Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Homeostasis
Uploaded by
TanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Homeostasis
Uploaded by
TanCopyright:
Available Formats
HOMEOSTASIS
Definition:
Homeostasis refers to the maintenance of the internal environment in the body of
an organism such as:
- Temperature
- Water
- Ph
- Blood pressure
to be in a balance condition so that the organism to work well.
Homeostasis In Human
Our body has a mechanism that can regulate body temperature, water
content and when to be in a balance and stable condition
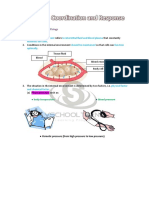
Homeostasis Control Process
Control Correctiv
e
centre
mechanis
Increase Decrease
Normal temperature Normal temperature
range range
Decrease Increase
Control Correctiv
e
centre
mechanis
The most important homeostasis in the human body are
(i) the regulation of water
(ii) the regulation of body temperature
THE REGULATION OF WATER
Brain Corrective Mechanism
Detected by the brain
Increase Water
content in the body decrease
NORMAL WATER LEVEL
Decrease Water content in the body
increase
Detected by the brain
Brain Corrective mechanism
THE REGULATION OF TEMPERATURE
Brain Corrective Mechanism
Detected by the brain
Increase
Body temperature decrease
NORMAL TEMPERATURE
Decrease Body temperature
increase
Detected by the brain
Brain Corrective mechanism
Higher Surrounding Temperature
1. Blood vessels dilated to let more blood flow close to the skin to increase heat
loss.
2. Hair lie flat to reduce air trapped on the skin so that heat can be release easily.
3. Sweat glands produce more sweat to cool the skin when sweat is evaporated.
Lower Surrounding Temperature
1. Blood vessels constrict to let more blood flow away from the skin to reduce heat
loss.
2. The hair is erect to trap a layer of air that acts as a layer of heat insulator.
You might also like
- Factors Affecting The State of Equilibrium - Angela TanghalDocument17 pagesFactors Affecting The State of Equilibrium - Angela TanghalTomTanghalNo ratings yet
- Tacloban City HospitalDocument20 pagesTacloban City HospitalReah Jayzel AlkuinoNo ratings yet
- LAB - Lung CapacityDocument5 pagesLAB - Lung CapacityWinnie LeeNo ratings yet
- Maintaining Fluid and Electrolyte BalanceDocument137 pagesMaintaining Fluid and Electrolyte BalanceNano Baddour100% (1)
- Le Chatelier's PrincipleDocument6 pagesLe Chatelier's PrincipleNurhajrina Jarawi100% (3)
- Analytical chemistry: Introduction to titration and its applicationsDocument11 pagesAnalytical chemistry: Introduction to titration and its applicationsLaiba ZulfiqarNo ratings yet
- Kidney Nephron Structure and FunctionDocument4 pagesKidney Nephron Structure and Functionxanxan4321No ratings yet
- Classification and Nomenclature of EnzymesDocument12 pagesClassification and Nomenclature of EnzymesmcgilicuttyNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Medication Doses for Pediatric and Geriatric PatientsDocument41 pagesCalculation of Medication Doses for Pediatric and Geriatric PatientsMark Angelo JaurigueNo ratings yet
- Practical 1-Far 161-FinishDocument10 pagesPractical 1-Far 161-FinishZulkifli Khairuddin100% (1)
- Fluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base BalanceDocument59 pagesFluid, Electrolyte and Acid-Base BalanceFlourence ZafranNo ratings yet
- Drug Excretion-August 2020Document67 pagesDrug Excretion-August 2020Mussa Mwaitolage100% (1)
- Week 14 - OBF Analysis (Gastric Fluid)Document19 pagesWeek 14 - OBF Analysis (Gastric Fluid)Astrud LabradorNo ratings yet
- 1 BloodDocument77 pages1 BloodVisaNathanNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System SummaryDocument3 pagesCirculatory System SummaryNiel S. DefensorNo ratings yet
- Gastric AnalysisDocument23 pagesGastric AnalysisAvi VermaNo ratings yet
