Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry - The P Block Elements Assignment
Uploaded by
Manickam GnanashekaranOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry - The P Block Elements Assignment
Uploaded by
Manickam GnanashekaranCopyright:
Available Formats
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.
com
p block elements
LEVEL-1 QUESTIONS
1. NH3 has higher boiling point than phosphine. Why?
AnsAmmonia is a polar molecule it form in-termolecular hydrogen bonding.
2. Why BiH3 the strongest reducing agent amongst all the hydrides of group 15 elements
?
126 | P a g e
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
Ans- Less B.E or longer bond length.
3. Why H2S is acidic and H2S is neutral ?
Ans-The S---H bond is weaker than O---H bond because the size of S atomis bigger than
that of O
atom . Hence H2S can dissociate to give H+ Ions in aqueous solution .
4. Name two poisonous gases which can be prepared from chlorine gas ?
Ans- Phosgene (COCl2) , tear gas (CCl3NO2)
5. Name the halogen which does not exhibit positive oxidation state .
Ans- Flourine being the most electronegative element does not show positive oxidation state .
6. Iodine forms I3- but F2 does not form F3- ions .why?
Ans- Due to the presence of vacant D-orbitals , I2 accepts electrons from I-ions to form I3-
ions , but because of d-orbitals F2 does not accept electrons from F-ions to form F3 ions.
7. Draw the structure of peroxosulphuric acid .
Ans-
8. Phosphorous forms PCl5 but nitrogen cannot form NCl5. Why?
Ans- Due to the availability of vacant d-orbital in p.
9. Give reasons for the following:
(i) Conc.HNO3 turns yellow on exposure to sunlight.
(ii) PCl5 behaves as an ionic species in solid state.
Ans- (i)Conc HNO3 decompose to NO2 which is brown in colour & NO2 dissolves in HNO3 to
it yellow.
(ii)It exists as [PCl4]+[PCl6]- in solid state.
10. How is ozone estimated quantitatively?
Ans- When ozone reacts with an excess of potassium iodide solution
Buffered with a borate buffer (Ph9.2), Iodide is liberated which can be titrated against a
standard solution of sodium thiosulphate . This is a quantitative method for estimating O 3gas.
11. Are all the five bonds in PCl5 molecule equivalent? Justify your answer.
Ans- PCl5 has a trigonal bipyramidal structure and the three equatorial P-Cl bonds are equivalent,
while the two axial bonds are different and longer than equatorial bonds.
12. NO2 is coloured and readily dimerises Why ?
Ans- NO2 contains odd number of valence electrons.It behaves as a typical odd molecules On
dimerization; it is converted to stable N204 molecule with even number of electrons.
13. Account for the following.
127 | P a g e
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
(i)SF6 is less reactive than.
(ii) 0f the noble gases only xenon chemical compounds.
Ans- (i)In SF6 there is less repulsion between F atoms than In SF4.
(ii)Xe has low ionisation enthalpy & high polarising power due to larger atomic size.
14. With what neutral molecule is ClO- Isoelectronic? Is that molecule a Lewis base?
ClF .Yes, it is Lewis base due to presence of lone pair of electron.
15.(i) why is He used in diving apparatus?
(ii)Noble gases have very low boiling points.Why?
(iii)Why is ICl moe reactive than I2?
Ans- (i)It is not soluble in blood even under high pressure.
(ii)Being monoatomic they have weak dispersion forces.
(iii)I-Cl bond is weaker than l-l bond
16. Account for the following.
(i)Noble gas form compounds with F2&O2 only.
(ii)Sulphur shows paramagnetic behavior.
(iii)HF is much less volatile than HCl.
(iv)White phosphorous is kept under water.
(v)Ammonia is a stronger base than phosphine.
Ans- (i)F2&O2 are best oxidizing agents.
(ii)In vapour state sulphur partly exists as S2 molecule which has two unpaired electrons in the
antibonding pi *orbitals like O2 and, hence, exhibit paramagnetism.
(iii)HF is associated with intermolecular H bonding.
(iv) Ignition temperature of white phosphorous is very low (303 K). Therefore on explosure to
air, it
spontaneously catches fire forming P4O10. Therefore to protect it from air, it is kept under water.
(v)Due to the smaller size of N, lone pair of electrons is readily available.
