Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dimensional Engineering Part1
Uploaded by
Avneet MaanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dimensional Engineering Part1
Uploaded by
Avneet MaanCopyright:
Available Formats
GM General Motors
Truck Group
Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing
Variation Simulation Modeling
Date of Publication: January 12, 1998
Latest Revision Date: May 1, 1999
GM General Motors
Truck Group
DIMENSIONAL
ENGINEERING
Based on the ASME Y14.5M-
1994 Dimensioning and
Tolerancing Standard
as amended by the GM Global
Addendum-1997
GM General Motors
Truck Group
Copyright c 1998 by General Motors Corp.
ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system,
or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, recording
or otherwise without prior written permission of the author and publisher.
Seminar Agenda
Objectives
Dimensional Engineering Concept
ASME Y14.5M-1994 and GM Global Addendum
Video - Introduction to GD&T
The Language of GD&T
Why Use GD&T ?
Engineering Drawings - General Review
Basic Rules and Definitions
Datum Function & Datum Reference Frames
Datum Planes, Features and Simulators
Datum Target Areas, Lines, Points
and Partial Datum Surfaces
Feature Control Frame Elements
Variation Simulation Modeling (VSM)
Tolerances of Form
Tolerances of Orientation
Tolerances of Runout
Tolerances of Profile
Tolerances of Location
Course Objectives
Develop an awareness of Dimensional Engineering
concepts and explain how the techniques are used to
understand, control, and help reduce variation in the
overall vehicle build process.
Introduction to the Build Tolerance Procedure.
Provide an overview of the Variation Simulation
Modeling (VSM) process and how it is used to
predict variation in the vehicle.
Provide an introduction to Geometric Dimensioning
and Tolerancing (GD&T), the ASME Y14.5M-1994
Standard including the GM Global Addendum and
how the concepts, symbols and terms of GD&T are
used in the engineering process.
Dimensional Engineering
Concept
Dimensional Engineering is a sub-process within the
overall vehicle development cycle, key to achieving
robust designs and controlling product definition.
-
through the entire Four Phase Vehicle Development
the GMTG Dimensional Engineering approach.
What is GD&T?
Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing is an international graphic
engineering language designed to allow designers and engineers
to on engineering drawings. The
concepts, symbols and mathematical structure of GD&T provide a
precise and logical way to describe the manufacturing tolerance
zones that are applied to individual features or groups of features
on parts or assemblies.
What is ASME Y14.5M-1994?
The ASME Y14.5M-1994 is the latest revised issue of the common
Industrial Standard on dimensioning and tolerancing. The Standard
establishes uniform practices for the dimensioning and tolerancing
of engineering drawings and related documents. All GD&T rules,
concepts, and practices are contained within the current Y14.5M
Standard and the GM Global Addendum.
Why a GM Global Addendum?
The GM Global Addendum was written to address and/or clarify
concepts and practices described within the ASME Y14.5M-1994
Standard. Sections 1-6 of the addendum represent the consensus
of the US Car GD&T Team and have been adopted by GM, Ford,
and Chrysler. Sections 7&8 apply specifically to General Motors.
The addendum replaces section A91 of the current GM Drafting
Standard.
The goal of GD&T is to improve communication !!
The Language of Geometric
Dimensioning & Tolerancing
Geometric Characteristic Symbols
TYPE OF
FEATURES TOLERANCE
CHARACTERISTIC SYMBOL
Straightness
For Flatness
Individual Form
Features Circularity (roundness)
Cylindricity
For Profile of a Line
Individual Profile
or Related Profile of a Surface
Features
Angularity
Orientation Perpendicularity
Parallelism
For Position
Related
Features Location Concentricity
Symmetry
Circular Runout *
Runout
Total Runout *
* Runout symbols may be filled or not filled
The Language of Geometric
Dimensioning & Tolerancing
Additional Symbols and Modifiers
TERM SYMBOL
Maximum Material Condition M
Least Material Condition L
Regardless of Feature Size ** s **
Free State Datum Modifier F
Projected Tolerance Zone P
Tangent Plane Modifier T
Diameter Symbol
All Around Symbol *
Between Symbol *
Radius R
Controlled Radius CR
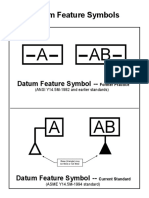
Datum Feature Symbol A *
Basic Dimension (or Angle) 234.5
Statistical Tolerance Symbol ST
* Symbols may be filled or not filled
** The RFS symbol is no longer used per ASME Y14.5M-1994. It is applicable only on
drawings using earlier standards.
