Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Atoms and Atomic Theory
Uploaded by
pauchanmnl0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views2 pagesatoms chemistry
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentatoms chemistry
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views2 pagesAtoms and Atomic Theory
Uploaded by
pauchanmnlatoms chemistry
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Atoms and Atomic Theory
Tuesday, March 21, 2017
11:00 PM
Law of Conservation of Mass
The total mass of substances present after a chemical reaction is the same
as the total mass of substances before the reaction
Law of Constant Composition
All samples of a compound have the same composition the same
proportions by mass of the constituent elements.
Dalton's Atomic Theory
1. Each chemical element is composed of minute, indivisible particles called
atoms. Atoms can be neither created nor destroyed during a chemical change.
2. All atoms of an element are alike in mass (weight) and other properties, but
the atoms of one element are different from those of all other elements.
3. In each of their compounds, different elements combine in a simple
numerical ratio, for example, one atom of A to one of B (AB), or one atom of A
to two of B.
Law of Multiple Proportions (Derived from Dalton's Atomic Theory)
If two elements form more than a single compound, the masses of one
element combined with a fixed mass of the second are in the ratio of small
whole numbers.
Discovery of Electrons
Cathode rays - type of radiation emitted by the negative terminal cathode.
Alternatively, the positive terminal is called anode.
Cathode rays became known as electrons later on.
Alpha particles carry two fundamental units of positive charge
Beta particles are negatively charged particles produced by changes
occurring within the nuclei of radioactive atoms.
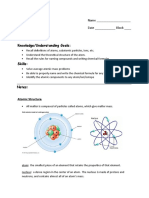
Protons and Neutrons
Atomic number - or the proton number
Atomic mass unit - defined as 1/12 of the mass of the atom known as carbon
- 12
Isotopes
Represent the composition of any particular atom
Atoms that have the same atomic number (Z) but different mass numbers (A)
are called isotopes.
Ions
When atoms lose or gain electrons, for example, in the course of a chemical
reaction, the species formed are called ions and carry net charges.
Removing electrons results in a positively charged ion
Atomic Mass
The atomic mass (weight)* of an element is the average of the isotopic
masses, weighted according to the naturally occurring abundances of the
isotopes of the element.
Periodic Table
Vertical - Group (families)
Horizontal - Period
Main group elements - 1, 2, 13 to 18; when main group metal atoms in
groups 1 and 2 form ions, tey lose the same number as the IUPAC group
number
When nonmetals form ions, they gain electrons. The number of electrons
gained is normally 18 minus the IUPAC group number.
Elements in groups 3 to 12 are the transition elements (metals)
Mole and Avogadro Constant
The number of elementary entities in a mole is the Avogadro constant
The Avogadro constant was purposely chosen so that the mass of one mole of
carbon-12 atoms exactly 12 g would have the same numeric value as the
mass of a single carbon-12 atom exactly 12 u
You might also like
- Chemistry Unit 2Document24 pagesChemistry Unit 2Auvan HilarioNo ratings yet
- KEY ATOMIC TERMS DEFINEDDocument1 pageKEY ATOMIC TERMS DEFINEDWafa OsmanNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: The Atomic Structure of MatterDocument3 pagesUnit 1: The Atomic Structure of MatterDanyel Rodriguez RomeraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2. Atomic StructureDocument4 pagesChapter 2. Atomic StructureUmerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Atoms and MatterDocument44 pagesChapter 2-Atoms and MatterNajma AqilahNo ratings yet
- Chem 1 Atomic Number Mass Number Periodic Table2Document15 pagesChem 1 Atomic Number Mass Number Periodic Table2Alexandria BaldedaraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Atoms ElementsDocument8 pagesLecture 1 Atoms ElementsshanecarlNo ratings yet
