Professional Documents
Culture Documents
f201508151439617857 PDF
Uploaded by
h_alimohamOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
f201508151439617857 PDF
Uploaded by
h_alimohamCopyright:
Available Formats
International Journal of Engineering Technology, Management and Applied Sciences
www.ijetmas.com August 2015, Volume 3, Issue 8, ISSN 2349-4476
Design and Analysis of Skid Frame Module for its Strength &
Stiffness
Aditi A. Godse, Prof. M.K.Wasekar
Sinhgad Academy of Engineering,Savitribai Phule University of Pune, India.
AbstractSkid base frame is a structural assembly consisting of beams of various cross sections or channel sections
and dimensions. This frame is to be designed for flow control system which is used to control and regulate the flow,
pressure, and temperature for fluids. These systems mainly include piping, pumps, valv es, and gauges. The flow control
application is mainly required for process industries like sugar plants, cement plants, power plants etc. Many times these
systems are locally operated & hence their elevation should be designed in such a way that it will r educe the hardship of
the operator. This frame is designed with conventional CAD design practices and then analyzed statically with FEA
software. The structural loads considered during analysis phase resemble the actual loading cases. The analysis is then
carried out to determine the induced stresses and the deflections at various locations on proposed frame and further
analytical calculations are done to verify the simulation results.
Keywords Skid frame, CA D model, FEA
I. INTRODUCTION resemble the actual loading cases. The analysis is
Skid Frame is a structural assembly consisting of then carried out to determine the induced stresses
beams of various cross sections and dimensions. and the deflections at various
The sections used may be of equal dimensions and Locations on proposed frame and further analytical
cross sections, or a combination can be used for calculations are done to verify the results.
optimum strength and weight. Different types of
sections are used for skid frames [2]. The sections
can be of IS standard dimension or custom made.
The base frame is subjected to gravitational loading
of all the components mounted viz. Compressor,
Air Receiver vessel, flow control system etc.
Depending on the type of loading, the optimum
design is made considering material properties and
type of welding. The Skid frame is required to
support various components that have been
designed by conventional design procedure. The
weights of the components mounted on the frame
are considered as static loads for designing. Some
simplifying assumptions are made at the initial
stages in order to decide the cross sections used for
various beams.
This frame is to be designed for flow control system
which is used to control and regulate the flow,
pressure, and temperature for fluids. These systems
mainly include piping, pumps, valves, and gauges.
The flow control application is mainly required for
process industries like sugar plants, cement plants,
power plants etc. Many times these systems are
locally operated & hence their elevation should be
designed in such a way that it will reduce the
hardship of the operator. This frame is designed
with conventional CAD design practices and then
analyzed statically with FEA software. The
structural loads considered during analysis phase Fig.1 Different type of base frames
59 Aditi A. Godse , Prof. M.K.Wasekar
International Journal of Engineering Technology, Management and Applied Sciences
www.ijetmas.com August 2015, Volume 3, Issue 8, ISSN 2349-4476
II. PROCEDURE FOR BASE FRAME DESIGN it has excellent strength and affordable cost, and is
A. SKID DESIGN most commonly used for skid frames.
TABLE I MATERIAL PROPERTIES USED FOR B. LOADING INPUTS
SKID DESIGN TABLE III WEIGHTS OF DIFFERENT
No Physical COMPONENTS
Values SI Units
. Properties Sr Weight
Tensile Part Name Qty.
1 510 Mpa or N/ mm2 No. in kg
Stress/Strength
Steam line
Yield
2 355 Mpa or N/ mm2 1 Gate valve 2 70
Stress/Strength
Youngs Modulus 2 Bypass valve 1 20
3 205 x 103 Mpa or N/ mm2 3 Globe valve 5 8
(E)
Shear Modulus 4 Pressure gauge 3 2
4 80 x 103 Mpa or N/ mm2
(G) 5 Thermometer 2 2
5 Poissons Ratio(v) 0.3 - 6 Globe control Valve 1 30
6 Density (p) 7850 Kg/m3 7 Safety Valve 1 36
Steam piping with
By observing the material properties for application 8 flanges for 5 mtr. 1 154
of skid frame, structural steel is used. The Chemical pipe
composition of Structural Steel is extremely 9 Desuperheater 1 65
important and highly regulated. In the following 10 Condensing Pot 1 70
table Max % levels of certain regulated elements 11 Moisture Separator 1 60
present in Structural steel grade S355 is shown.
