Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sugar Manufacturing Process
Uploaded by
tesfayregs gebretsadik0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
96 views20 pagessugar industry
Original Title
sugarindustryii-090323011804-phpapp01
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentsugar industry
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
96 views20 pagesSugar Manufacturing Process
Uploaded by
tesfayregs gebretsadiksugar industry
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPSX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 20
Sugar Manufacturing Process:
1. Growing & Harvesting the
Cane.
2. Cane preparation for
Milling.
3. Milling.
4. Clarification.
5. Evaporation.
6. Crystallization.
7. Centrifugation.
8. Drying.
Sugar Manufacturing
Process
Cane weighting: -
The cane is generally weighted on
large platform scale in the transport
unit in which it is received at the mill-
railway car, trailer cart o the like,
where direct weighting is
impracticable.
Cane cleaning equipment: -
As apart of the cane carrier or
auxiliary to it, is a process of
cleaning the cane by water from
associated mud resulting due to
harvesting.
Preparations of Cane for milling: -
The milling process may be separated into tow
steps, the preparation of the cane by breaking
down the hard structure and purring the cell, and
the actual grinding the cane. The preparation of
the cane is accomplished in several ways:
1. By revolving cane knifes that cut the cane into
chips but extracted no juice.
2. By shredders that tear the cane into shreds
but extract no juice.
3. By crushers that break and crush the structure
of the cane, extracting a large proportion of the
juice.
4. By combination of any or all of the previous
ways.
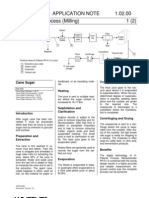
Milling machinery: -
Milling Machinery is composed of three
rollers arranged in triangular form.
A set of three to seven machines.
Each mill unit is commonly driven by
separate motor power, steam engine,
electric motor, or steam turbine.
The three rolls are known respectively as
the top roll, the cane roll (entering) or feed
roll, the bagasse roll or discharge roll.
Adding water or thin juice to the bagasse
after each mill dilutes the content juice
and increases the extraction as this juice is
expressed.
Milling machinery: -
Clarification
The primary object of the clarification
is to remove from the juice the
maximum quantity of impurities.
The degree of clarification has great
bearing on the subsequent stations
of the factory, affecting the pan
boiling, the centrifuging, the quality
of the products, and most important
of all, the yield of raw sugar.
Clarification
Added Chemicals as follows:
1. Soluble phosphates (P2O5)
clearer juice.
fewer lime salts in clarified
juice.
more rapid settling.
faster mud filtration.
better sugar.
Clarification
2. Polymer flocculants:
increases settling rate.
reduces mud volume.
decreases poly in cake.
and most important increases the
clarity of the clarified juice.
3. Lime: (as milk) in order to raise pH
to 7.
Clarification
Result of clarification:
The clarification process divides the
whole juice into tow portions: -
1. The clarification that comprises 80
to 90% of the original juice, almost
invariable, goes to the evaporators
without further treatment.
2. The precipitated settling, the scrums
or mud waters; which are filtered
after various methods of treatment.
Filtration:
In filtration process the rotary -type
vacuum filter in common use.
The filter consists of rotating drum covered
with perforated plate of copper or other
metal, which dips into a bath containing
the mud water.
The filter divided into four sections.
Hot water and Bagacillo are added to the
mud to increase filtration efficiency.
Filtration Result:
Clarified Juice Sent directly to the
evaporators.
Filtration:
Evaporation &
Crystallization:
Evaporation of water from the sugar
solution to yield a final crystalline
product.
The evaporation is done in tow
stages:
1. First in an evaporator station to
concentrate the solution.
2. Second in Evapo- Crystallizer to
crystallize the sugar from solution.
Evaporation:
Removes about 90% of the water
from the clarified juice;
The multiple-effect is usually
extended to three, four, and more
effects.
Evaporation increasing the juice
solids from about 15 Brix to about
65-70 Brix. Which is the Syrup.
Evaporation:
Evapo- Crystallizers:
There fore the function of evapo-
crystallizer is to produce satisfactory
sugar crystals from syrup
(seed grain) to serve as the nuclei for
the sugar syrup.
When Brix reaches 78-80, crystals
begin to appear and the nature of
the material changes.
