Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HT-027 Solution
Uploaded by
KTINE08Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
HT-027 Solution
Uploaded by
KTINE08Copyright:
Available Formats
CHEMICAL ENGINEERING SERIES: HEAT TRANSFER
SOLVED PROBLEMS
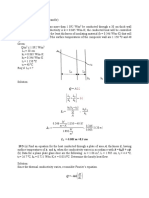
A stainless steel (AISI 304), k = 14.2 W/mK, tube used to transport a chilled pharmaceutical
has an inner diameter of 36 mm and a wall thickness of 2 mm. A 10-mm thick layer of calcium
silicate insulation (k = 0.05 W/mK) is applied to the tube. The pharmaceutical and ambient air
are at temperatures of 6 C and 23 C respectively, while the corresponding inner and outer
convection coefficients are 400 W/m2K and 6 W/m2K, respectively. What is the heat gain per
unit tube length.
Source: Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer 6 th edition, by Incropera, et al
SOLUTION:
Mode of Heat Transfer: conduction with resistances
in series + convection
T air T
q=
RT
RT =Rconv ,i + Rsteel + Rins + Rconv ,o
1 1 K m
Rconv ,i= = =0.0221
2 r i hi 18 W W
2 ( 1000 m )(400
m K) 2
r2 20 mm
ln ln
r1 18 mm K m
Rsteel= = =0.001181
2 k W W
2 14.2(m K )
r2 3 0 mm
ln ln
r1 20 mm K m
Rins = = =1.29064
2 k W W
(
2 0.05
m K )
1 1 K m
Rconv ,o = = =0.884194
2 r o ho 30 W W
2 ( 1000 m )(6
m K )
2
ENGR. RONNIE V. FLORES Page 1
CHEMICAL ENGINEERING SERIES: HEAT TRANSFER
SOLVED PROBLEMS
K m
RT =0.0221+0.001181+1.29064+ 0.884194=2.198115
W
T air T ( 236 ) K
q= =
RT K m
2.1981151
W
W
q=7.7339
m
ENGR. RONNIE V. FLORES Page 2
You might also like
- Heat Transfer Solved Problems: Thermal Resistance of Composite WallDocument2 pagesHeat Transfer Solved Problems: Thermal Resistance of Composite WallKTINE08100% (2)
- Ampacity CalculationDocument6 pagesAmpacity CalculationMohamad HishamNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer 7th Edition Incropera Solutions Manual20190709 74173 2j05lf PDFDocument20 pagesFundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer 7th Edition Incropera Solutions Manual20190709 74173 2j05lf PDFAndiNo ratings yet
- NSCP 2010 Deadload and Live Load Specifications for Steel StructuresDocument7 pagesNSCP 2010 Deadload and Live Load Specifications for Steel StructuresIan Dave AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- Gas Absorption Lecture NotesDocument11 pagesGas Absorption Lecture NotesMark Guevarra0% (1)
- Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer 7th Edition Incropera Solutions Manual PDFDocument20 pagesFundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer 7th Edition Incropera Solutions Manual PDFMeilindaNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Crystallizer SelectionDocument8 pagesCrystallizer SelectionKTINE08No ratings yet
- Heat loss calculation for a steel tankDocument3 pagesHeat loss calculation for a steel tankpamiNo ratings yet
- 2013 4M3 Liquid Liquid ExtractionDocument74 pages2013 4M3 Liquid Liquid ExtractionAndré Mendes PiolNo ratings yet
- CRYSTALLIZATION PROCESS OPTIMIZATIONDocument42 pagesCRYSTALLIZATION PROCESS OPTIMIZATIONKTINE0894% (16)
- Solution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsFrom EverandSolution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 SolutionsDocument6 pagesChapter 3 SolutionsAnonymous GjWVoVAnWYNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Home Work # 1: 3-14C Convection Heat Transfer Through The Wall Is Expressed AsDocument6 pagesSolutions To Home Work # 1: 3-14C Convection Heat Transfer Through The Wall Is Expressed Aspriyadarshini212007No ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer 7th Edition Incropera Solutions Manual PRDocument20 pagesToaz - Info Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer 7th Edition Incropera Solutions Manual PRzainab tariqNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer 7th Edition Incropera Solutions ManualDocument33 pagesFundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer 7th Edition Incropera Solutions Manualxulet60% (5)
