Professional Documents
Culture Documents
02 Switchgears Abhishek Goyal
Uploaded by
Abhishek GoyalCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
02 Switchgears Abhishek Goyal
Uploaded by
Abhishek GoyalCopyright:
Available Formats
Agenda:
Definition of Switchgear
Busbar & Types
Contactor
Fuse
Meters
Electrical Panel
Earthing
12/3/2016
In an electric power system, switchgear is the combination of electrical
disconnect switches, fuses or circuit breakers used to control, protect
and isolate electrical equipment.
Switchgear is used both to de-energize equipment to allow work to be
done and to clear faults downstream. This type of equipment is
important because it is directly linked to the reliability of the electricity
supply.
Bus bar / Cables
Circuit breaker/ Fuses
Relays
MCC/ PCC Panel/ Bus duct
Control Panel
Contactors
Timers
Insulators
Meters (KWH, V,I,PF,F etc.)
Battery Chargers
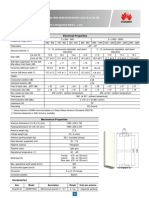
Busbar is an electrical conductor material (copper or aluminum),
suitably sized to carry specified currents both thermal and short
circuit for a defined time.
It supported on insulators or surrounded by insulation materials,
used to make common connections between many circuits or
interconnect incoming power supply and outgoing feeders.
The shape of busbar material can be any, but widely seen are
rectangular, circular tubes, wires etc.
The major types are :
(1) Rigid bus-bars, used at low, medium, and high voltage;
(2) Strain bus-bars, used mainly for high voltage;
(3) Insulated-phase bus-bars, used at medium voltage; and
(4)Sulfur hexafluoride (SF6)-insulated bus-bars, used
medium- and high-voltage systems.
in
The rigid bus-bar is an aluminum or copper bar, which is supported by
porcelain insulators.
The strain bus-bar is a flexible, stranded conductor which is strung between
substation metal structures and held by suspension-type insulators.
The insulated-phase bus-bar is a rigid bar supported by insulators and
covered by a grounded metal shield. The main advantage of this system is
the elimination of short circuits between adjacent phases.
The sulfur hexafluoride-insulated bus-bar is a rigid aluminum tube,
supported by insulators and installed in a larger metal tube, which is filled
with high-pressure sulfur hexafluoride gas
Size of busbar (W*H*L)
Sleeves (Poly vinylidene Fluoride)
Heat Shrink Wire Connector
Dielectric strength: 2kV
A contactor is an electrically controlled switch used for switching a power
circuit, similar to a relay except with higher current ratings. A contactor is
controlled by a circuit which has a much lower power level than the switched
circuit.
Contactor Specification
1. Rated voltage, Rated current
2. Short circuit current
3. Frequency
4. Nos of Pole
5. Nos of NO/NC contact
6. Type, model etc.
Contactor coil specification
1. AC Supply 1Ph,2Ph, 50HZ/60HZ
2. DC Supply 5/12/24/48/110 VDC
Fuse use for protection into the electrical
circuit or system (one time). If current go
beyond the fuse limit it will be blow
during operation & stop the electrical
equipment (For safer side).
In electronics and electrical engineering a
fuse is a type of low resistance resistor
that acts as a sacrificial device to provide
over-current protection, of either the
load or source circuit. When current go
beyond the fuse rated current, it will
disconnect the live circuit.
Types of Fuse:
1. Glass Fuse
2. HRC Fuse
3. Cylindrical HRC Fuse
4. HT HRC Fuse (3.6KV to 36KV)
5. Bottle Fuse
6. Rewirable Fuse
An electricity meter or energy meter is a device that
measures the amount of electrical energy consumed
by a residence, business or an electrically powered
device.
The most common unit of measurement on the
electricity meter is the Kilowatt hour [kWh], which is
equal to the amount of energy used by a load of one
kilowatt over a period of one hour, or 3,600,000
joules.
