Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nephrotic Syndrome
Uploaded by
Usman Ali Akbar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views2 pagesadsadas
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentadsadas
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views2 pagesNephrotic Syndrome
Uploaded by
Usman Ali Akbaradsadas
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
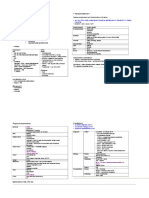
Nephrotic Syndrome
Complications of Nephrotic Syndrome
Definition 1. Susceptibility to UTI, peritonitis, septicaemia
infections Due to:-
Hypoalbuminaemia <30g/L Loss of IgG
Proteinuria >3.5g/day Immunosuppression by steroids or immunosuppressants
Oedema Lost of factor B of the alternate complement activation
pathway
Causes Loss of transferrin
T cell abnormalities
Primary Glomerular diseases
2. Thrombosis & DIVC, pulmonary embolism, renal vein thrombosis
1. Minimal Change Nephropathy Commonest dx in children embolism Hypercoagulability due to
2. Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis Commoner dx in middle-aged &
plasma antithrombin III (urinary loss)
3. Membranous GN elderly
plasma fibrinogen & clotting factors V & VIII
4. Mesangioproliferative GN
5. Membranoproliferative GN Haemoconcentration
3. volaemia Shock
Secondary Glomerular diseases
Acute Tubular Necrosis / Acute renal failure
1. Diabetic nephropathy
2. Autoimmune SLE, HSP 4. lipidaemia apolipoprotein (urinary loss)
3. Infections Post-streptococcal infection increased risk of CHD & atherosclerosis
4. Drugs TCM, gold 5. calcaemia Urinary loss of Vit D binding proteins
5. Amyloidosis Bone demineralization in the long term
6. Metabolic diseases 6. Negative Due to Proteinuria, LOA & nausea
7. Vascular diseases nitrogen balance
8. Hereditary nephritis eg Alports 7. ESRF
8. Steroid toxicity
Presentation
General condition Anorexia, wt gain, lethargy, xanthomata, xanthelasma Investigations
Oedema Periorbital, pedal, sacral, scrotal, ascites Bloods Dx and Cx:
Pleural effusion SOB FBC & ESR haemoconcentration, infections, hypoCa, inflammation
Urinary Oliguria, haematuria, concentrated urine U/E/Cr
Others Infections, HPT, abdominal pain, hepatomegaly Albumin assess severity
Lipid profile assess hyperlipidaemia
Other things to note in Long case
Immunoglobulins & serum electrophoresis
Past History to note
Causes:
1. Initial diagnosis date, symptoms, investigations, aetiology identified, Rx
Serum C3 & C4 in MCGN & SLE
2. No. of episodes / year precipitants, usual Rx
3. No. of hospitalizations AutoAbs ANA, ANCA, anti-dsDNA, anti-GBM
4. Cxs & Mx ASOT in post-strep. GN
Management Hep B serology associated with membranous nephritits
1. Diet Hep C serology associated with MCGN
2. Medication & compliance Urine Dipstick proteinuria, haematuria
3. Management problems Urinalysis microscopic haematuria & casts
4. Present Rx for current admission C/S UTI
5. Previous drugs used 24hr UTP & CCT
6. Drug side effects Albumin:creatinine ration - > 200mg/mmol
7. Home urine testing and nephrotic diary Na Concentration - <20mmol/L if hypovolaemic
8. F/U
Throat swab For microscopy, C/S.