Water line
TABLE II CHEMICAL COMPOSITION OF
12 Gate Valve 2 12
STRUCTURAL STEEL
13 Bypass Valve 1 14
Grade C% Mn% P% S% Si%
14 Non return valve 1 12
S55 0.23 1.60 0.05 0.05 0.05
15 Globe control Valve 1 18
1. Factor of Safety: 1.2 (For Static Load Cases) Water piping with
2. Allowable Stress: Yield Strength/Factor of 16 1 12
flanges
Safety
= 355 / 1.2
= 296 Mpa(For Static Load Cases)
B. SELECTION OF BEAM SECTION
Beams are the most critical members in structure.
Therefore their design should not only be
economical but also safe. It is a difficult task for
designer to select a beam size for a given span and
load that will satisfy all the conditions. A number of
rolled steel structures are used in construction.
However angles and T-sections are inherently weak
in bending while channels can only be used for light
loads. A circular beam would be a waste of
material. When dealing with bending stresses all the
stress is acting on the top and bottom of the beam. If
we take a circular beam max cross sectional area
would be at the center of the beam where no
bending stress occurs. If we take a square beam it
will have more cross sectional area at the top and Fig. 2 Flow Control System
bottom. It will also have less material in the center D. LOADING CALCULATIONS
of the beam where no stress is acting. Hence square Beam is considered as a continuous beam, Using
hollow section is most efficient and economical, as moment distribution method reactions are
calculated.
60 Aditi A. Godse , Prof. M.K.Wasekar
International Journal of Engineering Technology, Management and Applied Sciences
www.ijetmas.com August 2015, Volume 3, Issue 8, ISSN 2349-4476
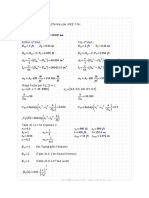
2. For calculating , taking moment at point C,
3. For calculating , taking moment at point C,
Similarly,
BC =0.35
CB =0.3511
CD =0.3319
DC =0.1514
Moments are fixed at the ends to calculate
and ,
=0.31
=0.39
Calculating Reactions at points A, B, C and D
Total weight =154 kg on one side of skid and length
is 5 meter so Udl is taken as,
Udl=
4. For calculating , taking moment at point B,
1. For calculating , taking moment at point B,
III. MODEL GEOMETRY AND TOPOLOGY
Skid frame is modeled in PRO-E 4.0 which is
excellent CAD software, which makes modeling so
easy and user friendly. The model is then
transferred in STEP format and imported into the
HYPERMESH 12.0. The Skid frame is analyzed in
three steps. First is preprocessing which involves
modeling, geometric clean up, meshing and element
property definition. Next step includes solution of
61 Aditi A. Godse , Prof. M.K.Wasekar
International Journal of Engineering Technology, Management and Applied Sciences
www.ijetmas.com August 2015, Volume 3, Issue 8, ISSN 2349-4476
problem, which involves imposing boundary V. FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS
conditions on the model and then solution runs. The figure shows maximum displacement which is
Next in sequence is post processing, which involves 4.2 mm and maximum stress is 50 Mpa.
analyzing the results plotting different parameters
like stress, strain, natural frequency.
Fig.3 Model of skid fame
IV. FINITE ELEMENT MODEL: MESHING &
LOAD CONNECTIONS Fig.5 The highlighted part shows maximum
Different type of elements used in meshing are displacement
listed below in table.
