Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Hidrogen Pentru Motor Cu Apa
Uploaded by
c1962Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Hidrogen Pentru Motor Cu Apa
Uploaded by
c1962Copyright:
Available Formats
Catalyzed Aluminum
CA.p65; October 2012 Page 1
Contents
Catalyzed Aluminulm produces Hydrogen for fuel ..................................................... 3
What is Catalytic Carbon? ............................................................................................. 4
www.PhillipsCompany.4T.com/HYDROGEN.html ........................................................... 4
CA material contains Catalytic Carbon ........................................................................ 5
Technology verification ................................................................................................... 5
www.PhillipsCompany.4T.com/CT.pdf .............................................................................. 6
Advantages of Catalyzed Aluminum .............................................................................. 6
Catalyzed Aluminum, CA, is a hydrogen-on-demand fuel .......................................... 6
Manufacturing process for Catalyzed Aluminum ........................................................ 7
Step 1 -- Convert scrap paper and scrap aluminum into carbonized aluminum ...... 7
Step 2 -- Convert carbonized aluminum into Catalyzed Aluminum, CA.................... 8
Safety is an important issue ............................................................................................ 8
www.PhillipsCompany.4T.com/MSDS-CA.pdf ................................................................. 8
Aluminum particle size..................................................................................................... 9
CA particle size measurement ...................................................................................... 10
Recycling options ........................................................................................................... 11
www.PhillipsCompany.4T.com/AHU.pdf .........................................................................11
More information available .......................................................................................... 12
hodinfo.com ...................................................................................................................... 12
www.PhillipsCompany.4T.com/CA.pdf ........................................................................... 12
hp@valliant.net .................................................................................................................. 12
efred.davey@biongroup.co.uk ......................................................................................... 12
www.PhillipsCompany.4T.com/HYDROGEN.html ......................................................... 12
Increasing MPG -- Commercialization of this new technology ................................ 13
More commercial applications for this new technology ........................................... 13
Catalyzed Aluminum is available now ......................................................................... 13
www.PhillipsCompany.4T.com/MCA.pdf ........................................................................ 13
CA.p65; October 2012 Page 2
New material produces Hydrogen for fuel
at high flow rates storage tank NOT required.
CA makes
Water Catalyzed Hydrogen
Aluminum
Catalyzed Aluminulm produces Hydrogen for fuel
Yes, it is that simple -- A new material has been produced that makes hydrogen when it is added to warm water.
The new material was produced in a research program to find a new and better way to produce hydrogen-on-
demand for use as a cost-saving supplemental fuel for engines that burn petroleum.
Fuel cost saving is the reason for using CA to produce hydrogen as a fuel supplement. 32% to 40% increases
in miles per gallon have been demonstrated by simply adding a small amount of hydrogen to the air used by an
automobile engine. One pint of the CA material produces hydrogen at a flow rate that is higher than that
required to increase the MPG of an automobile by more than 30%.
Catalyzed Aluminulm (CA), a new hydrogen-producing material is now available for commercialization of
systems that will use hydrogen for fuel supplements. Samples of the new material are available from Phillips
Company.
Hydrogen fuel storage tanks are no longer needed because of this new low-cost, safe method for producing
hydrogen fuel at high flow rates using a mixture of aluminum and carbon, two of the worlds safest and lowest-
cost industrial materials. The hydrogen-from-water breakthrough was a result of a catalytic chemistry
development that successfully splits water to produce hydrogen, while retaining oxygen in the water. That
breakthrough was rapidly used to develop CA which is a mixture of aluminum and catalytic carbon, a material
optimized to generate hydrogen by simply adding warm water to the CA material.
CA.p65; October 2012 Page 3
For many years, experts have agreed that hydrogen will command a key role in future renewable energy when a
relatively cheap, safe, efficient and non-polluting means of producing hydrogen can be developed, on demand,
at very high rates which make hydrogen storage tanks unnecessary. That goal has been met, for the first time,
using the new CA process.
Before this new process was developed, the use of hydrogen fuel was limited by the lack of an inexpensive
catalyst that can speed up the generation of hydrogen from water. A vital part of the CA development success
was combining predictive theoretical chemistry and verification testing to accelerate the process of identifying
catalytic carbon as a new catalyst for use with aluminum to split water and obtain hydrogen.
