Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Assessment
Uploaded by
Janine PelayoCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Assessment
Uploaded by
Janine PelayoCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Assessment
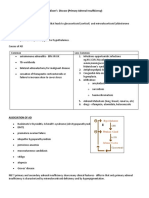
Assessment of a patient with DHF should include:
Evaluation of the patients heart rate, temperature, and blood pressure.
Evaluation of capillary refill, skin color and pulse pressure.
Assessment of evidence of bleeding in the skin and other sites.
Assessment of increased capillary permeability.
Measurement and assessment of the urine output.
Nursing Diagnosis
Based on the assessment data, the major nursing diagnoses for a patient with DHF are:
Risk for bleeding related to possible impaired liver function.
Deficient fluid volume related to vascular leakage.
Pain related to abdominal pain and severe headaches.
Risk for ineffective tissue perfusion related to failure of the circulatory system.
Risk for shock related to dysfunction in the circulatory system.
Nursing Care Planning and Goals
The goals in a patient with DHF are:
Be free of signs of bleeding.
Display laboratory results within normal range for individuals.
Maintain fluid volume at a functional level.
Report pain is relieved or controlled.
Follow prescribed pharmacologic regimen.
Demonstrate adequate tissue perfusion.
Display hemodynamic stability.
Be afebrile and free from other signs of infection.
Nursing Interventions
Nursing interventions appropriate for a patient with DHF include:
Blood pressure monitoring. Measure blood pressure as indicated.
Monitoring pain. Note client report of pain in specific areas, whether pain is
increasing, diffused, or localized.
Vascular access. Maintain patency of vascular access for fluid administration or
blood replacement as indicated.
Medication regimen. There must be a periodic review of the medication regimen
of the client to identify medications that might exacerbate bleeding problems.
Fluid replacement. Establish 24-hour fluid replacement needs.
Managing nose bleeds. Elevate position of the patient and apply ice bag to the
bridge of the nose and to the forehead.
Trendelenburg position. Place the patient in Trendelenburg position to restore
blood volume to the head.
Evaluation
A successful nursing care plan has achieved the following:
Absence of signs of bleeding.
Displayed laboratory results within normal range for individuals.
Maintained fluid volume at a functional level.
Reported pain is relieved or controlled.
Followed prescribed pharmacologic regimen.
Demonstrated adequate tissue perfusion.
Displayed hemodynamic stability.
Afebrile and free from other signs of infection.
Nursing Assessment Nursing Care Plan for Dengue Fever
1.
Review the basic data, the need for bio-psycho-social-spiritual patients from various sources
(patients, families, medical records and other health team members).
2.
Identify potential sources and available to meet patient needs.
3.
Review the history of nursing.
4.
Assess the increase in body temperature, signs of bleeding, nausea, vomiting, no appetite,
heartburn, sore muscles and joints, signs of shock (rapid and weak pulse, hypotension, cold
and moist skin, especially on the extremities, cyanosis , restlessness, decreased
consciousness).
Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Care Plan for Dengue Fever
1.
Hypovolemic shock related to hemorrhage
2.
Imbalanced Nutrition: Less than body requirements related to nausea, vomiting, no
appetite.
3.
Increased body temperature related to the process of dengue virus infection.
4.
Risk for bleeding related to thrombocytopenia.
5.
Deficient Fluid Volume related to increased capillary permeability, bleeding, vomiting and
fever.
6.
Deficient Knowledge: about the disease process related to a lack of information.
