Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Test Series Heat & Thermodynamics, KTG For NEET 2017
Uploaded by
umved singh yadavOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Test Series Heat & Thermodynamics, KTG For NEET 2017
Uploaded by
umved singh yadavCopyright:
Available Formats
(9027187359, 7351266266) More than 15 years Teaching Experience
XI &XII (CBSE & ICSE BOARD) IIT-JEE/AIIMS/AIPMT/CPMT/UPTU
Best of Luck for Your Competitive Exams (a) 3/2 (b) 23/15
(c) 35/23 (d) 4/3
1. If the length of a cylinder on heating increases by 2%,
8. If a gas has n degrees of freedom ratio of specific
the area of its base will increase by heats of gas is
(a) 0.5% (b) 2% 1n 1
(a) (b) 1
(c) 1% (d) 4% 2 n
n 2
(c) 1 (d) 1
2. A beaker is completely filled with water at 4C. It will 2 n
overflow if
(a) Heated above 4C 9. Gas at a pressure P0 in contained is a vessel. If the
(b) Cooled below 4C masses of all the molecules are halved and their
(c) Both heated and cooled above and below 4C speeds are doubled, the resulting pressure P will be
respectively equal to
(d) None of the above (a) 4P0 (b) 2P0
P0
3. Work done in converting one gram of ice at 10C (c) P0 (d)
2
into steam at 100C is
(a) 3045 J (b) 6056 J 10. Volume-temperature graph at atmospheric pressure
(c) 721 J (d) 616 J for a monoatomic gas (V in m3 , T in oC) is
4. At 0C the density of a fixed mass of a gas divided by V V
pressure is x. At 100C, the ratio will be (a) (b)
273
(a) x (b) x
373
T(oC) T(oC)
373 100
(c) x (d) x
273 273 (c) V (d) V
5. If an ideal gas has volume V at 27C and it is heated
at a constant pressure so that its volume becomes T(oC) T(oC)
1.5V. Then the value of final temperature will be
(a) 600C (b) 177C
11. The first law of thermodynamics is concerned with the
(c) 817C (d) None of these conservation of
6. At a given temperature the root mean square (a) Momentum (b) Energy
velocities of oxygen and hydrogen molecules are in (c) Mass (d) Temperature
the ratio
12. 110 J of heat is added to a gaseous system, whose
(a) 16 : 1 (b) 1 : 16
internal energy change is 40 J, then the amount of
(c) 4 : 1 (d) 1 : 4
external work done is
7. One mole of ideal monoatomic gas ( 5 / 3) is mixed (a) 150 J (b) 70 J
with one mole of diatomic gas ( 7 / 5). What is (c) 110 J (d) 40 J
for the mixture? denotes the ratio of specific heat at
constant pressure, to that at constant volume
NEET -2 TEST SERIES TEST -4 (HEAT, THERMODYNAMICS & KTG)
POTENTIAL PHYSICS ACADEMY
9027187359, 7351266266 P.L. SHARMA ROAD, OPP. SAGAR COPUTEX, MEERUT Page 1
(9027187359, 7351266266) More than 15 years Teaching Experience
XI &XII (CBSE & ICSE BOARD) IIT-JEE/AIIMS/AIPMT/CPMT/UPTU
13. Which of the following is not thermodynamical 20. Two kg of water is converted into steam by boiling at
function atmospheric pressure. The volume changes from
(a) Enthalpy (b) Work done 2 10 3 m 3 to 3.34m 3 . The work done by the system
(c) Gibb's energy (d) Internal energy is about
(a) 340 kJ (b) 170 kJ
14. In a given process for an ideal gas, dW 0 and (c) 170 kJ (d) 340 Kj
dQ 0. Then for the gas
21. A Container having 1 mole of a gas at a temperature
(a) The temperature will decrease
27C has a movable piston which maintains at
(b) The volume will increase constant pressure in container of 1 atm. The gas is
(c) The pressure will remain constant compressed until temperature becomes 127C. The
(d) The temperature will increase work done is (Cp for gas is 7.03 cal/molK)
(a) 703 J (b) 814 J
15. Which of the following statements is correct for any (c) 121 J (d) 2035 J
thermodynamic system
(a) The internal energy changes in all processes 22. The temperature of sink of Carnot engine is 27o C .