What is Catalytic Carbon?
Catalyzed Aluminum (CA) material contains Catalytic Carbon (CC). Catalytic chemistry research resulted in
the discovery that an inexpensive activation process can convert normal carbon into a carbon catalyst, called
Catalytic Carbon, or CC. For more information on the development and use of Catalytic Carbon, please see
www.PhillipsCompany.4T.com/HYDROGEN.html
The use of CC to produce hydrogen from aluminum and water is illustrated below:
For more information on Catalytic Carbon, please see
www.PhillipsCompany.4T.com/PRH3.pdf and www.PhillipsCompany.4T.com/PRH4.pdf
CA.p65; October 2012 Page 4
CA material contains Catalytic Carbon
When used as a fuel, CA can effectively generate hydrogen gas from water. The aluminum does not have to be
pure, making the fuel less expensive. CA is made from scrap aluminum to keep the cost down. The CA process
does not require electrolytes or organic additives. It can operate in pH-neutral water, even if it is dirty, and can
operate in sea water, the most abundant source of hydrogen on earth.
Hydrogen purity measurements were made by an independent test laboratory. Hydrogen was produced in the
test laboratory using aluminum and catalytic carbon. The process produced 93% pure hydrogen with 7% water
vapor.
Hydrogen is an energy dense and clean fuel, which upon combustion releases only water vapor. Today, most
hydrogen is produced from electrolysis which requires large amounts of electrical energy or from natural gas
thermoforming which results in excessive carbon-dioxide emissions. An alternative, clean method is to make
hydrogen from water using Catalyzed Aluminum.
The unique thing about this new process is that it requires no power input after the hydrogen-producing reaction
is started and brought to thermal equilibrium; making possible, for the first time, the scale-up to high rates of
hydrogen on demand (HOD). A hydrogen output of 1 liter per minute can be achieved with the CA
consumption of only 0.67 grams/minute. This is about three times more hydrogen flow rate than is needed for a
typical automobile to increase the gas mileage by 32% to 40%.
Technology verification
CC has been provided to 45 evaluation sites internationally with very positive results. Independent evaluators
have produced hydrogen at high flow rates ranging from 1 to 40 liters per minute.
1. Flame test
2. Hydrogen purity test
3. Flow rate demonstration
4. Car test
5. World-wide
test program
@ 45 locations
CA.p65; October 2012 Page 5
For more information on automobile test results, please see
www.PhillipsCompany.4T.com/CT.pdf
Advantages of Catalyzed Aluminum
Previously, Catalytic Carbon (CC) and aluminum were combined with water to produce hydrogen by
experimentalists (mostly for mileage improvement for vehicles) and by company operations for various
applications. The advantage of Catalytic Aluminum (CA) are:
1 The use of CA is more simple than using aluminulm + CC. The user requires no chemistry knowledge.
2 The CA granule size is optimum for hydrogen production. A larger granule size (lower surface-to-
volume) would result in a slower production of hydrogen per pound of fuel, requiring more fuel and a
larger vessel to produce hydrogen at a given rate. A smaller granule size (higher surface-to-volume)
would result in the fuel being consumed more quickly than necessary to produce hydrogen at a given
rate.
3 CA is safe to handle, ship and store because of the granule size. If aluminum powder is used to make
hydrogen, the aluminum powder can become chemically unstable, and possibly explosive, if the powder
has a particle size less than 30 microns. CA has an average granule size of approximately 0.2 mm, or
about 200 microns.
4 The ratios of aluminum and CC are optimized in the formulation and manufacturing of CA.
5 The ratio of aluminum to carbon is higher when CA is used (instead of CC + aluminum). CA is almost
all fuel; more than 98% aluminum and less than 2% carbon.
6 The mixture of CA and water is not critical. Each aluminum granule has a local source of catalyst (CC)
integrated into the granule.
Catalyzed Aluminum, CA, is a hydrogen-on-demand fuel
The new material used to produce hydrogen is called Catalyzed Aluminum, CA. This new fuel is a hydrogen on
demand material that produces hydrogen simply by adding it to warm water. The hydrogen production rate is
controlled by water temperature. Water is two-thirds hydrogen. Heating the water to about 180F causes water
to be split by the CA, thereby releasing hydrogen in the form of a gas which can be used for fuel. The chemical
reaction is
2Al + 6[H2O] + CC = CC + 2[Al(OH)3] + 3[H2]
CA.p65; October 2012 Page 6
Manufacturing process for Catalyzed Aluminum
Now The price of Catalytic Aluminum will
Relative (Research) be only 30% of the current cost, when
price of CA is produced in volume.