Its then called massecuite.
Centrifugal Machines:
The basic function of the Centrifugal
machines is to the crystals in the
massecuite from the surrounding
molasses or syrup by centrifugal
force.
The Raw sugar is then sent to dryers
or refining unit according to the type
of desired final product.
Molasses is by-product which is used
as a raw material for other products.
Dryers:
The wet raw sugar from centrifuges
goes to rotary drier to remove the
water from the wet sugar to reduce
moisture content to 0.5-2%; using
hot air at 110C which flow counter
currently with sugar.
Dryers:
You might also like
- Sugar Manufacturing ProcessDocument20 pagesSugar Manufacturing ProcessYadav ShwetaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 B DataDocument2 pagesChapter 1 B DataMamoon RasheedNo ratings yet
- Industrial Training Report On DSMDocument14 pagesIndustrial Training Report On DSMVipul Sharma0% (1)
- 06 - Sugar Industry (B)Document35 pages06 - Sugar Industry (B)waleed chNo ratings yet
- Sugar Manufacturing and Fermentation - FinalDocument30 pagesSugar Manufacturing and Fermentation - FinalGADAANKITNo ratings yet
- Kessem Final PresentationDocument43 pagesKessem Final PresentationShasho LikisaNo ratings yet
- Inside A Sugar Factory June 2014Document21 pagesInside A Sugar Factory June 2014Nikola PuljićNo ratings yet
- AbebeDocument19 pagesAbebesofi dollaNo ratings yet
- Sugar Industry Case Stdy FNL PDFDocument46 pagesSugar Industry Case Stdy FNL PDFpraneeth bmNo ratings yet
- SSP Pumps in Sugar ProcessingDocument44 pagesSSP Pumps in Sugar Processingverderusa100% (1)
- Chemical Process Industries (Ch-211) Sugar Industry Instructor: Abdul Wahab Department of Chemical Engineering (Dche)Document41 pagesChemical Process Industries (Ch-211) Sugar Industry Instructor: Abdul Wahab Department of Chemical Engineering (Dche)ibrahim AbbasNo ratings yet
- Sugar Manufacturing Process DiscriptionDocument6 pagesSugar Manufacturing Process DiscriptionMuhammad JunaidNo ratings yet
- CHP 5. Milling & Refining of CaneDocument5 pagesCHP 5. Milling & Refining of CaneAsia AmirNo ratings yet
- Unit Operations For Sugarcane PlantDocument3 pagesUnit Operations For Sugarcane PlantJohn Christian Usero100% (1)
- Sugar Plant Project ReportDocument5 pagesSugar Plant Project ReportBryan TanNo ratings yet
- Flow DiagramDocument13 pagesFlow DiagramMILTON SALINASNo ratings yet
- Sugar BeetDocument21 pagesSugar BeetAnurag SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Roduction of Sugar: Tamkanat Saad Redha Khalid Uswa Zahid Kaneez FizzaDocument35 pagesRoduction of Sugar: Tamkanat Saad Redha Khalid Uswa Zahid Kaneez FizzaMudassir Mehmood yousafNo ratings yet
- Sugar IndustriesDocument46 pagesSugar Industriesshine king100% (1)
- Manufacturing Process of Sugarcane To SugarDocument12 pagesManufacturing Process of Sugarcane To SugarNur Hanani100% (1)
- K-Patents Cane Sugar Processing and RefiningDocument2 pagesK-Patents Cane Sugar Processing and RefiningRaymund GatocNo ratings yet
- Raw Sugar ProcessingDocument6 pagesRaw Sugar ProcessingJan April MahinayNo ratings yet
- Ch7 Food Industries Part 2Document17 pagesCh7 Food Industries Part 2فرحNo ratings yet
- Sugarcane Composition and ProcessingDocument7 pagesSugarcane Composition and Processingpacoto livingstoneNo ratings yet
- chemical process technology (Autosaved)Document19 pageschemical process technology (Autosaved)septicmoneyNo ratings yet
- Summer Training Presentation at UNITED BREWERIES LTD. LUDHIANADocument21 pagesSummer Training Presentation at UNITED BREWERIES LTD. LUDHIANAketan171092No ratings yet