The Language of Geometric
Dimensioning & Tolerancing
Basic Feature Control Frame
Datum Reference Frame
1 A BC
Tolerance
Value
Tertiary
Primary
Geometric Datum
Datum
Characteristic
Symbol Secondary
Datum
Each feature control frame contains information identifying a specific feature
characteristic to be controlled (geometric characteristic symbol),the limits of
error or variation allowed for that characteristic (tolerance value), the point(s)
or surfaces from which the characteristic is to be measured (datum reference
frame), and the theoretical shape of the tolerance zone that applies (diameter
symbol and material condition modifiers). Feature control frame are the basic
building blocks of the GD&T language. The ability to accurately interpret the
feature control frame is fundamental to understanding other GD&T concepts.
The Language of Geometric
Dimensioning & Tolerancing
Feature Control Frame with Material
Condition Modifiers and Diameter Symbol
Tolerance Material
Condition Symbol
Diameter Datum Material
Symbol Condition Symbol
1M A BM C
As required, additional symbols are used along with the basic feature control
frame to identify specific geometric or dimensional requirements. The above
example shows a diameter symbol and two maximum material condition (MMC)
symbols that have been added to precisely describe the feature requirements.
The diameter symbol describes the cylindrical shape of the feature tolerance
zone while the maximum material condition symbols indicate both the feature
and secondary datum material condition in which the stated tolerance applies.
You might also like
- Manual of Engineering Drawing: British and International StandardsFrom EverandManual of Engineering Drawing: British and International StandardsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- GD&T12Document136 pagesGD&T12Roshan KhedkarNo ratings yet
- The Geometrical Tolerancing Desk Reference: Creating and Interpreting ISO Standard Technical DrawingsFrom EverandThe Geometrical Tolerancing Desk Reference: Creating and Interpreting ISO Standard Technical DrawingsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- Geometrical Dimensioning and Tolerancing for Design, Manufacturing and Inspection: A Handbook for Geometrical Product Specification Using ISO and ASME StandardsFrom EverandGeometrical Dimensioning and Tolerancing for Design, Manufacturing and Inspection: A Handbook for Geometrical Product Specification Using ISO and ASME StandardsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Basics GD TDocument97 pagesBasics GD Tjsridhar_347100% (5)
- Geometrical Dimensioning and TolerancingDocument51 pagesGeometrical Dimensioning and TolerancingMahender Kumar100% (3)
- GD&T StdsDocument4 pagesGD&T StdsSri PupNo ratings yet
- GD&T NotesDocument24 pagesGD&T NotesDarshan Sn100% (1)
- D W G 1Document1 pageD W G 1Avneet MaanNo ratings yet
- Dimensional Engineering Part3Document10 pagesDimensional Engineering Part3Avneet MaanNo ratings yet
- GD&T Basics (Level-1)Document85 pagesGD&T Basics (Level-1)Thiyagu rajNo ratings yet
- Asme 14.5M 2009Document25 pagesAsme 14.5M 2009aguiladezcalza69100% (5)
- Geometrical Dimensioning & Tolerancing: Based On The ASME Y14.5M - 1994 Dimensioning and Tolerancing StandardDocument86 pagesGeometrical Dimensioning & Tolerancing: Based On The ASME Y14.5M - 1994 Dimensioning and Tolerancing Standardmohtram1037100% (4)
- 04 GD&T IntroTutorialDocument73 pages04 GD&T IntroTutorialrust_02No ratings yet
- Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing: Navigation Search Citations Reliable and Independent SourcesDocument8 pagesGeometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing: Navigation Search Citations Reliable and Independent SourcesDeepak LogesonNo ratings yet
