Professional Documents
Culture Documents
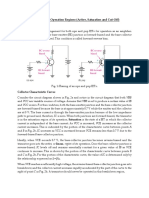
P V I P P P: Since The Base-Emitter Junction Is Just A Diode in The Forward Bias, The Value of
Uploaded by
Gopi Srikanth VegiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
P V I P P P: Since The Base-Emitter Junction Is Just A Diode in The Forward Bias, The Value of
Uploaded by
Gopi Srikanth VegiCopyright:
Available Formats
525511-10-2E AID: 20556 | 03/09/2016
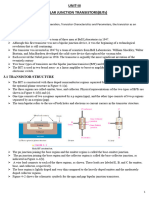
From the transistor switching circuit shown in FIGURE 10.7
A bipolar transistor is connected to a resistive load.
The source voltage is VCC 40 V
Load resistance RL 10
Bipolar junction transistor is said to be in cut-off region, when both the junctions of the
transistor are reverse biased.
In cut-off condition, emitter current is zero and collector current consists of small reverse
saturation currents.
IE 0
IC IB 0
IB IC
In the cut-off region, the transistor parameters are:
The collector current is IC 10 mA
The base current is IB 10 mA
a) The Load power in a transistor circuit is:
PL VCC IC
PL 40 10 10 3
PL 400 103
PL 0.4 W
b) When the transistor is in cut-off region, the collector-emitter voltage value is equals to
The source voltage minus voltage drop across the loads
VCE VCC RL IC
3
VCE 40 10 10 10
VCE 40 0.1
VCE 39.9
The losses in the collector-emitter circuit are:
PCE IC VCE
PCE 10 10 3 39.9
PCE 399 10 3
PCE 0.399
The losses in the base-emitter circuit are:
PBE IB VBE
Since the base-emitter junction is just a diode in the forward bias, the value
of
VBE is in the range of 0 VBE 0.5
Considering the value of VBE is 0.4V
PBE 10 10 3 0.4
Therefore, PBE 0.004
The input power in a transistor circuit is equals to Load power in a transistor circuit
Plus losses in a transistor circuit
PI PL PBE PCE
PI 0.4 0.004 0.399
PI 0.795
PI 0.795 W
The efficiency of the circuit is
PL
100%
PI
0.4
100%
0.795
0.50314 100%
50.314%
You might also like
- Bipolar Junction TransistorsDocument26 pagesBipolar Junction TransistorsEng Abdulkadir MahamedNo ratings yet
- 4 - BJTsDocument15 pages4 - BJTsSethiSheikhNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronics:: AssignmentDocument15 pagesAnalog Electronics:: AssignmentRenuka SarmishtaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document18 pagesChapter 4Waqas Ahmad GhummanNo ratings yet
- Common Emitter Curves:: BE 1 B CEDocument4 pagesCommon Emitter Curves:: BE 1 B CEHarish KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document45 pagesChapter 4api-394738731No ratings yet
- ET 212 Electronics: Bipolar Junction TransistorsDocument29 pagesET 212 Electronics: Bipolar Junction TransistorsPaula JaneNo ratings yet
- BJT SummaryDocument65 pagesBJT SummaryRutendo SedeyaNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTS) : S. Hashim BukhariDocument55 pagesBipolar Junction Transistors (BJTS) : S. Hashim BukharinasiruddinNo ratings yet
- VTU Notes Basic ElectronicsDocument22 pagesVTU Notes Basic ElectronicsCicira BNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4. BJTPPTDocument52 pagesLecture 4. BJTPPTjthanikNo ratings yet
- Analogue Electronic Design Module E EEE2039 / EEE2026 / EEE2042Document36 pagesAnalogue Electronic Design Module E EEE2039 / EEE2026 / EEE2042Arvish RamseebaluckNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6Document10 pagesLecture 6Altaher Bushra AdamNo ratings yet
- TransistorDocument93 pagesTransistorIbnu Zaqi Firdaus100% (2)
- Unit-2 Part-3Document11 pagesUnit-2 Part-3rogithprathapNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)Document42 pagesBipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)Muhammad AmeenNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)Document36 pagesBipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)Muhammad AmeenNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 10:: Biploar TransistorDocument21 pagesLecture - 10:: Biploar TransistorGEORGENo ratings yet