- Ch2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions 1Document18 pagesCh2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions 1Ariyandi PurnamaNo ratings yet
- Additional MathematicsDocument6 pagesAdditional Mathematicslonydon23No ratings yet
- Che101 Chap 2Document60 pagesChe101 Chap 2Ruhi AfsaraNo ratings yet
- Mass Relationship in Chemical Reaction - Atomic MassDocument5 pagesMass Relationship in Chemical Reaction - Atomic MassLovely RamNo ratings yet
- Notes 2 - Atoms and Atomic TheoryDocument6 pagesNotes 2 - Atoms and Atomic Theoryochiengjoseph122No ratings yet
- Gen Chem 2Document35 pagesGen Chem 2jennierubyjane KimNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Molecules, Ions & FormulasDocument60 pagesAtoms, Molecules, Ions & FormulasDavid MaranzhyanNo ratings yet
- Atoms and MoleculesDocument4 pagesAtoms and MoleculesHitesh kalraNo ratings yet
- Eastern Samar National Comprehensive High School Chemistry 1Document3 pagesEastern Samar National Comprehensive High School Chemistry 1Isaac PiaoNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Molecules, & IonsDocument13 pagesAtoms, Molecules, & IonsyeunbiNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 Week 1.2Document34 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 Week 1.2Giovanni Gumahad Jr.No ratings yet
- Atoms Molecules and IonsDocument3 pagesAtoms Molecules and Ionsapi-304350501No ratings yet
- Chemistry For PhysiciansDocument14 pagesChemistry For PhysiciansenzlibraryNo ratings yet
- QUARTER 1 LESSON 2 Atom Ions and MoleculesDocument60 pagesQUARTER 1 LESSON 2 Atom Ions and MoleculesMichelle De VillaNo ratings yet
- Basic ChemistryDocument14 pagesBasic ChemistryPitherNo ratings yet
- Chemistry STPM Chapter 1 by STUDY SMART WWW - Studysmart.page - TLDocument8 pagesChemistry STPM Chapter 1 by STUDY SMART WWW - Studysmart.page - TLAcyl Chloride Hariprem95% (40)
- L2-Atoms and Atomic StructureDocument49 pagesL2-Atoms and Atomic Structurekoladejoy49No ratings yet
- Unit 1 Notes: Subatomic Particle Relative Mass Relative Charge Symbol Proton Neutron ElectronDocument3 pagesUnit 1 Notes: Subatomic Particle Relative Mass Relative Charge Symbol Proton Neutron ElectronAdnan ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Atoms and Isotopes ExplainedDocument4 pagesAtoms and Isotopes ExplainedLilaNo ratings yet
- CHAP4 AtomicStructureDocument34 pagesCHAP4 AtomicStructureJex AsupardoNo ratings yet
- ChemDocument13 pagesChemMj CaraanNo ratings yet
- Handout - Element & AtomsDocument4 pagesHandout - Element & AtomsAnonymous l6Qs8YONo ratings yet
- UNIT 3 y 4 ATOMSDocument3 pagesUNIT 3 y 4 ATOMSLucia OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Principles: Atomic Structure and MacromoleculesDocument4 pagesBiochemical Principles: Atomic Structure and MacromoleculesJona KoçiNo ratings yet
- Atomic Number, Mass Number, and IsotopesDocument24 pagesAtomic Number, Mass Number, and IsotopesB.Ed. Wing SundargarhNo ratings yet
- Topic 1.1 Atomic Structure: 1.1a A Model of The AtomDocument5 pagesTopic 1.1 Atomic Structure: 1.1a A Model of The Atomking atikNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: The Structure of The Atom Mass Spectrometry Electronic Structure Ionisation EnergiesDocument22 pagesAtomic Structure: The Structure of The Atom Mass Spectrometry Electronic Structure Ionisation EnergiesVijithaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 2 - CLD - 10004 - February - 2014 - Structure of Atoms and MatterDocument46 pagesChapter - 2 - CLD - 10004 - February - 2014 - Structure of Atoms and MatterwanizalilNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Protons, Neutrons, ElectronsDocument9 pagesAtomic Structure: Protons, Neutrons, ElectronshenryNo ratings yet
- Atoms and Elements: ObjectivesDocument5 pagesAtoms and Elements: ObjectivesAngel RingorNo ratings yet
- Ions and Molecules: General Chemistry 1Document43 pagesIons and Molecules: General Chemistry 1Mariane CarandangNo ratings yet
- Electronic Structure Notes by Aung Kyaw SwarDocument9 pagesElectronic Structure Notes by Aung Kyaw Swarေအာင္ ေက်ာ္ စြာNo ratings yet
- Corrosion ChemistryDocument7 pagesCorrosion ChemistryaamirsaddiqNo ratings yet
- Concept of Atomic StructureDocument24 pagesConcept of Atomic StructureNoor Mohammad NofaerNo ratings yet
