Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Respiration: Link Reaction
Uploaded by
AuriceliaOliveiraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Respiration: Link Reaction
Uploaded by
AuriceliaOliveiraCopyright:
Available Formats
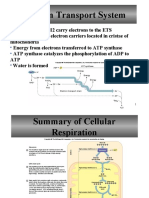
4.
The
acetyl group 1. Pyruvate
combines with is actively
CoA to give transported
acetyl-CoA to the
(2 carbons) matrix of the
mitochondria
3. An acetyl 2. Pyruvate
group (2 is oxidised
carbons) is Link reaction to convert
formed from NAD to NADH
the pyruvate 1. Acetyl-CoA
combines with
a 4 carbon
3. The TP 4. TP is Pyruvate + molecule
is oxidised, converted NAD + CoA - to give a
converting into pyruvate > acetyl-CoA + 6 carbon
NAD into (3 carbons) NADH + CO2 molecule
NADH
Occurs in the
cytoplasm
and does not Glycolysis Respiration Krebs cycle
require oxygen
2. The 6
3. During carbon
2. The glucose 1. Glucose is
1. NADH and this cycle molecule is
is converted to activated by 5. The
FADH donate NADH, FADH, converted back
2 molecules of phosphorylation electrons then
electrons to ATP and 3 to the 4 carbon
TP (3 carbons) (addition of combine with
begin the ETC molecules of molecule to
2 phosphate the protons to
carbon dioxide begin the
molecules make water
cycle again
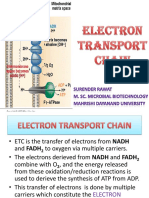
Electron
transport chain
2. Protons are
4. The protons also released
that have and actively
accumulated transported
in the inner to the inner
3. The
membrane membrane
electrons travel
now diffuse of the
down the ETC
back into mitochondria
losing energy
the matrix
as they go, this
energy is used
to synthesise
ATP
You might also like
- Strained Organic Molecules: Organic Chemistry: A Series of Monographs, Vol. 38From EverandStrained Organic Molecules: Organic Chemistry: A Series of Monographs, Vol. 38No ratings yet
- Comprehensive Handbook on HydrosilylationFrom EverandComprehensive Handbook on HydrosilylationB. MarciniecNo ratings yet
- Cellular-Respiration BioDocument7 pagesCellular-Respiration BioKiyomi LabradorNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument2 pagesCellular Respirationapi-327711832No ratings yet
- Electron Transport System: ATP Adp + ATP Synthase P Nadh + H EnergyDocument12 pagesElectron Transport System: ATP Adp + ATP Synthase P Nadh + H EnergyTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Krebs - Anaerobic ReviewerDocument6 pagesKrebs - Anaerobic ReviewerdenyelNo ratings yet
- (E BOOK) Martini Essentials of Anatomy PhysiologyDocument3 pages(E BOOK) Martini Essentials of Anatomy PhysiologyRaisa sya12No ratings yet
- Glycolysis SummaryDocument3 pagesGlycolysis Summaryapi-327731714No ratings yet
- Cellular MetabolismDocument5 pagesCellular MetabolismAshNo ratings yet
- Step 2: Transportation What Is Respiration?Document1 pageStep 2: Transportation What Is Respiration?iffatNo ratings yet
- Cell Respiration and PhotosynthesisDocument10 pagesCell Respiration and PhotosynthesisMorgan LockeNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Study GuideDocument30 pagesCellular Respiration Study Guideroselyn acpacNo ratings yet
- The Cellular RespirationDocument9 pagesThe Cellular RespirationRufas MacksonNo ratings yet
- Cellualr Respiration in DetailDocument3 pagesCellualr Respiration in DetailMotie KassabNo ratings yet
- Week 5 - GenBio1 CELLULAR RESPIRATION 1st Term SY 2021-2022Document2 pagesWeek 5 - GenBio1 CELLULAR RESPIRATION 1st Term SY 2021-2022JAN PAULINE BABINANo ratings yet
- Beta Oxidation of Fatty Acids: Consumes 2 ATPDocument4 pagesBeta Oxidation of Fatty Acids: Consumes 2 ATPKarla Faye UcangNo ratings yet
- Week 7 Cellular RespirationDocument32 pagesWeek 7 Cellular RespirationJiverlyn PatNo ratings yet
- Topic 8 Cell Respiration and PhotosynthesisDocument12 pagesTopic 8 Cell Respiration and PhotosynthesisCedric Williams100% (1)
- Glycolysis TCA ETCDocument61 pagesGlycolysis TCA ETCLê Trà GiangNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Final ReviewerDocument7 pagesGen Bio Final Reviewermailforprinting101No ratings yet
- Glycolysis & Respiration 2Document15 pagesGlycolysis & Respiration 2kayannaNo ratings yet