Type
1. Electromechanical meter
2. Microprocessor meter
3. Electronic meter
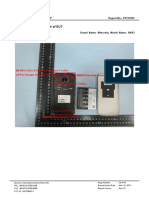
Meter connected with voltage supply (3Ph) and
current transformer wire. It can be show the voltage,
current, PF, KWH, and frequency as per the meter
model.
Diagram of 3Phase LT meter
Required 440VAC: Meter, CT, Fuse and Cable.
Types (In terms of principle)
1. Solid state Meter
2. Electromechanical Meter
Types (In terms of value)
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Ammeter
Voltmeter
Phase Sequence Meter
Frequency Meter
Power Factor Meter
Trivector Meter (KWH Meter)
Synchronous Meter
Temperature Meter
Type of panels:
1.MCC Panel
2.PCC Panel
3.RTCC Panel
4.APFC Panel
5.HT Panel
Parts are:
1. Power & Control Panel
2. Cables
3. SFU
4. Fuse
5. MCB
6. Power & Control Contactors
7. Control Relay
8. Relays
9. Connectors & Terminals
10. Timer
11.Volt & Current Meters
12.CT
13.Busbars
14.Motors
15.Push Button
16.Selector Switch
17.Indication Lamp
18.Interlocks RTD , Level etc.
19.Transformer
APFC or Automatic Power Factor Control Panels are mainly used for the improvement of
Power Factor. Power Factor can be explained as ratio of active power to apparent power
and it is a key factor in measuring electrical consumption.
The main features of our control panels are:
1. Maintains high Power Factor constantly
2. High efficiency
3. In-built independent fuses/MCB's/MCCB's
4. Protection from excess power in the system.
5. Prevents leading Power Factor in low load conditions
6. Clearly marked buttons and indicators
7. Line Reactors (5.67%, 7%, 14%) for minimizing Harmonic.
8. Easy to use
9. Corrosion-resistant
10. Long lasting
11. Electrical insulation
12. Protects electrical equipments.
13. Capacitor Switching- Contactor/Thyristor.
14. Auto/Manual Switching function.
15. Online Capacitor health Check function.
KVA=KW+ KVAR
And KVAR=KW*tan
Electrical Earthing is classified into many types as
1)
2)
3)
4)
5)
6)
7)
Neutral Earthing
Body Earthing
Pipe Earthing
Plate Earthing
Chemical Earthing
Ground Compound Earthing
Grid Earthing (<0.2ohm)
Inverter used for converting D.C to A.C supply. Inverter we
can use in industry for controlling the electrical motor speed
by controlling a voltage, frequency and current etc.
Thank you
12/3/2016 ABHISHEK KUMAR GOYAL BE
/MBA / PGDBA
19
You might also like
- 06 Transformer Abhishek GoyalDocument21 pages06 Transformer Abhishek GoyalAbhishek GoyalNo ratings yet
- 07 Generator Abhishek GoyalDocument13 pages07 Generator Abhishek GoyalAbhishek GoyalNo ratings yet
- 05 Motor Abhishek GoyalDocument18 pages05 Motor Abhishek GoyalAbhishek GoyalNo ratings yet
- 04 Circuit Breaker Abhishek GoyalDocument14 pages04 Circuit Breaker Abhishek GoyalAbhishek GoyalNo ratings yet
- 00 Basic Electrical Abhishek GoyalDocument22 pages00 Basic Electrical Abhishek GoyalAbhishek GoyalNo ratings yet
- 01 Transmission Abhishek GoyalDocument8 pages01 Transmission Abhishek GoyalAbhishek GoyalNo ratings yet
- 03 Relay Abhishek GoyalDocument13 pages03 Relay Abhishek GoyalAbhishek GoyalNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Section 4 Varicap Diodes: Selection Guide Data Sheet Type NumberDocument6 pagesSection 4 Varicap Diodes: Selection Guide Data Sheet Type NumberrowataNo ratings yet