- Chemistry & Physics Elements: Atoms, Electrons, Protons, Ions, Molecules & NeutronsDocument7 pagesChemistry & Physics Elements: Atoms, Electrons, Protons, Ions, Molecules & NeutronsMangalraj MadasamyNo ratings yet
- (L3) Atoms and MoleculesDocument20 pages(L3) Atoms and MoleculesPeaceNo ratings yet
- Dalton's Atomic Theory and Fundamental ParticlesDocument21 pagesDalton's Atomic Theory and Fundamental Particlesbadisa booksNo ratings yet
- STPM Physical Chemistry Introductory Class Prepared by Julian VoongDocument12 pagesSTPM Physical Chemistry Introductory Class Prepared by Julian VoongJohnson116No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Notes - Teacher 2Document13 pagesUnit 2 Notes - Teacher 2noNo ratings yet
- The Chemical Earth-Ahmad ShahDocument46 pagesThe Chemical Earth-Ahmad ShahYouseffNo ratings yet
- CHEM 11/L Module 2 - Atomic Structure and Periodic TableDocument15 pagesCHEM 11/L Module 2 - Atomic Structure and Periodic TableFrancis RecocoNo ratings yet
- 2.atoms, Elements & CompoundDocument6 pages2.atoms, Elements & CompoundhenryNo ratings yet
- Ringkasan KIMIADocument4 pagesRingkasan KIMIACheetah NurNo ratings yet
- Css Atom StructureDocument20 pagesCss Atom StructureHaris AzizNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Material Structure and BondingDocument34 pagesChapter 2-Material Structure and BondingMohd AziziNo ratings yet
- Atoms and IonsDocument13 pagesAtoms and IonsYousuf Al ManjiNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Periodic Table ExplainedDocument4 pagesAtomic Structure and Periodic Table Explainedeugene_970418755No ratings yet
- Physical Science Reference GuideDocument27 pagesPhysical Science Reference GuideCarlos MasikaNo ratings yet
- Laws of Atoms and MoleculesDocument5 pagesLaws of Atoms and MoleculesPranav ShindeNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Molecules Their Interaction Relevant To Biology CSIR UGC NET Life SciencesDocument5 pagesUnit 1 Molecules Their Interaction Relevant To Biology CSIR UGC NET Life SciencesKishan KoyaniNo ratings yet
- Sparkle - Kimi No Na WaDocument1 pageSparkle - Kimi No Na WapauchanmnlNo ratings yet
- Competency Appraisal II Respiratory ExamDocument5 pagesCompetency Appraisal II Respiratory ExampauchanmnlNo ratings yet
- Stardew Valley Community Center ChecklistDocument7 pagesStardew Valley Community Center Checklistpauchanmnl100% (2)
- Anime RecommendationsDocument8 pagesAnime Recommendationspauchanmnl100% (1)
- Rationale Urinary and PeriopDocument2 pagesRationale Urinary and PerioppauchanmnlNo ratings yet
- Sexual Orientation and Suicide RiskDocument13 pagesSexual Orientation and Suicide RiskpauchanmnlNo ratings yet
- Avps and PowerpointDocument2 pagesAvps and PowerpointpauchanmnlNo ratings yet
- Chan, Pauline - Machine Problem 6 Ccs002lDocument4 pagesChan, Pauline - Machine Problem 6 Ccs002lpauchanmnlNo ratings yet
- Funding LetterDocument1 pageFunding LetterpauchanmnlNo ratings yet
- Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesNursing ResponsibilitiespauchanmnlNo ratings yet
- Mass SongsDocument3 pagesMass SongspauchanmnlNo ratings yet
- Aira Tuliao RationaleDocument1 pageAira Tuliao RationalepauchanmnlNo ratings yet
- Insights and Journal - CHANDocument7 pagesInsights and Journal - CHANpauchanmnlNo ratings yet
- Checklist For Technical CommitteeDocument2 pagesChecklist For Technical CommitteepauchanmnlNo ratings yet
- Competency Appraisal II Respiratory ExamDocument5 pagesCompetency Appraisal II Respiratory ExampauchanmnlNo ratings yet
- Competency Appraisal II Musculo and CADocument5 pagesCompetency Appraisal II Musculo and CApauchanmnlNo ratings yet
- Fluid RationaleDocument4 pagesFluid RationalepauchanmnlNo ratings yet
- Competency Appraisal II Git Acce Endo ExamDocument11 pagesCompetency Appraisal II Git Acce Endo ExampauchanmnlNo ratings yet
- BBQ RatioDocument5 pagesBBQ RatiopauchanmnlNo ratings yet
- CA 2 RationalizationDocument1 pageCA 2 RationalizationpauchanmnlNo ratings yet
- Tabigo On Urinary Preop RatioDocument2 pagesTabigo On Urinary Preop RatiopauchanmnlNo ratings yet
- Kayle Locquiao RationaleDocument2 pagesKayle Locquiao RationalepauchanmnlNo ratings yet
