Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Finance 2017
Uploaded by
AamirCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Finance 2017
Uploaded by
AamirCopyright:
Available Formats
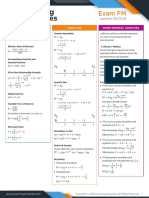
Exam FM
Adapt to Your Exam
INTEREST MEASUREMENT
INTEREST MEASUREMENT Perpetuity YIELD RATES YIELD RATES
Perpetuity-immediate:
Effective Rate of Interest 1 Two methods for comparing investments:
1 = H| = + 7 + = Net Present Value (NPV): Sum the present value
" =
1 Perpetuity-due: of cash inflows and cash outflows. Choose
1 investment with greatest positive NPV.
Effective Rate of Discount = | = 1 + + 7 + = Internal Rate of Return (IRR): The rate such that
1
" = H| = 1 + H| the present value of cash inflows is equal to the
present value of cash outflows. Choose
Accumulation Function and Amount Function investment with greatest IRR.
= 0
MORE GENERAL ANNUITIES
MORE GENERAL ANNUITIES
All-in-One Relationship Formula LOAN AMORTIZATION AND SINKING FUNDS
- -" - /-" j-effective method is used when payments are more LOAN AMORTIZATION AND SINKING FUNDS
or less frequent than the interest period.
1 + "
= 1+ = 1 /"
= 1 = 1"
Outstanding Balance Calculation
j-effective Method Prospective: " = B/"| , = level payments
Simple Interest Convert the given interest rate to the equivalent
= 1 + Present value of future payments.
effective interest rate for the period between Retrospective: " = 1 + " "|
Variable Force of Interest each payment.
Accumulated value of original loan amount L
3 Example: To find the present value of monthly
" = minus accumulated value of all past payments.
payments given annual effective rate of i, define
Accumulate 1 from time 4 7 : as the monthly effective rate where
Retrospective Prospective
"> = 1 + 4 47 1. Then apply = B| using j. Accumulating Discounting
= exp <
"? Payments in Arithmetic Progression Past Payments Future Payments
PV of n-year annuity-immediate with payments of Bt
Discount Factor
1 , + , + 2, , + 1
= = 1 B| B
1 + = B| +
0 n
= = Calculator-friendly version: t
1 + L
B
= + +
B|
Loan Amortization
ANNUITIES ANNUITIES = , = in % , = + , =
For a loan of B| repaid with n payments of 1:
Annuity-Immediate
PV of n-year annuity-immediate with payments of
1 B Period Total till time t
= B| = + 7 + + B = 1, 2, 3, ,
ab| /Bc b Interest " 1 B/"F4 B| B/"|
= B| = 1 + 1 + + + 1 + B/4 Unit increasing: B| =
d
Principal
1 + B 1 P&Q version: = 1, = 1, = B/"F4 B| B/"|
=
repaid "
PV of n-year annuity-immediate with payments of Total 1 t
a s , 1, 2, , 1
B/ab|
n n Unit decreasing: B| = General Formulas for Amortized Loan with
$1 1 1 1
d Level/Non-Level Payments
P&Q version: = , = 1, = " = "/4
1 2 n1 n PV of perpetuity-immediate and perpetuity-due " = "/4 1 + " = "/4 "
with payments of 1, 2, 3, " = " "
1 1 1 1
Annuity-Due H| = = + H| = 7 "Fp = " 1 + p (only for Level Payments)
1 B 7
= B| = 1 + + 7 + + B/4 = Payments in Geometric Progression Sinking Fund
= B| = 1 + + 1 + 7 + + 1 + B PV of an n-year annuity-immediate with payments Loan payment consists of (i) interest paid to the
1 + B 1 of 1, 1 + , 1 + 7 , , 1 + B/4 lender based on the total loan amount and (ii)
= 1 + B the sinking fund deposit .
1
= 1 + , Interest paid = rstu
a!! s
!!