CA De
vel
op
me
nt
Commerc
ial Produc
ts
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Metric Tons per quarter
The CA material is made from scrap materials -- aluminum and paper. These two materials are oxidized at a
high temperature which converts the paper to carbon.
Step 1 -- Convert scrap paper and scrap aluminum into carbonized aluminum
Step 1 (above) is much like a controlled burn. Step 1 is carried out at temperatures high enough to carbonize
paper but lower than the melting temperature of aluminum. Because the paper and aluminum are scrap materials,
this is a very low-cost starting material when used in high volume manufacturing. The aluminum-carbon mixture is
then chemically activated to transform the carbon into catalytic carbon, as described by Step 2, on the following
page..
CA.p65; October 2012 Page 7
Step 2 -- Convert carbonized aluminum into Catalyzed Aluminum, CA
The name CA denotes catalyzed aluminum. The aluminum is not a catalyst, but it is catalyzed by the presence of
catalytic carbon. CA is mostly aluminum, with a carbon content less than 2%. The carbon is in direct physical
contact with the aluminum, making the hydrogen production process very efficient.
Safety is an important issue
MSDS: The Materials Safety Data Sheet for Catalyzed Aluminulm is online at
www.PhillipsCompany.4T.com/MSDS-CA.pdf
The CA granule size is about 0.2 mm, making it safe to handle in dry air. Handling and storage of aluminum
granules is much more safe than the handling and storage of gasoline, diesel or other hydrocarbon fuels. A
safety-engineering analysis summarized the comparison of fuels by noting that in the worst case of an
automobile accident, would you rather have volatile and explosive gasoline leaking all over the place or would
you rather have non-flamable water and aluminum?
Aluminum particle size selection for CA is based on considerations of safety, hydrogen production rate, time
required to consume a particle when used as fuel and volume of the hydrogen-producing cell. Each of these
parameters have an effect on the other parameters. The following page gives information for the selection of
aluminum particle size for CA.
CA.p65; October 2012 Page 8
Aluminum particle size
For a specific application, the aluminum particle size can be selected for optimum performance. One application
of interest is the production of hydrogen for use as a fuel supplement for increasing the mileage (MPG) of a
vehicle such as an automobile or truck. Similar considerations apply for diesel generators having an output of up
to 50 KW. Recent work has focused on the fuel (particle size) that might be considered about right for
producing hydrogen at a rate of about 0.5 LPM using about a pound of aluminum in a cell having a volume of
about one quart.
Comments
Size too large. Hydrogen production rates low, for
amounts of aluminum in the range of a half-pound.
Size about right for producing hydrogen at 0.5 LPM using
about a half-pound of aluminum granules. Not a safety
hazard; for storage, shipping and use, if kept dry until
used in water; in a properly-designed hydrogen cell.
Size too small. Hydrogen production rate is high, but
particles this size can be consumed within half an hour,
making continuous feed necessary for sustained
hydrogen production at a nearly-constant rate.
Size too small. This size, considered to be atomized
powder is a potential safety hazard; for storage, shipping
and use.
The comments above are based on the selection of aluminum particle size (0.2 mm = 200 microns) for only one
application of interest -- the production of hydrogen for use as a fuel supplement for increasing the mileage (MPG)
of vehicles. For other applications, such as reducing fuel costs for ships, and large-scale uses of hydrogen, the
optimum aluminum particle size may be different.
The particles of CA are of graded size, which means CA contains a range of particle sizes; approximately 2 mm.
CA.p65; October 2012 Page 9
CA particle size measurement
A measuring microscope was used to obtain a measurement of CA particle size. The particles ranged from
about 0.07 mm to about 0.29mm; these particles are graded over a range of particle sizes.
CA.p65; October 2012 Page 10
Recycling options
When CA is used to split water, hydrogen is realeased in the form of a gas, and the oxygen remains in the water
in the form of aluminum hydroxide.
