstrate: Pain Coping TechniquesDocument4 pagesDemonstrate: Pain Coping TechniquesMae Therese B. MAGNO100% (1)
- Afinidad, Jiezl A: Davao Doctors College Nursing ProgramDocument4 pagesAfinidad, Jiezl A: Davao Doctors College Nursing ProgramJiezl Abellano AfinidadNo ratings yet
- NCP - ConstipationDocument2 pagesNCP - Constipationgringo1388No ratings yet
- Case Study NCPDocument4 pagesCase Study NCPKelly OstolNo ratings yet
- Understanding Biopsy ProcedureDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Biopsy ProcedureDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Post-Surgical PainDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Post-Surgical PainAngelgodess Athena-envyNo ratings yet
- Emj Cases : Questions For Case 1Document8 pagesEmj Cases : Questions For Case 1Azmyza Azmy100% (1)
- NCP Inactivity ToleranceDocument16 pagesNCP Inactivity ToleranceChrisTine M. MoralesNo ratings yet
- NCP Sensory PerceptionDocument2 pagesNCP Sensory PerceptionGina TangneneiNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN FOR ASTHMA MANAGEMENTDocument3 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN FOR ASTHMA MANAGEMENTPaul Cubacub100% (1)
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument5 pagesIneffective Tissue PerfusionKryza Dale Bunado BaticanNo ratings yet
- Disturbed Body Image Nursing InterventionsDocument11 pagesDisturbed Body Image Nursing InterventionsNdel LindaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Objective: Admission DiagnosisDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Objective: Admission DiagnosisJe ZalNo ratings yet
- Disharge Plan Patient'S Outcome Criteria Nursing OrderDocument2 pagesDisharge Plan Patient'S Outcome Criteria Nursing OrderDianne Loregas SanchezNo ratings yet
- NCP UtiDocument1 pageNCP UtiAgentpiinkkNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument6 pagesNCPgenevieve kryzleiNo ratings yet
- Impaired Physical Mobility...Document3 pagesImpaired Physical Mobility...Christy BerryNo ratings yet
- DP Discharge Plan@@@@@@@@Document6 pagesDP Discharge Plan@@@@@@@@Maemae SumalinogNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument14 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationJennifer ArdeNo ratings yet
- NCP Intra FinalDocument7 pagesNCP Intra FinalRoxanne Ganayo ClaverNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPJohn Reiner JimenezNo ratings yet
- Improving Dental Hygiene in Grade III StudentsDocument3 pagesImproving Dental Hygiene in Grade III Studentsx483xDNo ratings yet
- NCP Self CaRE DeficitDocument1 pageNCP Self CaRE Deficitnicole pageNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument10 pagesNCPCristina L. JaysonNo ratings yet
- Risk For Bleeding - Cirrhosis NCPDocument2 pagesRisk For Bleeding - Cirrhosis NCPPaula AbadNo ratings yet
- Metro Manila Development Screening TestDocument3 pagesMetro Manila Development Screening TestMae PonceNo ratings yet
- Final Course in The WardDocument4 pagesFinal Course in The WardMichael Boado100% (1)
- HTP Ineffective BreathingDocument3 pagesHTP Ineffective BreathingShyrra Edades PinderNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN FOR POSTPARTUM HEMORRHAGEDocument3 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN FOR POSTPARTUM HEMORRHAGEKrizzy Chen100% (1)
- Dynastat: What Is in This LeafletDocument4 pagesDynastat: What Is in This LeafletBenj GilbuenaNo ratings yet
- 3 Drug Study & 1 NCPDocument4 pages3 Drug Study & 1 NCPAnnie Christine RiveraNo ratings yet
- NCP AgeDocument1 pageNCP AgecaressmeNo ratings yet
- TAHBSO ReportDocument4 pagesTAHBSO ReportsachiiMeNo ratings yet
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDocument3 pagesImpaired Gas Exchange NCPRomel BaliliNo ratings yet
- NcpsDocument10 pagesNcpskotoirNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument10 pagesNCPNefre Dayap DarrocaNo ratings yet
- Aaa Gastrectomy NCP FinalDocument13 pagesAaa Gastrectomy NCP Finallexzaf100% (1)
- NCP 6-10Document4 pagesNCP 6-10Junabel EmNo ratings yet
- Assignment For Oxy. Online BasedDocument5 pagesAssignment For Oxy. Online BasedNurhassem Nor AkangNo ratings yet