Sinking fund deposit: =
v
n n wb| x
Level and Increasing Continuous Annuity yz
$1 1 1 1 B
1 B Net loan amount at t: "| {yz
B| = " = = B|
1 2 n1 n
h INTi=i It It It
B B| B loan
i=iloan
B| = " = 0 1 2 n
Immediate vs. Due h B0
B| = B| 1 + = 1 + B/4| SFi=j SFDt SFDt SFDt
B| = B| 1 + = BF4| 1
SF
i=jSF
0 1 2 n
B0
Deferred Annuity
m-year deferred n-year annuity-immediate:
= -| B| = - B| = -FB| -|
www.coachingactuaries.com Copyright 2017 Coaching Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 1
BONDS
BONDS
BONDS BONDS SPOT RATES AND FORWARD RATES
SPOT RATES AND FORWARD RATES
SPOT RATES AND FORWARD RATES
SPOT RATES AND FORWARD RATES DETERMINANTS OF INTEREST RATES
DETERMINANTS OF INTEREST RATES
DETERMINANTS OF INTEREST RATES
DETERMINANTS OF INTEREST RATES
Bond Pricing Formulas
Bond Pricing Formulas
Bond Pricing Formulas "" is the t-year spot rate
is the t-year spot rate
" is the t-year spot rate Interest rate can be viewed as the equilibrium
Interest rate can be viewed as the equilibrium
Interest rate can be viewed as the equilibrium
Price of bond
Price of bond
Price of bond is the forward rate from time
""??","?,",">>> is the forward rate from time to time 777, , ,
to time
is the forward rate from time 444 to time price of money.
price of money.
price of money.
Par value (face amount) of bond
Par value (face amount) of bond
Par value (face amount) of bond expressed annually.
expressed annually.
expressed annually. Interest rate can be decomposed into five
Interest rate can be decomposed into five
Interest rate can be decomposed into five
(not a cash flow)
(not a cash flow)
(not a cash flow)
- components:
components:
components:
Coupon rate per payment period
Coupon rate per payment period ++BBB BBB 111+
111+ ++B,BF- --=
B,BF-
== 111+
++BF- BF-
BF-
BF-
Coupon rate per payment period
B,BF- BF-
BF- oo Real risk-free rate
o Real risk-free rate
Real risk-free rate
Amount of each coupon payment
Amount of each coupon payment
Amount of each coupon payment oo Maturity risk premium
o Maturity risk premium
Maturity risk premium
Redemption value of bond (1+sn+m)n+m oo Default risk premium
Default risk premium
Redemption value of bond
Redemption value of bond o Default risk premium
(
(
(= == unless otherwise stated)
unless otherwise stated)
unless otherwise stated) oo Inflation premium
o Inflation premium
Inflation premium
Interest rate per payment period
Interest rate per payment period
Interest rate per payment period oo Liquidity premium
o Liquidity premium
Liquidity premium
Number of coupon payments 0 n n+m
Number of coupon payments
Number of coupon payments Four theories explaining why interest rates
Four theories explaining why interest rates
Four theories explaining why interest rates
Basic Formula
Basic Formula
Basic Formula differ by terms:
differ by terms:
differ by terms:
=
==
B|d BBB
+
+
(1+sn)n (1+f[n,n+m])m oo Market segmentation theory
Market segmentation theory
B|d +
B|d o Market segmentation theory
Premium/Discount Formula:
Premium/Discount Formula:
Premium/Discount Formula: oo Preferred habitat theory
o Preferred habitat theory
Preferred habitat theory
=== +
++
++BBB BBB=
111+ == 111+
++h,4 1 ++4,7
h,4 11+
111+
4,7
++B/4,B
B/4,B oo Liquidity preference theory/Opportunity cost
B|d Liquidity preference theory/Opportunity cost
h,4 4,7 B/4,B
B|d
B|d
o Liquidity preference theory/Opportunity cost
theory
theory
theory
Premium vs. Discount
Premium vs. Discount
Premium vs. Discount oo Expectations theory
Expectations theory
(1+sn)n o Expectations theory
Premium
Premium
Premium Discount
Discount
Discount Federal Reserve facilitates a countrys payment
Federal Reserve facilitates a countrys payment
Federal Reserve facilitates a countrys payment
>
>>
<
<<
operations and functions as a last resort lender
operations and functions as a last resort lender
operations and functions as a last resort lender
Condition or or to commercial banks.
to commercial banks.
to commercial banks.
