Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Careplan
Uploaded by
api-3538873220 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
128 views2 pagesOriginal Title
careplan
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
128 views2 pagesCareplan
Uploaded by
api-353887322Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
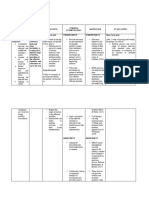
JMU School of Nursing
Spring 2017
Detailed Careplan
NURSING EXPECTED PATIENT ASSESSMENT ACTION TEACHING
DIAGNOSES OUTCOMES interventions: interventions: interventions:
(consider orders, (consider home
(note priority for Be sure they are S. M. (assess / monitor
safety, allergies, regimens,
each below) A. R. T. (Specific, for )
code status, fall procedures,
measureable,
(Be sure to use risk, etc.) discharge plan,
achievable/ attainable,
related to and etc.)
relevant and time-
as evidenced by)
bound)
Instability r/t high The patient will walk 1. Assess mobility 1. To use non-slip 1. Teach the
fall risk AEB inability independently with of body. socks for patient patient about the
to walk steadily. the assistance of a to help promote importance of
2. Monitor
(Ackley, 2014) walker not relying on stability. wearing non-slip
assessments of
assistance from a shoes or socks at
strength and grip. 2. Use a walker to
person. home.
help promote
(Ackley, 2014)
(Ackley, 2014) balance. 2. Give the
patients
(Ackley, 2014)
suggestions on
how to be safe
when walking on
uneasy ground.
(Ackley, 2014)
Weakness r/t Increased range of 1. Monitor 1. Encouragement 1. Teach the
instability of right motion in right arm by patients ADLs. during therapy. patient the
arm AEB inability to actively participating importance of
use full ROM in right 2. Monitor therapy 2. Continually
in therapy. keeping his arm in
arm while activity. remind patient to
the sling when he
performing ADLs. try and keep the
JMU School of Nursing
Spring 2017
Detailed Careplan
(Ackley, 2014) (Ackley, 2014) (Ackley, 2014) arm in the sling is not using it.
when he is not
2. Give patient
trying to promote
suggestions on
movement.
strengthening
(Ackley, 2014) activities outside
of therapy.
(Ackley, 2014)
References used written in APA format using your APA book (a required course textbook):
Ackley, B. J., & Ladwig, G. B. (2014). Nursing diagnosis handbook: an evidence-based guide to planning care. Maryland Heights,
MO: Elsevier.
You might also like
- Care Plan 9 27Document2 pagesCare Plan 9 27api-381528127100% (1)
- NCP OrthoDocument14 pagesNCP OrthoMichelle DuNo ratings yet
- Careplan ExampleDocument2 pagesCareplan Exampleapi-381092565No ratings yet
- Bhima Devi Poudel Adhikari 220179000 hsns370 Assessment 3 Case Study 1Document15 pagesBhima Devi Poudel Adhikari 220179000 hsns370 Assessment 3 Case Study 1api-525310113100% (1)
- Nursing Careplan WeeblyDocument2 pagesNursing Careplan Weeblyapi-379673485No ratings yet
- Applied Ergonomics 76 (2019) 64-72Document9 pagesApplied Ergonomics 76 (2019) 64-7206trahosNo ratings yet
- Date/ Time Cues Diagnosis Goals Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesDate/ Time Cues Diagnosis Goals Interventions Rationale EvaluationRomel BaliliNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mapeh 3 - Q1 - W3Document11 pagesDLL - Mapeh 3 - Q1 - W3blessed joy silvaNo ratings yet
- Assistive DevicesDocument3 pagesAssistive DevicesEden Rose RiveraNo ratings yet
- Body Mechanics ViosDocument3 pagesBody Mechanics ViosIra Velle ViosNo ratings yet