TABLE IV DIFFERENT ELEMENTS USED
Elements Type Number
Mass elements CONM1 35
Rigid elements RBE2 29
Bar elements CBAR 1478
TRIA elements CTRIA3 64
QUAD elements CQUAD4 54783
Total Elements: 56389
Any continuous object has infinite degrees of
freedom and its just not possible to solve the
problem in this format. Finite element method
reduces degrees of freedom from infinite to finite
with the help of discretization i.e. meshing. Weld Fig.6 The highlighted part shows maximum stress
elements are highlighted in red color, rigid elements
are highlighted in blue color and mass elements are VI.MODAL ANALYSIS
highlighted in green color as shown in below figure. Modal Analysis determines natural frequencies and
mode shapes of a structure. Each natural frequency
sets up specific deformation pattern, i.e. mode
shape. The same phenomenon can occur in a Skid
frame during working condition. To avoid
mechanical damage due to Resonance, the structure
must undergo Modal Analysis. For Modal Analysis,
the model should be kept free from all the loads and
constrains. First six frequencies were supposed to
be zero, as they represent translational and
rotational vibrations about X, Y, Z axes. For given
natural frequency, mode shape defines the way in
which the structure would deform. Mode Shape for
Fig.4 Meshed model of skid frame
62 Aditi A. Godse , Prof. M.K.Wasekar
International Journal of Engineering Technology, Management and Applied Sciences
www.ijetmas.com August 2015, Volume 3, Issue 8, ISSN 2349-4476
first six resonant frequencies is shown as follows-
Fig.7 Mode 1: Natural Frequency: 7.703 Hz Fig.11 Mode 5: Natural Frequency: 8.65 Hz
Fig.8 Mode 2: Natural Frequency: 13.28 Hz Fig.12 Mode 6: Natural Frequency: 8.59 Hz
VII. CONCLUSION
TABLE V COMPARISON OF RESULTS
Numerical Analytical
Reactions
value value
0.75 0.56
1.7 1.8
2.68 2.81
0.4 0.34
Fig.9 Mode 3: Natural Frequency: 13.19Hz The Skid Frame Module including Steel Skid Frame
& other structural members are analyzed for Linear
Static Loads using Finite Element Method
(FEM).The Module is qualified for the given load
values & various load combinations as per
specification. From above results, it is seen that the
analytical values of reactions shows very good
match with the software results and also maximum
stresses, welds in the skid frame members are less
than the corresponding allowable stresses. Hence,
the Module is safe, qualifies and passes as per
specifications for the design, operating conditions.
Fig.10 Mode 4: Natural Frequency: 12.25 Hz
63 Aditi A. Godse , Prof. M.K.Wasekar
International Journal of Engineering Technology, Management and Applied Sciences
www.ijetmas.com August 2015, Volume 3, Issue 8, ISSN 2349-4476
REFERENCES
[1] Chris Harper, Hongfa Wu Optimized Skid [5] Herman Van der Auweraer Structural
Design for Compressor Packages; Gas Dynamics Modeling using Modal Analysis:
Machinery Conference 2013 October 7 - 10, Applications, Trends and Challenges,IEEE
2013. Instrumentation and Measurement Technology
[2] Prof. Pandhare A. P. *, Chaskar S. T., Patil J. Conference,Budapest, Hungary, May 21-23,
N.,Jagtap A. S., Bangal P. M. Design, Analysis 2005
and Optimization of Skid Base Frame [6] Strength of Materials; M. Ramarutham;
[3] kishor d. jadhav & maneet.r.dhanvijay, design Dhanpat Rai Publications; Edition 12; 2012
and standardization of base frame & anti- [7] W. B. Riley, A. R. George, Design, Analysis
vibration mounts for balanced opposed piston and testing of a Formula SAE Car Chassis,
air compressorInternational Journal of Applied Motorsport engineering Conference and
Research in Mechanical Engineering (IJARME) Exhibition Indianapolis, Indiana, Dec 2-5, 2002.