Condition
Condition or
or or
or 0 1 2 n1 n
>>
>
<<
<
U.S. T-bills are quoted:
U.S. T-bills are quoted:
U.S. T-bills are quoted:
360
360
Amortization
Amortization
Amortization Write-Down (1+f[0,1]) (1+f[1,2]) (1+f[n1,n]
) Quoted Rate
Quoted Rate
Quoted Rate= == 360
Process
Process
Write-Down
Write-Down Write-Up
Write-Up
Write-Up
Process Canadian T-bills are quoted:
B/"F4 Canadian T-bills are quoted:
Canadian T-bills are quoted:
B/"F4
B/"F4
365
365
Amount
Amount
Amount == "/4 """ =
== """ INTEREST RATE SWAP Quoted Rate
Quoted Rate
Quoted Rate= == 365
= "/4
"/4 INTEREST RATE SWAP
INTEREST RATE SWAP
INTEREST RATE SWAP
General Formulas for Bond Amortization
General Formulas for Bond Amortization
General Formulas for Bond Amortization where N is the number of days to maturity, I is the
where N is the number of days to maturity, I is the
where N is the number of days to maturity, I is the
An agreement between two parties in which both
An agreement between two parties in which both
An agreement between two parties in which both
Book value:
Book value:
Book value: amount of interest, C is the maturity value and P is
amount of interest, C is the maturity value and P is
amount of interest, C is the maturity value and P is
B/" parties agree to exchange a series of cash flows
parties agree to exchange a series of cash flows
parties agree to exchange a series of cash flows the price.
==
"""=
B/"|d +
+ B/"
B/"= ==+
++
B/"|d the price.
the price.
B/"|d +
B/"|d B/"|d
B/"|d
based on interest rates.
Interest earned = based on interest rates.
based on interest rates.
Interest earned =
Interest earned = "/4 "/4
"/4
Swap Rate
Swap Rate
Swap Rate
Callable Bonds
Callable Bonds
Callable Bonds INTEREST MEASUREMENT OF A FUND
INTEREST MEASUREMENT OF A FUND
INTEREST MEASUREMENT OF A FUND
The swap rate can be calculated by equating the
The swap rate can be calculated by equating the INTEREST MEASUREMENT OF A FUND
Calculate the lowest price for all possible
Calculate the lowest price for all possible
Calculate the lowest price for all possible The swap rate can be calculated by equating the
redemption dates at a certain yield rate. This is the present value of swap payments with the present
present value of swap payments with the present
present value of swap payments with the present Dollar-weighted Interest Rate
Dollar-weighted Interest Rate
Dollar-weighted Interest Rate
redemption dates at a certain yield rate. This is the
redemption dates at a certain yield rate. This is the
highest price that guarantees this yield rate. value of expected variable payments. The yield rate computation depends on the amount
The yield rate computation depends on the amount
The yield rate computation depends on the amount
highest price that guarantees this yield rate.
highest price that guarantees this yield rate. value of expected variable payments.
value of expected variable payments.
invested.
invested.
invested.
Premium bond call the bond on the FIRST
Premium bond call the bond on the FIRST
Premium bond call the bond on the FIRST If notional amount is not level:
If notional amount is not level:
If notional amount is not level:
possible date. Method:
Method:
Method:
possible date.
possible date. 44
4 + 77
7 +
Discount bond call the bond on the LAST
Discount bond call the bond on the LAST
Discount bond call the bond on the LAST ++44 ++ 111+
111+ 4
++77 777++ 111+
7
++
Calculate amount of interest:
Calculate amount of interest:
Calculate amount of interest: = ==
44h,4
774,7
h,4 + 4,7 +
7, :
: Amount at the beginning of period
:Amount at the beginning of period
Amount at the beginning of period
possible date.
possible date. == 4 h,4 7 4,7 7, 7,
++
possible date. = ++44 ++ 111+++77 777++ 111+
111+ :
: Amount at the end of period
:Amount at the end of period
4 7 Amount at the end of period
If notional amount is level:
If notional amount is level:
If notional amount is level: :
: Deposit/withdrawal
:Deposit/withdrawal
Deposit/withdrawal
STOCKS
STOCKS
STOCKS STOCKS
Since an interest rate swap is equivalent to
Since an interest rate swap is equivalent to
Since an interest rate swap is equivalent to Calculate the dollar-weighted interest rate:
Calculate the dollar-weighted interest rate:
Calculate the dollar-weighted interest rate:
borrowing at a floating rate to buy a fixed-rate
borrowing at a floating rate to buy a fixed-rate
borrowing at a floating rate to buy a fixed-rate
Price of Level Dividend-Paying Stock
Price of Level Dividend-Paying Stock
Price of Level Dividend-Paying Stock bond, fixed swap rate is the coupon rate on a par =
==
+ """ 111
++
bond, fixed swap rate is the coupon rate on a par
bond, fixed swap rate is the coupon rate on a par
== coupon bond.