- Final - FALL 2023 - NSE203 Weekly Outline - Advance Health Assessment Fall 2023Document12 pagesFinal - FALL 2023 - NSE203 Weekly Outline - Advance Health Assessment Fall 2023saemhatdsbNo ratings yet
- NCP (BD)Document5 pagesNCP (BD)Nursing LectureNo ratings yet
- Nag Lilinis NG Sugat Ko, Hindi Ko Kasi Kaya. Mahina Kasi Kalahati NG Katawan Ko" AsDocument4 pagesNag Lilinis NG Sugat Ko, Hindi Ko Kasi Kaya. Mahina Kasi Kalahati NG Katawan Ko" AsNursing LectureNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mapeh 3 - Q1 - W4Document9 pagesDLL - Mapeh 3 - Q1 - W4blessed joy silvaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Implementation Scientific Rationale Evaluation Subjective CuesDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Implementation Scientific Rationale Evaluation Subjective Cues24 PAULINO ALDRIN MUJARNo ratings yet
- 4 Congenital Hip Dysplasia Nursing Care PlansDocument4 pages4 Congenital Hip Dysplasia Nursing Care PlansItstineeNo ratings yet
- Post ThenDocument9 pagesPost ThenAbe YorkeNo ratings yet
- AimsDocument2 pagesAimsDr UmeeNo ratings yet
- Nurse'S Duty in Wards: ObjectivesDocument7 pagesNurse'S Duty in Wards: ObjectivesMeldaNo ratings yet
- Adl Feeding Assignment 2Document11 pagesAdl Feeding Assignment 2api-631747744No ratings yet
- Careplan On Paper Fall 17 1Document3 pagesCareplan On Paper Fall 17 1api-379557456No ratings yet
- Student Name: Makaela Etheridge Date: 2/3/2021 University of South Alabama College of Nursing Adult Health Nursing Nursing Plan of CareDocument3 pagesStudent Name: Makaela Etheridge Date: 2/3/2021 University of South Alabama College of Nursing Adult Health Nursing Nursing Plan of CareMakaela EtheridgeNo ratings yet
- NCP-Form 1Document1 pageNCP-Form 1queen rholynNo ratings yet
- AIMS. Scales-Abnormal-Involuntary-Movement-Scale PDFDocument2 pagesAIMS. Scales-Abnormal-Involuntary-Movement-Scale PDFVictoria RomeroNo ratings yet
- Performing An A-G Patient Assessment: A Step-By-Step GuideDocument3 pagesPerforming An A-G Patient Assessment: A Step-By-Step GuidenasimhsNo ratings yet
- Black and Brown Business BrochureDocument2 pagesBlack and Brown Business BrochureMa. Ferimi Gleam BajadoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (Surgical, Indiv Patient)Document3 pagesNursing Care Plan (Surgical, Indiv Patient)Nursing LectureNo ratings yet
- NCP-Benign-Vertigo - Impaired Physical MobilityDocument2 pagesNCP-Benign-Vertigo - Impaired Physical MobilityStephen S. Padayhag83% (6)
- Careplan Week 8Document3 pagesCareplan Week 8api-353681121No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Sample 7Document17 pagesNursing Care Plan Sample 7GEN ERIGBUAGASNo ratings yet
- Clinical PresDocument2 pagesClinical Pres300447586No ratings yet
- THE NURSING PROCESS (Your Plan of Care) : DirectionsDocument3 pagesTHE NURSING PROCESS (Your Plan of Care) : Directionsapi-340395081No ratings yet
- Upper Extremity Skill SheetDocument1 pageUpper Extremity Skill SheetMuhammed ElgasimNo ratings yet
- Hyg GD 1 Term 1Document14 pagesHyg GD 1 Term 1vincent mugendiNo ratings yet
- Parkinson's Diseases (RISK FOR INJURY) REVISED!Document2 pagesParkinson's Diseases (RISK FOR INJURY) REVISED!Benjie DimayacyacNo ratings yet
- APA 7th Edition Template Student VersionDocument14 pagesAPA 7th Edition Template Student VersionAndrei ArtiedaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Standing DocumentDocument15 pagesClinical Standing DocumentPrivat EtavirpNo ratings yet
- NCP GbsDocument2 pagesNCP GbsChristine Lebico100% (1)