ISSN: 2231 5950, Vol-2, Iss-2, 2012
[4] Joshi. A. M. *, Jadhav T. A. Analysis and
Testing of Skid of Frame of Compressor
International Journal of Applied Research and
Studies (iJARS) ISSN: 2278-9480 Volume 2,
Issue9(Sep-2013)
64 Aditi A. Godse , Prof. M.K.Wasekar
You might also like
- Technical Writing A-Z: A Commonsense Guide to Engineering Reports and Theses, Second Edition, British English: A Commonsense Guide to Engineering Reports and Theses, U.S. English Second EditionFrom EverandTechnical Writing A-Z: A Commonsense Guide to Engineering Reports and Theses, Second Edition, British English: A Commonsense Guide to Engineering Reports and Theses, U.S. English Second EditionNo ratings yet
- ASME B16.47!75!300# Series B Flanges With FLEXSEAL Spiral Wound GasketsDocument5 pagesASME B16.47!75!300# Series B Flanges With FLEXSEAL Spiral Wound Gasketserik aranaNo ratings yet
- Pipe Wall Thickness, Hoop Stress and Sustain Stress QuestionDocument10 pagesPipe Wall Thickness, Hoop Stress and Sustain Stress QuestionSharun Suresh100% (1)
- Jis g3456 Grade STPT 410 Pipes PDFDocument1 pageJis g3456 Grade STPT 410 Pipes PDFMitul MehtaNo ratings yet
- Hinge DesignDocument2 pagesHinge Designpare222No ratings yet
- BS 5151Document18 pagesBS 5151Steva76No ratings yet
- Nozzle Interference Error SolvingDocument2 pagesNozzle Interference Error SolvingSakthi VelNo ratings yet
- Easyheat s27 - 02 SarcoDocument8 pagesEasyheat s27 - 02 SarcoMarcelo ResckNo ratings yet
- Flange Leakage 6Document2 pagesFlange Leakage 6hamid sobirinNo ratings yet
- Attachment-5 API 6AF FLANGE - 2 Inch Node 3Document2 pagesAttachment-5 API 6AF FLANGE - 2 Inch Node 3BhaumikNo ratings yet
- 1 - Ansi Flange CheckDocument3 pages1 - Ansi Flange CheckJorge Hugo CorreaNo ratings yet
- Fibrelogic Flowtite Engineering Guidelines DES M-004 REFER PDFDocument122 pagesFibrelogic Flowtite Engineering Guidelines DES M-004 REFER PDFA.Subin DasNo ratings yet
- Ccsviiid1 2260Document2 pagesCcsviiid1 2260DieguitoOmarMoralesNo ratings yet
- En 13121-3 (2016) (E)Document10 pagesEn 13121-3 (2016) (E)jasonNo ratings yet
- RRC 271 DDocument64 pagesRRC 271 Drfuentes73No ratings yet
- BS en Iso 14692-3-2017Document46 pagesBS en Iso 14692-3-2017SRIDHAR BABU KONADANo ratings yet
- PVP2016 Final ProgramDocument76 pagesPVP2016 Final Programthaivinhtuy100% (1)
- PD 5500Document1 pagePD 5500Nagendra SunkariNo ratings yet
- Facilities On Offshore Installations: Guide For Building and ClassingDocument209 pagesFacilities On Offshore Installations: Guide For Building and ClassingKarthick VenkatswamyNo ratings yet
- H H Optimum 0,2: Instructions For Using NomogramDocument4 pagesH H Optimum 0,2: Instructions For Using NomogrammithunjobsNo ratings yet
- Slug FlowDocument7 pagesSlug FlowharishtokiNo ratings yet
- Joule Thomson EffectDocument2 pagesJoule Thomson EffectElliott100% (1)
- Calculo de Brida Segun ASMEDocument29 pagesCalculo de Brida Segun ASMEakarcz6731No ratings yet
- EJMA Example 06Document5 pagesEJMA Example 06Mayank GodhaNo ratings yet
- FPSO - Automating Structural DeflectionsDocument10 pagesFPSO - Automating Structural DeflectionsJP EDSNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Loading Specified in GDocument3 pagesEarthquake Loading Specified in GMas Arman TewoNo ratings yet
- Improved Analysis of External Loads On Flanged JointsDocument1 pageImproved Analysis of External Loads On Flanged JointsTiHoRNo ratings yet
- Technical DataDocument48 pagesTechnical Datashekhar2681No ratings yet
- Autopipe Msrs Example1XzDocument29 pagesAutopipe Msrs Example1XzFabio MiguelNo ratings yet
- Harmonic Analysis REV. 1Document7 pagesHarmonic Analysis REV. 1Amro SalahNo ratings yet
- Conversion ASME Unit ConversionDocument3 pagesConversion ASME Unit ConversionMohdBadruddinKarimNo ratings yet
- Flange GradesDocument8 pagesFlange Gradesaateka02No ratings yet
