Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Differences Between Metals and Nonmetals Explained
Uploaded by
Senthil Kumar P0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views2 pagesThe document discusses the differences between metals and nonmetals. Metals are classified based on properties like being lustrous, good conductors of heat and electricity, and having 1-3 electrons in their outer shell. They corrode easily and form basic oxides. Nonmetals are dull, poor conductors, and have 4-8 outer shell electrons. They readily gain or share electrons and form acidic oxides. The document separates elements into metals and nonmetals on the periodic table based on these physical and chemical characteristics.
Original Description:
material science
Original Title
Metals and Nonmetals
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the differences between metals and nonmetals. Metals are classified based on properties like being lustrous, good conductors of heat and electricity, and having 1-3 electrons in their outer shell. They corrode easily and form basic oxides. Nonmetals are dull, poor conductors, and have 4-8 outer shell electrons. They readily gain or share electrons and form acidic oxides. The document separates elements into metals and nonmetals on the periodic table based on these physical and chemical characteristics.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views2 pagesDifferences Between Metals and Nonmetals Explained
Uploaded by
Senthil Kumar PThe document discusses the differences between metals and nonmetals. Metals are classified based on properties like being lustrous, good conductors of heat and electricity, and having 1-3 electrons in their outer shell. They corrode easily and form basic oxides. Nonmetals are dull, poor conductors, and have 4-8 outer shell electrons. They readily gain or share electrons and form acidic oxides. The document separates elements into metals and nonmetals on the periodic table based on these physical and chemical characteristics.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
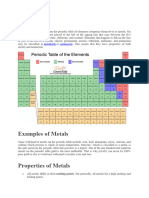
Elements may be classified as either metals or nonmetals, based on their properties.
Here's a look
at the differences between the metals and nonmetals.
Metals
Most elements are metals. On the periodic table , metals are separated from nonmetals by a zig-
zag line stepping through carbon, phosphorus, selenium, iodine and radon. These elements and
those to the right of them are nonmetals. Elements just to the left of the line may be termed
metalloids or semimetals and have properties intermediate between those of the metals and
nonmetals. The physical and chemical properties ofthe metals and nonmetals may be
used to tell them apart.
Metal Physical Properties
lustrous (shiny)
good conductors of heat and electricity
high melting point
high density (heavy for their size)
malleable (can be hammered)
ductile (can be drawn into wires)
usually solid at room temperature (an exception is mercury)
opaque as a thin sheet (can't see through metals)
metals are sonorous or make a bell-like sound when struck
Metal Chemical Properties
have 1-3 electrons in the outer shell of each metal atom
corrode easily (e.g., damaged by oxidation such as tarnish or rust)
lose electrons easily
form oxides that are basic
have lower electronegativities
are good reducing agents
Nonmetals
Nonmetal Physical Properties
not lustrous (dull appearance)
poor conductors of heat and electricity
nonductile solids
brittle solids
may be solids, liquids or gases at room temperature
transparent as a thin sheet
nonmetals are not sonorous
Nonmetal Chemical Properties
usually have 4-8 electrons in their outer shell
readily gain or share valence electrons
form oxides that are acidic
have higher electronegativities
are good oxidizing agents
You might also like
- Metals and NonmetalsDocument2 pagesMetals and NonmetalsAnnisa Ekaputri FebrianiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Properties:: M M M MDocument13 pagesChemical Properties:: M M M MRana BarakatNo ratings yet
- SaveDocument2 pagesSaveSteven TiczonNo ratings yet
- Groups in The Periodic Table of ElementsDocument7 pagesGroups in The Periodic Table of ElementsBRYAN bryan MacadangdangNo ratings yet
- Barath Kavin Chemistry Project 2Document11 pagesBarath Kavin Chemistry Project 2clockw916No ratings yet
- Metals and Non MetalDocument1 pageMetals and Non MetalHanehs NoLsubNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non Metals 1Document34 pagesMetals and Non Metals 1Alessandra myrnaNo ratings yet
- Properties of MetalsDocument4 pagesProperties of MetalsYanika BarasNo ratings yet
- Properties of MetalsDocument4 pagesProperties of MetalsKevin Joe CuraNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument12 pagesPeriodic TableFysal JanjowaNo ratings yet