- HG253s V2 Home Gateway Product DescriptionDocument14 pagesHG253s V2 Home Gateway Product DescriptionceitNo ratings yet
- Nama: Andi Ihzan Iznain NIM: 1926042013 Prodi: Pendidikan Vokasional MekatronikaDocument9 pagesNama: Andi Ihzan Iznain NIM: 1926042013 Prodi: Pendidikan Vokasional MekatronikaAndi Ihzan IznainNo ratings yet
- DSTVDocument3 pagesDSTVMega ByteNo ratings yet
- Eltek Smps SpecDocument2 pagesEltek Smps SpecJohn100% (2)
- Comanda Electols Fisier Public ElforumDocument4 pagesComanda Electols Fisier Public ElforumsumodicaNo ratings yet
- Alcatel One Touch 535 735 User ManualDocument49 pagesAlcatel One Touch 535 735 User ManualEdgar Jose Aranguibel MorilloNo ratings yet
- HArmonics NotinghamDocument27 pagesHArmonics NotinghamRyanNo ratings yet
- Antenna Scenario 20-AQU4518R23v06-1963 DatasheetDocument2 pagesAntenna Scenario 20-AQU4518R23v06-1963 DatasheetvictorNo ratings yet
- BSE Electronics SyllabusDocument110 pagesBSE Electronics SyllabusJinu MadhavanNo ratings yet
- Yacine 2017Document6 pagesYacine 2017hao.nguyenismeNo ratings yet
- Online Parking ReservationDocument13 pagesOnline Parking ReservationYesha PatelNo ratings yet
- QBE2002-PDocument4 pagesQBE2002-PAnonymous 7z6OzoNo ratings yet
- 2004 Lincoln Navigator Owner's GuideDocument384 pages2004 Lincoln Navigator Owner's GuideKristinaNo ratings yet
- 950g 3jw Elect.Document10 pages950g 3jw Elect.Miguel Angel Garrido CardenasNo ratings yet
- 2007 KJ Liberty ManualDocument417 pages2007 KJ Liberty Manualcarlos100% (1)
- Face Detection SystemDocument2 pagesFace Detection SystemWagner Quezada IparraguirreNo ratings yet
- Altimatic Iiic Service ManualDocument239 pagesAltimatic Iiic Service ManualDRAGONFLYDF63% (8)
- Install Windows 7 From USB PDFDocument2 pagesInstall Windows 7 From USB PDFemonwreNo ratings yet
- Centrifuges Training GuideDocument19 pagesCentrifuges Training GuideMoe MoeNo ratings yet
- Photographs of EUTDocument32 pagesPhotographs of EUTBaron MunchausenNo ratings yet
- Physics Mock Exam 2017Document6 pagesPhysics Mock Exam 2017sulayajannyNo ratings yet
- Interfacing Temperature Sensor With MPLAB Xpress Evaluation Board Using I2C CommunicationDocument13 pagesInterfacing Temperature Sensor With MPLAB Xpress Evaluation Board Using I2C CommunicationsivaNo ratings yet
- C172R Checklist PDFDocument2 pagesC172R Checklist PDFNirgunaRamkissoonNo ratings yet
- Austin Isolation TransformerDocument9 pagesAustin Isolation TransformermithunprayagNo ratings yet
- RTU5015 User Manual V1.3Document12 pagesRTU5015 User Manual V1.3EuuE20080% (1)
- Fundamentals of Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing by Alex Krulikowski Downloads TorrentDocument3 pagesFundamentals of Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing by Alex Krulikowski Downloads TorrentAshok MadhanNo ratings yet
- Oss Commands NotesDocument95 pagesOss Commands NotessonnyNo ratings yet
- Assistant Electrician PDFDocument169 pagesAssistant Electrician PDFRajat SharmaNo ratings yet
- Epa300 Epa900 QSG WWDocument17 pagesEpa300 Epa900 QSG WWJavierLopezNo ratings yet