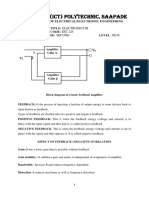
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ArresterWorks ArresterFacts-002 Field Testing Arresters
Uploaded by
ChepelosCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ArresterWorks ArresterFacts-002 Field Testing Arresters
Uploaded by
ChepelosCopyright:
Available Formats
ArresterFacts-002
Field Testing Arresters
ArresterWorks.com
ArresterFacts are information
modules pertaining to the
arrester world.
This Field Testing of Arresters
module will clarify the many
questions about assessing the
quality of an installed high voltage
arrester as applied to power
systems.
Anyone interested in commenting on this
module is welcome to do so. Send
comments to Jonathan Woodworth at
jwoodworth@arresterworks.com
ArresterWorks.com all rights reserved 1
ArresterFacts-002
Field Testing Arresters
ArresterWorks.com
Field testing arresters
comes in many forms.
Vref Tests
Partial Discharge Tests
Thermal Tests
Leakage Current
Dielectric Tests
Watts Loss Tests
This ArresterFacts
will show you the Typical Substation Arrester Mounting
Is this a well functioning arrester or is the small
Facts on each!
hole in the side a problem? Line personnel are
faced with this question on a routine basis.
ArresterWorks.com all rights reserved 2
ArresterFacts-002
Field Testing Arresters
ArresterWorks.com
Why Do Arresters Require Testing at
all?
It is common knowledge that arresters age just
like all other components on power systems.
Since most arresters are directly connected
to the system, they are exposed to voltage
stress continuously.
Since most arresters are exposed to the
elements during their entire life, their seals
are stressed continuously.
Since most arresters are exposed to surges of
many amplitudes some are over stressed.
Since most arresters are stressed in the most
onerous ways, they do experience an end-of-life
event at some time.
In short, arresters are
The purpose of field testing is then to predict the
tested to avoid this
arresters end-of-life and remove it from the
system avoiding an outage due to an unexpected
failure.
ArresterWorks.com all rights reserved 3
ArresterFacts-002
Field Testing Arresters
ArresterWorks.com
Common characteristics of arresters
nearing end-of-life
Example of an Arrester with 1. The unit can exhibit higher
a significantly reduced VI temperatures through-out or in one
Characteristic spot.
2. Partial discharge may be present at
steady state voltages.
3. The VI Characteristic might have
changed.
4. Leakage currents may have increased
significantly.
5. Watts loss may have increased.
6. Physical damage
Note: None of the above may be present and
an arrester may be near end-of-life so
standard high voltage precautions should be
used at all times
ArresterWorks.com all rights reserved 4
ArresterFacts-002
Field Testing Arresters
ArresterWorks.com
Common Arrester Field Testing Methods
Infrared Thermography
Partial Discharge Detection
VI Characteristics Change
Leakage Current
Watts Loss
ArresterWorks.com all rights reserved 5
ArresterFacts-002
Field Testing Arresters
ArresterWorks.com
Infrared Thermography
*>31.9C
What is the
30.0
temperature
difference that 25.0
should cause 20.0 16.5
37.2
concern?
15.0
*<10.0C
ArresterWorks.com all rights reserved 6
ArresterFacts-002
Field Testing Arresters
ArresterWorks.com
Infrared Thermography
The fastest growing method of assessing
the condition of arresters is with the use
of infrared thermography. The reason for
its popularity is its clear differentiation
between a good arrester and one nearing
the end of life.
The reasons for its lack of pervasive use
however is because of two issues.
1. The equipment to perform the
analysis is not common toolbox gear.
2. The process can be time consuming.
ArresterWorks.com all rights reserved 7
ArresterFacts-002
Field Testing Arresters
ArresterWorks.com
Infrared Thermography
This is only
The most significant possible if the
arrester has
issue with Infrared been energized
Thermography is that if for a number of
hours
the arrester is not
energized, it will not
exhibit overheating and
cannot be assessed.
ArresterWorks.com all rights reserved 8
ArresterFacts-002
Field Testing Arresters
ArresterWorks.com
Infrared Thermography
This difference
of 20C is
*>31.9C definitely
What is the
reason for
concern
30.0
temperature
difference that 25.0
should cause 20.0 16.5
37.2
concern?