=
coupon bond.
coupon bond.
Time-weighted Interest Rate
+
+ 11 Time-weighted Interest Rate
Time-weighted Interest Rate
+ + + + 1B = = 1 The yield rate computation depends on successive
=
==par value,
par value,
par value, =
==fixed dividend rate
fixed dividend rate
fixed dividend rate 111+ ++444++ 111+ ++777 777++++ 111+++BBB BB =1 1 The yield rate computation depends on successive
The yield rate computation depends on successive
sub-intervals of the year each time a deposit or
sub-intervals of the year each time a deposit or
sub-intervals of the year each time a deposit or
Price of Increasing Dividend-Paying Stock
Price of Increasing Dividend-Paying Stock
Price of Increasing Dividend-Paying Stock 111
B
BB withdrawal is made.
=
== withdrawal is made.
withdrawal is made.
444+
++
777+
++ ++
===
+ BB
B Method:
..Method:
.Method:
Net Swap Payment 7
B
=
==expected first dividend,
expected first dividend, =
==growth rate
growth rate Net Swap Payment
Net Swap Payment 1
11+ ++ =
== 77 BB
expected first dividend, growth rate
The difference between the fixed interest payment
The difference between the fixed interest payment
The difference between the fixed interest payment
444
777 B/4
B/4
B/4
and variable interest payment.
and variable interest payment.
and variable interest payment. Date 1
Date 1
Date 1 Date 2
Date 2
Date 2
Account
Account
Account
Net Interest Payment
Net Interest Payment
Net Interest Payment 444
777
Before CF
Before CF
Before CF
The combination of the net swap payment and the
The combination of the net swap payment and the
The combination of the net swap payment and the Cash Flow
Cash Flow
Cash Flow
interest payment made by the borrower to the
interest payment made by the borrower to the 444
777
interest payment made by the borrower to the (CF)
(CF)
(CF)
lender.
lender.
lender. Account
Account
Account
444=
==
444+ ++
444
777=
==
777+ ++
777
After CF
After CF
After CF
Deferred Interest Rate Swap
Deferred Interest Rate Swap
Deferred Interest Rate Swap
For a x-year deferred n-year swap with level
For a x-year deferred n-year swap with level
For a x-year deferred n-year swap with level
notional amount:
notional amount:
notional amount:
FB
FB
=
== FB
F4 +
F4+
F4
+F7 ++
F7+
F7
+++
FB
FB
FB
Market Value of a Swap
Market Value of a Swap
Market Value of a Swap
The market value of a swap at time t is the
The market value of a swap at time t is the
The market value of a swap at time t is the
present value at time t of its expected future
present value at time t of its expected future
present value at time t of its expected future
cash flows.
cash flows.
cash flows.
The market value of a swap is 0 at inception.
The market value of a swap is 0 at inception.
The market value of a swap is 0 at inception.
www.coachingactuaries.com Copyright 2017 Coaching Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 2
DURATION AND CONVEXITY
DURATION AND CONVEXITY
DURATION AND CONVEXITY BA-II PLUS CALCULATOR GUIDELINE
BA-II PLUS CALCULATOR GUIDELINE
BA-II PLUS CALCULATOR GUIDELINE
Duration
Duration Basic Operations
Basic Operations
BB
3 3 "h
""
"h
" " ENTER (SET) : Send value to a variable (option)
ENTER (SET) : Send value to a variable (option)
== ==
BB
"h
"h
" "
"" : Navigate through variables
: Navigate through variables
33 BB "F4
"F4 2ND : Access secondary functions (yellow)
2ND : Access secondary functions (yellow)
"h
"h
" "
== ==
BB
"h
"h
" "
""
STO + 0~9 : Send on-screen value into memory
STO + 0~9 : Send on-screen value into memory
==
RCL + 0~9 : Recall value from a memory
RCL + 0~9 : Recall value from a memory
-year zero-coupon bond
-year zero-coupon bond == Time Value of Money (TVM)
Time Value of Money (TVM)
11++ Good for handling annuities, loans and bonds.
Good for handling annuities, loans and bonds.
geometrically increasing perpetuity
geometrically increasing perpetuity ==
Note: Be careful with signs of cash flows.
Note: Be careful with signs of cash flows.
