Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Worksheet No.: 5
Uploaded by
ARPITOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Worksheet No.: 5
Uploaded by
ARPITCopyright:
Available Formats
WORKSHEET NO.
: 5
CLASS: 10 LIGHT: REFLECTION PHYSICS
1. The radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is 30 cm. what is its focal length?
2. Name a mirror that can give an erect and enlarged image of an object.
3. Why do we prefer a convex mirror as a rear-view mirror in vehicles?
4. A concave mirror produces three times magnified virtual image of an object placed 10 cm
in front of it. Where is the image located?
5. What is the angle of reflection if a ray falls normally on a plane mirror?
6. A man standing in front of a mirror, finds his image having a very small head, a fat body
and legs of normal size. What types of mirrors are used in these three parts?
7. Differentiate between virtual image of a concave mirror and of a convex mirror.
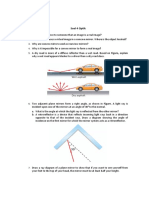
8. The angles between an incident ray and the mirror is 40o
i) What is the angel of incidence?
ii) What is the angle of reflection?
iii) What is the total angle turned by the ray of light?
9. The angle between an incident ray and the mirror is . The total angle turned by the ray
of light is 80o. What is the value of ?
10. Distinguish between real and virtual image.
11. How can you distinguish between a plane mirror, a concave mirror and a convex mirror
without touching them?
12. Name the type of mirror used in the following:
i) Headlights of a car ii) Solar furnace.
Support your answer with reason.
You might also like
- LightDocument4 pagesLightjillgoldNo ratings yet
- Light - Reflection and Refraction Part 1Document6 pagesLight - Reflection and Refraction Part 1Saji JayarajNo ratings yet
- Reflection of Light Set 1Document2 pagesReflection of Light Set 1XxxxxxNo ratings yet
- Books Doubtnut Question BankDocument135 pagesBooks Doubtnut Question Bankvedha mungaraNo ratings yet
- Light NoteDocument6 pagesLight NoteGaming ApocalypseNo ratings yet
- PHYS131 Tutorial Chapter 23 Part 1 Geometric Optics PDFDocument1 pagePHYS131 Tutorial Chapter 23 Part 1 Geometric Optics PDFKgethi MasipaNo ratings yet
- LightDocument6 pagesLightVivek saklaniNo ratings yet
- Soal 4 Optik PDFDocument4 pagesSoal 4 Optik PDFMuhammad NaufalNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1 On LightDocument2 pagesWorksheet 1 On LightAmaan HaiderNo ratings yet
- Light-NCERT Notes Class 10Document2 pagesLight-NCERT Notes Class 10akashraj7713No ratings yet
- Assignment Based On Reflection of LightDocument3 pagesAssignment Based On Reflection of Lightnamansaraswat2007No ratings yet
- Special and Previous PapersDocument19 pagesSpecial and Previous PapersKrishna KishoreSarvaNo ratings yet
- 10th Physics WorksheetDocument1 page10th Physics WorksheetArsh ChhetriNo ratings yet
- 0318reflection of Light1160289021239053260Document2 pages0318reflection of Light1160289021239053260KUNAL GAMING 007No ratings yet
- Light Test No 1Document1 pageLight Test No 1Devyansh 9207No ratings yet
- Light - Reflection and Refraction: Questions To PracticeDocument4 pagesLight - Reflection and Refraction: Questions To PracticeH E Man ShuNo ratings yet
- Holiday Homework Physics Class 10thDocument1 pageHoliday Homework Physics Class 10thKalindi UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- G-10 Physics Important Questions FinalDocument29 pagesG-10 Physics Important Questions FinalRohan SenapathiNo ratings yet
- Reflection Light 3Document31 pagesReflection Light 3api-296824694No ratings yet
- Paper Mirrors: by Group 6 Dani Anisa Imanda (20129258) Intan Dwi Puspita (20129296) Tiara Utari (20129356)Document13 pagesPaper Mirrors: by Group 6 Dani Anisa Imanda (20129258) Intan Dwi Puspita (20129296) Tiara Utari (20129356)tiara utariNo ratings yet
- COT PresentationDocument42 pagesCOT PresentationCedric BaldozaNo ratings yet
- 9TH - Icse - Physics - Worksheet - Reflection of Light 2Document5 pages9TH - Icse - Physics - Worksheet - Reflection of Light 2manojboa100% (3)
- St. Teresa School: Holiday Homework Class-X Subject-Physics Chapter-10 (Light)Document4 pagesSt. Teresa School: Holiday Homework Class-X Subject-Physics Chapter-10 (Light)Raghav ghaiNo ratings yet
- Class 10 CBSE Reflection and Refraction Extra QuestionsDocument3 pagesClass 10 CBSE Reflection and Refraction Extra QuestionsTapan GoudaNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Chapter 12 LightDocument12 pagesClass 7 Chapter 12 Lightsiddharthsg37No ratings yet