- Coupling Calculations and Ug-32 Unstayed Head CalculationsDocument9 pagesCoupling Calculations and Ug-32 Unstayed Head CalculationsLcm TnlNo ratings yet
- NPS - 'Nominal Pipe Size' and DN - 'Diametre Nominal'Document3 pagesNPS - 'Nominal Pipe Size' and DN - 'Diametre Nominal'harisNo ratings yet
- R 015987Document63 pagesR 015987shaffeti100% (2)
- BS 5276-2Document20 pagesBS 5276-2Ali Alizadeh100% (1)
- TES-ME-STRTN-GL Design and Fabrication of Butt-Welded Transition Joints Specification (CAN-US-MEX)Document19 pagesTES-ME-STRTN-GL Design and Fabrication of Butt-Welded Transition Joints Specification (CAN-US-MEX)BetoCostaNo ratings yet
- Pipe Stress Analysis by Computer CAESAR II PDFDocument11 pagesPipe Stress Analysis by Computer CAESAR II PDFAbhijeetNo ratings yet
- Stresses in Large Horizontal Cylindrical Pressure Vessels On Two Saddle SupportsDocument12 pagesStresses in Large Horizontal Cylindrical Pressure Vessels On Two Saddle SupportsAnonymous qhVGVpNo ratings yet
- Importing Nozzle Loads From Autopipe Into Autopipe NozzleDocument3 pagesImporting Nozzle Loads From Autopipe Into Autopipe NozzlegchammaNo ratings yet
- A.W.W.A Manual M11 Harness Restraint: Romac Industries, IncDocument1 pageA.W.W.A Manual M11 Harness Restraint: Romac Industries, IncAresteo Victor AquinoNo ratings yet
- API 650 Storage Tank HRD - SubDocument7 pagesAPI 650 Storage Tank HRD - SubBimal DeyNo ratings yet
- MSS SP-97-2012Document21 pagesMSS SP-97-2012Marco CarrieriNo ratings yet
- BS 5500 Appendix K and DDocument14 pagesBS 5500 Appendix K and DCRISTIAN SILVIU IANUCNo ratings yet
- Overhead Crane Governing Bodies and Specs PDFDocument1 pageOverhead Crane Governing Bodies and Specs PDFscofiel1No ratings yet
- Air Valve BrochureDocument27 pagesAir Valve Brochuredamith030No ratings yet
- ASME 2286-2 Alternative Rules For Determining Allowable External PressureDocument16 pagesASME 2286-2 Alternative Rules For Determining Allowable External PressureMike Dukas100% (1)
- SIF's For TrunnionDocument10 pagesSIF's For TrunnionfileseekerNo ratings yet
- Stack Wind CalculationsDocument5 pagesStack Wind CalculationsJosé García100% (2)
- Fatigue Analysis of 6300 Liters Pressure Vessel by Using Cyclic ServiceDocument7 pagesFatigue Analysis of 6300 Liters Pressure Vessel by Using Cyclic ServiceFisul RahumanNo ratings yet
- Beam Deflections and Stresses During Lifting PDFDocument10 pagesBeam Deflections and Stresses During Lifting PDFManoj KumarNo ratings yet
- BS5500 - 1994-1Document65 pagesBS5500 - 1994-1paeg6512100% (1)
- How To Use Code Case in PV EliteDocument2 pagesHow To Use Code Case in PV EliteMukeshChopraNo ratings yet
- Seismic Load Calculation of The Tank As Per IS 1893Document1 pageSeismic Load Calculation of The Tank As Per IS 1893ParthibanNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Skid Frame For Pumping StationDocument6 pagesDesign and Analysis of Skid Frame For Pumping StationtizioNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Compressor Package Skid FrameDocument7 pagesDesign and Analysis of Compressor Package Skid FramezsmithNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of Unburied and Buried Pipeline Structure in Seismic Zone Using Caesar IiDocument6 pagesComparative Analysis of Unburied and Buried Pipeline Structure in Seismic Zone Using Caesar IiDinesh Kumar CNo ratings yet
- IRJET - Research Paper v5Document6 pagesIRJET - Research Paper v5Ram SinghNo ratings yet
- Fatigue Assessment IJETT-V13P205Document4 pagesFatigue Assessment IJETT-V13P205MehdiNo ratings yet
- Api 6XDocument3 pagesApi 6XSandra SandersNo ratings yet
- Construction and Building Materials: Alessio Cascardi, Fabio Longo, Francesco Micelli, Maria Antonietta AielloDocument15 pagesConstruction and Building Materials: Alessio Cascardi, Fabio Longo, Francesco Micelli, Maria Antonietta AielloHussein ElsanadedyNo ratings yet