- Sugar Mill Training ReportDocument16 pagesSugar Mill Training ReportDevesh Pratap Yadav86% (14)
- Sugar Processing TechnologyDocument36 pagesSugar Processing TechnologyYonas TarekegnNo ratings yet
- Sugar ManufacturingDocument55 pagesSugar Manufacturingamrialifa100% (3)
- Operations at Daurala Sugar ComplexDocument2 pagesOperations at Daurala Sugar ComplexShubhamNo ratings yet
- Sugarcane Manufacturing ProcessDocument3 pagesSugarcane Manufacturing Processdante224No ratings yet
- Sugarbeet ProcessingDocument12 pagesSugarbeet ProcessingyanatryNo ratings yet
- Sugar Industries PPT SRM - 5Document32 pagesSugar Industries PPT SRM - 5Nishiket DobalNo ratings yet
- The Sugar IndustryDocument22 pagesThe Sugar IndustryAbraham wisdomNo ratings yet
- 9.10.1.1 Sugarcane ProcessingDocument7 pages9.10.1.1 Sugarcane ProcessingAshish SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- RefineryDocument14 pagesRefinerykrishna sharmaNo ratings yet
- Sugar and Confectionery Technology: Processing and Industry DevelopmentDocument26 pagesSugar and Confectionery Technology: Processing and Industry Developmentgrace mwenjeNo ratings yet
- F Softdrink Sugar SyrupsDocument4 pagesF Softdrink Sugar SyrupsNE89No ratings yet
- Sugarcane Processing GuideDocument7 pagesSugarcane Processing GuideYogendra JaiswalNo ratings yet
- F&B Service Unit-2 (Beer Making) - 1Document6 pagesF&B Service Unit-2 (Beer Making) - 1Kalash BaliyanNo ratings yet
- Process of Sugar Manufacturing From Sugar Grinding Mill To Packing.20140530.234410Document2 pagesProcess of Sugar Manufacturing From Sugar Grinding Mill To Packing.20140530.234410amount03heatNo ratings yet
- Boiling House EfficiencyDocument14 pagesBoiling House EfficiencyManoj KageNo ratings yet
- (Chapter-2) Ugar Cane FinalDocument49 pages(Chapter-2) Ugar Cane FinalteweleNo ratings yet
- Visit Report SevanagalaDocument13 pagesVisit Report SevanagalaNishat AhmadNo ratings yet
- Visit Report SevanagalaDocument13 pagesVisit Report SevanagalaNishat AhmadNo ratings yet
- Module 8-c Sugar Manufacturing Process - Clarification Steps and CrystalisationDocument29 pagesModule 8-c Sugar Manufacturing Process - Clarification Steps and CrystalisationDaudNo ratings yet
- Sugar CaneDocument10 pagesSugar Cane68vycsz74sNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Basics Lec (5) Sugar Production T. Alaa KhalidDocument37 pagesChemical Engineering Basics Lec (5) Sugar Production T. Alaa KhalidjoNo ratings yet
- Sugar Industry (Autosaved)Document39 pagesSugar Industry (Autosaved)Divyansh NagarNo ratings yet
- Tan Quiz 2Document3 pagesTan Quiz 2Bryan TanNo ratings yet
- Process DescriptionDocument2 pagesProcess DescriptionKathamuthu KottaichamyNo ratings yet
- Milk PowderDocument32 pagesMilk Powderhtc587uyNo ratings yet
- Sugar Industry, Group 1Document23 pagesSugar Industry, Group 1Abraham wisdomNo ratings yet
- Description of Process - Nbsm-1Document10 pagesDescription of Process - Nbsm-1avisheklochunNo ratings yet
- How Reverse Osmosis Works: A Look at Industrial ROFrom EverandHow Reverse Osmosis Works: A Look at Industrial RORating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (2)
- Soap-Making Manual A Practical Handbook on the Raw Materials, Their Manipulation, Analysis and Control in the Modern Soap Plant.From EverandSoap-Making Manual A Practical Handbook on the Raw Materials, Their Manipulation, Analysis and Control in the Modern Soap Plant.Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- Energy Usage Trends PPT (Lecture - 2)Document14 pagesEnergy Usage Trends PPT (Lecture - 2)tesfayregs gebretsadik100% (1)