15.0
*<10.0C
ArresterWorks.com all rights reserved 9
ArresterFacts-002
Field Testing Arresters
ArresterWorks.com
Infrared Thermography
As a Rule:
1. Scan 2 or more of the same arrester types
and vintage
2. Compare the temps of all scanned arresters
3. If hot spots on one are more than 10C
different than the others, have it removed
in the near future
ArresterWorks.com all rights reserved 10
ArresterFacts-002
Field Testing Arresters
ArresterWorks.com
Cost Effective and Fast
Infrared Thermography
A cost effective IR
Thermometer that
measures temperature
from as close as a few
inches to a 100 feet are
readily available. Not only
faster, but can be safer
than working near a hot
arrester.
ArresterWorks.com all rights reserved 11
ArresterFacts-002
Field Testing Arresters
ArresterWorks.com
Partial Discharge Detection
Partial Discharge (PD) is a
localized dielectric
breakdown of a small
portion of a solid or liquid
electrical insulation
It can sometimes be seen in
system under high voltage
the dark if it is external to an
stress. arrester.
It can sometimes be heard if
external to the arrester
ArresterWorks.com all rights reserved 12
ArresterFacts-002
Field Testing Arresters
ArresterWorks.com
Partial Discharge Detection
Partial Discharge is Many arresters near end of
sometimes referred to life will exhibit partial
discharge but not always.
as Radio Interference
Voltage (RIV) If partial discharge is
associated with an arrester,
and cannot not be eliminated
by adjusting the external
connections, then it is likely
in a long term failure mode.
Typical treeing
along the internal If there is no sign of partial
components of a
failing arrester. discharge however it could
This PD would most still be near end of life.
likely be detectable
ArresterWorks.com all rights reserved 13
ArresterFacts-002
Field Testing Arresters
ArresterWorks.com
Partial Discharge Detection
PD Detection
Equipment is widely
available, however few
models are portable
and could not be
considered common
toolbox gear
ArresterWorks.com all rights reserved 14
ArresterFacts-002
Field Testing Arresters
ArresterWorks.com
Partial Discharge Detection
AM Radios can very effectively
be used as a partial discharge
detector. The AM bands on a
radio are very sensitive to
damaging levels of Partial
Discharge.
This is why it is sometimes
referred to as Radio
Interference Voltage.
No! Satellite
Radio wont
work..
ArresterWorks.com all rights reserved 15
ArresterFacts-002
Field Testing Arresters
ArresterWorks.com
Partial Discharge Detection
Portable Acoustic
Detectors are an option
Acoustic Detectors can be used
to locate partial discharge,
however the level must be quit
high to detect.
ArresterWorks.com all rights reserved 16
ArresterFacts-002
Field Testing Arresters
ArresterWorks.com
VI Characteristic Change
120.0
The arrester VI characteristic is
100.0 Typical VI Characteristic one of the most fundamental
for a 22kV MCOV Arrester
descriptors of the health of an
80.0
Voltage (kV)
arrester.
60.0
Leakage Current, Watts Loss and Vref
40.0 tests all measure different aspects of
this characteristic.
20.0
0.0
0.00001 0.001 0.1 10 1000
Current (A)
ArresterWorks.com all rights reserved 17
ArresterFacts-002
Field Testing Arresters
ArresterWorks.com
VI Characteristic Change
VI of a
healthy
22kV
Arrester
VI of an un
healthy 22kV
Arrester
ArresterWorks.com all rights reserved 18
ArresterFacts-002
Field Testing Arresters
ArresterWorks.com
Vref Testing
Vref of non defective
A sensitive point on the arrester is 42kV
curve regarding any change
in character is Vref.
Vref is defined as the Vref of defective
voltage measured across arrester is 36kV
the arrester when Iref is
applied.
For an Iref defined
Iref is defined as any at 5ma
reference current applied to
a arrester that results in
conduction above its
capacitive current level
ArresterWorks.com all rights reserved 19
ArresterFacts-002
Field Testing Arresters
ArresterWorks.com
Vref Testing
Vref of non defective
arrester is 42kV
Measuring Vref is a positive way to
determine if an arrester is near end of
life..
Vref of defective
However arrester is 36kV
It cannot be done easily while the
arrester is on the system.
The arrester must be partially isolated For an Iref defined
at 5ma
from the circuit to perform this analysis.
This method also requires that several
arresters be tested to set the reference
voltage of the non-defective arrester
ArresterWorks.com all rights reserved 20
ArresterFacts-002
Field Testing Arresters
ArresterWorks.com
Vref Testing
Vref of non defective
arrester is 42kV
A very positive aspect of this test
method is that it can be
accomplished by using standard hi- Vref of defective
pot test equipment. arrester is 36kV
The value of Iref is not
significant, as long as the test is For an Iref defined
done at the same level each time. at 5ma
ArresterWorks.com all rights reserved 21
ArresterFacts-002
Field Testing Arresters
ArresterWorks.com
Leakage Current Testing
Arrester Leakage current testing
to assess the character of an VI of a healthy
arrester is by far the most 22kV Arrester
common method used in the
industry.