- XXX Taffesdsse2017 XXXDocument14 pagesXXX Taffesdsse2017 XXXRibeiro Elias ConcursosNo ratings yet
- In Uence of Vibration On The Performance of Tunnel Boring MachinesDocument7 pagesIn Uence of Vibration On The Performance of Tunnel Boring MachinesVesangi Lakshmi PrasadNo ratings yet
- IS 3370 Part 2 - 2009-Readable PDFDocument14 pagesIS 3370 Part 2 - 2009-Readable PDFpradip ghodeswarNo ratings yet
- (EngineeringEBookspdf) Corrosion of Copper PDFDocument468 pages(EngineeringEBookspdf) Corrosion of Copper PDFFathi GabsiNo ratings yet
- Cartech Trimrite® Stainless: IdentificationDocument7 pagesCartech Trimrite® Stainless: IdentificationYassinSalahNo ratings yet
- Essential Technical Data On Steel Reinforcement: InforcingDocument68 pagesEssential Technical Data On Steel Reinforcement: InforcingNil DGNo ratings yet
- Detent Pins Carr LaneDocument3 pagesDetent Pins Carr LaneDaniel OlguínNo ratings yet
- Fastners ComparisonDocument6 pagesFastners ComparisonIndunil Prasanna Bandara WarnasooriyaNo ratings yet
- CEPE1S - Title Page - Design Details FormatDocument3 pagesCEPE1S - Title Page - Design Details FormatRobert MacalanaoNo ratings yet
- Api 6aDocument23 pagesApi 6aumairahmedbaig75% (4)
- Code of Practice For Design and Construction of Raft FoundationsDocument26 pagesCode of Practice For Design and Construction of Raft FoundationsZiya Ul Haq SagriNo ratings yet
- Innothane: Innotooling Ie-644-02Document2 pagesInnothane: Innotooling Ie-644-02Arieza PerdhanaNo ratings yet
- Richards & Read (2007) NZ Greywacke Characteristics and Influences On Rock Mass BehaviorDocument6 pagesRichards & Read (2007) NZ Greywacke Characteristics and Influences On Rock Mass BehaviordanNo ratings yet
- Tribology International: Masanobu Kubota, Kenji HirakawaDocument10 pagesTribology International: Masanobu Kubota, Kenji HirakawaPhúc TuấnNo ratings yet
- TesstDocument34 pagesTesstMark D VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- MCQ Materials Science Part1Document4 pagesMCQ Materials Science Part1fotickNo ratings yet
- Slotted Spring Pins: ISO 8752 ASME B18.8.2 ASME B18.8.4MDocument8 pagesSlotted Spring Pins: ISO 8752 ASME B18.8.2 ASME B18.8.4MAhmed ElsafouryNo ratings yet
- Continum and Discontinum Modelling On Tunnel EngineeringDocument14 pagesContinum and Discontinum Modelling On Tunnel EngineeringDedi Geo SetionoNo ratings yet
- Designing With Composite DeckDocument17 pagesDesigning With Composite Deckhuynhvanchau0% (1)
- Thorplas Engineering ManualDocument32 pagesThorplas Engineering ManualNguyen JohnNo ratings yet
- Masterflow 920 Ans: Epoxy Acrylate (Styrene-Free) Resin Based High Performance Anchoring GroutDocument5 pagesMasterflow 920 Ans: Epoxy Acrylate (Styrene-Free) Resin Based High Performance Anchoring GroutMuhammad Fadhil ImansyahNo ratings yet
- StrunetDocument10 pagesStrunetVictor CalderónNo ratings yet
- Ems Tsg50 4 50% GF Nylon 66Document2 pagesEms Tsg50 4 50% GF Nylon 66elevendotNo ratings yet
- Belt Caster Feed NozzlesDocument1 pageBelt Caster Feed NozzlesManoj ChitreNo ratings yet
- WTE162 Chapter 1 Introduction To Wood PropertiesDocument22 pagesWTE162 Chapter 1 Introduction To Wood PropertiesHuzairee IsmailNo ratings yet
- Extrusion ToolingDocument17 pagesExtrusion ToolingSantosh Kumar100% (1)
- Fluctuating Stresses1Document11 pagesFluctuating Stresses1Shubham Sharma0% (1)
- BS en - 14532 2 2004 PDFDocument26 pagesBS en - 14532 2 2004 PDFPacoNo ratings yet
- To Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignFrom EverandTo Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (138)
- ChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindFrom EverandChatGPT Money Machine 2024 - The Ultimate Chatbot Cheat Sheet to Go From Clueless Noob to Prompt Prodigy Fast! Complete AI Beginner’s Course to Catch the GPT Gold Rush Before It Leaves You BehindNo ratings yet