For post-strep GN
Imaging CXR
Renal U/S
Renal biopsy
DGIM Last updated March 2005
Management
1. Bed rest, monitoring U/E, BP, fluid I/O charting, weight
2. Fluid restriction 1-1.5L/day
salt restriction
high protein diet
3. Diuretics Frusemide 80-250 mg PO spironolactone
Aim for loss of 1kg/day
Occasionally high dose frusemide + IV salt-poor albumin to
promote diuresis. However, risk of renal failure secondary to
hypovolaemia with over diuresis
4. Chronic nephrotic Consider reducing proteinuria with ACEI or cyclosporine
syndrome
5. Hyperlipidaemia Consider statin.
Usually improves with resolution of nephrotic syndrome
6. Hypertension Conventional regimens
7. Anticoagulation Prophylactic heparin for immobile PTs
Warfarin for symptomatic thrombosis
8. Infections Prophylactic ABx
Pneumococcal vaccination during remission
9. Mx of minimal change High dose corticosteroids
nephropathy in cyclophosphamide / cyclosporine in steroid dependant NS
children
DGIM Last updated March 2005
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- BDMS Trauma Algorithm Version 2.0Document32 pagesBDMS Trauma Algorithm Version 2.0Aungkhena Noomnim100% (2)
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy: Instructor's ManualDocument68 pagesCognitive-Behavioral Therapy: Instructor's ManualzingpalmsNo ratings yet
- Saliha - Thesis ReportDocument63 pagesSaliha - Thesis ReportSaliha Kabeer100% (2)
- Chronic Renal Failure: Concise Long Case ApproachDocument3 pagesChronic Renal Failure: Concise Long Case ApproachUsman Ali AkbarNo ratings yet
- GI Bleeding Team Work - 2nd EditionDocument9 pagesGI Bleeding Team Work - 2nd EditionUsman Ali AkbarNo ratings yet
- Polycystic Kidneys: Adult PKD: ComplicationsDocument1 pagePolycystic Kidneys: Adult PKD: ComplicationsUsman Ali AkbarNo ratings yet
- Renal Tubular Acidosis Summary - AdjDocument1 pageRenal Tubular Acidosis Summary - AdjUsman Ali AkbarNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection & PyelonephritisDocument3 pagesUrinary Tract Infection & PyelonephritisUsman Ali AkbarNo ratings yet
- Recurrent Nausea Andor VomitingDocument8 pagesRecurrent Nausea Andor VomitingUsman Ali AkbarNo ratings yet
- King Khalid University Hospital Department of Obstetrics & Gyncology Course 481Document40 pagesKing Khalid University Hospital Department of Obstetrics & Gyncology Course 481Usman Ali AkbarNo ratings yet
- DialysisDocument2 pagesDialysisUsman Ali AkbarNo ratings yet
- Obstructive Airway Disease: Dr. Khalid Al-Mobaireek King Khalid University HospitalDocument53 pagesObstructive Airway Disease: Dr. Khalid Al-Mobaireek King Khalid University HospitalUsman Ali AkbarNo ratings yet
- Anaemia in PregnancyDocument13 pagesAnaemia in PregnancyUsman Ali AkbarNo ratings yet
- Through The Strange WindsDocument5 pagesThrough The Strange WindsUsman Ali AkbarNo ratings yet
- Subject: Permission For Badminton Court NID, Multan: TH THDocument1 pageSubject: Permission For Badminton Court NID, Multan: TH THUsman Ali AkbarNo ratings yet
- DR Othman Alharbi, MBBS FRCPC Assistance Professor & Consultant Gastroenterology College of Medicine King Saud UniversityDocument18 pagesDR Othman Alharbi, MBBS FRCPC Assistance Professor & Consultant Gastroenterology College of Medicine King Saud UniversityUsman Ali AkbarNo ratings yet
- Recurrent VomitingDocument16 pagesRecurrent VomitingUsman Ali AkbarNo ratings yet
