Professional Documents
Culture Documents
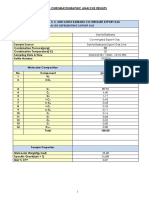
Definition of Separation Problem: Table 1. Molar Flowrate of Each Feed Component
Uploaded by
christinaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Definition of Separation Problem: Table 1. Molar Flowrate of Each Feed Component
Uploaded by
christinaCopyright:
Available Formats
Definition of Separation Problem
Table 1. Molar flowrate of each feed component
Component molar
Component
flowrate (mol/s)
CO2 17331.26
N2 30.73
C1 914.09
C2 336.06
C3 291.89
i-C4 42.25
n-C4 111.38
i-C5 40.33
n-C5 42.25
C6 30.73
C7 + 23.04
H2S 9.60
Total 19203.61
In this project, three alternative schemes to produce different streams of a C1-rich fuel, a
recycle CO2 and H2S-free natural gas of C2+ hydrocarbons will be established. Carbon dioxide
reduces the gas heating value of natural gas and in concentrations of more than 2% or 3 % the
gas is unmarketable. Sulfuric acid is an extremely toxic gas that is also tremendously corrosive to
equipment (Metrohm, 2015). Sweetening processes remove these contaminants so that the gas is
marketable and suitable for transportation. Calculations are done under the assumption that each
operation has achieved steady state. The sets of key separation equipment for each scheme are to
be specified and accordingly described. Moreover, an approximate material balance, using data
from literature, is to be given for each stream. The pros and cons of each process scheme are also
to be discussed.
You might also like
- Introduction To Environmental Eng - Gilbert M. Masters & Wendell P. ElaDocument1,568 pagesIntroduction To Environmental Eng - Gilbert M. Masters & Wendell P. Elamhbenne67% (60)
- ENCH607-ENPE625 Assignment-03 Fall 2020Document3 pagesENCH607-ENPE625 Assignment-03 Fall 2020Ghost RiderNo ratings yet
- Connector Quick Reference Guide: Detail E Beneath LH SeatDocument2 pagesConnector Quick Reference Guide: Detail E Beneath LH SeatАндрей Маркин100% (1)
- Flash Gas Compressor Package-TechnicalDocument18 pagesFlash Gas Compressor Package-Technicalsamuel100% (2)
- MixingDocument11 pagesMixingchristinaNo ratings yet
- ERT 317 Biochemical Engineering Tutorial 1 CalculationsDocument3 pagesERT 317 Biochemical Engineering Tutorial 1 CalculationschristinaNo ratings yet
- Construction of Phase DiagramDocument5 pagesConstruction of Phase DiagramSwagata SahaNo ratings yet
- Netralizer Koil JozDocument44 pagesNetralizer Koil JozPradika WibowoNo ratings yet
- Gas Reservoirs: Abdul Basit Khan 2 0 1 2 - P E T - 3 9Document22 pagesGas Reservoirs: Abdul Basit Khan 2 0 1 2 - P E T - 3 9Sunny BbaNo ratings yet
- Definition of Separation Problem: Table 1. Composition of Natural GasDocument1 pageDefinition of Separation Problem: Table 1. Composition of Natural GaschristinaNo ratings yet
- School of Engineering & Physical Sciences Chemical EngineeringDocument14 pagesSchool of Engineering & Physical Sciences Chemical EngineeringTurkan AliyevaNo ratings yet
- Gas Chromatographic Analysis ResultsDocument3 pagesGas Chromatographic Analysis ResultssterlingNo ratings yet
- Exercise - Gas CalculationDocument1 pageExercise - Gas CalculationZegera MgendiNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/32Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Chemistry 0620/32RamY El NahasNo ratings yet
- BBBBBBBBBBBBBXDocument43 pagesBBBBBBBBBBBBBXTri YaniNo ratings yet
- 7 Fuel Types for ProcessDocument2 pages7 Fuel Types for ProcessDhanny MiharjaNo ratings yet
- LK/HK I Comp: I, F I, D I, B I IDocument13 pagesLK/HK I Comp: I, F I, D I, B I IMuhammad Putra RamadhanNo ratings yet