-year par bond
-year par bond ==B|B| N : Number of periods
N : Number of periods
"B"B= =
"h
"h I/Y : Effective interest rate per period (in %)
I/Y : Effective interest rate per period (in %)
First-order Modified Approximation
First-order Modified Approximation PV : Present value
PV : Present value
BB [1
[1 BB
] ] PMT : Amount of each payment of an annuity
PMT : Amount of each payment of an annuity
First-order Macaulay Approximation
First-order Macaulay Approximation
FV : Future value
FV : Future value
11++ a
a
BB CPT + (one of above): Solve for unknown
CPT + (one of above): Solve for unknown
11++BB
2ND + BGN : Switch between annuity immediate
2ND + BGN : Switch between annuity immediate
Duration of a portfolio
Duration of a portfolio
and annuity due
and annuity due
For a portfolio of m securities where invested
For a portfolio of m securities where invested
2ND + P/Y : Please keep P/Y and C/Y as 1
2ND + P/Y : Please keep P/Y and C/Y as 1
amount ==44++77++++
amount -- at time 0,
at time 0,
44 77
--
2ND + CLR TVM : Clear TVM worksheet
2ND + CLR TVM : Clear TVM worksheet
==
44++
77++++
-- 2ND + AMORT : Amortization (See Below)
2ND + AMORT : Amortization (See Below)
Convexity
Convexity
BB
For bonds (
For bonds ( ==
B|d
B|d+ BB ):
+ ):
3333 "h +
"h +11 "F7 "F7
" "
== == BB N =
N =; I/Y =
; I/Y =; PV =
; PV =; PMT =
; PMT =; FV =
; FV =.
.
"h
"h
" " " "
3333 BB 77 ""
"h
"h " " Cash Flow Worksheet ( CF , NPV , IRR )
Cash Flow Worksheet ( CF , NPV , IRR )
== == BB " "
"h
"h
" " Good for non-level series of payments.
Good for non-level series of payments.
77
== ++
Input ( CF )
Input ( CF )
-year zero-coupon bond ==77
-year zero-coupon bond
CF0: Cash flow at time 0
CF 0: Cash flow at time 0
CCn: n
n: n cash flow
thth cash flow
FFn: Frequency of the cash flow
n: Frequency of the cash flow
IMMUNIZATION
IMMUNIZATION IMMUNIZATION
Output ( NPV , IRR )
Output ( NPV , IRR )
Redington and Full Immunization
Redington and Full Immunization I: Effective interest rate (in %)
I: Effective interest rate (in %)
NPV + CPT : Solve for net present value
NPV + CPT : Solve for net present value
Redington
Redington Full
Full IRR + CPT : Solve for internal rate of return
IRR + CPT : Solve for internal rate of return
ww"w=
ww"w =
vdadd"dw
vdadd"dw Amortization Schedule ( 2ND + AMORT )
Amortization Schedule ( 2ND + AMORT )
==
vv or
or 33
=v3v 3 Good for finding outstanding balance of the loan and
Good for finding outstanding balance of the loan and
=
interest/principal portion of certain payments.
interest/principal portion of certain payments.
There has to be asset
There has to be asset Note: BA-II Plus requires computing the unknown
Note: BA-II Plus requires computing the unknown
>>vv
cash flows before and
cash flows before and TVM variable before entering into AMORT
TVM variable before entering into AMORT
or
or
3333 after each liability
after each liability function.
function.
>
>v33v33
cash flow.
cash flow. P1: Starting period
P1: Starting period
Immunizes against
Immunizes against Immunizes against
Immunizes against P2: Ending period
P2: Ending period
small changes in
small changes in any changes in
any changes in BAL: Remaining balance of the loan after P2
BAL: Remaining balance of the loan after P2
PRN: Sum of the principal repaid from P1 to P2
PRN: Sum of the principal repaid from P1 to P2
INT: Sum of the interest paid from P1 to P2
INT: Sum of the interest paid from P1 to P2
www.coachingactuaries.com Copyright 2017 Coaching Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 3
NOTES
Copyright 2017 Coaching Actuaries. All Rights Reserved. 4
www.coachingactuaries.com
www.coachingactuaries.com Personal copies
Copyright permitted.
2017 Resale
Coaching or distribution
Actuaries. is prohibited.