- International Journal of Industrial ErgonomicsDocument10 pagesInternational Journal of Industrial ErgonomicsTirta AjiNo ratings yet
- Repositioning A Passive Patient in Bed: Choosing An Ergonomically Advantageous Assistive DeviceDocument8 pagesRepositioning A Passive Patient in Bed: Choosing An Ergonomically Advantageous Assistive DevicelnarimotoNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing Module 2 Mobility: TitleDocument8 pagesFundamentals of Nursing Module 2 Mobility: Titlesharahcatherine romanaNo ratings yet
- Prioritization of Problems Rank Problem Identified: San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesDocument5 pagesPrioritization of Problems Rank Problem Identified: San Francisco St. Butuan City 8600, Region XIII Caraga, PhilippinesTom CuencaNo ratings yet
- Finalize Nursing CareplanDocument20 pagesFinalize Nursing Careplanglaizarosario8No ratings yet
- Modul English 1 - MuklaDocument9 pagesModul English 1 - MuklaEga BagustNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Gong's Mobilization Versus Scapular and Glenohumeral Mobilization in Subjects With Periarthritis of The ShoulderDocument4 pagesEffectiveness of Gong's Mobilization Versus Scapular and Glenohumeral Mobilization in Subjects With Periarthritis of The ShoulderInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Review of Related Literature: Motor Vehicle AccidentDocument8 pagesReview of Related Literature: Motor Vehicle AccidentJ. TSNo ratings yet
- Kupit 2 PDFDocument26 pagesKupit 2 PDFwayan sudarsanaNo ratings yet
- Jognn Jognn: A Practical Approach To Labor SupportDocument10 pagesJognn Jognn: A Practical Approach To Labor SupportWulan CerankNo ratings yet
- Careplan - WeeblyDocument2 pagesCareplan - Weeblyapi-354529854No ratings yet
- Juarascio Et Al 2013Document10 pagesJuarascio Et Al 2013Stela PenkovaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Goal & Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Goal & Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationRenie SerranoNo ratings yet
- Anatomical PositionsDocument36 pagesAnatomical PositionsrlinaoNo ratings yet
- On Behalf of Ms. Melendrez, Let's Proceed To: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesOn Behalf of Ms. Melendrez, Let's Proceed To: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMCA OmadtoNo ratings yet
- Land 2017 - Effect of Manual Physiotherapy in Homogeneous Individuals With Subacromial Shoulder Impingement - A Randomized Controlled TrialDocument14 pagesLand 2017 - Effect of Manual Physiotherapy in Homogeneous Individuals With Subacromial Shoulder Impingement - A Randomized Controlled TrialJime PENo ratings yet
- Health AssessmentDocument13 pagesHealth AssessmentImee TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Female Pelvic Floor 2 Assessment and Rehabilitation PDFDocument4 pagesFemale Pelvic Floor 2 Assessment and Rehabilitation PDFVikiNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mapeh 3 - Q1 - W3Document5 pagesDLL - Mapeh 3 - Q1 - W3Daffodil Rona CedenioNo ratings yet
- Twins Bootcamp StudyDocument5 pagesTwins Bootcamp Studyandi dirhanNo ratings yet
- Principles of Manual Medicine for Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction: Arthrokinematic Approach-Hakata MethodFrom EverandPrinciples of Manual Medicine for Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction: Arthrokinematic Approach-Hakata MethodShigehiko KatadaNo ratings yet