- SolidWorks 2015 Learn by doing-Part 3 (DimXpert and Rendering)From EverandSolidWorks 2015 Learn by doing-Part 3 (DimXpert and Rendering)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (5)
- PsychFirstAidSchools PDFDocument186 pagesPsychFirstAidSchools PDFAna ChicasNo ratings yet
- GD&T 1Document69 pagesGD&T 1JayanthiANo ratings yet
- ANSI and ISO Geometric Tolerancing Symbols1Document5 pagesANSI and ISO Geometric Tolerancing Symbols1Mahender KumarNo ratings yet
- Profile ToleranceDocument34 pagesProfile ToleranceGopinathNo ratings yet
- Solidworks 2018 Learn by Doing - Part 3: DimXpert and RenderingFrom EverandSolidworks 2018 Learn by Doing - Part 3: DimXpert and RenderingNo ratings yet
- Geometric Dimensioning and TolerancingDocument4 pagesGeometric Dimensioning and TolerancingAshokNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of GD&TDocument7 pagesFundamentals of GD&TPalani TrainerNo ratings yet
- ElementsDocument75 pagesElementsAbhishek AnandNo ratings yet
- Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing (GD&T)Document43 pagesGeometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing (GD&T)Victor Manuel Estrada0% (1)
- Dimensional Engineering SeminarDocument71 pagesDimensional Engineering Seminardramilt100% (4)
- M&I 05-GeometricalTolerancing2017 v01Document20 pagesM&I 05-GeometricalTolerancing2017 v01Akash100% (1)
- DLL Week 5Document3 pagesDLL Week 5Nen CampNo ratings yet
- Case - Marico SCMDocument26 pagesCase - Marico SCMChandan Gupta50% (2)
- GT&D SymbolsDocument8 pagesGT&D SymbolsshawntsungNo ratings yet
- GDT Day1Document119 pagesGDT Day1Narendrareddy RamireddyNo ratings yet
- GD&T Symbols - GD&T Terms - Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing Glossary - GD&T Free ResourceDocument5 pagesGD&T Symbols - GD&T Terms - Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing Glossary - GD&T Free Resourcebbbsample0% (1)
- Lecture #6 - Geometric Tolerancing (2018) - Part IDocument98 pagesLecture #6 - Geometric Tolerancing (2018) - Part IakinhaciNo ratings yet
- SolidWorks 2016 Learn by doing 2016 - Part 3From EverandSolidWorks 2016 Learn by doing 2016 - Part 3Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- GD&TDocument33 pagesGD&TShasank PramodeNo ratings yet
- GD&T StandardDocument100 pagesGD&T StandardsudhirNo ratings yet
- Mitochondrial Mechanisms of PhotobiomodulationDocument4 pagesMitochondrial Mechanisms of PhotobiomodulationGabrielNo ratings yet
- 5G System Design: Architectural and Functional Considerations and Long Term ResearchFrom Everand5G System Design: Architectural and Functional Considerations and Long Term ResearchNo ratings yet
- Dimensional Engineering PDFDocument71 pagesDimensional Engineering PDFAvneet MaanNo ratings yet
- GD&TDocument5 pagesGD&TkbhattacNo ratings yet
- Dimensional Engineering Seminar: Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing Variation Simulation ModelingDocument71 pagesDimensional Engineering Seminar: Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing Variation Simulation Modelingprasungovindan100% (1)
- Linear Dimensions Datum ReferenceDocument4 pagesLinear Dimensions Datum ReferenceVetrivel KanagavelNo ratings yet
- GDT TutorialDocument76 pagesGDT Tutorialscience ki DuniyaNo ratings yet
- GD&T, Symbols & TermsDocument19 pagesGD&T, Symbols & TermsOmkar VibhuteNo ratings yet
- Geometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing (GD&T) Workshop: Gdt3D 3 Days Related CoursesDocument4 pagesGeometric Dimensioning & Tolerancing (GD&T) Workshop: Gdt3D 3 Days Related CoursesMFNo ratings yet
- Geometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing - WikipediaDocument4 pagesGeometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing - WikipediaEdryle AtanacioNo ratings yet
- Introduction To GD&T?Document11 pagesIntroduction To GD&T?AravindNo ratings yet
- GD&T SymbolsDocument4 pagesGD&T SymbolspolumathesNo ratings yet
- GD&TDocument21 pagesGD&TJochelle Mae PecsonNo ratings yet
- 美国机械制图标准简介Document82 pages美国机械制图标准简介Han HuangNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument24 pagesIntroductionVictor PirvulescuNo ratings yet
- CourseDocument1 pageCoursePalani TrainerNo ratings yet
- GD&T For Mpii 26-4-22Document134 pagesGD&T For Mpii 26-4-22sai tejaNo ratings yet
- Geometric Dimensioning and TolerancingDocument10 pagesGeometric Dimensioning and Tolerancing25aprilNo ratings yet
- ASME Y 14.5: CNC MachiningDocument6 pagesASME Y 14.5: CNC MachiningAnil ETNo ratings yet
- G4 - Advance GD&T and Tolerance Stack-UpDocument9 pagesG4 - Advance GD&T and Tolerance Stack-UpAnkit NaphadeNo ratings yet
- Metrology Measurement Slide PresentDocument13 pagesMetrology Measurement Slide PresentNo NameNo ratings yet
- Review of The 2009 ASME Y14 - 5 StandardDocument25 pagesReview of The 2009 ASME Y14 - 5 StandardsajuNo ratings yet
- Geometric TolerancingDocument57 pagesGeometric TolerancingKewell LimNo ratings yet
- GD&T 011621Document11 pagesGD&T 011621Astle RebelloNo ratings yet
- Basics of GD&TDocument50 pagesBasics of GD&T2023ht30006No ratings yet
- Week 7 Geometric Dimenisoning and Tolerancing by Olaf Pippel of HYDACDocument40 pagesWeek 7 Geometric Dimenisoning and Tolerancing by Olaf Pippel of HYDACZubairAhmedNo ratings yet
- A Classification System to Describe Workpieces: DefinitionsFrom EverandA Classification System to Describe Workpieces: DefinitionsW. R. MacconnellNo ratings yet
- Properties of Material3Document1 pageProperties of Material3Avneet MaanNo ratings yet
- Datum QuizDocument1 pageDatum QuizAvneet MaanNo ratings yet
- Properties of Material2Document1 pageProperties of Material2Avneet MaanNo ratings yet
- Properties of Material1Document1 pageProperties of Material1Avneet MaanNo ratings yet
- BDocument1 pageBAvneet MaanNo ratings yet
- Manuf ProcDocument1 pageManuf ProcAvneet MaanNo ratings yet
- MPDocument1 pageMPAvneet MaanNo ratings yet
- Datum FsDocument1 pageDatum FsAvneet MaanNo ratings yet
- Definition FSCDocument1 pageDefinition FSCAvneet MaanNo ratings yet
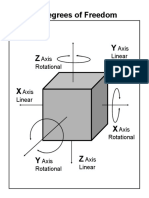
- Six Degree of FreedomDocument1 pageSix Degree of FreedomAvneet MaanNo ratings yet
- Datum Reference Frame: Tertiary Datum Plane Secondary Datum PlaneDocument1 pageDatum Reference Frame: Tertiary Datum Plane Secondary Datum PlaneAvneet MaanNo ratings yet
- Dimensional Engineering Part2Document10 pagesDimensional Engineering Part2Avneet MaanNo ratings yet
- CBD 2516Document1 pageCBD 2516Avneet MaanNo ratings yet
- Netzsch Pump 12KDocument1 pageNetzsch Pump 12KAvneet MaanNo ratings yet
- BlenderDocument1 pageBlenderAvneet MaanNo ratings yet
- MTechDesignEngineering Jan2017Document2 pagesMTechDesignEngineering Jan2017Avneet MaanNo ratings yet
- MTechDesignEngineering Jan2017Document2 pagesMTechDesignEngineering Jan2017Avneet MaanNo ratings yet
- Mahindra Truxo 25Document1 pageMahindra Truxo 25Avneet MaanNo ratings yet
- A AaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaDocument1 pageA AaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaAvneet MaanNo ratings yet