The low cost of producing hydrogen using CA often results in the aluminum hydroxide simply being discarded.
A second option is the recycling of aluminum hydroxide as illustrated above. A third option is the use of
aluminum oxide for other industrial purposes.
Aluminum hydroxide is used in the production of industrial chemicals. Products include alum (aluminum sulfate),
poly aluminum chloride (PAC), sodium aluminate, zeolites, aluminum fluoride, and as a raw material in the
manufacture of glass, glazes and frits.
Aluminum hydroxide is used as a raw material in catalyst production, for fertilizers, and fibre cement board
products, It is also used as an extender and bodying agent in paper, solvent-borne and water-borne paints, UV
curable coatings, inks, and adhesives.
Aluminum hydroxide is also used as a polishing and cleansing agent, mould wash and separating agent.
The many industrial uses of aluminum hydroxide are described online at
www.PhillipsCompany.4T.com/AHU.pdf
CA.p65; October 2012 Page 11
More information available
The process for the materials and technology discussed in this document are widely known. Patent applications
have been filed. Technical papers have been presented and published. Because we operate as a not-for-profit
company, our business is not based on trade secrets. Our trade secrets have been widely distributed to many
companies, both in the USA and internationally. For more technical information, inquiries can be directed to
Phillips Company or to our strategic alliance partners in Europe and Japan.
For open discussion of hydrogen on demand, please visit the international web site dedicated to this and related
technology applicatons:
hodinfo.com
The CA process for producing hydrogen from water is described online at
www.PhillipsCompany.4T.com/CA.pdf
This document will be updated. Please check back for updates from time to time.
Inquiries from companies in the USA and Canada can be directed to Phillips Company, at the following email
address:
hp@valliant.net
Inquiries from Europe can be directed to Bion Energy, Ltd., our strategic alliance and authorized agent in
England. Contact Fred Davey by sending email to the following address:
efred.davey@biongroup.co.uk
Please see our company web site for contact information for our partners in Japan and other international
locations:
www.PhillipsCompany.4T.com/HYDROGEN.html
CA.p65; October 2012 Page 12
Increasing MPG -- Commercialization of this new technology
As described above, when hydrogen from this process was added to the air intake of an otherwise unmodified
Buick test vehicle, mileage improvement ranged from 32% to 40%.
Converting existing engines to use CA is the next step toward commercialization. The new Catalyzed Aluminum
fuel was developed by Phillips Company, an Oklahoma-based FDA-registered pharmaceutical manufacturing
company. Phillips is not an energy products company. Accordingly, the development and commercialization of
hardware products will be done by other companies. That is the next step forward for this new technology.
The chemistry technology is completely developed, well understood, and ready for commercialization. We are
in discussion with potential licensees. Business agreements with additional licensees, particularly manufacturing
companies, are planned, said a company spokesman.
More commercial applications for this new technology
Phillips Company is searching for companies that can produce hardware and commercialize the technology in
the form of supplemental fuel for vehicles, hydrogen fuel for heating, and hydrogen fuel for water distillation.
We think using hydrogen to fuel ships is promising because the process works well with sea water. More
importantly, we think it makes sense to use hydrogen to fuel electric power generators on islands or in remote
locations where water is plentiful and cheap, compared to the cost of importing oil/diesel via tanker ships, said
a spokesman for the company.
These applications are now possible because this process is the worlds first process that can be scaled up to
produce hydrogen on demand at very high flow rates. Because the hydrogen-producing process uses pH-
neutral chemistry, the hardware corrosion problems can be virtually nil.
In the 2012 State of The Union address, the President said, This country needs an all-out, all-of-the-above
strategy that develops every available source of American energy - a strategy thats cleaner, cheaper, and full of
new jobs. Most Americans agree. We are searching for companies that can become strategic alliances to
produce the equipment and commercialize the use of hydrogen for fuel, said A. Shravah, the licensing agent for
Philllips Company. He can be reached via email: ashravah@gmail.com via email.
Catalyzed Aluminum is available now
CA is available in commercial quantities.
CA is also available in sample quantities for evaluation.