There are several reasons for its
popularity.
1. Highly dependable
2. Can be done on line both
momentarily and VI of an un
continuously healthy 22kV
Arrester
3. Is cost effective
4. Can be done off line with a
separate voltage source
ArresterWorks.com all rights reserved 22
ArresterFacts-002
Field Testing Arresters
ArresterWorks.com
Leakage Current Testing
The Issue
The difficulty of leakage current testing is
separating the capacitive and resistive
currents. The only leakage current of Voltage
any value is the resistive current. The
capacitive current is quite insensitive to
changes in the arrester as it nears end of
life.
For this reason, simple clamp-on amp
meters cannot be used for this purpose.
Capacitive Current
Total Current
Resistive Current
ArresterWorks.com all rights reserved 23
ArresterFacts-002
Field Testing Arresters
ArresterWorks.com
Leakage Current Testing
MOV Arrester Conduction Simulation
The Solution Disk Voltage Capacitive Current Resistive Current Total Current
To effectively measure leakage5 current, test 2
equipment that can differentiate
4 the
1.5
capacitive component from the
3 resistive
component must be used.
2
1
Disk Current (mA)
Disk Voltage (kV)
0.5
1
Oscilloscopes with sensitive voltage and
0 0
resistive current probes as well as 3rd
-1
harmonic meters are two examples that work -0.5
-2
well. -1
-3
-1.5
-4
-5 -2
ArresterWorks.com all rights reserved 24
ArresterFacts-002
Field Testing Arresters
ArresterWorks.com
Leakage Current Testing
Arrester Base Insulators
Another consideration with leakage
current testing is that the arrester
current must be guided through a
unique ground cable where the
current can then be metered. This is
done by raising the arrester off of
ground with insulators and running the
ground lead to the Current monitor
Graphic Courtesy ABB
Insulators Leakage Current Monitor
ArresterWorks.com all rights reserved 25
ArresterFacts-002
Field Testing Arresters
ArresterWorks.com
Watts Loss Measurement
Watts loss measurement of an arrester can be
very effective, however very difficult to
measure.
Many manufacturers measure watts loss during
final production tests since the IEEE
standards implies that it be measured. The
measurement is generally done near the units
MCOV where it is a valid measurement. At
any other voltage it is only a relative number.
The problem with all the watts loss meters
available for the field is that the maximum
voltage used in the test is 10kV. A 10kV
watts loss on a 120kV MCOV arrester is not
very accurate at best.
ArresterWorks.com all rights reserved 26
ArresterFacts-002
Field Testing Arresters
ArresterWorks.com
Ineffective Arrester Field
Tests
It is not recommended that a watts loss
measurement of an arrester be used as a reliable
means to assess the quality of an arrester without
repeating the test many times on many arresters.
The use of a meg-ohm or tera-ohm meters to
measure the quality of an arrester under any
circumstances is not recommended.
Using a surge counter to assess the quality of an
arrester is not recommended under any
circumstances.
ArresterWorks.com all rights reserved 27
ArresterFacts-002
Field Testing Arresters
ArresterWorks.com
In Summary
There are several methods for effectively
measuring the quality of an arrester in
the field.
Thermal testing and leakage current
testing are the most reliable and cost The use of a simple
effective. cost effective
Infrared
Vref Testing, Watts Loss Testing and Partial Thermometer is the
Discharge testing can be used, but are fastest, safest, and
difficult and not as cost effective. most effective means
of assessing the
Watt Loss Testing, Ohm status of an arrester
measurement, and surge counting are in the field.
not considered effective field testing.
ArresterWorks.com all rights reserved 28
ArresterFacts-002
Field Testing Arresters
ArresterWorks.com
Thank you for using ArresterFacts
This ArresterFacts is just one of many that make up the ArresterFacts Tutorial
Series on Arresters.
All ArresterFacts are Copyrighted.
If you use any part of this presentation for training material, please give
ArresterWorks proper reference.
Thank you for using ArresterWorks as your source of information on Arresters.