- Chapter 04Document55 pagesChapter 04Mohammad SubhanNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction Transistors: 1 Dr. Paulraj M P, Associate Professor, Blok A, School of Mechatronic EngineeringDocument51 pagesBipolar Junction Transistors: 1 Dr. Paulraj M P, Associate Professor, Blok A, School of Mechatronic EngineeringPrabhuNo ratings yet
- Publication 12 4449 82Document10 pagesPublication 12 4449 82Samz AdrianNo ratings yet
- EdcDocument21 pagesEdcThiaga RajanNo ratings yet
- BJTDocument22 pagesBJTAliyan TahirNo ratings yet
- #1 Tutorial - Introduction To BJTDocument3 pages#1 Tutorial - Introduction To BJTAlbert GenceNo ratings yet
- Transistors: Transfer ResistorDocument75 pagesTransistors: Transfer ResistorMuhammadAfriNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTS)Document48 pagesBipolar Junction Transistors (BJTS)Oscar BoshaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - BJTDocument30 pagesChapter 4 - BJTAlwani IzzatiNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorsDocument55 pagesBipolar Junction Transistorshuy PhamNo ratings yet
- Transistors: Transfer ResistorDocument75 pagesTransistors: Transfer ResistorNagarajan RajaNo ratings yet
- L10 BJT Applications and BiasingDocument23 pagesL10 BJT Applications and BiasingpojanopeNo ratings yet
- BJT BasicsDocument14 pagesBJT BasicsabrarkabirNo ratings yet
- Module2 PDFDocument16 pagesModule2 PDFSrihari UttanurNo ratings yet
- IV. Bipolar Junction Transistors: LED 10302: Introduction To Electronics Meet Prepared By: AZO, AZJ, ATA, MSHDocument9 pagesIV. Bipolar Junction Transistors: LED 10302: Introduction To Electronics Meet Prepared By: AZO, AZJ, ATA, MSHNaim NizamNo ratings yet
- 8 - Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument38 pages8 - Bipolar Junction TransistorShahnail MemonNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument60 pagesBipolar Junction TransistorDfm-Crisna RadityaNo ratings yet
- CE ConnectionDocument18 pagesCE Connectionaye1216shaNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTS) : DR Derek Molloy, DCUDocument17 pagesBipolar Junction Transistors (BJTS) : DR Derek Molloy, DCUraja_ramalingam07No ratings yet
- 11-BJT DC Characteristics and Analysis-20!02!2024Document15 pages11-BJT DC Characteristics and Analysis-20!02!2024ashbinny1No ratings yet
- Chapter 17Document48 pagesChapter 17MahmoudKhedrNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorsDocument38 pagesBipolar Junction TransistorsMuhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Prof.. Mohammed Gulam AhamadDocument75 pagesProf.. Mohammed Gulam AhamadMohammad Gulam Ahamad100% (1)
- Chapter 3 (Ii) : BJT (DC Analysis)Document17 pagesChapter 3 (Ii) : BJT (DC Analysis)matlela92No ratings yet
- Lab 07Document3 pagesLab 07Juan TarquiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Transistor CharacteristicsDocument23 pagesChapter 4 Transistor CharacteristicsHydian Genos YTNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Junction TransistorsDocument50 pagesBipolar Junction Transistorspcjoshi02No ratings yet
- HW 2 SolutionDocument18 pagesHW 2 SolutionMei QiiNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Rev1 - Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTS) - Syed PDFDocument53 pagesCH 1 Rev1 - Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTS) - Syed PDFMuhammad Anaz'sNo ratings yet
- Study Materials - EDC 01Document104 pagesStudy Materials - EDC 01pandaros000No ratings yet
- MCQ in DC Biasing - BJTsDocument6 pagesMCQ in DC Biasing - BJTsPaolo PerezNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 (A) To Study Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) Emitter Bias Configuration and Its StabilityDocument14 pagesExperiment 3 (A) To Study Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) Emitter Bias Configuration and Its StabilityNayyab MalikNo ratings yet