- Urine Formation: Reabsorption and Secretion, and Water ConservationDocument5 pagesUrine Formation: Reabsorption and Secretion, and Water ConservationAshraf Moby100% (1)
- Muscular System Lecture: Anatomy and ContractionDocument63 pagesMuscular System Lecture: Anatomy and ContractionJr BalagtasNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System NotesDocument4 pagesCirculatory System Notesputri aisheNo ratings yet
- Volumetric Analysis of Aspirin 1. Purpose: CH229 General Chemistry Laboratory Dr. Deborah ExtonDocument4 pagesVolumetric Analysis of Aspirin 1. Purpose: CH229 General Chemistry Laboratory Dr. Deborah ExtonSusána SgfNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Notes Chapter 1 IntroDocument4 pagesPharmacology Notes Chapter 1 Introridley45No ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapeutics, Pharmacodynamics & Pharmacokinetics ExplainedDocument47 pagesPharmacotherapeutics, Pharmacodynamics & Pharmacokinetics ExplainedAshaNo ratings yet
- Digestive System NotesDocument10 pagesDigestive System NotesArchanna VyassNo ratings yet
- Bioavailability and Bioequivalence: By: Kris May Lyn A. RamosDocument77 pagesBioavailability and Bioequivalence: By: Kris May Lyn A. RamosValar Morghulis100% (1)
- Hospital Pharmacy Roles and ResponsibilitiesDocument27 pagesHospital Pharmacy Roles and ResponsibilitiesMisty CheifNo ratings yet
- Acute Phase Proteins: Blood Markers for InflammationDocument29 pagesAcute Phase Proteins: Blood Markers for InflammationMorgan100% (1)
- Naming and Writing Formulae of Coordination Compounds - HandoutsDocument11 pagesNaming and Writing Formulae of Coordination Compounds - HandoutsJayr SibayanNo ratings yet
- 1-Mechanism and Regulation of Respiration ModifiedDocument10 pages1-Mechanism and Regulation of Respiration Modifiedخالد القرشيNo ratings yet
- Decisions & Strategies: Product MixDocument20 pagesDecisions & Strategies: Product MixniceheirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 BIOCHEMDocument50 pagesChapter 2 BIOCHEMDentist_2011No ratings yet
- Mutations: Causes, Types and Genetic DisordersDocument18 pagesMutations: Causes, Types and Genetic DisordersSushanthNo ratings yet
- Membrane Transport Mechanisms and HomeostasisDocument29 pagesMembrane Transport Mechanisms and Homeostasisramadan100% (1)
- ExcretionDocument35 pagesExcretionHely PatelNo ratings yet
- CHP 1 CarbohydrateDocument79 pagesCHP 1 Carbohydrateستي نوراسيقينNo ratings yet
- Baculovirus: A Viral Bioagent For Biological ControlDocument56 pagesBaculovirus: A Viral Bioagent For Biological ControlA PrashantNo ratings yet
- Anti Anemia DrugsDocument36 pagesAnti Anemia DrugsArabelle GONo ratings yet
- FIBRINOLYTICS, ANTIPLATELETS AND ANTIFIBRINOLYTICSDocument46 pagesFIBRINOLYTICS, ANTIPLATELETS AND ANTIFIBRINOLYTICSBidyut BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Dr. Niranjan Murthy H.L Assistant Professor Dept of Physiology SSMCDocument37 pagesDr. Niranjan Murthy H.L Assistant Professor Dept of Physiology SSMCnirilib100% (2)
- Case Histo PDFDocument19 pagesCase Histo PDFsomayya waliNo ratings yet
- Enhancement of Bioavailability Pharm DDocument33 pagesEnhancement of Bioavailability Pharm DPallavi PNo ratings yet
- Drug ExcretionDocument20 pagesDrug ExcretionRajalingam BalaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System - Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument24 pagesRespiratory System - Anatomy & PhysiologySarthak ShahNo ratings yet
- Plant Antibiotics Production Through Tissue CultureDocument5 pagesPlant Antibiotics Production Through Tissue CulturedushyantrockyNo ratings yet
- Enzymology: Discuss About Regulation of Enzyme ActivityDocument4 pagesEnzymology: Discuss About Regulation of Enzyme ActivityNorrifhan Akmal IsmailNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesEndocrine SystemJel de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Glomerular Function TestsDocument26 pagesGlomerular Function TestsAvi Verma100% (1)