(b) Internal energy and entropy are state functions Efficiency of engine is 25%. Then temperature of
source is
(c) The change in entropy can never be zero
(d) The work done in an adiabatic process is always (a) 227o C (b) 327o C
zero (c) 127o C (d) 27o C
16. First law of thermodynamics is a special case of 23. In a Carnot engine, when T2 0 o C and T1 200 o C,
(a) Newton's law its efficiency is 1 and when T1 0 o C and
(b) Law of conservation of energy T2 200 C , Its efficiency is 2 , then what is 1 / 2
o
(c) Charle's law (a) 0.577
(d) Law of heat exchange
(b) 0.733
17. The isothermal Bulk modulus of an ideal gas at (c) 0.638
pressure P is (d) Can not be calculated
(a) P (b) P
24. Even Carnot engine cannot give 100% efficiency
(c) P / 2 (d) P / because we cannot
(a) Prevent radiation
18. An ideal gas at 27o C is compressed adiabatically to (b) Find ideal sources
8 5
of its original volume. If , then the rise in (c) Reach absolute zero temperature
27 3
(d) Eliminate friction
temperature is
(a) 450 K (b) 375 K 25. A monoatomic ideal gas, initially at temperature T1 , is
(c) 225 K (d) 405 K enclosed in a cylinder fitted with a frictionless piston.
The gas is allowed to expand adiabatically to a
19. We consider a thermodynamic system. If U temperature. T2 by releasing the piston suddenly. If
represents the increase in its internal energy and W the L1 and L2 are the lengths of the gas column before
work done by the system, which of the following and after expansion respectively, then T1 / T2 is given
statements is true
by
2/3
(a) U W in an adiabatic process L L1
(a) 1 (b)
(b) U W in an isothermal process L2 L2
(c) U W in an isothermal process 2/3
L2 L
(d) U W in an adiabatic process (c) (d) 2
L1 L1
NEET -2 TEST SERIES TEST -4 (HEAT, THERMODYNAMICS & KTG)
POTENTIAL PHYSICS ACADEMY
9027187359, 7351266266 P.L. SHARMA ROAD, OPP. SAGAR COPUTEX, MEERUT Page 2
(9027187359, 7351266266) More than 15 years Teaching Experience
XI &XII (CBSE & ICSE BOARD) IIT-JEE/AIIMS/AIPMT/CPMT/UPTU
26. A gas mixture consists of 2 moles of oxygen and 4 30. When fluids are heated from the bottom, convection
moles argon at temperature T. Neglecting all currents are produced because
vibrational modes, the total internal energy of the (a) Molecular motion of fluid becomes aligned
system is (b) Molecular collisions take place within the fluid
(a) 4 RT (b) 15 RT (c) Heated fluid becomes more dense than the cold
(c) 9 RT (d) 11 RT fluid above it
(d) Heated fluid becomes less dense than the cold
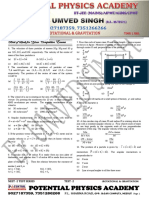
27. In the following figure, four curves A, B, C and D are fluid above it
shown. The curves are
31. The earth radiates in the infra-red region of the
P P spectrum. The spectrum is correctly given by
A (a) Wiens law
(b) Rayleigh jeans law
B
(c) Plancks law of radiation
C
(d) Stefans law of radiation
D
V V 32. An ideal black body at room temperature is thrown
into a furnace. It is observed that
(a) Initially it is the darkest body and at later times the
(a) Isothermal for A and D while adiabatic for B and
brightest
C
(b) It is the darkest body at all times
(b) Adiabatic for A and C while isothermal for B and
(c) It cannot be distinguished at all times
D
(d) Initially it is the darkest body and at later times it
(c) Isothermal for A and B while adiabatic for C and cannot be distinguished
D
33. How is the temperature of stars determined by
(d) Isothermal for A and C while adiabatic for B and
(a) Stefans law
D
(b) Weins displacement law
28. For cooking the food, which of the following type of (c) Kirchhoffs law
utensil is most suitable (d) Ohms law
(a) High specific heat and low conductivity
34. A body radiates energy 5W at a temperature of
(b) High specific heat and high conductivity
127o C . If the temperature is increased to 927o C ,
(c) Low specific heat and low conductivity
then it radiates energy at the rate of
(d) Low specific heat and high conductivity (a) 410W (b) 81 W
(c) 405 W (d) 200 W
29. Two metal cubes A and B of same size are arranged
as shown in the figure. The extreme ends of the 35. If the suns surface radiates heat at 6.3 107 Wm2 .