To obtain Catalyzed Aluminum, please see the ordering information online at
www.PhillipsCompany.4T.com/MCA.pdf
CA.p65; October 2012 Page 13
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Drilling Waste Management Technology ReviewDocument102 pagesDrilling Waste Management Technology ReviewPham Duc100% (1)
- Perfumed Laundry Detergent PowdersDocument7 pagesPerfumed Laundry Detergent PowdersNur AmaninaNo ratings yet
- Ripening of CheeseDocument18 pagesRipening of CheeseHASVRDNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Kinetics NotesDocument2 pagesEnzyme Kinetics NotesMarc Imhotep Cray, M.D.No ratings yet
- Carbon Monoxide PoisoningDocument22 pagesCarbon Monoxide PoisoningSunilNo ratings yet
- Determination of Amount of CaCO3 in Eggshell by Back Titration MethodDocument5 pagesDetermination of Amount of CaCO3 in Eggshell by Back Titration MethodMg H100% (2)
- RRLDocument5 pagesRRLSupremo Family100% (1)
- Cuellar Bermudez S P Aguilar Hernandez I PDFDocument20 pagesCuellar Bermudez S P Aguilar Hernandez I PDFJader MendozaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1687157X17300288 MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 S1687157X17300288 Mainnagi jainNo ratings yet
- Oxy Fuel System Set Up & Shut Down Procedure Checklist - Acetylene Fuel GasDocument6 pagesOxy Fuel System Set Up & Shut Down Procedure Checklist - Acetylene Fuel GasVinay KapadnisNo ratings yet
- OVERVIEW (4 Points) : CH116 General and Organic Principles LabDocument4 pagesOVERVIEW (4 Points) : CH116 General and Organic Principles Labapi-557329548No ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0011916414004986 MainDocument6 pages1 s2.0 S0011916414004986 Mainvikash chourasiaNo ratings yet
- Pipebook ADocument2 pagesPipebook APRAKASH PANDEYNo ratings yet
- Recycling OF Aluminum Salt Cake: ANL/CP - 73449 DE92 003408Document20 pagesRecycling OF Aluminum Salt Cake: ANL/CP - 73449 DE92 003408Vijaykumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- 1 - Pharmacokinetics IDocument20 pages1 - Pharmacokinetics IabdallaNo ratings yet
- Xanthan Gum-USPDocument2 pagesXanthan Gum-USPLaboratorium FarmasiNo ratings yet
- 1 ElectrochemistryExercise PDFDocument46 pages1 ElectrochemistryExercise PDFDivyanshi TiwaryNo ratings yet
- UV-Curing Screen InksDocument2 pagesUV-Curing Screen InksJavier RealNo ratings yet
- C 4721Document2 pagesC 4721Eileen TylerNo ratings yet
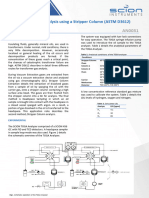
- Analisis de Gas de Aceite de Transformador Utilizando Una Columna de Separacion Astm d3612 KasalabDocument2 pagesAnalisis de Gas de Aceite de Transformador Utilizando Una Columna de Separacion Astm d3612 KasalabJohnatan HernándezNo ratings yet
- Combustion: Navigation SearchDocument10 pagesCombustion: Navigation SearchMashrekin HossainNo ratings yet
- Ion ChannelsDocument3 pagesIon ChannelsMizrab NadeemNo ratings yet
- Entropy Changes in Thermodynamic ProcessesDocument33 pagesEntropy Changes in Thermodynamic ProcessesJessica AndersonNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE (9-1) : PHYSICS 0972/41Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE (9-1) : PHYSICS 0972/41dowanahamidNo ratings yet
- Test Report E-Liquid: 1 Sample InformationDocument10 pagesTest Report E-Liquid: 1 Sample InformationVangel PetrovNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer BasicsDocument20 pagesHeat Transfer BasicshellboytonmoyNo ratings yet
- Effects of CN Ratios and Turning Frequencies On The Composting Process of Food Waste and Dry LeavesDocument8 pagesEffects of CN Ratios and Turning Frequencies On The Composting Process of Food Waste and Dry LeavesJonathan SotoNo ratings yet
- Lattice VibrationDocument21 pagesLattice VibrationPandu lalNo ratings yet
- Du Et Al 2020Document12 pagesDu Et Al 2020Deise Dalazen CastagnaraNo ratings yet
- Kinkelder StandardDocument24 pagesKinkelder StandardJason StephensNo ratings yet