16. Arrange the following in the increasing order of the property mentioned.
(i)HOCl, HClO2, HClO3, HClO4 (Acidic strength)
(ii)As2O3, ClO2, GeO3, Ga2O3 (Acidity)
(iii)NH3, PH3, AsH3, SbH3 (HEH bond angle)
(iv)HF, HCl, HBr, HI (Acidic strength)
(v)MF, MCl, MBr, MI (ionic character)
Ans- (i)Acidic strength: HOCl<HClO2<HCIO3<HCIO4
(ii)Acidity: Ga2O3<GeO2<AsO3<CIO2
(iii)Bond angle: SbH3<AsH3<PH3<NH3
(iv)Acidic strength: HF<HCl<HBr<HI
(v)Ionic character: MI<MBr<MCl<MF
LEVEL-2 QUESTIONS
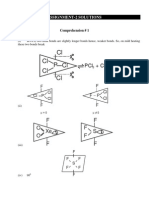
1 Draw the structure of following compounds-
a) N2O, NO, N2O3 NO2 and N2O5.
b) Oxoacides of Phosphorous, Sulphur and chlorine
c) Compounds of Xenon
Ans- a)
128 | P a g e
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
B)
129 | P a g e
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
c)
2. What happens when white P is heated with conc.NaOH solution in an atmosphere of CO2?
Give equation.
Ans- Phosphorus gas will be formed. P4+3NaOH+3H2OPH3+3NaH2PO2
3. Give example of a molecule having geometry T- shaped.
Ans- Br Cl3 (lp=2 and bp=3)
4. Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction of Cl2 with hot and concentrated
NaOH .Is this reaction a dispropotionation reaction? Justify:
3Cl2+6NaOH5NaCl+NaClO3+3H2O
5. Why is HF acid stored in wax coated glass bottles?
Ans- This is because HF does not attack wax but reacts with glass.It dissolves SiO2 present in
glass forming hydrofluorosilicic acid.
SiO2 +6HFH2SiF6+2H2O
6. What is laughing gas? Why is it so called? How is it prepared?
Ans- Nitrous oxide (N2O) is called laughing gas, because when inhaled it produced hysterical
laughter. It is prepared by gently heating ammonium nitrate.
NH4NO3N2O+2H2O
130 | P a g e
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
LEVEL-3 QUESTIONS
1. A translucent white waxy solid (A) on heating in inert atmosphere is converted to its
allotropic form (B). Allotrope (A) on reaction with very dilute aqueous KOH liberates a
highly poisonous gas (C) having rotten fish smell. With excess of chlorine it forms (D) which
hydrolyses to compound (E). Identify compounds (A) to (E).
Ans: A= White phosphorus B= Red phosphorous C= Phosphine
D= Phophoruspentachloride E= Phosphoric acid.
2. When conc. H2SO4 was added into an unknown salt present in a test tube, a brown gas
(A) was evolved. This gas intensified when copper turnings were also added into this test tube.
On cooling, the gas (A) changed into colorless gas (B).
a. Identify the gases A and B.
b. Write the equations for the reactions involved
Ans- a) MNO3 + H2SO4 MHSO4+ HNO3
4HNO3 4NO2 + 2H2O + O2
Cu + 4HNO3 Cu(NO3)2 + 2H2O+ 2NO2
2NO2 N2O4
3. A colorless inorganic salt A decomposes at about 250 C to give only two produces B
and C leaving no residue. The oxide C is a liquid at room temperature and is neutral to litmus
paper while B is neutral oxide. White phosphorus burns in excess of B to produce Strong
dehydrating agent. Give balanced equations for above processes.
Ans: A= NH4NO3
B=N2O
C=H2O
Reactions involved:
NH4NO3 N2O + 2H2O
10N2O + P4 10 N2 + P4O10
4. On heating lead (II) nitrate gives a brown gas A. The gas A on cooling changes to
colorless solid B. Solid B on heating with NO changes to a blue Solid C. Identify A,
B and C.
Ans: 2Pb (NO3)2 2PbO +NO2+O2
2NO2 N2O4 (on cooling)
2NO + N2O4 2N2O3
A=NO2 B=N2O4 and C=2N2O3
5.An amorphous solid A burns in air to form a gas B which turns lime water milky. The
gas is also produced as a by-product during roasting of sulhpide ore. This gas decolorizes
acidified aqueous KMnO4 solution and reduces Fe2 and Fe3. Identify the solid A and the gas
B.
Ans: A=S8 B=SO2
S8 + 8O2 8 SO2
2ZnS + 3O2 2ZnO + 2SO2
6.Why does PCl3 fume in moisture ?