combination are maintained at the indicated Calculate the temperature of the sun assuming it to be
temperatures. The arrangement is thermally insulated. a black body ( 5.7 108 Wm2 K 4 )
The coefficients of thermal conductivity of A and B
are 300 W / m o C and 200 W / m o C , respectively. After (a) 5.8 10 3 K (b) 8.5 10 3 K
steady state is reached, the temperature of the (c) 3.5 108 K (d) 5.3 108 K
interface will be 36. According to Newtons law of cooling, the rate of
(a) 45 o C cooling of a body is proportional to ( )n , where
o
(b) 90 C is the difference of the temperature of the body and
100oC A B 0oC
(c) 30 o C the surroundings, and n is equal to
(d) 60 o C (a) One (b) Two
(c) Three (d) Four
NEET -2 TEST SERIES TEST -4 (HEAT, THERMODYNAMICS & KTG)
POTENTIAL PHYSICS ACADEMY
9027187359, 7351266266 P.L. SHARMA ROAD, OPP. SAGAR COPUTEX, MEERUT Page 3
(9027187359, 7351266266) More than 15 years Teaching Experience
XI &XII (CBSE & ICSE BOARD) IIT-JEE/AIIMS/AIPMT/CPMT/UPTU
37. For a gas if ratio of specific heats at constant pressure 42. The average translational energy and the r.m.s. speed
and volume is then value of degrees of freedom is of molecules in a sample of oxygen gas at 300 K are
3 1 6.21 10 21 J and 484 m/s respectively. The
(a)
2 1 corresponding values at 600 K are nearly (assuming
2 ideal gas behaviour)
(b)
1 (a) 12.42 10 21 J , 968 m / s
9
(c) ( 1) (b) 8.78 10 21 J , 684 m / s
2
(c) 6.21 10 21 J , 968 m / s
25
(d) ( 1) (d) 12.42 10 21 J , 684 m / s
2
38. Which of the following statement is true 43. A gas mixture consists of 2 mole of oxygen and 4
(a) Absolute zero degree temperature is not zero mole of argon at temperature T. Neglecting all
vibrational modes, the total internal energy of the
energy temperature
system is
(b) Two different gases at the same temperature (a) 4 RT (b) 15 RT
pressure have equal root mean square velocities (c) 9 RT (d) 11 RT
(c) The root mean square speed of the molecules of 44. An ideal gas is initially at temperature T and volume
different ideal gases, maintained at the same V. Its volume is increased by V due to an increase in
temperature T , pressure remaining constant. The
temperature are the same
quantity V /(VT) varies with temperature as
(d) Given sample of 1 cc of hydrogen and 1 cc of
oxygen both at NTP; oxygen sample has a large
(a) (b)
number of molecules
39. For a gas at a temperature T the root-mean-square T
T
velocity vrms , the most probable speed vmp , and the Temp. (K)
Temp. (K)
average speed vav obey the relationship
(a) vav vrms vmp (c) (d)
(b) vrms vav vmp
(c) vmp vav vrms
(d) vmp vrms vav T T
Temp. (K) Temp. (K)
40. The kinetic energy, due to translational motion, of
45. Density of substance at 0C is 10 gm/cc and at 100C,
most of the molecules of an ideal gas at absolute
its density is 9.7 gm/cc. The coefficient of linear
temperature T is expansion of the substance will be
(a) kT (b) k/T (a) 102 (b) 102
(c) T/k (d) 1/Kt (c) 103 (d) 104
41. The average translational kinetic energy of O2 (molar
mass 32) molecules at a particular temperature is
0.048 eV. The translational kinetic energy of N 2
(molar mass 28) molecules in eV at the same
temperature is
(a) 0.0015 (b) 0.003
(c) 0.048 (d) 0.768
NEET -2 TEST SERIES TEST -4 (HEAT, THERMODYNAMICS & KTG)
POTENTIAL PHYSICS ACADEMY
9027187359, 7351266266 P.L. SHARMA ROAD, OPP. SAGAR COPUTEX, MEERUT Page 4
You might also like
- Testpapaer Neet - 2017 Ray & Wave Optics, Modern Physics, Electronics & Semiconductor DevicesDocument4 pagesTestpapaer Neet - 2017 Ray & Wave Optics, Modern Physics, Electronics & Semiconductor Devicesumved singh yadavNo ratings yet
- Theory Notes of Newton's Laws of Motion For NEET & IIT 2017Document18 pagesTheory Notes of Newton's Laws of Motion For NEET & IIT 2017umved singh yadav90% (10)