You might also like
- San Pedro Hospitai of Davao City, Inc.: Nurses' NotesDocument7 pagesSan Pedro Hospitai of Davao City, Inc.: Nurses' NotesRosaree Mae Pantoja100% (1)
- Management of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)From EverandManagement of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)No ratings yet
- Phobias - See What Makes Some People AfraidDocument2 pagesPhobias - See What Makes Some People Afraidbeep777No ratings yet
- Case Presentation HydrocephalusDocument48 pagesCase Presentation HydrocephalusSu Osman50% (2)
- Hydrocephalus NCP - DayanghirangDocument2 pagesHydrocephalus NCP - DayanghirangEdnar DayanghirangNo ratings yet
- MAPEH 7 3rd Summative TestDocument5 pagesMAPEH 7 3rd Summative TestFerlyn Bautista Pada100% (1)
- Mobilization of CabinDocument1 pageMobilization of CabinRashidi RahmanNo ratings yet
- LSENs Handbook 1Document39 pagesLSENs Handbook 1Maria Lea Unabia CabudbudNo ratings yet
- NCP GeDocument14 pagesNCP GeSuluhTriUtomoNo ratings yet
- Etiology of OCDDocument47 pagesEtiology of OCDdavinlkrNo ratings yet
- Minggu 5 LP THALASSEMIADocument14 pagesMinggu 5 LP THALASSEMIAMuhammad PanduNo ratings yet
- JDM Care PlanDocument5 pagesJDM Care PlangopscharanNo ratings yet
- Case Study OligoDocument7 pagesCase Study OligomutiaNo ratings yet
- Alteration in Fluid and Electrolyte Status Lecture NotesDocument11 pagesAlteration in Fluid and Electrolyte Status Lecture Notes0912247251No ratings yet
- Amoebiasis Case StudyDocument12 pagesAmoebiasis Case StudyGrace NazarenoNo ratings yet
- Addison's Disease (Primary Adrenal Insufficiency)Document5 pagesAddison's Disease (Primary Adrenal Insufficiency)sunnnydayNo ratings yet
- Addison's DiseaseDocument14 pagesAddison's Diseasedivya4nirmalaNo ratings yet
- Jaundice NeonatalDocument26 pagesJaundice Neonatalhunk2662No ratings yet
- Translational Research: Generating Evidence For PracticeDocument24 pagesTranslational Research: Generating Evidence For Practicebeer_ettaaNo ratings yet
- Acute Cholecystitis SeminarDocument42 pagesAcute Cholecystitis SeminarNatnaelNo ratings yet
- HydronephrosisDocument6 pagesHydronephrosisJamaluddin Ahmad A.MNo ratings yet
- Bulimia NervosaDocument17 pagesBulimia Nervosamaya juwindaNo ratings yet
- German MeaslesDocument8 pagesGerman MeaslesYdynn Parejas GavinaNo ratings yet
- LaryngitisDocument9 pagesLaryngitisjonna casumpangNo ratings yet
- NCP RiskDocument2 pagesNCP RiskNorries Jonell CaballarNo ratings yet
- The Pathophysiology of PPROMDocument2 pagesThe Pathophysiology of PPROMNano KaNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology PrintDocument4 pagesPa Tho Physiology Printaiconjucea0% (1)
- Oesophageal Atresia by GabriellaDocument7 pagesOesophageal Atresia by GabriellaGabrielleNo ratings yet
- SiadhDocument10 pagesSiadhehjing75% (4)
- Health Teaching Plan Non Pharmacological Pain ManagementDocument2 pagesHealth Teaching Plan Non Pharmacological Pain ManagementJohn Carl ElpedesNo ratings yet
- Care of HemophiliaDocument7 pagesCare of HemophiliaBasant karn100% (4)
- Biliary AtresiaDocument8 pagesBiliary AtresiaBrooke MauriNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument9 pagesCase StudyPalwasha KhanNo ratings yet
- Addison'sDocument4 pagesAddison'sKoRnflakesNo ratings yet
- PEDIA CASE 3 FinalDocument9 pagesPEDIA CASE 3 FinalXandra BnnNo ratings yet
- Group B1 (Cholera)Document66 pagesGroup B1 (Cholera)Krisianne Mae Lorenzo FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument7 pagesChronic Renal FailureMary Jane Tiangson100% (1)
- EndometriosisDocument6 pagesEndometriosissalamredNo ratings yet
- DRUG Formulas Ivtt: Divide With The Number of Times The Drugs Will Be GivenDocument7 pagesDRUG Formulas Ivtt: Divide With The Number of Times The Drugs Will Be Givenmaymay737No ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIO (Megaloblastic Anemia)Document3 pagesPATHOPHYSIO (Megaloblastic Anemia)Giselle EstoquiaNo ratings yet
- Birth Asphyxia: by Anne E. Odaro MCM/2017/69852Document26 pagesBirth Asphyxia: by Anne E. Odaro MCM/2017/69852ElvisNo ratings yet
- Nursing Interventions CHFDocument3 pagesNursing Interventions CHFbanyenye25100% (1)
- Case Presentation On Chronic Osteomyelitis: Prepared By: Sital Gautam MN1 Year, 2012Document55 pagesCase Presentation On Chronic Osteomyelitis: Prepared By: Sital Gautam MN1 Year, 2012Rabina RajbanshiNo ratings yet
- PericarditisDocument45 pagesPericarditisBrenda WardshoneNo ratings yet
- Careplan For Sickle Cell DiseaseDocument21 pagesCareplan For Sickle Cell DiseaseEcaroh Hew SmailliwNo ratings yet
- Care PlanDocument4 pagesCare PlangopscharanNo ratings yet