Ans- In the presence of (H2O) , PCl3 undergoes hydrolysis giving fumes of HCl
ie, PCl3 + 3H2O H3PO3 + 3HCl
131 | P a g e
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
7.What Happens when H3PO3 is Heated ?
Ans- It disproportionate to give orthophosphoric acid and Phosphine .
4H3PO3 3H3PO4 + PH3
8. When Conc. H2SO4 was added to an unknown salt present in a test tube, a brown gas (A)
was evolved. This gas intensified when copper turnings were added in to test tube. On cooling
gas (A) changed in to a colourless gas (B).
(a)Identify the gases A and B
(b)Write the equations for the reactions involved
Ans- The gas A is NO2 whereas B is N2O4.
XNO3 + H2SO4XHSO4 + HNO3
Salt (conc.)
Cu + 4HNO3 (Conc.) Cu (NO3)2 + 2NO2 + 2H2O
Blue Brown (A)
2NO2 (on cooling) N2O4
Colourless(B)
9. Complete the following equations.
(i)XeF4+H2O
(ii)Ca3P2+H2O
(iii)AgCl(s) +NH3 (aq)
Ans- (i) 6XeF4+12H2O4Xe+2XeO3+24HF+3O2
(ii)Ca2P2+6H2O3Ca (OH) 2+2PH3
(iii)AgCl(s) +2NH3 (aq)[Ag(NH3)2]Cl(aq)
10. (i)How is XeOF4 prepared ?Draw its structure.
(ii)When HCl reacts with finely powdered iron, it forms ferrous chloride and not ferric
chloride
Why?
Ans- (i)Partial hydrolysis of XeOF4
XeF6+H2OXeOF4+2HF
Structure-square pyramidal. See Fig7.9
(ii) Its reaction with iron produces h2
Fe+2HClFeCl2+H2
Liberation of hydrogen prevents the formation of ferric chloride.
132 | P a g e
Downloaded from www.studiestoday.com
You might also like
- Previous Year Board Exam QuestionsDocument19 pagesPrevious Year Board Exam QuestionsRishabh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- 6.P Block ElementsDocument24 pages6.P Block ElementsSSSSSSSSSSSSNo ratings yet
- 12th Chemistry Practice Sheet Unit 07: P Block: PART - A (MCQ Based)Document4 pages12th Chemistry Practice Sheet Unit 07: P Block: PART - A (MCQ Based)Bloody DemonNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3 P-Block Elements-Ii: WWW - Nammakalvi.inDocument5 pagesUnit - 3 P-Block Elements-Ii: WWW - Nammakalvi.inAakaash C.K.100% (1)
- Namma Kalvi 12th Chemistry Unit 3 Study Material em 215020Document5 pagesNamma Kalvi 12th Chemistry Unit 3 Study Material em 215020Aakaash C.K.No ratings yet
- P Block Elements Notes For Entrance ExaminationDocument13 pagesP Block Elements Notes For Entrance ExaminationSrijan ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- 16.p Block Element ExerciseDocument27 pages16.p Block Element ExerciseKIRAN ALLUNo ratings yet
- P Block Give Reasons (Without Answers)Document6 pagesP Block Give Reasons (Without Answers)zxcvb100% (1)
- The P-Block Elements: White P: White Waxy/poisonous/ Soluble in CSDocument2 pagesThe P-Block Elements: White P: White Waxy/poisonous/ Soluble in CSSsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 The P Block ElementsDocument25 pagesChapter 7 The P Block Elementspriyanka kNo ratings yet
- 16Document4 pages16Shazia FarheenNo ratings yet
- P Block NotesDocument4 pagesP Block NotesKunalKumarSinghNo ratings yet
- Leep507 PDFDocument15 pagesLeep507 PDFUdit ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- One Mark Questions: Subject: Chemistry Chapter - 11: P-Block ElementDocument13 pagesOne Mark Questions: Subject: Chemistry Chapter - 11: P-Block ElementudaysrinivasNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equations Ws AnsDocument4 pagesChemical Equations Ws AnsRia AlbertNo ratings yet
- Reasoning Questions in P Block ElementsDocument15 pagesReasoning Questions in P Block ElementsAbhi WaliaNo ratings yet
- 7 The P-Block Elements: Level - IDocument22 pages7 The P-Block Elements: Level - IFasahatNo ratings yet
- P Block Elements II WorkbookDocument53 pagesP Block Elements II WorkbookStudy BuddyNo ratings yet
- Mycbseguide: Class 12 - Chemistry Term 1 - Some P-Block Elements - 05Document5 pagesMycbseguide: Class 12 - Chemistry Term 1 - Some P-Block Elements - 05you monsterNo ratings yet
- 12th Chemistry CH-4NotesDocument6 pages12th Chemistry CH-4NotesMajid HafeezNo ratings yet
- Chem (Soln) CH 8Document27 pagesChem (Soln) CH 8RahulMittalNo ratings yet
- Group 16 ElementsDocument40 pagesGroup 16 Elementstapas kunduNo ratings yet