All Rights Reserved. 4
You might also like
- Pension Finance: Putting the Risks and Costs of Defined Benefit Plans Back Under Your ControlFrom EverandPension Finance: Putting the Risks and Costs of Defined Benefit Plans Back Under Your ControlNo ratings yet
- Exam FM: You Have What It Takes To PassDocument5 pagesExam FM: You Have What It Takes To Passenquiry no100% (2)
- FM Formula Sheet 2022Document3 pagesFM Formula Sheet 2022Laura StephanieNo ratings yet
- ADAPT Formula Sheet PDFDocument2 pagesADAPT Formula Sheet PDFMariahDeniseCarumbaNo ratings yet
- Exam PDocument517 pagesExam PHuy Do TruongNo ratings yet
- Examp Formula SheetsDocument6 pagesExamp Formula SheetsSanjay GhimireNo ratings yet
- Exam LTAM: You Have What It Takes To PassDocument12 pagesExam LTAM: You Have What It Takes To Passderianfg100% (1)
- A&J Questions Bank For SOA Exam MFE/ CAS Exam 3FDocument24 pagesA&J Questions Bank For SOA Exam MFE/ CAS Exam 3Fanjstudymanual100% (1)
- Fullpassion 1Document9 pagesFullpassion 1api-457232170100% (1)
- Actuarial Jimmy Sept20Document105 pagesActuarial Jimmy Sept20dom0% (1)
- Ltam Formula Sheet PDFDocument7 pagesLtam Formula Sheet PDFbemiphucro50% (2)
- STAM Formula SheetDocument4 pagesSTAM Formula Sheetkosaunderground100% (2)
- A&J Flashcards For Exam SOA Exam FM/ CAS Exam 2Document39 pagesA&J Flashcards For Exam SOA Exam FM/ CAS Exam 2anjstudymanualNo ratings yet
- Deeper Understanding Spring 11 Manual For PDocument443 pagesDeeper Understanding Spring 11 Manual For PJordan Zipkin100% (2)
- SOA Exam MFE Flash CardsDocument21 pagesSOA Exam MFE Flash CardsSong Liu100% (2)
- Exam C Manual PDFDocument2 pagesExam C Manual PDFJohnathan0% (1)
- Exam P FormulasDocument2 pagesExam P Formulasasdfg888100% (1)
- Guo Spring 08 PDocument434 pagesGuo Spring 08 PYutaro TanakaNo ratings yet
- Formula SheetDocument31 pagesFormula Sheetkarthik Ravichandiran100% (1)
- ADAPT Formula Sheet 2015 - SOA Exam P PDFDocument3 pagesADAPT Formula Sheet 2015 - SOA Exam P PDFTommyYapNo ratings yet
- Formulas For SOA/CAS Exam FM/2Document15 pagesFormulas For SOA/CAS Exam FM/2jeff_cunningham_11100% (3)
- Guo-Deeper Understanding Faster Calc SOA MFE PDFDocument538 pagesGuo-Deeper Understanding Faster Calc SOA MFE PDFPierre-Louis TruchetNo ratings yet
- SOA Exam P SyllabusDocument3 pagesSOA Exam P SyllabusMuneer DhamaniNo ratings yet
- Construction and Evaluation of Actuarial Models Exam GuideDocument6 pagesConstruction and Evaluation of Actuarial Models Exam GuideNoDriverNo ratings yet
- Arch MLCDocument471 pagesArch MLCStéphanie Gagnon100% (3)
- A&J Flashcards For SOA Exam P/CAS Exam 1Document28 pagesA&J Flashcards For SOA Exam P/CAS Exam 1anjstudymanualNo ratings yet
- Actuarial Mathematics Ii: AboutDocument107 pagesActuarial Mathematics Ii: AboutClerry SamuelNo ratings yet
- Arcones Manual Chapter 1 Interest TheoryDocument1,368 pagesArcones Manual Chapter 1 Interest TheorySolomonJOBSNo ratings yet
- MFEDocument531 pagesMFEJi Li100% (3)
- 10-12 Assignment 1Document4 pages10-12 Assignment 1Pavan Kasireddy100% (1)
- Actuarial Mathematics (Lecture Notes) PDFDocument168 pagesActuarial Mathematics (Lecture Notes) PDFVladimir Montero100% (1)
- Christian Notes For Exam PDocument9 pagesChristian Notes For Exam Proy_getty100% (1)
- FM GuoDocument664 pagesFM GuoLoh Hui Yin86% (7)
- Exam FM Practice Exam With Answer KeyDocument71 pagesExam FM Practice Exam With Answer KeyAki TsukiyomiNo ratings yet
- Sample Chapter From Yufeng Guo's Study GuideDocument22 pagesSample Chapter From Yufeng Guo's Study Guide赤铁炎No ratings yet