- Tabigo On GI RatioDocument2 pagesTabigo On GI RatiopauchanmnlNo ratings yet
- Rabies and Fire Prevention Month ProgramDocument13 pagesRabies and Fire Prevention Month ProgrampauchanmnlNo ratings yet
- Health and IllnessDocument15 pagesHealth and IllnesspauchanmnlNo ratings yet
- January 9 Excuse LetterDocument1 pageJanuary 9 Excuse LetterpauchanmnlNo ratings yet
- Progress NotesDocument2 pagesProgress NotespauchanmnlNo ratings yet
- Resource Tool 03ADocument3 pagesResource Tool 03ApauchanmnlNo ratings yet
- Relate To Patient's Case PleaseDocument1 pageRelate To Patient's Case PleasepauchanmnlNo ratings yet
- Stanhope: Public Health Nursing, 9th EditionDocument1 pageStanhope: Public Health Nursing, 9th EditionpauchanmnlNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 HBODocument19 pagesChapter 4 HBOfirebirdshockwaveNo ratings yet
- NetAct Plan Editor 4.9-4 CNDocument4 pagesNetAct Plan Editor 4.9-4 CNAshraf JarjeesNo ratings yet
- Q4-Hinge Theorem-ActivityDocument2 pagesQ4-Hinge Theorem-ActivityEmelie HernandezNo ratings yet
- Object Relations Group PsychotherapyDocument6 pagesObject Relations Group PsychotherapyJonathon BenderNo ratings yet
- Content-Based Image Retrieval System Using SketchesDocument50 pagesContent-Based Image Retrieval System Using SketchesHoney Merrin SamNo ratings yet
- The Occult WorldDocument256 pagesThe Occult WorldJewell Elliott100% (1)
- ACS SCPI Programming Guide V1 0Document29 pagesACS SCPI Programming Guide V1 0Pedro Boanerges Paz RomeroNo ratings yet
- FGD on Preparing Learning Materials at Old Cabalan Integrated SchoolDocument3 pagesFGD on Preparing Learning Materials at Old Cabalan Integrated SchoolRAQUEL TORRESNo ratings yet
- Activities For Teens and AdultsDocument130 pagesActivities For Teens and AdultsDonata Marletta100% (12)
- LZW Fundamentals: Lempel Ziv 1977 1978 Terry Welch's 1978 Algorithm 1984Document9 pagesLZW Fundamentals: Lempel Ziv 1977 1978 Terry Welch's 1978 Algorithm 1984Vishal PatilNo ratings yet
- Annals of Medicine and Surgery: Bliss J. ChangDocument2 pagesAnnals of Medicine and Surgery: Bliss J. ChangroromutiaraNo ratings yet
- A+ Guide to Managing Your PC Hardware & SoftwareDocument34 pagesA+ Guide to Managing Your PC Hardware & Software2AdvanceNo ratings yet
- 2020 Agent Price ListDocument2,732 pages2020 Agent Price ListEngr XsadNo ratings yet
- In The Bedroom Missing Letters in Words Esl WorksheetDocument2 pagesIn The Bedroom Missing Letters in Words Esl Worksheetgirl_blueeyes89No ratings yet
- Project Vetting Worksheet-9472538Document4 pagesProject Vetting Worksheet-9472538kovzsanNo ratings yet
- Cascade Approach of DWT-SVD Digital Image WatermarkingDocument5 pagesCascade Approach of DWT-SVD Digital Image WatermarkingPrashant SangulagiNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Acoustics PDFDocument296 pagesAn Introduction To Acoustics PDFmatteo_1234No ratings yet
- Aneka Cloud IntroductionDocument36 pagesAneka Cloud IntroductionPradeep Kumar Reddy ReddyNo ratings yet
- Axiomatic Product Development LifecycleDocument4 pagesAxiomatic Product Development LifecyclegschiroNo ratings yet
- Forced Cooling of Steam Turbines: Answers For EnergyDocument2 pagesForced Cooling of Steam Turbines: Answers For EnergyShameer MajeedNo ratings yet
- Basculas Con MIGO SAPDocument3 pagesBasculas Con MIGO SAPmizraimNo ratings yet
- Spitler McQuiston Lindsey 93 2Document11 pagesSpitler McQuiston Lindsey 93 2Shafawati ShahneelNo ratings yet
- DLL CSS Week 5Document3 pagesDLL CSS Week 5Juanits BugayNo ratings yet
- Mcqs Pa OrignalDocument55 pagesMcqs Pa OrignalMuhammad Youneeb100% (1)
- Commerzbank. Frankfurt, Germany. Sir Norman Foster & PartnersDocument7 pagesCommerzbank. Frankfurt, Germany. Sir Norman Foster & PartnersRehana P NawassNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document30 pagesChapter 10Fernando Alcala Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Osmotic Power Potential Questions and AnswersDocument12 pagesOsmotic Power Potential Questions and AnswersAishwar RavichandranNo ratings yet
- TCS NotesDocument10 pagesTCS Notesdhana sethupathyNo ratings yet
- BSC Nautical Science 2015 16 PDFDocument173 pagesBSC Nautical Science 2015 16 PDFMerchant Navy PlanetNo ratings yet