- Inorganic ChemistryDocument13 pagesInorganic Chemistrybhargavthegreat123No ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry Handguide by Ri DaDocument2 pagesInorganic Chemistry Handguide by Ri DaGAME DEVNo ratings yet
- P BlockDocument6 pagesP BlockRajbir ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- 5 Marks Question and AnswerDocument10 pages5 Marks Question and AnswerHeartyscorpionNo ratings yet
- C - Sol - Ch-15 - The P-Block Elements (Group 13 To Group 18)Document9 pagesC - Sol - Ch-15 - The P-Block Elements (Group 13 To Group 18)mysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- Group 7 Fluorine Chlorine Bromine and IodineDocument6 pagesGroup 7 Fluorine Chlorine Bromine and IodinePAUL KOLERENo ratings yet
- The P-Block Elements (Summary)Document49 pagesThe P-Block Elements (Summary)nickan876No ratings yet
- Ammonia Question and AnswerDocument14 pagesAmmonia Question and AnswerGanesh sargarNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Chapter 4.I ANSWERSDocument2 pagesWorksheet Chapter 4.I ANSWERSkhalid badranNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Redox-ReactionsDocument33 pagesChapter 8 Redox-ReactionsRohan PatelNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 12 Chemistry The P-Block ElementsDocument41 pagesImportant Questions For CBSE Class 12 Chemistry The P-Block ElementsyndtfndtgndNo ratings yet
- P Block ElementDocument5 pagesP Block ElementrshirayNo ratings yet
- Group 15 - The Elements NitrogenDocument19 pagesGroup 15 - The Elements NitrogenHarold Isai Silvestre GomezNo ratings yet
- Hsslive-12. Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic AcidsDocument12 pagesHsslive-12. Aldehydes, Ketones & Carboxylic Acidssindhumv631No ratings yet
- Mycbseguide: Class 12 - Chemistry Term 1 - Some P-Block Elements - 02Document5 pagesMycbseguide: Class 12 - Chemistry Term 1 - Some P-Block Elements - 02you monsterNo ratings yet
- Chem NotesDocument27 pagesChem NotesRaya DhanushNo ratings yet
- Mycbseguide: Class 12 - Chemistry Term 1 - Some P-Block Elements - 01Document5 pagesMycbseguide: Class 12 - Chemistry Term 1 - Some P-Block Elements - 01Aditya SharmaNo ratings yet
- The P-Block Elements-2020 PDFDocument5 pagesThe P-Block Elements-2020 PDFShamma AshrafNo ratings yet
- Some More QuestionsDocument18 pagesSome More QuestionsGauravNo ratings yet
- Alcohol, Phenols and Ethers PDFDocument13 pagesAlcohol, Phenols and Ethers PDFRahul JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Important-Question-ICSE-2010-Class-10th - Acids-Bases-Salts-CDocument5 pagesImportant-Question-ICSE-2010-Class-10th - Acids-Bases-Salts-CYash KapoorNo ratings yet
- Important Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 1Document21 pagesImportant Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 1Darshuram DudheNo ratings yet
- Surface Chemistry RS-01Document5 pagesSurface Chemistry RS-01Vishesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Subjective Type Questions Also Useful For XII Board Exam.: The P - Block ElementsDocument13 pagesSubjective Type Questions Also Useful For XII Board Exam.: The P - Block ElementsAbhiNo ratings yet
- P Block Group 16 & 15 MCQDocument3 pagesP Block Group 16 & 15 MCQVaradaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and Equations Activity Based Question 10thDocument18 pagesChemical Reactions and Equations Activity Based Question 10thBharatharaj123No ratings yet
- SHC IxDocument3 pagesSHC IxVishnuanand ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- HydrogenDocument10 pagesHydrogenAyush DasNo ratings yet
- P Block Exercise MCQDocument75 pagesP Block Exercise MCQChesta MalhotraNo ratings yet
- THE P - Block Elements-Anil-Hsslive PDFDocument19 pagesTHE P - Block Elements-Anil-Hsslive PDFKochuzNo ratings yet
- Test1 Goc & Poc Tough by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atDocument3 pagesTest1 Goc & Poc Tough by S.K.sinha See Chemistry Animations atmyiitchemistry100% (1)
- (Game Changer 1.0) - P Block, D & F Block - 6 JanDocument102 pages(Game Changer 1.0) - P Block, D & F Block - 6 JanRama KrishnaNo ratings yet
- 10th Chemical Reaction and Equation Questions With Solution 03Document3 pages10th Chemical Reaction and Equation Questions With Solution 03Vaibhav SunnyNo ratings yet