- All Questions Are Compulsory: Topic - Reflection & RefractionDocument3 pagesAll Questions Are Compulsory: Topic - Reflection & Refractionshivanshu kushwahaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet CBSE Class 10 LightDocument6 pagesWorksheet CBSE Class 10 Lightroythomasc50% (4)
- Kiit World School Class-7 Subject: Science, Chapter: Light Assignment Choose The Correct OptionDocument2 pagesKiit World School Class-7 Subject: Science, Chapter: Light Assignment Choose The Correct Optionkirti rupelaNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Light RevDocument24 pagesGrade 10 Light RevDanny BlessyNo ratings yet
- CbseDocument15 pagesCbseYaaroNo ratings yet
- One Mark Questions: ISD/X/WKST/SS/2019-20Document3 pagesOne Mark Questions: ISD/X/WKST/SS/2019-20Febronia GraceNo ratings yet
- Module 6Document9 pagesModule 6chef curryNo ratings yet
- SCAssign 1Document1 pageSCAssign 1lokimanNo ratings yet
- LIGHTDocument3 pagesLIGHTphysicsbooks.storeNo ratings yet
- QUARTER 2 - A4Document3 pagesQUARTER 2 - A4Monique MangubatNo ratings yet
- FHSC1034 Tutorial 6Document2 pagesFHSC1034 Tutorial 6Krishnaah SmuglerzzNo ratings yet
- Chapter Light Class 7 Chapter Q and ADocument9 pagesChapter Light Class 7 Chapter Q and ADaiwik GuptaNo ratings yet
- Light QuestionsDocument9 pagesLight QuestionsTxv RushNo ratings yet
- Class 7 L 15 Light QADocument3 pagesClass 7 L 15 Light QAMinnilaNo ratings yet
- Expt 4. Reflection of Light ConclusionDocument2 pagesExpt 4. Reflection of Light ConclusionKiara De Leon67% (3)
- TS Physics DCEB QuestionsDocument16 pagesTS Physics DCEB QuestionsKrishna KishoreSarvaNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper - 2011 Class - X Subject - Physics Light: Reflection and RefractionDocument2 pagesSample Paper - 2011 Class - X Subject - Physics Light: Reflection and RefractionArslaan MD BelalNo ratings yet
- State The Laws of ReflectionDocument2 pagesState The Laws of ReflectionSuman DasNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Answers - VII - LIGHT (PART 1)Document9 pagesWorksheet - Answers - VII - LIGHT (PART 1)Suvam DasguptaNo ratings yet
- Physics Revision Worksheet Grade X ChlightDocument3 pagesPhysics Revision Worksheet Grade X ChlightKhushi AgarwalNo ratings yet
- 7th ch-16 Light and Its Reflaction Solution Living ScienceDocument3 pages7th ch-16 Light and Its Reflaction Solution Living SciencesabletarsingNo ratings yet
- Reqelford International Schoo: Light - Worksheet 1Document2 pagesReqelford International Schoo: Light - Worksheet 1shivaNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions - Ch-9Document2 pagesPractice Questions - Ch-9sujatalam1921No ratings yet
- SCIENCE10 Q2 M4 LightsMirrorsandLenses v3-EDITEDDocument22 pagesSCIENCE10 Q2 M4 LightsMirrorsandLenses v3-EDITEDRusty Gabriel Suyom100% (1)
- Light Reflection Extra QuestionsDocument7 pagesLight Reflection Extra Questionskrishna priyaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Answers - Vii - Light (Part 2)Document6 pagesWorksheet Answers - Vii - Light (Part 2)Suvam Dasgupta100% (1)
- Worksheet - 1 8.6.23Document1 pageWorksheet - 1 8.6.23imraan smNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 7 Science Worksheet (6) - 0Document2 pagesCBSE Class 7 Science Worksheet (6) - 0Yatish TiwariNo ratings yet
- 10 Sci Light NotesDocument23 pages10 Sci Light NotesankitrathoreagentNo ratings yet
- Light Re Action and Refraction: 1. One Mark QuestionsDocument19 pagesLight Re Action and Refraction: 1. One Mark Questionsmayank007aggarwal100% (1)
- Ws Light-1 - Reflection 1Document1 pageWs Light-1 - Reflection 1Dj PowerNo ratings yet
- Reflection of Light - PPRDocument2 pagesReflection of Light - PPRharshvardhanmoundekarNo ratings yet
- 7 (1) - Light AssignmentDocument7 pages7 (1) - Light Assignmentsirsa11No ratings yet
- Physics 2Document11 pagesPhysics 2bort kortNo ratings yet
- The Lensball Photography Handbook: The Ultimate Guide to Mastering Refraction Photography and Creating Stunning ImagesFrom EverandThe Lensball Photography Handbook: The Ultimate Guide to Mastering Refraction Photography and Creating Stunning ImagesNo ratings yet
- Nsea Code A423Document1 pageNsea Code A423ARPITNo ratings yet
- Common NamesDocument6 pagesCommon NamesARPIT50% (2)
- What Is The Expansion (Full Form) of ADIDAS?: Check Ur GKDocument3 pagesWhat Is The Expansion (Full Form) of ADIDAS?: Check Ur GKARPITNo ratings yet
- Asian Games FAQ: Frequently Asked QuestionsDocument3 pagesAsian Games FAQ: Frequently Asked QuestionsARPITNo ratings yet
- Holiday Homework AssignmentDocument4 pagesHoliday Homework AssignmentARPITNo ratings yet
- European History/World War I: The Road To WarDocument9 pagesEuropean History/World War I: The Road To WarARPITNo ratings yet
- Wwi ImpactDocument34 pagesWwi ImpactARPITNo ratings yet