Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Acs NCP
Uploaded by
Elisa KerrOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Acs NCP
Uploaded by
Elisa KerrCopyright:
Available Formats
V.
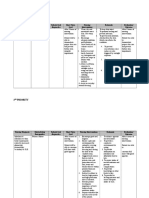
NURSING CARE PLAN
1ST PRIORITY
Nursing Diagnosis
Ineffective cardiac
tissue perfusion
related to reduced
coronary blood
flow.
Related drug
therapeutics
Captopril
Trimetazidine
Isosorbide
Mononitrate
Clopidrogrel
Related Lab
diagnostics
Chest x-ray
Electrocardiogr
am
Arterial Blood
Gases
Capillary refill
Short Term
Goal
After 8 hours of
nursing
intervention:
Patient will be
able to exhibit
no further
worsening/repet
ition of deficits
and maintain
maximum
tissue perfusion
to vital organs
as evidenced by
warm and dry
skin, present
and vitals
within patients
normal range,
normal ABGs
and absence of
chest pain.
Nursing
Interventions
1. Asses for
signs of
decreased
tissue
perfusion.
2. Check for
respiration
and absence
of work or
breathing.
3. Check
Hemoglobin
levels and
pallor,
quality of
pulse.
4. Promote
active/passiv
e ROM
exercises
5. Administer
medications
as prescribed
such as
antiplatelet
and antihypertensive
s.
Rationale
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Provides baseline
for future
comparison.
Ischemic pain may
result in respiratory
distress.
Low levels reduce
the uptake of
oxygen at the
alveolar-capillary
membrane and
oxygen delivery to
tissues.
To prevent venous
stasis and further
circulatory
compromise.
To facilitate
perfusion by
reducing blood
viscosity and
coagulation and to
reduce systemic
vascular resistance
and optimize cardiac
output and
perfusion.
Evaluation/
Outcome
After 8 hours of
nursing
intervention:
Patient was able
to:
To exhibit no
further
worsening/repetit
ion of deficits
and maintain
maximum tissue
perfusion to vital
organs as
evidenced by
warm and dry
skin, present and
vitals within
patients normal
range, normal
ABGs and
absence of chest
pain.
2ND PRIORITY
Nursing Diagnosis
Decrease cardiac
output related to
alteration heart rate,
rhythm and
conduction.
Related drug
therapeutics
Captopril
Trimetazidine
Isosorbide
Mononitrate
Related Lab
diagnostics
Chest x-ray
Electrocardiogram
Short Term
Goal
After 8 hours
of nursing
intervention:
Patient will be
able to
demonstrate
adequate
cardiac output
as evidenced
by blood
pressure and
pulse rate
within normal
parameters
and ability to
tolerate
activity
without
dyspnea or
chest pain.
Nursing
Interventions
1. Assess the patient
on the following:
a. Skin color
b. Alteration in
LOC
c. Heart rate and
Blood
pressure
1. Administer
cardiac
medications such
as ACE inhibitors.
2. Record intake and
output
3. Position patient in
semi to high
fowlers
4. Administer
oxygen as
prescribed.
Rationale
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Assessment is required
in order to possible
problems that may lead
to worsening of
condition. Pale skin is
secondary to compensate
low cardiac output.
Restlessness and
irritability reflected
decreased cerebral
perfusion. Tachycardia
and low BP is a response
to compensate reduced
cardiac output.
Assess patients
tolerance before giving
medication.
Reduced cardiac output
results in reduced
perfusion of the kidneys.
To reduce preload and
ventricular filling when
fluid overload is the
cause.
Failing heart may not be
able to respond to
increased oxygen
demands.
Evaluation/
Outcome
After 8 hours of
nursing
intervention:
Patient was able
to:
Demonstrate
adequate
cardiac output
as evidenced
by blood
pressure and
pulse rate
within normal
parameters and
ability to
tolerate activity
without
dyspnea or
chest pain.