- Boiler Design and OperationDocument11 pagesBoiler Design and Operationtesfayregs gebretsadikNo ratings yet
- Conclusions and RecommendationsDocument2 pagesConclusions and Recommendationstesfayregs gebretsadikNo ratings yet
- Intro To ChE PDFDocument38 pagesIntro To ChE PDFShirat MohsinNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering FundamentalsDocument2 pagesChemical Engineering FundamentalsTengku Alif Tengku Mizam0% (1)
- Chemical (Process) Engineering Program My Hosting Company Is Dashen Brewery Case Study Biogas Production From BSG By: Asmare Tezera Id Eit/Ur0827/03Document76 pagesChemical (Process) Engineering Program My Hosting Company Is Dashen Brewery Case Study Biogas Production From BSG By: Asmare Tezera Id Eit/Ur0827/03tesfayregs gebretsadikNo ratings yet
- Dashen Brewery internship report on beer production process and quality controlDocument92 pagesDashen Brewery internship report on beer production process and quality controltesfayregs gebretsadikNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering A Review For The Professional ExaminationDocument274 pagesChemical Engineering A Review For The Professional Examinationtesfayregs gebretsadikNo ratings yet
- Ethanol MyDocument1 pageEthanol Mytesfayregs gebretsadikNo ratings yet
- Material and Energy Balance in Industrial PlantDocument26 pagesMaterial and Energy Balance in Industrial Plantconan45No ratings yet
- The AICHE Student Pocket HandbookDocument68 pagesThe AICHE Student Pocket Handbookpapaas100% (1)
- Intro To ChE PDFDocument38 pagesIntro To ChE PDFShirat MohsinNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Energy Storage Systems EditedDocument46 pagesElectrochemical Energy Storage Systems Editedtesfayregs gebretsadikNo ratings yet
- ELG3311 Solutions for Assignment 1 ProblemsDocument14 pagesELG3311 Solutions for Assignment 1 Problemstesfayregs gebretsadik100% (1)
- Heatexchangers 140603082139 Phpapp01Document67 pagesHeatexchangers 140603082139 Phpapp01esamhamadNo ratings yet
- Pandey Okstate 0664M 2851Document82 pagesPandey Okstate 0664M 2851tesfayregs gebretsadikNo ratings yet
- Induction MachinesDocument81 pagesInduction MachinesaswardiNo ratings yet
- ESO 210 Lecture-22 - 2014Document40 pagesESO 210 Lecture-22 - 2014Amit MondalNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 4 - The Chlor-Alkali IndustryDocument31 pagesChapter - 4 - The Chlor-Alkali Industrytesfayregs gebretsadik100% (1)
- Introduction to Electrical Machines Chapter One: Electromagnetic PrinciplesDocument286 pagesIntroduction to Electrical Machines Chapter One: Electromagnetic Principlestesfayregs gebretsadik100% (1)
- SETTLING TANKS THEORY OPERATION DESIGNDocument33 pagesSETTLING TANKS THEORY OPERATION DESIGNpandeysekhar100% (2)
- Se PDFDocument840 pagesSe PDFtesfayregs gebretsadikNo ratings yet
- Leaching 7Document37 pagesLeaching 7tesfayregs gebretsadikNo ratings yet
- Ammonia and NitricDocument67 pagesAmmonia and Nitrictesfayregs gebretsadikNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactor Analysis and Design Fundamentals - RawlingsDocument319 pagesChemical Reactor Analysis and Design Fundamentals - Rawlingstesfayregs gebretsadikNo ratings yet
- SugarDocument20 pagesSugarHarshit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Ammonia Paper Little TheoryDocument59 pagesAmmonia Paper Little TheoryThabangNo ratings yet
- Cement Industry Environment Report 2003Document24 pagesCement Industry Environment Report 2003tesfayregs gebretsadik100% (2)