- Advanced Modelling Techniques in Structural DesignFrom EverandAdvanced Modelling Techniques in Structural DesignRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Arduino: The complete guide to Arduino for beginners, including projects, tips, tricks, and programming!From EverandArduino: The complete guide to Arduino for beginners, including projects, tips, tricks, and programming!Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Artificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureFrom EverandArtificial Intelligence Revolution: How AI Will Change our Society, Economy, and CultureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Carpentry Made Easy - The Science and Art of Framing - With Specific Instructions for Building Balloon Frames, Barn Frames, Mill Frames, Warehouses, Church SpiresFrom EverandCarpentry Made Easy - The Science and Art of Framing - With Specific Instructions for Building Balloon Frames, Barn Frames, Mill Frames, Warehouses, Church SpiresRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (2)
- PLC Programming & Implementation: An Introduction to PLC Programming Methods and ApplicationsFrom EverandPLC Programming & Implementation: An Introduction to PLC Programming Methods and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Onshore Structural Design Calculations: Power Plant and Energy Processing FacilitiesFrom EverandOnshore Structural Design Calculations: Power Plant and Energy Processing FacilitiesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- SAM: One Robot, a Dozen Engineers, and the Race to Revolutionize the Way We BuildFrom EverandSAM: One Robot, a Dozen Engineers, and the Race to Revolutionize the Way We BuildRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Structural Cross Sections: Analysis and DesignFrom EverandStructural Cross Sections: Analysis and DesignRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (19)
- Digital Twin Development and Deployment on the Cloud: Developing Cloud-Friendly Dynamic Models Using Simulink®/SimscapeTM and Amazon AWSFrom EverandDigital Twin Development and Deployment on the Cloud: Developing Cloud-Friendly Dynamic Models Using Simulink®/SimscapeTM and Amazon AWSNo ratings yet
- Building with Virtual LEGO: Getting Started with LEGO Digital Designer, LDraw, and MecabricksFrom EverandBuilding with Virtual LEGO: Getting Started with LEGO Digital Designer, LDraw, and MecabricksNo ratings yet
- The AI Generation: Shaping Our Global Future with Thinking MachinesFrom EverandThe AI Generation: Shaping Our Global Future with Thinking MachinesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Mechanics of Flow-Induced Sound and Vibration, Volume 2: Complex Flow-Structure InteractionsFrom EverandMechanics of Flow-Induced Sound and Vibration, Volume 2: Complex Flow-Structure InteractionsNo ratings yet
- Bridge Engineering: Classifications, Design Loading, and Analysis MethodsFrom EverandBridge Engineering: Classifications, Design Loading, and Analysis MethodsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (16)
- Marine Structural Design CalculationsFrom EverandMarine Structural Design CalculationsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- Non-destructive Testing and Evaluation of Civil Engineering StructuresFrom EverandNon-destructive Testing and Evaluation of Civil Engineering StructuresJean-Paul BalayssacNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence: The Complete Beginner’s Guide to the Future of A.I.From EverandArtificial Intelligence: The Complete Beginner’s Guide to the Future of A.I.Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- Artificial Intelligence: Learning about Chatbots, Robotics, and Other Business ApplicationsFrom EverandArtificial Intelligence: Learning about Chatbots, Robotics, and Other Business ApplicationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)