3rd PRIORITY
Nursing Diagnosis
Risk for
imbalanced fluid
volume related to
inadequate fluid
intake.
Related drug
therapeutics
Related Lab
diagnostics
Short Term
Goal
After 8 hours of
nursing
intervention:
Patient will
maintain
adequate fluid
intake as
evidenced by
systolic BP
greater than or
equal to 90
mmHg and
normal skin
turgor.
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Nursing
Interventions
Monitor and
document VS
especially BP
and HR.
Assess skin
turgor and oral
mucous
membranes for
dehydration/
Urge patient to
drink prescribed
amount of fluid.
Emphasize
importance of
oral hygiene.
Emphasize the
relevance of
maintaining
proper nutrition
and hydration.
Rationale
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Decrease in circulating
blood volume can cause
hypotension and
tachycardia.
Poor skin turgor may
indicate dehydration.
Older patient have a
decrease sense of thirst
and may need ongoing
reminders to drink.
Fluid deficit can cause a
dry, sticky mouth.
Attention to mouth care
promotes interest in
drinking an reduces
discomfort of dry
mucous membranes.
Increase the patients
knowledge level will
assist in preventing and
managing the problem.
Evaluation/
Outcome
After 8 hours of
nursing
intervention:
Patient was able
to:
Patient will
maintain
adequate fluid
intake as
evidenced by
systolic BP
greater than or
equal to 90
mmHg and
normal skin
turgor.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Asthma PathophysiologyDocument1 pageAsthma PathophysiologyElisa Kerr100% (2)
- Bachelor of Science Biomedical ScienceDocument1 pageBachelor of Science Biomedical SciencePasipanodya Muzenda100% (1)
- Mantoux TestDocument3 pagesMantoux Testfarrukhhussain2006No ratings yet
- Community Herbal MedicineDocument4 pagesCommunity Herbal MedicineMary Joyce Ariem100% (1)
- Workplace Site Audit Checklist PharmacyDocument3 pagesWorkplace Site Audit Checklist PharmacyWaqar LatifNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure ChartDocument5 pagesBlood Pressure Chartmahajan1963100% (1)
- Related LitDocument8 pagesRelated LitElisa KerrNo ratings yet
- Acs NCPDocument3 pagesAcs NCPElisa KerrNo ratings yet
- CVD PathoohysiologyDocument1 pageCVD PathoohysiologyElisa KerrNo ratings yet
- Systemic Lupuc ErthymosusDocument3 pagesSystemic Lupuc ErthymosusElisa KerrNo ratings yet
- Nursing care plan for skin lesions, nutrition, and activity toleranceDocument3 pagesNursing care plan for skin lesions, nutrition, and activity toleranceElisa Kerr100% (1)
- Bronchial Asthma PathophysiologyDocument1 pageBronchial Asthma PathophysiologyElisa Kerr100% (2)
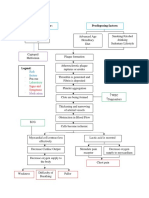
- Risk Factors and Processes Leading to Myocardial InfarctionDocument1 pageRisk Factors and Processes Leading to Myocardial InfarctionElisa KerrNo ratings yet
- Acute Gout Case StudyDocument2 pagesAcute Gout Case StudyElisa KerrNo ratings yet
- Safe and Effective CareDocument4 pagesSafe and Effective CareElisa KerrNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology CVD InfarctDocument1 pagePathophysiology CVD InfarctElisa KerrNo ratings yet
- SchizophreniaDocument7 pagesSchizophreniaElisa KerrNo ratings yet
- Notification Letter EnglishDocument1 pageNotification Letter EnglishJovele OctobreNo ratings yet