- ElementsDocument13 pagesElementsahmad batataNo ratings yet
- Me Non MeDocument25 pagesMe Non MeTulga EddieNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-MetalsDocument11 pagesMetals and Non-MetalsRoty005100% (4)
- Metals Non Metals MetalloidsDocument37 pagesMetals Non Metals MetalloidsVilma Hebron CruzNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table To Use 15-16Document37 pagesPeriodic Table To Use 15-16Janeth GoritNo ratings yet
- Metal and Non MetalDocument14 pagesMetal and Non MetalZia UllahNo ratings yet
- Properties of Metals and NonmetalsDocument21 pagesProperties of Metals and NonmetalsJackiequeencess TentadoNo ratings yet
- MetalsDocument4 pagesMetalsdeepasanmughamNo ratings yet
- CHE882Unit3 L15Document8 pagesCHE882Unit3 L15Ms Mayank YadavNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary Words: - Dull - Sonorous - Brittle - Malleable - Insulator - Conductor - Density - Luster - Magnetic - DuctileDocument35 pagesVocabulary Words: - Dull - Sonorous - Brittle - Malleable - Insulator - Conductor - Density - Luster - Magnetic - Ductilejoan m. espejoNo ratings yet
- Classification of ElementsDocument1 pageClassification of Elementsdan964No ratings yet
- The Periodic Table of ElementsDocument30 pagesThe Periodic Table of ElementsVillamor BaculiNo ratings yet
- Metals and NonmetalsDocument37 pagesMetals and NonmetalsLeila PascuaNo ratings yet
- Mulch Benefits Soil HealthDocument5 pagesMulch Benefits Soil HealthindaneNo ratings yet
- Groups of The Periodic TableDocument5 pagesGroups of The Periodic TableEmikah TaylorNo ratings yet
- 118 Elements in the Modern Periodic TableDocument5 pages118 Elements in the Modern Periodic TableAakarshNo ratings yet
- Classification of MatterDocument17 pagesClassification of MatterAshmyra ManaloNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non MetalsDocument1 pageMetals and Non MetalsTerence FocasanNo ratings yet
- Non-Metals MetalsDocument16 pagesNon-Metals MetalsOhm PawatNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non - MetalsDocument7 pagesMetals and Non - MetalsAshton PaulNo ratings yet
- Properties of MetalsDocument10 pagesProperties of MetalsKawaii SamaNo ratings yet
- TextDocument3 pagesTextTaofeek Damilola100% (1)
- Introduction To The Periodic TableDocument0 pagesIntroduction To The Periodic TableAdnan ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Properties of Metals: Luster, Ductility, Malleability & MoreDocument16 pagesProperties of Metals: Luster, Ductility, Malleability & MoreQuila QuaboNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non Metals Revision NotesDocument22 pagesClass 10 Science Chapter 3 Metals and Non Metals Revision Notesrohan thakurNo ratings yet
- Metals and Non-MetalsDocument10 pagesMetals and Non-MetalsCherry IkemNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table InformationDocument2 pagesPeriodic Table InformationDaily ScienceNo ratings yet
- Properties of Metals Non-Metals MetalloidsDocument23 pagesProperties of Metals Non-Metals MetalloidsConnie Joy CalawagNo ratings yet
- The Modern Periodic Table Explained in 40 CharactersDocument37 pagesThe Modern Periodic Table Explained in 40 CharactersMadeleine CookiesNo ratings yet
- Learning The Periodic Table of ElementsDocument31 pagesLearning The Periodic Table of ElementshypezakramNo ratings yet
- Metals, Nonmetals, MetalloidsDocument17 pagesMetals, Nonmetals, Metalloidszendy llima malicdemNo ratings yet
- Chemical PropertiesDocument1 pageChemical PropertiesNaseer HumayunNo ratings yet
- PWSUNP223620230816131206848PPT - Metals, Nonmetals, MetalloidsDocument18 pagesPWSUNP223620230816131206848PPT - Metals, Nonmetals, Metalloidsrishit.yadav1102No ratings yet
- Part Ii: Metals: Rhona C. AdajarDocument58 pagesPart Ii: Metals: Rhona C. AdajarRalph CimanesNo ratings yet
- Metallic Bonding: How Atoms Form Metal CrystalsDocument10 pagesMetallic Bonding: How Atoms Form Metal CrystalsArmando Alberto MassingueNo ratings yet
- Basic Properties: 1.alkali MetalsDocument5 pagesBasic Properties: 1.alkali MetalsGanesh sargarNo ratings yet
- SIM SCIENCE 7 Metals and NonmetalsDocument4 pagesSIM SCIENCE 7 Metals and NonmetalsAileen I ReyesNo ratings yet
- Comparing Kinds of MatterDocument39 pagesComparing Kinds of MattereriNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Power Point Presentation: Concept: Metals and Non-MetalsDocument15 pagesChemistry Power Point Presentation: Concept: Metals and Non-MetalsBhavesh BhaveshNo ratings yet
- Lec 05 - Chemistry - Metals and Non-metalsDocument4 pagesLec 05 - Chemistry - Metals and Non-metalsManjyot KourNo ratings yet
- Metals Nonmetals and Metalloids ReadingDocument2 pagesMetals Nonmetals and Metalloids Readingapi-293084509100% (1)