- Antiinflammatorydrugs: Beatriz Monteiro,, Paulo V. SteagallDocument19 pagesAntiinflammatorydrugs: Beatriz Monteiro,, Paulo V. SteagallYohan Oropeza VergaraNo ratings yet
- Regional Victoria's RoadmapDocument12 pagesRegional Victoria's RoadmapTara CosoletoNo ratings yet
- Abstrak EnglishDocument1 pageAbstrak EnglishputrapaninjauanNo ratings yet
- Factitious DisorderDocument6 pagesFactitious DisorderRon JaredNo ratings yet
- Module One Wellness Plan: GO TO FILE - Choose SAVE AS - Save A Copy of This To Your Computer!Document8 pagesModule One Wellness Plan: GO TO FILE - Choose SAVE AS - Save A Copy of This To Your Computer!Marko DesnicaNo ratings yet
- Health 8 - 1st Grading ExamDocument3 pagesHealth 8 - 1st Grading Exammaria luzNo ratings yet
- 2008 04 Lecture 1 Interface Dermatitis FrishbergDocument6 pages2008 04 Lecture 1 Interface Dermatitis FrishbergYudistra R ShafarlyNo ratings yet
- Improving Lives of South Sudanese Communities Through Water and Sanitation: The Story of Salva DutDocument1 pageImproving Lives of South Sudanese Communities Through Water and Sanitation: The Story of Salva DutUNICEF South SudanNo ratings yet
- Mini Clinical Examination (Mini-CEX)Document21 pagesMini Clinical Examination (Mini-CEX)Jeffrey Dyer100% (1)
- Typology of Nursing Problems in Family Nursing PracticeDocument4 pagesTypology of Nursing Problems in Family Nursing PracticeLeah Abdul KabibNo ratings yet
- TheraDocument4 pagesTheramaircusNo ratings yet
- ComplaintDocument28 pagesComplaintLia TabackmanNo ratings yet
- ERAS Protocols For Thyroid andDocument9 pagesERAS Protocols For Thyroid andOskar MartinezNo ratings yet
- Food StampsDocument80 pagesFood StampsAnvitaRamachandranNo ratings yet
- Uti StudiesDocument10 pagesUti Studiesapi-302840362No ratings yet
- Mental Health Issues - ADHD Among ChildrenDocument9 pagesMental Health Issues - ADHD Among ChildrenFelixNo ratings yet
- Dibasic Sodium PhosphateDocument0 pagesDibasic Sodium PhosphateWilliam ChandraNo ratings yet
- PARS 19 - Slide PDFDocument23 pagesPARS 19 - Slide PDFNorsyaliza Abd Razak100% (1)
- Calcipotriol Ointment Vs Bethametason 17 Valerate in Treatment of Lichen AmyloidosisDocument3 pagesCalcipotriol Ointment Vs Bethametason 17 Valerate in Treatment of Lichen AmyloidosisNanda Shaskia LarasatyNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Exam in Nursing Part 2Document41 pagesComprehensive Exam in Nursing Part 2Ariane-Gay Cristobal DuranNo ratings yet
- Job Chart of Physical Education Teachers - AP GOVTDocument3 pagesJob Chart of Physical Education Teachers - AP GOVTRamachandra Rao100% (1)
- IJHPM - Volume 7 - Issue 12 - Pages 1073-1084 Complex LeadershipDocument12 pagesIJHPM - Volume 7 - Issue 12 - Pages 1073-1084 Complex Leadershipkristina dewiNo ratings yet
- ELC - Assignment Cover SheetDocument4 pagesELC - Assignment Cover Sheetbharti guptaNo ratings yet
- PNA 2012 National Convention LectureDocument60 pagesPNA 2012 National Convention LectureHarby Ongbay AbellanosaNo ratings yet
- NIH Public Access: Author ManuscriptDocument17 pagesNIH Public Access: Author ManuscriptJoyBoyXNo ratings yet
- B Biokinetics 2023Document10 pagesB Biokinetics 2023ZandileNo ratings yet
- CephalosporinsDocument20 pagesCephalosporinsBianca Andrea RagazaNo ratings yet
- JUMPSTART TO SKINNY by Bob Harper: Rule #1Document8 pagesJUMPSTART TO SKINNY by Bob Harper: Rule #1Random House Publishing GroupNo ratings yet
- Hazard Analysis in The WorkplaceDocument7 pagesHazard Analysis in The WorkplaceUghlahnNo ratings yet
- Azibact MMDocument37 pagesAzibact MMરહીમ હુદ્દાNo ratings yet