- Numerical Bank of Electrostatics For Iit PMT PDFDocument16 pagesNumerical Bank of Electrostatics For Iit PMT PDFumved singh yadav100% (1)
- 100 Question 100 Min. Series ElectrostaticsDocument13 pages100 Question 100 Min. Series Electrostaticsumved singh yadavNo ratings yet
- AIIMS MBBS Sample Papers 3 (Aiims Mbbs Question Papers 2013)Document32 pagesAIIMS MBBS Sample Papers 3 (Aiims Mbbs Question Papers 2013)Firdosh KhanNo ratings yet
- Neet - 2017 Test Series Two Dimensional Motion & Work Power EnergyDocument4 pagesNeet - 2017 Test Series Two Dimensional Motion & Work Power Energyumved singh yadav100% (1)
- Numerical Bank of Electrostatics For Iit PMT PDFDocument16 pagesNumerical Bank of Electrostatics For Iit PMT PDFumved singh yadav100% (1)
- Physics Question Bank 2017 Xii C.B.S.E. Board StudentsDocument30 pagesPhysics Question Bank 2017 Xii C.B.S.E. Board Studentsumved singh yadavNo ratings yet
- 100 Questions 100 Min. Capacitance NEET-2017/IIT MAINS 2017Document11 pages100 Questions 100 Min. Capacitance NEET-2017/IIT MAINS 2017umved singh yadav100% (9)
- Neet - 2 Test Series Properties of Matter and Fluid Mechanics 3Document4 pagesNeet - 2 Test Series Properties of Matter and Fluid Mechanics 3umved singh yadavNo ratings yet
- Neet - 2 Test Series One D 2 D NLM Final2Document4 pagesNeet - 2 Test Series One D 2 D NLM Final2umved singh yadavNo ratings yet
- Neet - 2 Test Series Rotational Motion and Gravitation 1 FinalDocument4 pagesNeet - 2 Test Series Rotational Motion and Gravitation 1 Finalumved singh yadavNo ratings yet
- Test Series NEET - 2017 Elasticity & Fluid DynamicsDocument4 pagesTest Series NEET - 2017 Elasticity & Fluid Dynamicsumved singh yadavNo ratings yet
- Theory of Magnetism, Magnetic Effect of Current For Iit PMTDocument10 pagesTheory of Magnetism, Magnetic Effect of Current For Iit PMTumved singh yadavNo ratings yet
- Test Paper Oscillation & WavesDocument3 pagesTest Paper Oscillation & Wavesumved singh yadav100% (1)
- Test Series Aipmt 2016 Current ElectricityDocument5 pagesTest Series Aipmt 2016 Current Electricityumved singh yadavNo ratings yet
- Test 17 Heat & ThermodynamicsDocument4 pagesTest 17 Heat & Thermodynamicsumved singh yadavNo ratings yet
- Test 20 Rotational DynamicssDocument4 pagesTest 20 Rotational Dynamicssumved singh yadavNo ratings yet
- Test Paper Neet - 2017 WavesDocument2 pagesTest Paper Neet - 2017 Wavesumved singh yadavNo ratings yet
- Physics Question Bank 2017 Xii C.B.S.E. Board StudentsDocument30 pagesPhysics Question Bank 2017 Xii C.B.S.E. Board Studentsumved singh yadavNo ratings yet
- Test Paper Neet - 2017 WavesDocument2 pagesTest Paper Neet - 2017 Wavesumved singh yadavNo ratings yet
- Theory of Alternating Current For Neet 2017Document10 pagesTheory of Alternating Current For Neet 2017umved singh yadavNo ratings yet
- Physics Question Bank 2017 Xii C.B.S.E. Board StudentsDocument30 pagesPhysics Question Bank 2017 Xii C.B.S.E. Board Studentsumved singh yadavNo ratings yet
- Theory of Ray Optics FOR IIT/NEETDocument27 pagesTheory of Ray Optics FOR IIT/NEETumved singh yadav100% (2)
- Numerical Bank Current Electricity For Neet 2017Document17 pagesNumerical Bank Current Electricity For Neet 2017umved singh yadavNo ratings yet
- Theory of Alternating Current For Neet 2017Document10 pagesTheory of Alternating Current For Neet 2017umved singh yadavNo ratings yet
- Theory of Atomic Structure For Neet 2017Document9 pagesTheory of Atomic Structure For Neet 2017umved singh yadavNo ratings yet
- Neet Class Test Semiconductor Devices 2017Document4 pagesNeet Class Test Semiconductor Devices 2017umved singh yadavNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- AJK Newslet-1Document28 pagesAJK Newslet-1Syed Raza Ali RazaNo ratings yet