- LK/HK I Comp: I, F I, D I, B I IDocument21 pagesLK/HK I Comp: I, F I, D I, B I IMuhammad Putra RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Gas ValueDocument3 pagesGas Valuemahi_kotaNo ratings yet
- Metro ViewerDocument5 pagesMetro ViewerSteve WanNo ratings yet
- Appendix D - X + 1 and X + 2 Values For Ions Containing Atoms of C and H Based On Isotope ContributionsDocument1 pageAppendix D - X + 1 and X + 2 Values For Ions Containing Atoms of C and H Based On Isotope ContributionselenitabastosNo ratings yet
- SPE-181168-MS Comparison Between Cyclic Gas Injection and Cyclic Solvent + Gas InjectionDocument8 pagesSPE-181168-MS Comparison Between Cyclic Gas Injection and Cyclic Solvent + Gas Injectioncamilo777No ratings yet
- Sheets ١٢٤٠٠٩Document8 pagesSheets ١٢٤٠٠٩hishamlashennNo ratings yet
- SPE-196758-MS Wag Design: Miscibility Challenge, Tools and Techniques For Analysis, Efficiency AssessmentDocument15 pagesSPE-196758-MS Wag Design: Miscibility Challenge, Tools and Techniques For Analysis, Efficiency AssessmentTrần VyNo ratings yet
- chemistry past paperDocument16 pageschemistry past paper0mentally.untable0No ratings yet
- Harum Rahma Putri p8Document6 pagesHarum Rahma Putri p8Bagus SetiajiNo ratings yet
- Data Aktual Komposisi Feed Gas dan Outlet GasDocument16 pagesData Aktual Komposisi Feed Gas dan Outlet GasAchmadJa'farShodiqShahabNo ratings yet
- Measurement details of utility buildingDocument54 pagesMeasurement details of utility buildingShitanshu SinghNo ratings yet
- Neraca Energi Reaktor Word Kelompok 14Document8 pagesNeraca Energi Reaktor Word Kelompok 14Rani khairaniNo ratings yet
- Edc Biology30 Released Items 2014Document36 pagesEdc Biology30 Released Items 2014Panda Is A BearNo ratings yet
- D Ouble Pitch Attachment Chains: Attach Men T CH Ain SDocument2 pagesD Ouble Pitch Attachment Chains: Attach Men T CH Ain SEcham HamidNo ratings yet
- Preprint - Methods of Stabilization of Gas Condensates PDFDocument10 pagesPreprint - Methods of Stabilization of Gas Condensates PDFمصطفى العباديNo ratings yet
- GPC Mass Balance 2Document1 pageGPC Mass Balance 2Omar WardehNo ratings yet
- Section 16Document15 pagesSection 16Asad KhanNo ratings yet
- Customer Lokasi Koordinat Permintaan X yDocument4 pagesCustomer Lokasi Koordinat Permintaan X yBagus SetiajiNo ratings yet
- Petrosannan Gas Analysis Report 18-1-23Document1 pagePetrosannan Gas Analysis Report 18-1-23hamadaNo ratings yet
- NP Corrosion Management ProcedureDocument11 pagesNP Corrosion Management ProcedureSamira NazeryNo ratings yet
- Table 1-9 Estimated LPG Volume (C Not in Sales Gas or Condensate)Document1 pageTable 1-9 Estimated LPG Volume (C Not in Sales Gas or Condensate)Nirmal SubudhiNo ratings yet
- Conversion and material balancesDocument22 pagesConversion and material balancesحسين الخزاعيNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/42Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/42Renesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Data Reference: Merk: FG-Wilson, Model: P700-1, 2014 Fuel ConsumptionDocument22 pagesData Reference: Merk: FG-Wilson, Model: P700-1, 2014 Fuel ConsumptionIrene 'septiriana'No ratings yet
- Molecular Structure of Calcium, Magnesium, Strontium and Barium M-NitrobenzoatesDocument6 pagesMolecular Structure of Calcium, Magnesium, Strontium and Barium M-NitrobenzoatesNurul HikmahNo ratings yet
- Spe 7477 PaDocument11 pagesSpe 7477 PaRavi SeedathNo ratings yet
- Column Design DataDocument45 pagesColumn Design DataLucas Construction SolutionsNo ratings yet
- Wet Air Volume Composition Dry Air Volume Composition: Volda (1) Volda (2) Volda (3) Volda (4) Volda (5)Document32 pagesWet Air Volume Composition Dry Air Volume Composition: Volda (1) Volda (2) Volda (3) Volda (4) Volda (5)papathsheilaNo ratings yet