- Good Knowledge of Powertrain Development Process and SystemsDocument1 pageGood Knowledge of Powertrain Development Process and SystemsAvneet MaanNo ratings yet
- A0Y2U4 - Attachment 99999999999999Document1 pageA0Y2U4 - Attachment 99999999999999Avneet MaanNo ratings yet
- What Is BIW - PDFDocument2 pagesWhat Is BIW - PDFAvneet MaanNo ratings yet
- A0Y2U4 - Attachment 99999Document1 pageA0Y2U4 - Attachment 99999Avneet MaanNo ratings yet
- What Is BIW - 11111111111111Document1 pageWhat Is BIW - 11111111111111Avneet MaanNo ratings yet
- What Is BIW - PDFDocument2 pagesWhat Is BIW - PDFAvneet MaanNo ratings yet
- A0Y2U4 - Attachment 99Document1 pageA0Y2U4 - Attachment 99Avneet MaanNo ratings yet
- Olinger v. The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter Day Saints Et Al - Document No. 1Document4 pagesOlinger v. The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter Day Saints Et Al - Document No. 1Justia.comNo ratings yet
- Commercial CrimesDocument3 pagesCommercial CrimesHo Wen HuiNo ratings yet
- International Human Rights LawDocument21 pagesInternational Human Rights LawRea Nica GeronaNo ratings yet
- Thesis Committee MeetingDocument7 pagesThesis Committee Meetingafknojbcf100% (2)
- Oedogonium: Class: Chlorophyceae Order: Oedogoniales Family: OedogoniaceaeDocument28 pagesOedogonium: Class: Chlorophyceae Order: Oedogoniales Family: OedogoniaceaeA SASIKALANo ratings yet
- BSCHMCTT 101Document308 pagesBSCHMCTT 101JITTUNo ratings yet
- WHO CDS HIV 19.8 EngDocument24 pagesWHO CDS HIV 19.8 EngMaykel MontesNo ratings yet
- Symbiosis National Aptitude Test (SNAP) 2004: InstructionsDocument21 pagesSymbiosis National Aptitude Test (SNAP) 2004: InstructionsHarsh JainNo ratings yet
- IUGRDocument4 pagesIUGRMichael Spica RampangileiNo ratings yet
- Friedman LawsuitDocument12 pagesFriedman LawsuitChris GothnerNo ratings yet
- Tugas, MO - REVIEW JURNAL JIT - Ikomang Aditya Prawira Nugraha (1902612010304)Document12 pagesTugas, MO - REVIEW JURNAL JIT - Ikomang Aditya Prawira Nugraha (1902612010304)MamanxNo ratings yet
- Excellent Inverters Operation Manual: We Are Your Excellent ChoiceDocument71 pagesExcellent Inverters Operation Manual: We Are Your Excellent ChoicephaPu4cuNo ratings yet
- OrthoDocument22 pagesOrthosivaleela gNo ratings yet
- The Role of Financial System in DevelopmentDocument5 pagesThe Role of Financial System in DevelopmentCritical ThinkerNo ratings yet
- Amor Vs FlorentinoDocument17 pagesAmor Vs FlorentinoJessica BernardoNo ratings yet
- Parwati DeviDocument25 pagesParwati DevikvntpcsktprNo ratings yet
- Confidential Recommendation Letter SampleDocument1 pageConfidential Recommendation Letter SamplearcanerkNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System Unit ExamDocument3 pagesEndocrine System Unit ExamCHRISTINE JULIANENo ratings yet
- PlayDocument121 pagesPlayellennelleNo ratings yet
- Not For Profit Governance WeilDocument224 pagesNot For Profit Governance WeillkjhmnvbNo ratings yet
- Customer Refund: Responsibility: Yodlee US AR Super User Navigation: Transactions TransactionsDocument12 pagesCustomer Refund: Responsibility: Yodlee US AR Super User Navigation: Transactions TransactionsAziz KhanNo ratings yet
- Character Sketch of Elizabeth BennetDocument2 pagesCharacter Sketch of Elizabeth BennetAiman AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three: Research MethodologyDocument3 pagesChapter Three: Research MethodologyEng Abdulkadir MahamedNo ratings yet
- Arsu and AzizoDocument123 pagesArsu and AzizoZebu BlackNo ratings yet
- Measure For Measure AngeloDocument1 pageMeasure For Measure AngeloRoger Knight100% (1)
- Lecture 6Document7 pagesLecture 6Shuja MirNo ratings yet