- PHBP Prelims - ReviewerDocument39 pagesPHBP Prelims - ReviewerAia RohaNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis InhibitorsDocument58 pagesProtein Synthesis InhibitorsmulatumeleseNo ratings yet
- Liver Physiology: Structure and Blood FlowDocument47 pagesLiver Physiology: Structure and Blood Flowasif shah0% (1)
- Signal TransductionDocument38 pagesSignal Transductionjuju100% (2)
- Mechanism of Buffering SystemDocument8 pagesMechanism of Buffering SystemRezaul Karim TutulNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument10 pagesLiterature Review006giriNo ratings yet
- Physiology of The PancreasDocument9 pagesPhysiology of The PancreasLazaros TsiatsiosNo ratings yet
- Mouse Handling Techniques PacketDocument24 pagesMouse Handling Techniques PacketLovely Ann AyapanaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report PDDocument17 pagesLab Report PDhaikalNo ratings yet
- Routes of Drug EliminationDocument17 pagesRoutes of Drug EliminationdahiphalehNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Terms: by WWW - Ipostforyou.infoDocument38 pagesAnatomical Terms: by WWW - Ipostforyou.infoShahid Maqbool100% (1)
- Homeostasis in Living Things ExplainedDocument12 pagesHomeostasis in Living Things ExplainedZern MegaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 Coordination ResponseDocument19 pagesCHAPTER 3 Coordination ResponseRozalina AzianNo ratings yet
- Coordination and ResponseDocument21 pagesCoordination and ResponseAisya Omeira60% (5)
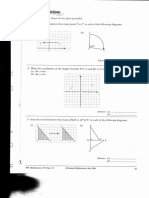
- Latihan Penjelmaan PMRDocument8 pagesLatihan Penjelmaan PMRTanNo ratings yet
- Let Us Look Together Now at MarkDocument21 pagesLet Us Look Together Now at MarkTanNo ratings yet
- Circles IIDocument8 pagesCircles IITanNo ratings yet
- F 2 TransformationDocument4 pagesF 2 TransformationTanNo ratings yet
- Exercises 1Document6 pagesExercises 1TanNo ratings yet
- QuestionDocument6 pagesQuestionTanNo ratings yet
- Form 1 StatisticDocument3 pagesForm 1 StatisticTanNo ratings yet
- Hebrews 9Document25 pagesHebrews 9TanNo ratings yet
- Adenium PropogationDocument1 pageAdenium PropogationTanNo ratings yet
- Exercises 1Document6 pagesExercises 1TanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document11 pagesChapter 11TanNo ratings yet
- Patriotism ReferenceDocument1 pagePatriotism ReferenceTanNo ratings yet
- Perjumpaan Makna Support Group TaipingDocument1 pagePerjumpaan Makna Support Group TaipingTanNo ratings yet
- Matthew 26: "My Time Is at Hand"Document7 pagesMatthew 26: "My Time Is at Hand"TanNo ratings yet
- Exercises 1Document6 pagesExercises 1TanNo ratings yet
- Form 1 - Science - Part 1Document5 pagesForm 1 - Science - Part 1Fendy11No ratings yet
- Koleksi Soalan Bab 5Document40 pagesKoleksi Soalan Bab 5Nurul Azuwin75% (4)
- Borang Penyelenggaraan KomputerDocument1 pageBorang Penyelenggaraan KomputerMohd Razak Mohd Yunus0% (1)
- Complex Numbers TutorialDocument8 pagesComplex Numbers TutorialTanNo ratings yet
- Jadual Es KV Shah Alam 2013Document7 pagesJadual Es KV Shah Alam 2013TanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document8 pagesChapter 1TanNo ratings yet
- Kertas 1 - Form 4 Final ExamDocument19 pagesKertas 1 - Form 4 Final ExamleocornNo ratings yet
- GRAMMAR EXERCISES UNDERLINE CORRECT WORDDocument1 pageGRAMMAR EXERCISES UNDERLINE CORRECT WORDTanNo ratings yet
- TeenDocument8 pagesTeenTanNo ratings yet
- Editing English Grammar and UsageDocument2 pagesEditing English Grammar and UsageTanNo ratings yet
- Section A (30 Marks) : Answer All QuestionsDocument10 pagesSection A (30 Marks) : Answer All QuestionsEna HamNo ratings yet
- Typingmaster, Inc. Software License AgreementDocument3 pagesTypingmaster, Inc. Software License AgreementSachin PatilNo ratings yet