- Quantitative Analysis Chapter SummariesDocument145 pagesQuantitative Analysis Chapter SummariesRajvi Sampat100% (2)
- YGM Manual MLCDocument285 pagesYGM Manual MLCNyikoEvensNo ratings yet
- A&J Study Manual For SOA Exam FM/ CAS Exam 2Document19 pagesA&J Study Manual For SOA Exam FM/ CAS Exam 2anjstudymanual70% (10)
- SOA Exam P - Yufeng Guo (Fall 2009)Document441 pagesSOA Exam P - Yufeng Guo (Fall 2009)Joseph Guy Evans HilaireNo ratings yet
- Actuaries' Survival Guide: How to Succeed in One of the Most Desirable ProfessionsFrom EverandActuaries' Survival Guide: How to Succeed in One of the Most Desirable ProfessionsRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (4)
- Actuarial Probability Exam (P): Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandActuarial Probability Exam (P): Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- ExamFM_2018Document3 pagesExamFM_2018nargizireNo ratings yet
- CA M K: Ayank OthariDocument4 pagesCA M K: Ayank Otharigagan vermaNo ratings yet
- Investment Portfolio Management: A Brief History of Risk and ReturnDocument43 pagesInvestment Portfolio Management: A Brief History of Risk and ReturnVenessa Yong100% (1)
- Accounting Ratios NewDocument3 pagesAccounting Ratios NewAnkit RoyNo ratings yet
- FIN2704 NotesDocument4 pagesFIN2704 NotesYan KaiNo ratings yet
- Notes Payable AccountingDocument2 pagesNotes Payable AccountingLaut Bantuas IINo ratings yet
- Shared by Ca Blog India: Cash Flow Statement: Indirect MethodDocument4 pagesShared by Ca Blog India: Cash Flow Statement: Indirect MethodRaghav BhatNo ratings yet
- Shared by Ca Blog India: Cash Flow Statement: Indirect MethodDocument4 pagesShared by Ca Blog India: Cash Flow Statement: Indirect MethodpoojaNo ratings yet
- TREASURY MODULE 3 KEY FINANCIAL FORMULASDocument9 pagesTREASURY MODULE 3 KEY FINANCIAL FORMULASmartinNo ratings yet
- Ratio Analysis ch-6Document11 pagesRatio Analysis ch-6IP MAXNo ratings yet
- 2 Financial Mathematics For Real EstateDocument31 pages2 Financial Mathematics For Real EstateLeon M. EggerNo ratings yet
- Accounting and Finance Formulas for Business Key MetricsDocument3 pagesAccounting and Finance Formulas for Business Key MetricsZOn YêuNo ratings yet
- FABM2 Q2 PPT 1 - Analysis and Interpretation of Financial StatementsDocument26 pagesFABM2 Q2 PPT 1 - Analysis and Interpretation of Financial StatementsSpencer Marvin P. EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Ratio AnalysisDocument35 pagesRatio AnalysisArya MahendruNo ratings yet
- Lesson CheDocument29 pagesLesson CheVwvwkjio MujedekovuNo ratings yet
- Common Financial RatiosDocument1 pageCommon Financial RatiosTuấn Phạm NgọcNo ratings yet
- REVELFrequentlyAskedQuestionsStudents PDFDocument10 pagesREVELFrequentlyAskedQuestionsStudents PDFAamirNo ratings yet
- Babylon1 StudentDocument4 pagesBabylon1 StudentAamirNo ratings yet
- Planet Labs SafyanDocument23 pagesPlanet Labs SafyanAamirNo ratings yet
- NMBR Thry 2Document16 pagesNMBR Thry 2AamirNo ratings yet
- Sexagesimal FractionsDocument3 pagesSexagesimal FractionsAamirNo ratings yet
- 3.5.2 Ratio AnalysisDocument49 pages3.5.2 Ratio AnalysisAbder AlamiNo ratings yet
- Buscom SPDocument16 pagesBuscom SPCatherine Joy Vasaya100% (1)
- The Debtors Are Electroglas, Inc. (EIN 77-0336101) and Electroglas International, Inc. (EIN 77-0345011)Document20 pagesThe Debtors Are Electroglas, Inc. (EIN 77-0336101) and Electroglas International, Inc. (EIN 77-0345011)Chapter 11 DocketsNo ratings yet