- Classification of General Properties: CationDocument1 pageClassification of General Properties: CationHarshaNo ratings yet
- Non MetalDocument2 pagesNon MetalLê Quang ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Sci Tech Chem PresentationDocument21 pagesSci Tech Chem Presentationapi-259406637No ratings yet
- M NM M Review and Practice Metals Nonmetals EtcDocument25 pagesM NM M Review and Practice Metals Nonmetals EtcdoloresfilipinoNo ratings yet
- Metals: Properties and Types of MaterialsDocument14 pagesMetals: Properties and Types of MaterialsWaseem AminNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences Metals RevisionDocument3 pagesIGCSE Co-ordinated Sciences Metals RevisionSky LimNo ratings yet
- Alkali Metals: MetalDocument8 pagesAlkali Metals: MetalKaitlynRanaNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookFrom EverandThe Periodic Table of Elements - Post-Transition Metals, Metalloids and Nonmetals | Children's Chemistry BookNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table of Elements - Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals and Transition Metals | Children's Chemistry BookFrom EverandThe Periodic Table of Elements - Alkali Metals, Alkaline Earth Metals and Transition Metals | Children's Chemistry BookNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Electronics Operational AmplifierDocument25 pagesUnit 5 Electronics Operational AmplifierYared Birhanu100% (1)
- EnbededDocument7 pagesEnbededSenthil Kumar PNo ratings yet
- EnbededDocument7 pagesEnbededSenthil Kumar PNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Metals and Nonmetals ExplainedDocument2 pagesDifferences Between Metals and Nonmetals ExplainedSenthil Kumar PNo ratings yet
- Printing QuestionDocument5 pagesPrinting QuestionSenthil Kumar PNo ratings yet
- PLC Notes at Last For ExamDocument72 pagesPLC Notes at Last For ExamSenthil Kumar PNo ratings yet
- Mechatronic 2017 PadeepzDocument112 pagesMechatronic 2017 PadeepzSenthil Kumar PNo ratings yet
- Material Science and Metallurgy: YugeshDocument38 pagesMaterial Science and Metallurgy: YugeshSenthil Kumar PNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Metals and Nonmetals ExplainedDocument2 pagesDifferences Between Metals and Nonmetals ExplainedSenthil Kumar PNo ratings yet
- Thermal Properties of Materials ComparedDocument18 pagesThermal Properties of Materials ComparedSenthil Kumar PNo ratings yet
- Material Selection Process Involves The Following ProcessesDocument8 pagesMaterial Selection Process Involves The Following ProcessesSenthil Kumar PNo ratings yet
- For Be PetroDocument6 pagesFor Be PetroSenthil Kumar PNo ratings yet
- Classification of Magnetic Materials TypesDocument4 pagesClassification of Magnetic Materials TypesTsubasa GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Materials and Construction of Ship PropellersDocument2 pagesMaterials and Construction of Ship PropellersSenthil Kumar PNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Alloying Elements On SteelsDocument36 pagesThe Effects of Alloying Elements On SteelsRahul PandeyNo ratings yet
- RECRYSTALISATIONDocument2 pagesRECRYSTALISATIONSenthil Kumar PNo ratings yet
- MCT Lab RequirementsDocument3 pagesMCT Lab RequirementsSenthil Kumar PNo ratings yet
- 2 MCT Edc 03.08.19 AnDocument1 page2 MCT Edc 03.08.19 AnSenthil Kumar PNo ratings yet
- MT8591 Sensors and InstrumentationDocument1 pageMT8591 Sensors and InstrumentationSenthil Kumar PNo ratings yet
- Park College of Engineering and Technology Department of Mechatronics Iii YearDocument2 pagesPark College of Engineering and Technology Department of Mechatronics Iii YearSenthil Kumar PNo ratings yet
- Latch: Logic Diagram of SR Flip-FlopDocument8 pagesLatch: Logic Diagram of SR Flip-FlopSenthil Kumar PNo ratings yet
- IV MCT TQM Test2Document1 pageIV MCT TQM Test2Senthil Kumar PNo ratings yet
- Digital Recording Definition ExplainedDocument9 pagesDigital Recording Definition ExplainedSenthil Kumar PNo ratings yet
- New Syllabus With Code Revised 2017Document1 pageNew Syllabus With Code Revised 2017Senthil Kumar PNo ratings yet
- Iv MCT TQM Ut - IiDocument1 pageIv MCT TQM Ut - IiSenthil Kumar PNo ratings yet
- POM ShortDocument130 pagesPOM ShortSenthil Kumar PNo ratings yet
- Park College of Engineering and Technology Unit Test-I MT8302 Analog Devices and CircuitsDocument1 pagePark College of Engineering and Technology Unit Test-I MT8302 Analog Devices and CircuitsSenthil Kumar PNo ratings yet
- Simply Flip and LatchDocument8 pagesSimply Flip and LatchSenthil Kumar PNo ratings yet
- MT6801 PDFDocument118 pagesMT6801 PDFSenthil Kumar PNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechatronics Engineering Unit Test-1Document1 pageDepartment of Mechatronics Engineering Unit Test-1Senthil Kumar PNo ratings yet