- Exemplar - Questions With Answer.Document12 pagesExemplar - Questions With Answer.Liveen .S100% (1)
- Reduced Syllabus 2020-21 P Block G 15 Important Questions Group 15Document3 pagesReduced Syllabus 2020-21 P Block G 15 Important Questions Group 15Kalpa DihingiaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Chemical Equation and ReactionDocument7 pagesChemistry Chemical Equation and Reactionsmriti khannaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: Neet - Chem-Electro-KerthanaDocument12 pagesElectrochemistry: Neet - Chem-Electro-KerthanaManickam GnanashekaranNo ratings yet
- Valence Electrons and Valency of An ElementDocument5 pagesValence Electrons and Valency of An ElementManickam GnanashekaranNo ratings yet
- NEET (UG) 2017 Paper Solution PDFDocument45 pagesNEET (UG) 2017 Paper Solution PDFManickam GnanashekaranNo ratings yet
- 029 - Property Law (971-994)Document24 pages029 - Property Law (971-994)Manickam GnanashekaranNo ratings yet
- Sree Vaishnavam - TamilDocument17 pagesSree Vaishnavam - TamilManickam GnanashekaranNo ratings yet
- Madhurashtakam in EnglishDocument2 pagesMadhurashtakam in EnglishManickam Gnanashekaran100% (1)
- The TattvaDocument212 pagesThe TattvaManickam GnanashekaranNo ratings yet
- Pancaraatra Agama - 1Document28 pagesPancaraatra Agama - 1raj100% (5)
- Ahaara NiyamamDocument28 pagesAhaara Niyamamajiva_rtsNo ratings yet
- Srivaishnava Prayer Book 2013Document101 pagesSrivaishnava Prayer Book 2013Manickam GnanashekaranNo ratings yet
- 2010 APP InternationalDocument2 pages2010 APP InternationalManickam GnanashekaranNo ratings yet
- 8 LipidsDocument5 pages8 LipidsManickam GnanashekaranNo ratings yet
- June 2017 Question Paper 21Document20 pagesJune 2017 Question Paper 21KaifNo ratings yet
- Class-7 Dlalal Simplified Elements Compound and Mixtures ICSE Chemistry SolutionsDocument15 pagesClass-7 Dlalal Simplified Elements Compound and Mixtures ICSE Chemistry SolutionssrobeNo ratings yet
- 2023-24 SR - Super60 (Incoming) STERLING Batch CHEMISTRY Teaching & Test Schedule Code@03!04!2023Document16 pages2023-24 SR - Super60 (Incoming) STERLING Batch CHEMISTRY Teaching & Test Schedule Code@03!04!2023K R I S H100% (1)
- Learn Periodic Table in HindiDocument21 pagesLearn Periodic Table in HindiSiobhan Reed67% (3)
- Muhammad Irfan Notes One Paper McqsDocument99 pagesMuhammad Irfan Notes One Paper McqsFaysal HayyatNo ratings yet
- Antimonos: Element Symbol Latin Name EnglishDocument3 pagesAntimonos: Element Symbol Latin Name EnglishAlma Mae CasabayNo ratings yet
- Activate 2 Chemistry Chapter1 AnswersDocument5 pagesActivate 2 Chemistry Chapter1 AnswersAlex LimNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 AnswerDocument5 pagesAssignment 2 AnswerVaibhav BacchavNo ratings yet
- C3.1.7 The Noble Gases WorksheetDocument2 pagesC3.1.7 The Noble Gases WorksheetmtauhidNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - MCQDocument30 pagesChemistry - MCQjoydeep_d32320% (1)
- Periodic Table of ElementsDocument5 pagesPeriodic Table of Elementsmichael tenajerosNo ratings yet
- The Periodic Table, Electron Shells, and OrbitalsDocument13 pagesThe Periodic Table, Electron Shells, and OrbitalsCandyAnonymousNo ratings yet
- MP2000 ENGLISH MANUAL APRIL 2011 Ver 1.3Document31 pagesMP2000 ENGLISH MANUAL APRIL 2011 Ver 1.3Hari PrasathNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table of ElementsDocument60 pagesPeriodic Table of ElementsFernadez RodisonNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Chart A4 WebDocument2 pagesPeriodic Table Chart A4 WebvibinNo ratings yet
- Group Chemistry LEDocument152 pagesGroup Chemistry LERupokNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table PNOC Reviewer 30 QuestionsDocument2 pagesPeriodic Table PNOC Reviewer 30 QuestionsMark Jay AquilloNo ratings yet
- SR Chem IPEDocument22 pagesSR Chem IPECHAKRI BABLUNo ratings yet
- 02.2 Dyeing Methods For Wool NotesDocument146 pages02.2 Dyeing Methods For Wool NotesAle CayambeNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Unit Test PDFDocument4 pagesPeriodic Table Unit Test PDFTon TonNo ratings yet