- Banking Law - PDF ProjectDocument18 pagesBanking Law - PDF ProjectNilotpal RaiNo ratings yet
- FAR - Module 2 - The Accounting EquationDocument5 pagesFAR - Module 2 - The Accounting EquationEva Katrina R. Lopez100% (1)
- General and Subsidiary Ledgers ExplainedDocument57 pagesGeneral and Subsidiary Ledgers ExplainedSavage NicoNo ratings yet
- Week 4 - ch16Document52 pagesWeek 4 - ch16bafsvideo4No ratings yet
- Financial StabilityDocument17 pagesFinancial StabilityJohn Franz OinezaNo ratings yet
- Ebook College Accounting Chapters 1 15 22Nd Edition Heintz Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument60 pagesEbook College Accounting Chapters 1 15 22Nd Edition Heintz Test Bank Full Chapter PDFconvive.unsadden.hgp2100% (12)
- Module 5 - Cost of Capital - QuestionsDocument7 pagesModule 5 - Cost of Capital - QuestionsLAKSHYA AGARWALNo ratings yet
- Data Analysis Penna Cement 1 NEWDocument22 pagesData Analysis Penna Cement 1 NEWShanmuka SreenivasNo ratings yet
- Anirban Chakraborty Project ReportDocument51 pagesAnirban Chakraborty Project Reportsandeepagarwal_83No ratings yet
- Accounting Dr. Ashraf Lecture 03 PDFDocument20 pagesAccounting Dr. Ashraf Lecture 03 PDFMahmoud AbdullahNo ratings yet
- 2CEXAM Mock Question Licensing Examination Paper 7Document10 pages2CEXAM Mock Question Licensing Examination Paper 7Tsz Ngong Ko100% (1)
- Ipo Prospectus GsDocument164 pagesIpo Prospectus GsSehrish MushtaqNo ratings yet
- Why Foreign Aid Is HarmfulDocument5 pagesWhy Foreign Aid Is HarmfulAnas TufailNo ratings yet
- BANKDocument25 pagesBANKAnand SharmaNo ratings yet
- PALS Mercantile Law-LibreDocument161 pagesPALS Mercantile Law-LibreDodong LamelaNo ratings yet
- Philippine High School Enhancement Review on Simple and Compound InterestDocument12 pagesPhilippine High School Enhancement Review on Simple and Compound InterestJames Earl AbainzaNo ratings yet
- The Symphonie Trader System GuideDocument71 pagesThe Symphonie Trader System GuideAdil BensellamNo ratings yet
- Classifying Accounts Into Assets, Liabilities, Owners Equity, Revenue or ExpenseDocument1 pageClassifying Accounts Into Assets, Liabilities, Owners Equity, Revenue or ExpenseSaif Ali KhanNo ratings yet
- India Infoline Finance LTD NCDs Listed On The Stock Exchanges at A PremiumDocument2 pagesIndia Infoline Finance LTD NCDs Listed On The Stock Exchanges at A PremiumIndiaInfoline IiflNo ratings yet
- Fundamental & Technical Analysis of Selected Commodities (Gold & Silver)Document4 pagesFundamental & Technical Analysis of Selected Commodities (Gold & Silver)Raghava PrusomulaNo ratings yet
- Report - Financial Report - January 2021 - TheresidencesatbrentDocument19 pagesReport - Financial Report - January 2021 - TheresidencesatbrentChaNo ratings yet
- Banking Basics: Understanding Commercial BanksDocument136 pagesBanking Basics: Understanding Commercial BanksAppleNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Basics of Banking ServicesDocument6 pagesTopic 1 - Basics of Banking ServicesCarlos Pereira100% (1)
- Business Accounting and Finance (Tony Davies, Ian Crawford)Document801 pagesBusiness Accounting and Finance (Tony Davies, Ian Crawford)ursisNo ratings yet
- Business Finance Lesson-Exemplar - Module 4Document15 pagesBusiness Finance Lesson-Exemplar - Module 4Divina Grace Rodriguez - Librea100% (1)
- Project Report "Banking System" in India Introduction of BankingDocument15 pagesProject Report "Banking System" in India Introduction of BankingshabnammerajNo ratings yet
- Final Account ProblemDocument22 pagesFinal Account ProblemAbhijeet Anand100% (1)