- SelectionDocument1 pageSelectionKTINE08No ratings yet
- Heat transfer calculations through pipes and wallsDocument26 pagesHeat transfer calculations through pipes and wallsAntonio MoralesNo ratings yet
- Heat Exchanger Design CalculationsDocument8 pagesHeat Exchanger Design Calculationskikokiko KarimNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer: Unit IDocument5 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer: Unit ISajad AsemNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - TutorialDocument4 pagesChapter 3 - TutorialDavidNo ratings yet
- Solved Examples - Heat Transfer - 1ET1010501 - CompressedDocument69 pagesSolved Examples - Heat Transfer - 1ET1010501 - CompressedPatel SarkarNo ratings yet
- Unit IV and V Solved ProplemsDocument30 pagesUnit IV and V Solved ProplemsRajasekar KaruppusamyNo ratings yet
- Ch2 PDFDocument8 pagesCh2 PDFAlanNo ratings yet
- HT Solved NumericalsDocument56 pagesHT Solved NumericalsKiran AkkoliNo ratings yet
- Full Download Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer 7th Edition Incropera Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesFull Download Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer 7th Edition Incropera Solutions Manualwhinyard.around.vb2c100% (41)
- مثال فصل 3Document10 pagesمثال فصل 3mohammadNo ratings yet
- Solución Problemas Extra Tema 5 - Nivel 2Document7 pagesSolución Problemas Extra Tema 5 - Nivel 2SpanishRacingNo ratings yet
- Δt R (T − T) +: T I O Ln (R2 R1) 2Πkl 1 Ho AoDocument3 pagesΔt R (T − T) +: T I O Ln (R2 R1) 2Πkl 1 Ho AoLj SalomonNo ratings yet
- A Long, Circular Aluminium Rod Attached at One End ToDocument6 pagesA Long, Circular Aluminium Rod Attached at One End TocaptainhassNo ratings yet
- Problem No.2 Conduction Through Cylindrical PipeDocument3 pagesProblem No.2 Conduction Through Cylindrical Pipeariel darisanNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Through Insulated Steel TubeDocument4 pagesHeat Transfer Through Insulated Steel TubeABDERRAZZAKNo ratings yet
- Ch2 ProblemsDocument56 pagesCh2 ProblemsFirdaus GarasiahNo ratings yet
- All 10Document11 pagesAll 10YacelinNo ratings yet
- Thermoproblemsetno 171217155514Document40 pagesThermoproblemsetno 171217155514ibong tiriritNo ratings yet
- Heat transfer analysis of insulated wallDocument3 pagesHeat transfer analysis of insulated wallAndres RamirezNo ratings yet
- Temperature Distributions in Solids and in Laminar FlowDocument4 pagesTemperature Distributions in Solids and in Laminar FlowSambasiva Rao KaturiNo ratings yet
- Problem 1.1 KNOWN: Heat Rate, Q, Through One-Dimensional Wall of Area A, Thickness L, ThermalDocument8 pagesProblem 1.1 KNOWN: Heat Rate, Q, Through One-Dimensional Wall of Area A, Thickness L, ThermalMarco Antonio Salcedo HinojosaNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Calculations for Thermal Insulation ProblemsDocument12 pagesHeat Transfer Calculations for Thermal Insulation ProblemsAdelia CristinaNo ratings yet
- (Unit 2) Me 366 Solutions Manual (28 - 05 - 2021)Document7 pages(Unit 2) Me 366 Solutions Manual (28 - 05 - 2021)somenewguyonthewebNo ratings yet
- Group # 3: 4cheaDocument16 pagesGroup # 3: 4cheaNishant ChughNo ratings yet
- Cengel Fluid Mechanics 6 Edition PDFDocument7 pagesCengel Fluid Mechanics 6 Edition PDFVenkat MacharlaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer Bergman 7th Edition Solutions ManualDocument22 pagesFundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer Bergman 7th Edition Solutions Manualcuongviolet1or0zm0% (1)
- Ch2 ProblemsDocument56 pagesCh2 ProblemsSayyadh Rahamath Baba0% (1)
- Physics Mechanics 1Document3 pagesPhysics Mechanics 1Dian Ratri CNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics-1-JEE Main and Advanced PDFDocument7 pagesElectrostatics-1-JEE Main and Advanced PDFbibhas_samantaNo ratings yet