- Penerapan E-Resep Meningkatkan Mutu Farmasi RS di JakartaDocument5 pagesPenerapan E-Resep Meningkatkan Mutu Farmasi RS di JakartaIim RimbaNo ratings yet
- Impetigo in NeonatusDocument5 pagesImpetigo in Neonatusasep budiyantoNo ratings yet
- EEReview PDFDocument7 pagesEEReview PDFragavendharNo ratings yet
- Adolescent Health and Youth ProgramDocument77 pagesAdolescent Health and Youth ProgramRijane Tabonoc OmlangNo ratings yet
- MCQ 23Document10 pagesMCQ 23Old driverNo ratings yet
- Tarsal Tunnel SyndromeDocument2 pagesTarsal Tunnel SyndromeMuhammad Amri KautsarNo ratings yet
- General AnaestheticDocument10 pagesGeneral AnaestheticFeyaNo ratings yet
- Under Guidance of Mr. Mali K.K. (Assistant Professor) : 1 Yspm, YtcDocument41 pagesUnder Guidance of Mr. Mali K.K. (Assistant Professor) : 1 Yspm, YtcSabiruddin Mirza DipuNo ratings yet
- De Vries Et Al. (1998) and Bolman & de Vries (1998)Document2 pagesDe Vries Et Al. (1998) and Bolman & de Vries (1998)Anonymous 8rsxG4No ratings yet
- 3 Most Common Biochemical ImbalancesDocument4 pages3 Most Common Biochemical Imbalancescarlos100% (1)
- Corresponding Author: Dr. K. Ramu, Hemalatha .S 1.principalDocument5 pagesCorresponding Author: Dr. K. Ramu, Hemalatha .S 1.principalBalaMuruganNo ratings yet
- The Open Dentistry Journal: The Effect of Chin-Cup Therapy in Class III Malocclusion: A Systematic ReviewDocument16 pagesThe Open Dentistry Journal: The Effect of Chin-Cup Therapy in Class III Malocclusion: A Systematic ReviewmilanmashrukNo ratings yet
- Why Bladder Training Prior To Foley Catheter Removal Is Not BestDocument10 pagesWhy Bladder Training Prior To Foley Catheter Removal Is Not BestManoj KumarNo ratings yet
- Mixed Connective Tissue DZ (SLE + Scleroderma)Document7 pagesMixed Connective Tissue DZ (SLE + Scleroderma)AshbirZammeriNo ratings yet
- Expanded Mobile Crisis Outreach Team (EMCOT)Document3 pagesExpanded Mobile Crisis Outreach Team (EMCOT)Kyle A McCallNo ratings yet
- Asclepius Consulting IntroductionDocument3 pagesAsclepius Consulting Introductionapi-3710510No ratings yet
- Medical and Dental Clearance.1 2017Document2 pagesMedical and Dental Clearance.1 2017cristina tamonteNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Environmental Health and Safety PlanDocument23 pagesCOVID-19 Environmental Health and Safety PlanolaogunNo ratings yet
- Cancer Ms LecDocument16 pagesCancer Ms LecJulia Rae Delos Santos100% (1)
- Presented by Animesh Amal: Brand Plan On Salbutamol + Ambroxol + GuaifenesinDocument36 pagesPresented by Animesh Amal: Brand Plan On Salbutamol + Ambroxol + GuaifenesinAnonymous 75aETJ8ONo ratings yet
- Urgent: Invented by William H. Gates (Aka Bill Gates) and Others, Listing Energy HarvestingDocument3 pagesUrgent: Invented by William H. Gates (Aka Bill Gates) and Others, Listing Energy HarvestingShayna A PitreNo ratings yet
- Tube+Aftercare+Tear Off+Sheets+PDFDocument8 pagesTube+Aftercare+Tear Off+Sheets+PDFNikola StojsicNo ratings yet
- AO CMFS During COVID-19Document6 pagesAO CMFS During COVID-19โสภาพรรณวดี รวีวารNo ratings yet
- Shalu Bathla - Chronic PeriodontitisDocument6 pagesShalu Bathla - Chronic PeriodontitisFerdinan PasaribuNo ratings yet