Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Human Cloning Insights Developmental Biology Diseases
Uploaded by
Rock Almighty0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views3 pagesu know
Original Title
Uses
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentu know
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views3 pagesHuman Cloning Insights Developmental Biology Diseases
Uploaded by
Rock Almightyu know
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
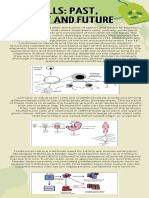
Uses of Human Cloning:
actual and potential
Work
on
cloning
techniques
has
advanced our basic understanding of
developmental
biology
in
humans.
Observing human pluripotent stem cells
grown in culture provides great insight
into human embryo development,
which otherwise cannot be seen.
Scientists are now able to better define
steps of early human development.
Studying signal transduction along with
genetic manipulation within the early
human embryo has the potential to
provide
answers
to
many
developmental diseases and defects.
Many human-specific signaling pathways
have been discovered by studying
human embryonic stem cells. Studying
developmental pathways in humans has
given developmental biologists more
evidence toward the hypothesis that
developmental pathways are conserved
throughout species. iPSCs and cells
2016-17
created by SCNT are useful for research
into the causes of disease, and as model
systems used in drug discovery. Cells
produced with SCNT, or iPSCs could
eventually be used in stem cell
therapy, or to create organs to be used
in
transplantation,
known
as
regenerative medicine. Stem cell
therapy is the use of stem cells to treat
or prevent a disease or condition. Bone
marrow transplantation is a widely
used form of stem cell therapy. No other
forms of stem cell therapy are in clinical
use at this time. Research is underway to
potentially use stem cell therapy to treat
heart disease, diabetes, and spinal cord
injuries. Regenerative medicine is not in
clinical
practice,
but
is
heavily
researched for its potential uses. This
type of medicine would allow for
autologous
transplantation,
thus
removing the risk of organ transplant
rejection by the recipient. For instance, a
person
with
liver
disease
could
potentially have a new liver grown using
their
same
genetic
material
and
transplanted to remove the damaged
2016-17
10
liver. In current research, human
pluripotent stem cells have been
promised as a reliable source for
generating human neurons, showing the
potential for regenerative medicine in
brain and neural injuries.
2016-17
10
You might also like
- Umbilical Cord Stem Cell Therapy: The Gift of Healing from Healthy NewbornsFrom EverandUmbilical Cord Stem Cell Therapy: The Gift of Healing from Healthy NewbornsNo ratings yet
- ISSCR 11 StemCellFactBrch FNLDocument8 pagesISSCR 11 StemCellFactBrch FNLНваневу СильванусNo ratings yet
- Stem Cells: A Key to Regenerative MedicineDocument12 pagesStem Cells: A Key to Regenerative MedicineIsha PrabhudesaiNo ratings yet
- Stem Cell Research - For The Benefit of Today and TomorrowDocument4 pagesStem Cell Research - For The Benefit of Today and Tomorrowjustasm100% (11)
- Human Cloning and Genetic ModificationDocument6 pagesHuman Cloning and Genetic ModificationaballacarlosjasonNo ratings yet
- Zubin Master and Amandine Truong - Stem Cells - Hope or Hype For Reproductive and Regenerative Medicine?Document3 pagesZubin Master and Amandine Truong - Stem Cells - Hope or Hype For Reproductive and Regenerative Medicine?Gmewop30mNo ratings yet
- 17d Stem Cells ScieMedPoliticalDocument4 pages17d Stem Cells ScieMedPoliticalbbdddNo ratings yet
- Human Cloning - WikipediaDocument96 pagesHuman Cloning - WikipediaHimanshu LathwalNo ratings yet
- Dissertation On Stem CellsDocument8 pagesDissertation On Stem CellsCollegePaperWritingHelpCanada100% (1)
- Stem Cell EssayDocument2 pagesStem Cell Essayapi-251078269No ratings yet
- Stem Cell ResearchDocument6 pagesStem Cell ResearchYeli CruzNo ratings yet
- Human CloningDocument7 pagesHuman CloningAashi JainNo ratings yet