- A Systematic Scoping Review of Sustainable Tourism Indicators in Relation To The Sustainable Development GoalsDocument22 pagesA Systematic Scoping Review of Sustainable Tourism Indicators in Relation To The Sustainable Development GoalsNathy Slq AstudilloNo ratings yet
- Ne 01 20 09 2018Document436 pagesNe 01 20 09 2018VaradrajNo ratings yet
- 01 Design of Flexible Pavement Using Coir GeotextilesDocument126 pages01 Design of Flexible Pavement Using Coir GeotextilesSreeja Sadanandan100% (1)
- Trove Research Carbon Credit Demand Supply and Prices 1 June 2021Document51 pagesTrove Research Carbon Credit Demand Supply and Prices 1 June 2021Ceren ArkancanNo ratings yet
- C11 RacloprideDocument5 pagesC11 RacloprideAvina 123No ratings yet
- Impact of Recruitment & Selection on Employee RetentionDocument39 pagesImpact of Recruitment & Selection on Employee RetentiongizawNo ratings yet
- Wsi PSDDocument18 pagesWsi PSDДрагиша Небитни ТрифуновићNo ratings yet
- Startups Helping - India Go GreenDocument13 pagesStartups Helping - India Go Greensimran kNo ratings yet
- 153C Final Exam Study Guide-2Document6 pages153C Final Exam Study Guide-2Soji AdimulaNo ratings yet
- Strain Gauge Sensor PDFDocument12 pagesStrain Gauge Sensor PDFMario Eduardo Santos MartinsNo ratings yet
- Future Design of Accessibility in Games - A Design Vocabulary - ScienceDirectDocument16 pagesFuture Design of Accessibility in Games - A Design Vocabulary - ScienceDirectsulaNo ratings yet
- Seminar #22 Vocabury For Speaking PracticeDocument7 pagesSeminar #22 Vocabury For Speaking PracticeOyun-erdene ErdenebilegNo ratings yet
- R4 User GuideDocument48 pagesR4 User GuideAaron SmithNo ratings yet
- Design and Analysis of Algorithms Prof. Madhavan Mukund Chennai Mathematical Institute Week - 01 Module - 01 Lecture - 01Document8 pagesDesign and Analysis of Algorithms Prof. Madhavan Mukund Chennai Mathematical Institute Week - 01 Module - 01 Lecture - 01SwatiNo ratings yet
- DAT MAPEH 6 Final PDFDocument4 pagesDAT MAPEH 6 Final PDFMARLYN GAY EPANNo ratings yet
- Research Paper On Organ DonationDocument8 pagesResearch Paper On Organ Donationsheeliya whiteNo ratings yet
- Raychem Price ListDocument48 pagesRaychem Price ListramshivvermaNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Information Technology and Innovation To Improve Business Performance Through Marketing Capabilities in Online Businesses by Young GenerationsDocument10 pagesThe Impact of Information Technology and Innovation To Improve Business Performance Through Marketing Capabilities in Online Businesses by Young GenerationsLanta KhairunisaNo ratings yet
- National Products Classification Code For Services in IndiaDocument92 pagesNational Products Classification Code For Services in Indiakalanemi0% (2)
- Lec 10 - MQueues and Shared Memory PDFDocument57 pagesLec 10 - MQueues and Shared Memory PDFUchiha ItachiNo ratings yet
- Product Catalog 2016Document84 pagesProduct Catalog 2016Sauro GordiniNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour Towards AppleDocument47 pagesConsumer Behaviour Towards AppleAdnan Yusufzai69% (62)
- Malaysia Year 2011 Calendar: Translate This PageDocument3 pagesMalaysia Year 2011 Calendar: Translate This PageStorgas FendiNo ratings yet
- 7 Tactical Advantages of Explainer VideosDocument23 pages7 Tactical Advantages of Explainer Videos4ktazekahveNo ratings yet
- Analysis of VariancesDocument40 pagesAnalysis of VariancesSameer MalhotraNo ratings yet
- IT SyllabusDocument3 pagesIT SyllabusNeilKumarNo ratings yet
- Using Snapchat For OSINT - Save Videos Without OverlaysDocument12 pagesUsing Snapchat For OSINT - Save Videos Without OverlaysVo TinhNo ratings yet
- The Invisible Hero Final TNDocument8 pagesThe Invisible Hero Final TNKatherine ShenNo ratings yet
- Believer - Imagine Dragons - CIFRA CLUBDocument9 pagesBeliever - Imagine Dragons - CIFRA CLUBSilvio Augusto Comercial 01No ratings yet