- Group VIII Noble Gases and Trends Across A PeriodDocument8 pagesGroup VIII Noble Gases and Trends Across A PeriodknjNo ratings yet
- Eva Chamorro-Perez Et Al - Low Argon Solubility in Silicate Melts at High PressureDocument4 pagesEva Chamorro-Perez Et Al - Low Argon Solubility in Silicate Melts at High PressureDrebuioNo ratings yet
- Brown Creative Travel Adventure Trifold BrochureDocument2 pagesBrown Creative Travel Adventure Trifold BrochureJana BantasNo ratings yet
- Taking Refuge in AltruismDocument85 pagesTaking Refuge in AltruismChoumphol BounthinhNo ratings yet
- SCH3U Chemistry Unit 1 MC ReviewDocument16 pagesSCH3U Chemistry Unit 1 MC Review1moeezafNo ratings yet
- Silo - Tips - Electron Configurations Isoelectronic Elements Ionization Reactions Chemistry 11Document30 pagesSilo - Tips - Electron Configurations Isoelectronic Elements Ionization Reactions Chemistry 11Shiza SajidNo ratings yet
- P - Block Reasoning 16, 17, 18 Very Simplified - (1) FDocument9 pagesP - Block Reasoning 16, 17, 18 Very Simplified - (1) FShazia FarheenNo ratings yet
- Cracking Bgcse Chemistry PDFDocument52 pagesCracking Bgcse Chemistry PDFKordell leydNo ratings yet
- The Group 18 Elements: The Noble GasesDocument3 pagesThe Group 18 Elements: The Noble GasesKeynner Andres Rodriguez GaleanoNo ratings yet
- Process Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityFrom EverandProcess Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincFrom EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (137)
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsFrom EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactFrom EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- AP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeFrom EverandAP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeNo ratings yet
- ICH Quality Guidelines: An Implementation GuideFrom EverandICH Quality Guidelines: An Implementation GuideAndrew TeasdaleNo ratings yet
- Sodium Bicarbonate: Nature's Unique First Aid RemedyFrom EverandSodium Bicarbonate: Nature's Unique First Aid RemedyRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (21)
- AP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeFrom EverandAP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- It's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingFrom EverandIt's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (10)
- Taste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodFrom EverandTaste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (20)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (90)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Formulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsFrom EverandFormulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsNo ratings yet
- Process Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersFrom EverandProcess Steam Systems: A Practical Guide for Operators, Maintainers, and DesignersNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactFrom EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Guidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsFrom EverandGuidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- The Production of Volatile Oils and Perfumery Plants in the United StatesFrom EverandThe Production of Volatile Oils and Perfumery Plants in the United StatesNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AnalysisFrom EverandGuidelines for Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- An Applied Guide to Water and Effluent Treatment Plant DesignFrom EverandAn Applied Guide to Water and Effluent Treatment Plant DesignRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Essential Chemistry for Formulators of Semisolid and Liquid DosagesFrom EverandEssential Chemistry for Formulators of Semisolid and Liquid DosagesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Piping Engineering Leadership for Process Plant ProjectsFrom EverandPiping Engineering Leadership for Process Plant ProjectsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideFrom EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideNo ratings yet