- Making Sense of Animal ResearchDocument16 pagesMaking Sense of Animal Researchthamizh555No ratings yet
- NRR-17-1867.primataDocument9 pagesNRR-17-1867.primatawi bowoNo ratings yet
- Script WPS OfficeDocument2 pagesScript WPS OfficeIvy VergaraNo ratings yet
- Stem Cell Controversies 2nd DraftDocument2 pagesStem Cell Controversies 2nd DraftzaheersbsNo ratings yet
- Stem Cell Research Essay TextDocument9 pagesStem Cell Research Essay Textapi-302123415No ratings yet
- Research Papers On Stem Cell TherapyDocument6 pagesResearch Papers On Stem Cell Therapyafeatoxmo100% (1)
- Stem Cell Research News PaperDocument5 pagesStem Cell Research News Paperafnkylqbkfazpp100% (1)
- Extended Response 6 QDocument2 pagesExtended Response 6 Q12-057 MOHAMMAD MUSHFIQUR RAHMANNo ratings yet
- Author's Accepted Manuscript: Seminars in Pediatric SurgeryDocument28 pagesAuthor's Accepted Manuscript: Seminars in Pediatric Surgerywibm23No ratings yet
- Attention Getter For Stem Cell Research PaperDocument5 pagesAttention Getter For Stem Cell Research Papertus0zaz1b1g3100% (1)
- Human Organoid NatureDocument14 pagesHuman Organoid NaturehalegaNo ratings yet
- November of 1998Document3 pagesNovember of 1998ArdeJenniferNo ratings yet
- 3D Printing in Stem Cell ResearchDocument3 pages3D Printing in Stem Cell ResearchAyush GoplaniNo ratings yet
- Human Organoids in Basic Research and Clinical ApplicationsDocument17 pagesHuman Organoids in Basic Research and Clinical ApplicationsLearning Space TutorsNo ratings yet
- StemcellessayDocument7 pagesStemcellessayapi-312649054No ratings yet
- Stem Cell Research Facts and ControversyDocument4 pagesStem Cell Research Facts and Controversyapi-298015184No ratings yet
- 10 11648 J Ijsts 20200801 12Document9 pages10 11648 J Ijsts 20200801 12Suhara SakimanNo ratings yet
- Uses of Stem To HumanDocument1 pageUses of Stem To Humanchan_1016No ratings yet
- Embryonic Stem Cell Research Term PaperDocument5 pagesEmbryonic Stem Cell Research Term Paperegtwfsaf100% (1)
- Stem Cells Research Paper ExampleDocument7 pagesStem Cells Research Paper Examplefyt3rftv100% (1)
- Titles For Stem Cell Research PaperDocument8 pagesTitles For Stem Cell Research Paperfvgcaatd100% (1)
- UntitledDocument3 pagesUntitledNida MasroorNo ratings yet
- Debate (Speech)Document5 pagesDebate (Speech)Jessie GlennNo ratings yet
- Stem Cell IsscrDocument8 pagesStem Cell Isscrcazzy_luvNo ratings yet
- Embryonic Stem Cells Research PaperDocument4 pagesEmbryonic Stem Cells Research Paperjizogol1siv3100% (1)
- FC501 Essay 2Document5 pagesFC501 Essay 2valNo ratings yet
- Thesis On Stem Cell Research PaperDocument8 pagesThesis On Stem Cell Research Paperkimberlyjonesshreveport100% (2)
- Research Paper Topics On Stem CellsDocument8 pagesResearch Paper Topics On Stem Cellswohekam1d0h3100% (1)
- HK Stem Cell Research - Facts and FallaciesDocument11 pagesHK Stem Cell Research - Facts and FallaciesSimon Adda-ReyssNo ratings yet
- Adult Stem CellSDocument28 pagesAdult Stem CellSshibu_83No ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Stem Cell ResearchDocument4 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Stem Cell ResearchSony JenniNo ratings yet
- Stem Cell Research Paper ConclusionDocument8 pagesStem Cell Research Paper Conclusionfvg1rph4100% (1)
- Running Head: The Role of Stem Cell Treatment in Medicine 1Document4 pagesRunning Head: The Role of Stem Cell Treatment in Medicine 1Joyce WanjiruNo ratings yet
- Research EssayDocument8 pagesResearch Essayapi-401167849No ratings yet
- Research Paper Stem CellsDocument8 pagesResearch Paper Stem Cellsafeaxdhwl100% (1)
- Embryonic Stem Cell ResearchDocument15 pagesEmbryonic Stem Cell ResearchAkhil NairNo ratings yet
- Do You Think We Should Use Cloning To Create Human Organs That Can Be Used in Transplants - Eva WuDocument3 pagesDo You Think We Should Use Cloning To Create Human Organs That Can Be Used in Transplants - Eva WuEvaNo ratings yet
- Embryonic Stem Cell Research Paper OutlineDocument5 pagesEmbryonic Stem Cell Research Paper Outlinejizogol1siv3100% (1)
- Chapter 8Document12 pagesChapter 8lala_0No ratings yet
- Research Paper Topics Stem Cell ResearchDocument6 pagesResearch Paper Topics Stem Cell Researchfvdh47rr100% (3)