- TCA Cycle MCQDocument2 pagesTCA Cycle MCQTinsae WorkuNo ratings yet
- 6.krebs Cycle and Oxidative Phosphorylation Corregido.Document6 pages6.krebs Cycle and Oxidative Phosphorylation Corregido.Felipe Henao AriasNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis + Cell Resp SLIDESDocument7 pagesGlycolysis + Cell Resp SLIDESDavid WoodyNo ratings yet
- 10.chemzone - Organic CompoundsDocument16 pages10.chemzone - Organic Compoundssincerely reverieNo ratings yet
- ADPATPand Cellular RespirationDocument43 pagesADPATPand Cellular RespirationJessa CabusaoNo ratings yet
- Cell Respiration (8.2) : Oxidation Is Loss, Reduction Is Gain or OIL RIGDocument12 pagesCell Respiration (8.2) : Oxidation Is Loss, Reduction Is Gain or OIL RIGRocio Guadalupe Lopez BlandonNo ratings yet
- Krebs CycleDocument2 pagesKrebs Cycleapi-327731714100% (1)
- G9 - Ch8 - Alkanes-1Document17 pagesG9 - Ch8 - Alkanes-1hamza arroubNo ratings yet
- Mitochondria and Its Pathways: Arvin G. Concha Mst-BioDocument17 pagesMitochondria and Its Pathways: Arvin G. Concha Mst-Biocassidy conchaNo ratings yet
- UNIT 13 Hydrocarbons For More Visit HTTP://WWW - Ncert.nic - In/textbooks/testing/index - HTMDocument33 pagesUNIT 13 Hydrocarbons For More Visit HTTP://WWW - Ncert.nic - In/textbooks/testing/index - HTMArun Kumar100% (1)
- Unit: 5 Main Topic: Energy Transformation Sub Topic: Cellular RespirationDocument4 pagesUnit: 5 Main Topic: Energy Transformation Sub Topic: Cellular RespirationAddisNo ratings yet
- SMSP MetabolismDocument10 pagesSMSP MetabolismPravesh NiraulaNo ratings yet
- PS and CRDocument34 pagesPS and CRErika MatiasNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration NotesDocument1 pageCellular Respiration NotesMike MesaNo ratings yet
- BiochemLecETCKrebs CycleDocument1 pageBiochemLecETCKrebs CycleReginald GironNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compounds - NotesDocument18 pagesCarbon and Its Compounds - NotesFitfulNo ratings yet
- Electrontransportchain 151027073626 Lva1 App6892Document29 pagesElectrontransportchain 151027073626 Lva1 App6892GobindaSahuNo ratings yet
- Biology 1: Major Features and Chemical Events of Cellular RespirationDocument5 pagesBiology 1: Major Features and Chemical Events of Cellular RespirationKaye Ann AbinalNo ratings yet
- Respiration - SimplifiedDocument11 pagesRespiration - SimplifiedVivaMapwaNo ratings yet
- CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC CCCCCCC: C C C CDocument9 pagesCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC CCCCCCC: C C C CSwati KhannaNo ratings yet
- TRANSES - BIOCHEM - Cellular Metabolism - Krebs Cycle, Electron Transport ChainDocument4 pagesTRANSES - BIOCHEM - Cellular Metabolism - Krebs Cycle, Electron Transport ChainPia LouiseNo ratings yet
- ReportingDocument2 pagesReportingpea.huquerizaNo ratings yet
- Alkanes Lecture Notes PDFDocument23 pagesAlkanes Lecture Notes PDFPrivate AccountNo ratings yet
- Organic Compound Nomenclature and CharacteristicDocument8 pagesOrganic Compound Nomenclature and CharacteristictasneemNo ratings yet
- Alkenes GroupDocument8 pagesAlkenes GroupHanna GalatiNo ratings yet
- Learners Activity Sheet in General Biology 1: "Cellular Respiration"Document2 pagesLearners Activity Sheet in General Biology 1: "Cellular Respiration"Cristine TingzonNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Theory 2Document12 pagesLecture 3 Theory 2Noor FarhanNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Chapter 2 Carbon CompoundDocument15 pagesForm 5 Chapter 2 Carbon CompoundChee Jin TangNo ratings yet
- 13 Cellular Respiration-KEYDocument6 pages13 Cellular Respiration-KEYgilNo ratings yet
- Lipids MetabolismDocument5 pagesLipids MetabolismPunzalanNo ratings yet
- Cellular Work SheetDocument4 pagesCellular Work Sheetlow. PathNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesismalek elyanNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis, Kreb Cycle Electron TransportDocument19 pagesGlycolysis, Kreb Cycle Electron TransportShahidatul4297100% (2)