- A Book Is Not EnoughDocument9 pagesA Book Is Not EnoughTanNo ratings yet
- Analisis Soalan KHB KTDocument2 pagesAnalisis Soalan KHB KTTanNo ratings yet
- Richard Herrmann-Fractional Calculus - An Introduction For Physicists-World Scientific (2011)Document274 pagesRichard Herrmann-Fractional Calculus - An Introduction For Physicists-World Scientific (2011)Juan Manuel ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Commonlit Bloody KansasDocument8 pagesCommonlit Bloody Kansasapi-506044294No ratings yet
- Sample Front Desk Receptionist ResumeDocument5 pagesSample Front Desk Receptionist ResumeReyvie FabroNo ratings yet
- Integrating GrammarDocument8 pagesIntegrating GrammarMaría Perez CastañoNo ratings yet
- Classroom Rules and RegulationsDocument1 pageClassroom Rules and RegulationsASHYJO28No ratings yet
- Practical and Mathematical Skills BookletDocument30 pagesPractical and Mathematical Skills BookletZarqaYasminNo ratings yet
- Dryer User ManualDocument118 pagesDryer User ManualAyman Alhassny100% (1)
- Existentialism Is A HumanismDocument4 pagesExistentialism Is A HumanismAlex MendezNo ratings yet
- Understanding EndogeneityDocument25 pagesUnderstanding EndogeneityagustinusNo ratings yet
- Elements of Service-Oriented Architecture: B. RamamurthyDocument15 pagesElements of Service-Oriented Architecture: B. RamamurthySaileshan SubhakaranNo ratings yet
- Bonding and Properties of Solids Worksheet Solutions 1kadax6Document4 pagesBonding and Properties of Solids Worksheet Solutions 1kadax6Mel Patricia M. CabreraNo ratings yet
- The ADDIE Instructional Design ModelDocument2 pagesThe ADDIE Instructional Design ModelChristopher Pappas100% (1)
- CV Jan 2015 SDocument4 pagesCV Jan 2015 Sapi-276142935No ratings yet
- WMCS Algebraic Simplification Grade 8 v1.0Document76 pagesWMCS Algebraic Simplification Grade 8 v1.0Vincent MartinNo ratings yet
- Unit 11 LeadershipDocument4 pagesUnit 11 LeadershipMarijana DragašNo ratings yet
- Touratsoglou, Coin Production and Circulation in Roman Peloponesus PDFDocument23 pagesTouratsoglou, Coin Production and Circulation in Roman Peloponesus PDFCromwellNo ratings yet
- Tips To Make Simple Lawn Attire Look StylishDocument2 pagesTips To Make Simple Lawn Attire Look StylishPakistani DressesNo ratings yet
- Jobgpt 9d48h0joDocument6 pagesJobgpt 9d48h0jomaijel CancinesNo ratings yet
- Einstein HoaxDocument343 pagesEinstein HoaxTS100% (1)
- Cambridge Intl. Sr. Sec. School Class: X, Preboard Examination-1 Subject: Mathematics Time Allowed: 3Hrs. M.M: 80Document5 pagesCambridge Intl. Sr. Sec. School Class: X, Preboard Examination-1 Subject: Mathematics Time Allowed: 3Hrs. M.M: 80Suyash PandeyNo ratings yet
- Cronograma Ingles I v2Document1 pageCronograma Ingles I v2Ariana GarciaNo ratings yet
- Duah'sDocument3 pagesDuah'sZareefNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Human Anatomy & Physiology (Marieb)Document3 pagesChapter 2 Human Anatomy & Physiology (Marieb)JayjayNo ratings yet
- Simon Baumberg - Prokaryotic Gene ExpressionDocument348 pagesSimon Baumberg - Prokaryotic Gene ExpressionBodhi Dharma0% (1)
- p240 MemristorDocument5 pagesp240 MemristorGopi ChannagiriNo ratings yet
- Downloaded From Uva-Dare, The Institutional Repository of The University of Amsterdam (Uva)Document12 pagesDownloaded From Uva-Dare, The Institutional Repository of The University of Amsterdam (Uva)Iqioo RedefiniNo ratings yet
- News CorpDocument17 pagesNews CorpIshita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Newton-Raphson MethodDocument32 pagesNewton-Raphson MethodnafisbadranNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Trade Discounts Cash Discounts MarkupDocument42 pagesUnit 4 Trade Discounts Cash Discounts MarkupChimwemwe MaoleNo ratings yet
- Group 1 RDL2Document101 pagesGroup 1 RDL2ChristelNo ratings yet