- Revised Stem CellDocument5 pagesRevised Stem Cellaaroncalebjeba70No ratings yet
- Stem Cells: Yes or NoDocument2 pagesStem Cells: Yes or NoAnisah FaiqohNo ratings yet
- Stem Cells Past, Present and FutureDocument3 pagesStem Cells Past, Present and FutureAndrés ChávezNo ratings yet
- Stem Cell Proposal Final 2003.Document13 pagesStem Cell Proposal Final 2003.Harshal GohilNo ratings yet
- Stem Cell Treatment-TherapyDocument1 pageStem Cell Treatment-TherapydavinderNo ratings yet
- 17 ManuscriptDocument10 pages17 ManuscriptBaru Chandrasekhar RaoNo ratings yet
- Medical Advancement On Cell: ContentDocument14 pagesMedical Advancement On Cell: Contentkirthana17No ratings yet
- Ly: Stem Cell Treatment For SCD: 1. What Is Stem Cells?Document6 pagesLy: Stem Cell Treatment For SCD: 1. What Is Stem Cells?Le Phuong LyNo ratings yet
- Physics SQP 2017Document7 pagesPhysics SQP 2017AmanNo ratings yet
- EP 1 OF SEASON 1 AND EP 1 OF SEASON 3 OF Sherlock Were Deleted Due To Salik Virus... Fuck You, SalikDocument1 pageEP 1 OF SEASON 1 AND EP 1 OF SEASON 3 OF Sherlock Were Deleted Due To Salik Virus... Fuck You, SalikRock AlmightyNo ratings yet
- 79 BiologyDocument22 pages79 Biologyapi-238757880No ratings yet
- Lesson Completed.: Question ResultsDocument11 pagesLesson Completed.: Question ResultsRock AlmightyNo ratings yet
- 65-1-B Mathematics PDFDocument11 pages65-1-B Mathematics PDFRock AlmightyNo ratings yet
- Burnpur Riverside School: Biology Practical ProjectDocument1 pageBurnpur Riverside School: Biology Practical ProjectRock AlmightyNo ratings yet
- 99-1 BiotechnologyDocument8 pages99-1 BiotechnologyRock AlmightyNo ratings yet
- 99 Bio TechnologyDocument8 pages99 Bio TechnologyRock AlmightyNo ratings yet
- Airtel Apps - 1Document3 pagesAirtel Apps - 1Rock AlmightyNo ratings yet
- Pre Exam Press Note 2015Document9 pagesPre Exam Press Note 2015Rock AlmightyNo ratings yet
- File HandlerDocument1 pageFile HandlerNishant ChaharNo ratings yet
- Lucknow Bond PDFDocument2 pagesLucknow Bond PDFRock AlmightyNo ratings yet
- Charlotte Charlotte Charlotte CharlotteDocument1 pageCharlotte Charlotte Charlotte CharlotteRock AlmightyNo ratings yet
- And GateDocument1 pageAnd GateRock AlmightyNo ratings yet
- The Realisation of AND GateDocument1 pageThe Realisation of AND GateRock AlmightyNo ratings yet
- Topic Page No.: 1 AND Gate 2 The Realisation of AND Gate 3 OR Gate 4 The Realisation of OR Gate 5 Bibliography 6Document1 pageTopic Page No.: 1 AND Gate 2 The Realisation of AND Gate 3 OR Gate 4 The Realisation of OR Gate 5 Bibliography 6Rock AlmightyNo ratings yet
- Ethical Issues of Human CloningDocument2 pagesEthical Issues of Human CloningRock AlmightyNo ratings yet
- Bibliography: NCERT Physics (Class XII) New Simplified Physics (Class XII) - S. L. AroraDocument1 pageBibliography: NCERT Physics (Class XII) New Simplified Physics (Class XII) - S. L. AroraRock AlmightyNo ratings yet
- Burnpur Riverside School: Biotechnology Practical ProjectDocument1 pageBurnpur Riverside School: Biotechnology Practical ProjectRock AlmightyNo ratings yet
- Pic 1Document1 pagePic 1Rock AlmightyNo ratings yet
- Or GateDocument1 pageOr GateRock AlmightyNo ratings yet
- TopicDocument1 pageTopicRock AlmightyNo ratings yet
- Biotech IntroDocument2 pagesBiotech IntroRock AlmightyNo ratings yet
- Dolly The Sheep: A Case Study of CloningDocument2 pagesDolly The Sheep: A Case Study of CloningRock AlmightyNo ratings yet
- ContentsDocument1 pageContentsRock AlmightyNo ratings yet
- Creating iPSCs: An Overview of Induced Pluripotent Stem CellsDocument2 pagesCreating iPSCs: An Overview of Induced Pluripotent Stem CellsRock AlmightyNo ratings yet
- Methods of Human Cloning: Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer (SCNT) ExplainedDocument1 pageMethods of Human Cloning: Somatic Cell Nuclear Transfer (SCNT) ExplainedRock AlmightyNo ratings yet
- A Comparison of SCNT and ReprogrammingDocument1 pageA Comparison of SCNT and ReprogrammingRock AlmightyNo ratings yet
- Current Laws on Human Cloning Around the WorldDocument2 pagesCurrent Laws on Human Cloning Around the WorldRock AlmightyNo ratings yet