- Cement: Dr. Prashant Mehta Assistant Professor, National Law University, JodhpurDocument26 pagesCement: Dr. Prashant Mehta Assistant Professor, National Law University, Jodhpurtesfayregs gebretsadikNo ratings yet
- Explore Asian CuisineDocument18 pagesExplore Asian CuisineSenthil KumarNo ratings yet
- Easy Moist Chocolate CakeDocument11 pagesEasy Moist Chocolate CakeMirna JelečaninNo ratings yet
- PIEDocument1 pagePIEDang AcajNo ratings yet
- Dewar's Guide To DebatingDocument13 pagesDewar's Guide To DebatingEd Luna100% (1)
- Feasibility Study Pizza Stick Barangay Sto. DomingoDocument1 pageFeasibility Study Pizza Stick Barangay Sto. DomingoWewew11No ratings yet
- Coffee Addiction Biology Investigatory PDocument19 pagesCoffee Addiction Biology Investigatory PKamranNo ratings yet
- Germany Poem Cup Waikoloa Spiegelau Import Crystal Brandy Glass White Wine Cup Ocean - Lazada PHDocument5 pagesGermany Poem Cup Waikoloa Spiegelau Import Crystal Brandy Glass White Wine Cup Ocean - Lazada PHjune dela cernaNo ratings yet
- Alchemist ExtractsDocument17 pagesAlchemist ExtractsCa KZNo ratings yet
- 12 Week Trainer Overview 111015141217 Phpapp01Document110 pages12 Week Trainer Overview 111015141217 Phpapp01Kshitij Guglani80% (5)
- P - 23 MicrotomyDocument2 pagesP - 23 MicrotomyDr. Tapan Kr. DuttaNo ratings yet
- 2013-11-14 The County TimesDocument40 pages2013-11-14 The County TimesSouthern Maryland OnlineNo ratings yet
- Internship Report On Marketing Strategies of PRAN-RFL Group: Daffodil International University Permanent CampusDocument37 pagesInternship Report On Marketing Strategies of PRAN-RFL Group: Daffodil International University Permanent CampusIftikhar JahanNo ratings yet
- Project Feasibility Study of Establishing Caffé Diverso Final Manuscript 1Document124 pagesProject Feasibility Study of Establishing Caffé Diverso Final Manuscript 1Gonzales JeromeNo ratings yet
- q1 ST 2 Gr.4 Science With TosDocument6 pagesq1 ST 2 Gr.4 Science With TosJunaly GarnadoNo ratings yet
- Desire Ncube WaiterDocument2 pagesDesire Ncube WaiterEDWINNo ratings yet
- Samyak Jain (A-49) Case StudyDocument8 pagesSamyak Jain (A-49) Case StudySamyak JainNo ratings yet
- Chasing the Evanescent Glow: Exploring Memories and MomentsDocument4 pagesChasing the Evanescent Glow: Exploring Memories and MomentsZofia TopiłkoNo ratings yet
- Waldorf SaladDocument6 pagesWaldorf SaladAnsya19No ratings yet
- Great British FoodDocument17 pagesGreat British FoodCarmenSaiocNo ratings yet
- Cooking MethodsDocument8 pagesCooking Methodsmaharana_rajaNo ratings yet
- The West Wing-102 - Post Hoc, Ergo Propter HocDocument53 pagesThe West Wing-102 - Post Hoc, Ergo Propter Hocv642336No ratings yet
- Propagating trees and fruit treesDocument7 pagesPropagating trees and fruit treesIra Kryst BalhinNo ratings yet
- Gestational Diabetes HandoutDocument2 pagesGestational Diabetes Handoutapi-228263644No ratings yet
- KCPLDocument2 pagesKCPLkanishk_bhallNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Text My White RabbitDocument8 pagesDescriptive Text My White RabbitIfahNo ratings yet
- Case Study 1: Yakult Production Plant ProcessDocument6 pagesCase Study 1: Yakult Production Plant ProcessRai Shaheryar BhattiNo ratings yet
- Simple Present READING - Journalist-Reporters - webeZHgRzYJDocument3 pagesSimple Present READING - Journalist-Reporters - webeZHgRzYJmustafayldz100% (1)
- Lifeforce Compact Ez 1Document4 pagesLifeforce Compact Ez 1ctaslacaNo ratings yet
- Breadman TR444 ManualDocument24 pagesBreadman TR444 ManualJeanette Ammann100% (1)
- Chapter 2, Wine Production ProcessDocument18 pagesChapter 2, Wine Production ProcessYonas Addam0% (1)