- 13 Areas of AssessmentDocument4 pages13 Areas of Assessmentnusdhockey0% (1)
- Dysfunction at The First Stage of Labor: Prolonged Latent PhaseDocument5 pagesDysfunction at The First Stage of Labor: Prolonged Latent PhaseRam Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Case Study Ugib Lower MBDocument65 pagesCase Study Ugib Lower MBQuolette Constante100% (1)
- Disturbed Sleeping PatternDocument5 pagesDisturbed Sleeping PatternEllenare RacionNo ratings yet
- NCP (Or) ThyroidectomyDocument3 pagesNCP (Or) ThyroidectomyChiz CorreNo ratings yet
- Disturbed Sleep PatternDocument1 pageDisturbed Sleep PatternHsintan HsuNo ratings yet
- Diarrhea Care PlanDocument2 pagesDiarrhea Care Planzepoli_zepoly6232100% (1)
- NCPDocument3 pagesNCPNika LoNo ratings yet
- Managing Fatigue Through Activity Pacing and RestDocument2 pagesManaging Fatigue Through Activity Pacing and ResthaniehaehaeNo ratings yet
- Reaction Paper ERDocument1 pageReaction Paper ERVann Anthony FuentesNo ratings yet
- Ncar (Sr. Nerlyn)Document9 pagesNcar (Sr. Nerlyn)nerlynNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Notes SMDocument24 pagesCardiovascular Notes SMshaleahNo ratings yet
- Fluid and ElectrolytesDocument13 pagesFluid and ElectrolytesshaleahNo ratings yet
- BSCI105Document1 pageBSCI105shaleahNo ratings yet
- Bsci201 NotesDocument4 pagesBsci201 NotesshaleahNo ratings yet
- Bsci201 NotesDocument4 pagesBsci201 NotesshaleahNo ratings yet
- European Project Semester MinorDocument3 pagesEuropean Project Semester MinorIrving Delgado SilvaNo ratings yet
- ACT-R Intro TutorialDocument64 pagesACT-R Intro TutorialSoheil EngineerNo ratings yet
- Finan ResumeDocument3 pagesFinan ResumeNhat HoangNo ratings yet
- 1 - Progress Test: Working With WordsDocument2 pages1 - Progress Test: Working With WordsSamNo ratings yet
- Family Breakdown PDFDocument11 pagesFamily Breakdown PDFSamantha GordonNo ratings yet
- Pancasila Character EducationDocument6 pagesPancasila Character EducationDaniel Prayoga D100% (1)
- MODULE 4 Semantics 201 PDFDocument5 pagesMODULE 4 Semantics 201 PDFShean Jerica SalemNo ratings yet
- Ethical Issues in Multicultural PopulationsDocument19 pagesEthical Issues in Multicultural Populationsapi-162851533No ratings yet
- Top Business Schools in South Asia and ComparisonDocument4 pagesTop Business Schools in South Asia and Comparisonraihans_dhk3378No ratings yet
- Dr. Atanas Kirjakovski: Social PsychologyDocument33 pagesDr. Atanas Kirjakovski: Social PsychologyAlmirMuratiNo ratings yet
- HDC CHÍNH THỨC TIẾNG ANH CHUYÊN 2022Document3 pagesHDC CHÍNH THỨC TIẾNG ANH CHUYÊN 2022Hoàng HuyNo ratings yet
- Characterization: ProcessDocument2 pagesCharacterization: ProcessVesselofhonour MontagueNo ratings yet
- Day 1 Introduction, Project Environment & Role of Project Manager (1) - Read-Only (53) - Read-OnlyDocument33 pagesDay 1 Introduction, Project Environment & Role of Project Manager (1) - Read-Only (53) - Read-OnlySuraj ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Oct 19, 2023Document10 pagesAdobe Scan Oct 19, 2023niladriputatunda1No ratings yet
- Assessment and Evaluation FinalDocument13 pagesAssessment and Evaluation Finalnuvish07No ratings yet
- Solution Architect/Analyst Boston, MADocument4 pagesSolution Architect/Analyst Boston, MAMohamamdNo ratings yet
- NLU Delhi Merit ListDocument6 pagesNLU Delhi Merit Listsarvagya vermaNo ratings yet
- Summary of PBB 2019 data for Region IX elementary schoolsDocument35 pagesSummary of PBB 2019 data for Region IX elementary schoolsVIRGILIO GUZONNo ratings yet
- GE 8 EthcsDocument22 pagesGE 8 EthcsWilliam Soneja CalapiniNo ratings yet
- NGSS & Common Core 5E Lesson Plan: Engaging in Argument From EvidenceDocument3 pagesNGSS & Common Core 5E Lesson Plan: Engaging in Argument From Evidenceapi-300263583No ratings yet
- Dr. Sarbari Guha Physics ProfileDocument5 pagesDr. Sarbari Guha Physics Profilevishwas gaurNo ratings yet
- Outside State Colleges Email DetailsDocument84 pagesOutside State Colleges Email Detailsuniquerealestate098No ratings yet