- 1-4 Coen 309Document20 pages1-4 Coen 309mahmoud sadiqNo ratings yet
- Lecture 24: BJT Operation Regions (Active, Saturation and Cut-Off)Document3 pagesLecture 24: BJT Operation Regions (Active, Saturation and Cut-Off)Huzaifa RehanNo ratings yet
- Unit 4Document15 pagesUnit 4Ama Serwaa YeboahNo ratings yet
- Be Unit-IiiDocument9 pagesBe Unit-IiidivyalakshmibharathilankaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 18-20 - Ideal Zener Diodes and BJTDocument27 pagesLecture 18-20 - Ideal Zener Diodes and BJTCHAITANYA KRISHNA CHAUHANNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronics: TransistorsDocument20 pagesBasic Electronics: Transistorssoumikbh100% (2)
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Transfomer With Half-Wave RectifierDocument2 pagesTransfomer With Half-Wave RectifierGopi Srikanth VegiNo ratings yet
- Transformer Threephasefourier ProblemDocument1 pageTransformer Threephasefourier ProblemGopi Srikanth VegiNo ratings yet
- DC 2 DcconvDocument1 pageDC 2 DcconvGopi Srikanth VegiNo ratings yet
- Interfacing MeaningDocument1 pageInterfacing MeaningGopi Srikanth VegiNo ratings yet
- Bode DiagramDocument1 pageBode DiagramGopi Srikanth VegiNo ratings yet
- Laplace Transforms With MATLABDocument3 pagesLaplace Transforms With MATLABJoão Gabriel LimaNo ratings yet
- Buck Converter Design NoteDocument17 pagesBuck Converter Design NoteZhao XuNo ratings yet
- Bode DiagramDocument1 pageBode DiagramGopi Srikanth VegiNo ratings yet
- 750 MVA SCL 10 Pu 75 MVA 75 MVA X 15% 15 MVA 0.15 5 0.75 PuDocument2 pages750 MVA SCL 10 Pu 75 MVA 75 MVA X 15% 15 MVA 0.15 5 0.75 PuGopi Srikanth VegiNo ratings yet
- Bode DiagramDocument1 pageBode DiagramGopi Srikanth VegiNo ratings yet
- Laplace Transforms With MATLABDocument3 pagesLaplace Transforms With MATLABJoão Gabriel LimaNo ratings yet
- Half-Wave Rectifier Example Using Power Elec.Document2 pagesHalf-Wave Rectifier Example Using Power Elec.Gopi Srikanth VegiNo ratings yet
- Half-Wave Rectifier Example Using Power Elec.Document2 pagesHalf-Wave Rectifier Example Using Power Elec.Gopi Srikanth VegiNo ratings yet
- Bode DiagramDocument1 pageBode DiagramGopi Srikanth VegiNo ratings yet
- Bode DiagramDocument1 pageBode DiagramGopi Srikanth VegiNo ratings yet
- ELG4152L5Document18 pagesELG4152L5Sachin YadavNo ratings yet
- DynamicDocument15 pagesDynamicGopi Srikanth VegiNo ratings yet
- Saturation and Its Current Is Given By,: R 680 I 16.67 MaDocument1 pageSaturation and Its Current Is Given By,: R 680 I 16.67 MaGopi Srikanth VegiNo ratings yet
- Buck Boost DesignDocument33 pagesBuck Boost DesignGopi Srikanth VegiNo ratings yet
- ELG4152L5Document18 pagesELG4152L5Sachin YadavNo ratings yet
- Saturation and Its Current Is Given By,: R 680 I 16.67 MaDocument1 pageSaturation and Its Current Is Given By,: R 680 I 16.67 MaGopi Srikanth VegiNo ratings yet
- IST Asst Prof Contract Notification Sep 2017Document2 pagesIST Asst Prof Contract Notification Sep 2017Gopi Srikanth VegiNo ratings yet
- QuesDocument2 pagesQuesGopi Srikanth Vegi0% (3)
- A Square With Sides 2 M - EMfieldsDocument14 pagesA Square With Sides 2 M - EMfieldsGopi Srikanth VegiNo ratings yet
- Answer 3Document1 pageAnswer 3Gopi Srikanth VegiNo ratings yet
- QuespraDocument3 pagesQuespraGopi Srikanth VegiNo ratings yet
- A Coaxial Capacitor of Length PDFDocument2 pagesA Coaxial Capacitor of Length PDFGopi Srikanth VegiNo ratings yet
- Power Electrnics Notes PDFDocument78 pagesPower Electrnics Notes PDFAditya SolankiNo ratings yet
- 2-Lecture Notes Lesson2 7Document8 pages2-Lecture Notes Lesson2 7kstu1112No ratings yet
- Answer 2Document1 pageAnswer 2Gopi Srikanth VegiNo ratings yet