Jon Woodworth
ArresterWorks.com all rights reserved 29
You might also like
- Arrester Book Ed 3 enDocument128 pagesArrester Book Ed 3 enNilan Suranga Karavita VidanelageNo ratings yet
- Annual Report 2015 SC B2Document6 pagesAnnual Report 2015 SC B2ChepelosNo ratings yet
- 952 Abb Awr Mittelspannung E LowDocument88 pages952 Abb Awr Mittelspannung E Lowrobert_rjcNo ratings yet
- 2015 02 PotM Mutual Coupling Test Analysis Protection Behaviour ENU PDFDocument10 pages2015 02 PotM Mutual Coupling Test Analysis Protection Behaviour ENU PDFChepelosNo ratings yet
- Standard For Overhead LinesDocument23 pagesStandard For Overhead LinesHappi Gwegweni0% (1)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Phys507 Lect 1Document18 pagesPhys507 Lect 1noura haqNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 10-Q2 Module 9 Week 9 REVISEDDocument30 pagesSCIENCE 10-Q2 Module 9 Week 9 REVISEDBuenavides P. Gerundio Jr.No ratings yet
- Eec 225Document15 pagesEec 225Ezekiel Iyamu100% (1)
- Source-Agnostic Time-Domain Distance RelayDocument10 pagesSource-Agnostic Time-Domain Distance Relaycalon presidenNo ratings yet
- PG Tutorial Munich STT SOTDocument87 pagesPG Tutorial Munich STT SOTLeon Fabricio Pino FargierNo ratings yet
- EMF Report For 230kV in Myanmar-20200816Document21 pagesEMF Report For 230kV in Myanmar-20200816sjcgraceNo ratings yet
- ARB220CW Tech SheetDocument2 pagesARB220CW Tech SheetJohn TrippNo ratings yet
- Magnetisum @kvpy - AspirantsDocument4 pagesMagnetisum @kvpy - AspirantssagarNo ratings yet
- DVCPR ADocument8 pagesDVCPR AkmessileNo ratings yet
- Ic 78Document56 pagesIc 78Patricio TorresNo ratings yet
- Proy. Electrónico DC Power MeterDocument20 pagesProy. Electrónico DC Power Metervpol25No ratings yet
- How To Invent (Almost) Anything - David StrakerDocument1,242 pagesHow To Invent (Almost) Anything - David StrakeramishcarNo ratings yet
- Enat O9 - : Physics - Part IDocument20 pagesEnat O9 - : Physics - Part Iajithlal_k_k1758No ratings yet
- EHYD3 Hydraulic Cartridge HY15-3501 CEsec1Document27 pagesEHYD3 Hydraulic Cartridge HY15-3501 CEsec1Humberto Augusto de Borba100% (1)
- Performance Evaluation of Modulation Techniques inDocument18 pagesPerformance Evaluation of Modulation Techniques inSampathNo ratings yet
- What Is A Transformer, Construction, Working, Types & ApplicationDocument5 pagesWhat Is A Transformer, Construction, Working, Types & Applicationlegasu zemeneNo ratings yet
- NI USB-9234 With Ni 9162Document23 pagesNI USB-9234 With Ni 9162Hazim HazimNo ratings yet
- 2017 NEC CodebookDocument52 pages2017 NEC CodebookVasanth Raghavan100% (2)
- Presentation 1Document12 pagesPresentation 1nitish dasNo ratings yet
- Antenna Calculator and Design SoftwareDocument2 pagesAntenna Calculator and Design SoftwarePriyadi As Saridin100% (1)
- Traction InstrumentsDocument8 pagesTraction InstrumentsTomuta StefanNo ratings yet
- Seminar Report Solar TreeDocument30 pagesSeminar Report Solar TreeAshish Kumar100% (1)
- 31029163Document9 pages31029163eoirjq3oiNo ratings yet
- Manuel Quesada Risk Assessment of SubstationsDocument36 pagesManuel Quesada Risk Assessment of SubstationsBarnabás KissNo ratings yet
- MHOA04 MHOB04 MHOC04 SalesenDocument16 pagesMHOA04 MHOB04 MHOC04 Salesendreamsky702243No ratings yet
- LG NeON 2 LG405N2W V5 72 Cell US Solar Panel DatasheetDocument2 pagesLG NeON 2 LG405N2W V5 72 Cell US Solar Panel Datasheetwane-chanNo ratings yet
- Brilliance - 64 - (ct101) - Site - Guidefor TrailerDocument19 pagesBrilliance - 64 - (ct101) - Site - Guidefor Trailerbody2030No ratings yet
- Power Transformer Testing and Commissioning PDFDocument6 pagesPower Transformer Testing and Commissioning PDFEric Stanton100% (1)
- G 9Document10 pagesG 9Phiw TabuzoNo ratings yet
- MV12 Protection Relays ManualDocument25 pagesMV12 Protection Relays ManualANOOP R NAIR100% (5)