- GRAM NEGATIVE RODS (5) Fastidious Organisms From Animal Sources (A)Document1 pageGRAM NEGATIVE RODS (5) Fastidious Organisms From Animal Sources (A)Usman Ali AkbarNo ratings yet
- Cord ProlapseDocument2 pagesCord ProlapseUsman Ali AkbarNo ratings yet
- Organophosphate PoisoningDocument23 pagesOrganophosphate PoisoningUsman Ali AkbarNo ratings yet
- Alas!! EmpytinessDocument2 pagesAlas!! EmpytinessUsman Ali AkbarNo ratings yet
- When Hope DiesDocument2 pagesWhen Hope DiesUsman Ali AkbarNo ratings yet
- Untold Stanza... : - Nasim Alam (N-61)Document1 pageUntold Stanza... : - Nasim Alam (N-61)Usman Ali AkbarNo ratings yet
- Lect 1:: M2Pasysl21 Urinary SystemDocument4 pagesLect 1:: M2Pasysl21 Urinary SystemUsman Ali AkbarNo ratings yet
- Death and The Mother For MergeDocument4 pagesDeath and The Mother For MergeUsman Ali AkbarNo ratings yet
- Emergency HandbookDocument96 pagesEmergency HandbookZenith Sabando Manawatao100% (1)
- PolicyDocument5 pagesPolicySriharsha ReddyNo ratings yet
- NauliDocument2 pagesNauliGurjit Singh BoparaiNo ratings yet
- Humanitarian Action For Children 2019 EngDocument16 pagesHumanitarian Action For Children 2019 EngsofiabloemNo ratings yet
- Subdermal HematomaDocument2 pagesSubdermal HematomaDristi KhanalNo ratings yet
- Checklist With RationalesDocument174 pagesChecklist With RationalesZoey Francisco100% (1)
- FANR-RG-019 Radiation Safety in Industrial RadiographyDocument31 pagesFANR-RG-019 Radiation Safety in Industrial RadiographyCyril J PadiyathNo ratings yet
- Benzoato de SodioDocument7 pagesBenzoato de SodioJennyferNo ratings yet
- Primary Containment For BiohazardsDocument21 pagesPrimary Containment For BiohazardschitradeviNo ratings yet
- ETCO2 ReadingDocument19 pagesETCO2 ReadingTuan TrinhNo ratings yet
- Inglés 8-2 AnexoDocument38 pagesInglés 8-2 AnexoEsperanza RiverosNo ratings yet
- Uterine AtonyDocument14 pagesUterine AtonyLady Jane CaguladaNo ratings yet
- Weekly Report 13 - 19 2017Document11 pagesWeekly Report 13 - 19 2017Sitha MahendrataNo ratings yet
- R.A 9710 - Magna Carta For WomenDocument15 pagesR.A 9710 - Magna Carta For WomenFrances Ann TevesNo ratings yet
- Cata 2012Document288 pagesCata 2012kiskalpNo ratings yet
- 10 Hours OshaDocument247 pages10 Hours OshaJose BastidasNo ratings yet
- Case 2 - The Global Biopharmaceutical IndustryDocument5 pagesCase 2 - The Global Biopharmaceutical IndustryTran Bao DuongNo ratings yet
- Exam Additional Sample Questions AudDocument6 pagesExam Additional Sample Questions AudAbouzr Mohammed ElsaidNo ratings yet
- AKAPULKODocument4 pagesAKAPULKOMaricelPlacioNo ratings yet
- Introductions: Important Grammar RulesDocument11 pagesIntroductions: Important Grammar RulesyazzNo ratings yet
- Pondicherry School Education RulesDocument17 pagesPondicherry School Education RulesAr Ramya Prasad0% (1)
- Jsa - New Hydro TestDocument2 pagesJsa - New Hydro TestDautsons InfratechNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infections ChildrenDocument26 pagesUrinary Tract Infections ChildrenbrianzflNo ratings yet
- Garden Trust Launches A CompetitionDocument3 pagesGarden Trust Launches A CompetitionCami GrossiNo ratings yet
- Indus Hospital - HR PDFDocument92 pagesIndus Hospital - HR PDFdeva kiranNo ratings yet
- Methods of Endotoxin Removal From Biological PreparationsDocument17 pagesMethods of Endotoxin Removal From Biological PreparationsexecNo ratings yet
- WECOC Final Announcement 29th CompressedDocument32 pagesWECOC Final Announcement 29th CompressedChristabella Natalia WijayaNo ratings yet