- TEST 1 SolutionDocument25 pagesTEST 1 Solutionsgupta_192494No ratings yet
- ESE CTQ Structural DynamicsDocument25 pagesESE CTQ Structural DynamicsAvikMukherjeeNo ratings yet
- CHE 306 - Solved Problems-2Document1 pageCHE 306 - Solved Problems-2Garcia Raph100% (2)
- M1 Assignment No. 1 OCAMPO PDFDocument8 pagesM1 Assignment No. 1 OCAMPO PDFJonica HarkessNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document3 pagesTutorial 2serizawa91No ratings yet
- Example Problems ConductionDocument9 pagesExample Problems ConductionAJNo ratings yet
- Valid of Turbulent Flow: The Chemical Engineers' Resource PageDocument8 pagesValid of Turbulent Flow: The Chemical Engineers' Resource PagebunnyNo ratings yet
- RISER STRESS ANALYSIS SLEEVE REPAIR PID 152Document2 pagesRISER STRESS ANALYSIS SLEEVE REPAIR PID 152Mahamad Azi Bin IshakNo ratings yet
- CH 01Document95 pagesCH 01김인웅No ratings yet
- Eoal Perpindahan PanasDocument4 pagesEoal Perpindahan Panasmei fenti andrianiNo ratings yet
- sm3 045Document2 pagessm3 045Sadie HnatowNo ratings yet
- Proposal ExampleDocument4 pagesProposal ExampleEce YağmurNo ratings yet
- LOW VOLTAGE CABLE FORMULAS AND RESISTANCE TABLEDocument4 pagesLOW VOLTAGE CABLE FORMULAS AND RESISTANCE TABLEamir amirNo ratings yet
- Adiabatic compression of air entropy and workDocument11 pagesAdiabatic compression of air entropy and workmina williamNo ratings yet
- No. 7Document3 pagesNo. 7阿尔坎塔拉约翰·肯尼斯No ratings yet
- Example 3p10 Incropera 6th Edition 2007Document3 pagesExample 3p10 Incropera 6th Edition 2007minhazul islamNo ratings yet
- Redulla Heat Transfer Assignment 3Document2 pagesRedulla Heat Transfer Assignment 3Alan RoyNo ratings yet
- 3 3.99PDocument3 pages3 3.99PYogeshThakurNo ratings yet
- Physical Electronics: Handbook of Vacuum PhysicsFrom EverandPhysical Electronics: Handbook of Vacuum PhysicsA. H. BeckNo ratings yet
- HT 036 SolutionDocument1 pageHT 036 SolutionKTINE08100% (2)
- Problem Set - Settling and SedimentationDocument1 pageProblem Set - Settling and SedimentationKTINE08100% (1)
- Evaluation Form Pnri SeminarDocument2 pagesEvaluation Form Pnri SeminarKTINE08No ratings yet
- HT-026 SolutionDocument2 pagesHT-026 SolutionKTINE08No ratings yet
- HT 034 SolutionDocument2 pagesHT 034 SolutionKTINE08No ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Series: Heat Transfer Solved Problems: Q A H T TDocument2 pagesChemical Engineering Series: Heat Transfer Solved Problems: Q A H T TKTINE08No ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Series: Heat Transfer Solved Problems: T t T t WC Mc K K θDocument1 pageChemical Engineering Series: Heat Transfer Solved Problems: T t T t WC Mc K K θKTINE08No ratings yet
- HT 030 SolutionDocument3 pagesHT 030 SolutionKTINE08No ratings yet
- HT 033 SolutionDocument6 pagesHT 033 SolutionKTINE08No ratings yet
- Manufacture of Sulfuric AcidDocument9 pagesManufacture of Sulfuric AcidDiajeng M.100% (1)
- HT 032 SolutionDocument2 pagesHT 032 SolutionKTINE08No ratings yet
- HT-029 SolutionDocument2 pagesHT-029 SolutionKTINE08No ratings yet
- Lenses Practice ProblemsDocument1 pageLenses Practice ProblemsKTINE08No ratings yet
- IEC Written ReportDocument9 pagesIEC Written ReportKTINE08No ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Process Dynamic Models PDFDocument9 pagesLecture 2 - Process Dynamic Models PDFnoteasytobebooNo ratings yet
- Floor Plan (Testimonial Dinner)Document1 pageFloor Plan (Testimonial Dinner)KTINE08No ratings yet
- Evaluation Form Pnri SeminarDocument2 pagesEvaluation Form Pnri SeminarKTINE08No ratings yet
- Case StudiesDocument46 pagesCase StudiesKTINE080% (1)
- Process 3 For Soda AshDocument2 pagesProcess 3 For Soda AshKTINE08No ratings yet
- How students evaluated their math tutorDocument5 pagesHow students evaluated their math tutorKTINE08No ratings yet
- Republic Act No. 318Document37 pagesRepublic Act No. 318KTINE08No ratings yet