- Case Study PneumoniaDocument6 pagesCase Study PneumoniaBrian CornelNo ratings yet
- NCP-Drug Study 2Document4 pagesNCP-Drug Study 2hsiriaNo ratings yet
- SAMDocument108 pagesSAMAlimyon Abilar MontoloNo ratings yet
- Care of Neonate With HyperbilirubinemiaDocument11 pagesCare of Neonate With HyperbilirubinemiaKakali ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Pathological Changes of DM - 2023Document53 pagesPathological Changes of DM - 2023Visura PrabodNo ratings yet
- Risk For Bleeding - Cirrhosis NCPDocument2 pagesRisk For Bleeding - Cirrhosis NCPPaula AbadNo ratings yet
- Medications and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument6 pagesMedications and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDarla JoyceNo ratings yet
- Final Hernioplasty Compilation RevisedDocument58 pagesFinal Hernioplasty Compilation RevisedRaidis PangilinanNo ratings yet
- DehydrationDocument19 pagesDehydrationIlyes FerenczNo ratings yet
- Hydrocephalus 9Document9 pagesHydrocephalus 9Shesly PhilominaNo ratings yet
- KamanJan ChloroquineDocument3 pagesKamanJan Chloroquinekimberly_caberteNo ratings yet
- Simmond's Disease MSDocument22 pagesSimmond's Disease MSRocel Devilles100% (1)
- NCP Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritisDocument12 pagesNCP Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritisScarlet ScarletNo ratings yet
- Imbalanced NutritionDocument3 pagesImbalanced NutritionIlisa ParilNo ratings yet
- Thalassemia Case StudyDocument13 pagesThalassemia Case StudyNellyWataNo ratings yet
- Guada A. Dumapit RN, ManDocument18 pagesGuada A. Dumapit RN, ManAnne B. BuenvenidaNo ratings yet
- Q2 Lesson 7Document25 pagesQ2 Lesson 7mint hvryNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Drug Calculations - PPTMDocument20 pagesLesson 2 Drug Calculations - PPTMThrecia RotaNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Spaces With Respect To Child PsychologyDocument28 pagesEvolution of Spaces With Respect To Child PsychologyDevvrat ChowdharyNo ratings yet
- Confined Space PDFDocument4 pagesConfined Space PDFshreyasNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Vaginosis Treatment - UpToDateDocument12 pagesBacterial Vaginosis Treatment - UpToDateAlex Esteban Espinoza CevallosNo ratings yet
- Final ThesisDocument58 pagesFinal Thesisgnanasegaram vithursanNo ratings yet
- Marriage and Later PartDocument25 pagesMarriage and Later PartDeepak PoudelNo ratings yet
- Managerial Epidemiology Concepts and Case, 2d Ed.: Full TextDocument2 pagesManagerial Epidemiology Concepts and Case, 2d Ed.: Full TextlovesunsetNo ratings yet
- Nominal Roll N035 1bnm10jDocument2 pagesNominal Roll N035 1bnm10jsubiNo ratings yet
- Sarcopenia, European Definition and DiagnosisDocument12 pagesSarcopenia, European Definition and DiagnosisRémi DelauzunNo ratings yet
- June 2021Document90 pagesJune 2021SEIYADU IBRAHIM KNo ratings yet
- Cossh Risk Assessment: Carried Out By: Department: Date: Substance Name: CRA NumberDocument2 pagesCossh Risk Assessment: Carried Out By: Department: Date: Substance Name: CRA NumberNiraNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument2 pagesAssignmentYahya TariqNo ratings yet
- Voice Therapy Does Science Support The ArtDocument5 pagesVoice Therapy Does Science Support The ArtYurleidys ZapaNo ratings yet
- Anemia ProjectDocument33 pagesAnemia ProjectNilesh BagalNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For InfectionDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan: Risk For Infectiongeorgeborja414726100% (3)
- 2231 - AMedP-5.1 EDA V1 EDocument52 pages2231 - AMedP-5.1 EDA V1 EDaniel CharlesNo ratings yet
- Micro Labs - STF Division Products...Document17 pagesMicro Labs - STF Division Products...micro sobanNo ratings yet
- EO-GA-32 Continued Response To COVID-19 IMAGE 10-07-2020Document7 pagesEO-GA-32 Continued Response To COVID-19 IMAGE 10-07-2020Jakob RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Background Info: ThesisDocument3 pagesBackground Info: ThesisCITLALI RAMIREZ MEDINANo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Phinma University of PangasinanDocument1 pageDrug Study: Phinma University of PangasinanVoid LessNo ratings yet
- Date/Hour of Shift Focus Note ProgressDocument2 pagesDate/Hour of Shift Focus Note Progressako at ang exoNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Chart.1Document6 pagesDiabetes Chart.1dr_vidyasagar41No ratings yet
- Drug Ana Surgery WardDocument11 pagesDrug Ana Surgery WardJames QuilingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document46 pagesChapter 1ZiziNo ratings yet
- CBT For KidsDocument34 pagesCBT For KidsJelena VisekrunaNo ratings yet