- Actividades de Aprendizaje Sobre Ciclo de Krebs en InglesDocument2 pagesActividades de Aprendizaje Sobre Ciclo de Krebs en InglesJesus Aguilar OlveraNo ratings yet
- ORGANIC CHEMISTRY - Tr. BDocument47 pagesORGANIC CHEMISTRY - Tr. BChishala IsaacNo ratings yet
- Chapt07 Lecture 2015F-3Document65 pagesChapt07 Lecture 2015F-3PaulNo ratings yet
- Section 1.2Document12 pagesSection 1.2Gmat PrepNo ratings yet
- Krebsov CiklusDocument30 pagesKrebsov CiklusÉvariste GaloisNo ratings yet
- RSC Advances: PaperDocument12 pagesRSC Advances: PapersuryaNo ratings yet
- How Write A Project For BioinformaticsDocument2 pagesHow Write A Project For BioinformaticsBrijesh Singh YadavNo ratings yet
- 91xtad8xw - Module 4 - Pe1 - Health and NutritionDocument6 pages91xtad8xw - Module 4 - Pe1 - Health and NutritionSteve Laurence PontilloNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates - Specific ReactionsDocument5 pagesCarbohydrates - Specific ReactionsVanessa ParaisoNo ratings yet
- Marshall Clinical Chemistry 8E (2017) PDFDocument383 pagesMarshall Clinical Chemistry 8E (2017) PDFafifah zabidi100% (3)
- Photosynthetic Research in Plant Science: Ayumi Tanaka and Amane MakinoDocument3 pagesPhotosynthetic Research in Plant Science: Ayumi Tanaka and Amane MakinoAidul07No ratings yet
- The Polycomb Group Protein Yaf2 Regulates The Pluripotency of Embryonic Stem Cells in A Phosphorylation-Dependent MannerDocument13 pagesThe Polycomb Group Protein Yaf2 Regulates The Pluripotency of Embryonic Stem Cells in A Phosphorylation-Dependent MannerSHUMETNo ratings yet
- Mapping The MindDocument8 pagesMapping The MindMario Saldivar100% (1)
- Rna M A Meets Transposable Elements and Chromatin: OmmentaryDocument5 pagesRna M A Meets Transposable Elements and Chromatin: OmmentaryRamona AnaNo ratings yet
- Assignment STARCHDocument5 pagesAssignment STARCHAinaNo ratings yet
- PPTDocument30 pagesPPTAimanNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument4 pagesBiochemistryPriya DhanaNo ratings yet
- LaValle - Dietary SupplementsDocument122 pagesLaValle - Dietary Supplementsortizjesus18No ratings yet
- Rev&pat&gen&rai&gup&7th PDFDocument708 pagesRev&pat&gen&rai&gup&7th PDFBkash Shah100% (3)
- Biological Psychology 13th Edition Kalat Test BankDocument23 pagesBiological Psychology 13th Edition Kalat Test BankAndrewBurgessfoyei100% (18)
- Dna Sequencing MethodsDocument29 pagesDna Sequencing MethodsWilson Anandaraj92% (13)
- Chapter 5 Active Reading GuisdeDocument11 pagesChapter 5 Active Reading Guisdelittle bunny foo fooNo ratings yet
- MFold OverviewDocument4 pagesMFold OverviewAshutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Summary Fatty Alcohols LFRMIDocument2 pagesSummary Fatty Alcohols LFRMILuis Fernando Ramos Méndez IrisNo ratings yet
- Metabolic EngineeringDocument9 pagesMetabolic EngineeringClaChristinaNo ratings yet
- Ladisch and Kohlmann 1992 - Recombinant Human InsulinDocument10 pagesLadisch and Kohlmann 1992 - Recombinant Human InsulinZooey HeNo ratings yet
- NAAS Rating of JournalsDocument44 pagesNAAS Rating of JournalssakshiNo ratings yet
- Delivering An Effective Journal Club PresentationDocument33 pagesDelivering An Effective Journal Club PresentationKam SereneNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument1 pageSyllabusriyaNo ratings yet
- Extracellular Vimentin Mimics VEGF and Is A Target For Anti-Angiogenic ImmunotherapyDocument20 pagesExtracellular Vimentin Mimics VEGF and Is A Target For Anti-Angiogenic ImmunotherapyElse HuijbersNo ratings yet
- ANAPH121 Part 2 Basic ChemistryDocument62 pagesANAPH121 Part 2 Basic ChemistryAB AlmazoraNo ratings yet
- AQA Biology Topic 8.3 Structures of Ribonucleic AcidDocument4 pagesAQA Biology Topic 8.3 Structures of Ribonucleic AcidfNo ratings yet
- MCQs in Clinical BiochemistryDocument15 pagesMCQs in Clinical Biochemistrysidharta_chatterjee79% (14)
- B1 - Test 1 Cell Biology Beginner: AQA - Combined Science BiologyDocument20 pagesB1 - Test 1 Cell Biology Beginner: AQA - Combined Science BiologyLabeenaNo ratings yet
- Adaptation of HIV-1 To Its Human HostDocument8 pagesAdaptation of HIV-1 To Its Human HostImperialAquillaNo ratings yet