- 1 Earth Work in Excavation in Foundation Upto 1.5 Depth COL Footing Taking Extra 300 For Face of RCCDocument12 pages1 Earth Work in Excavation in Foundation Upto 1.5 Depth COL Footing Taking Extra 300 For Face of RCCSajal9474No ratings yet
- Experimental_Investigation_and_ModellingDocument12 pagesExperimental_Investigation_and_ModellingjorgejscarNo ratings yet
- Homework Solutions Chapter 11 2nd AssignmentDocument4 pagesHomework Solutions Chapter 11 2nd AssignmentLija BinuNo ratings yet
- Calculation Sheet For Flares: User Supplied Inputs (Grey Cells)Document1 pageCalculation Sheet For Flares: User Supplied Inputs (Grey Cells)Satria 'igin' Girindra NugrahaNo ratings yet
- PVT AnalysisDocument54 pagesPVT AnalysisAdmirerNo ratings yet
- Complex Engineering Problem Project-1Document19 pagesComplex Engineering Problem Project-1Shehzad khanNo ratings yet
- Design of Drainage SystemDocument9 pagesDesign of Drainage SystemNaung Saw Min HanNo ratings yet
- Footing ConcreteDocument10 pagesFooting ConcreteParthJainNo ratings yet
- T2 - Abastecimiento de Agua y AlcantarilladoDocument1 pageT2 - Abastecimiento de Agua y AlcantarilladoBrianNo ratings yet
- Report Jet Fuel Thermochemical Properties v6Document23 pagesReport Jet Fuel Thermochemical Properties v6Garip GerçeklerNo ratings yet
- Energies 1868825 SupplementaryDocument5 pagesEnergies 1868825 SupplementaryEdmundo Antonio Carrillo VerdugoNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: CHEMISTRY 9701/53Document12 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: CHEMISTRY 9701/53hasanmahamudchistyNo ratings yet
- Determination and Prediction of CO Minimum Miscibility PressuresDocument11 pagesDetermination and Prediction of CO Minimum Miscibility PressuresDarryan DhanpatNo ratings yet
- Fundaciones SP-2 DesignDocument9 pagesFundaciones SP-2 DesignPablo Andrés Sepúlveda MerinoNo ratings yet
- Energies: Miscible CO Flooding For EOR in The Presence of Natural Gas Components in Displacing and Displaced FluidsDocument12 pagesEnergies: Miscible CO Flooding For EOR in The Presence of Natural Gas Components in Displacing and Displaced FluidsMarcellinus SatrioNo ratings yet
- Absorption of CO Unit: Assumption: CO2 Removal in CO2 Absorber 97% Assumption: CO2 Removal in Flash Separtor 99%Document7 pagesAbsorption of CO Unit: Assumption: CO2 Removal in CO2 Absorber 97% Assumption: CO2 Removal in Flash Separtor 99%Muhammad Umer RanaNo ratings yet
- Lampiran PerhitunganDocument15 pagesLampiran PerhitunganAchmadJa'farShodiqShahabNo ratings yet
- Cutting-Edge Technology for Carbon Capture, Utilization, and StorageFrom EverandCutting-Edge Technology for Carbon Capture, Utilization, and StorageKarine Ballerat-BusserollesNo ratings yet
- Semi BatchDocument1 pageSemi BatchchristinaNo ratings yet
- Poblem SetDocument2 pagesPoblem SetchristinaNo ratings yet
- Flow TankDocument2 pagesFlow TankchristinaNo ratings yet
- Flow TankDocument2 pagesFlow TankchristinaNo ratings yet
- Water SupplyDocument3 pagesWater SupplychristinaNo ratings yet
- Key Separation EquipmentDocument1 pageKey Separation EquipmentchristinaNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of DataDocument1 pageEvaluation of DatachristinaNo ratings yet
- Semi BatchDocument1 pageSemi BatchchristinaNo ratings yet
- V Const: 10.1.1 Batch ReactorDocument1 pageV Const: 10.1.1 Batch ReactorchristinaNo ratings yet
- DehydrateDocument3 pagesDehydratechristinaNo ratings yet
- Definition Problem: Metrohm, A.G. Dec 22, 2015Document1 pageDefinition Problem: Metrohm, A.G. Dec 22, 2015christinaNo ratings yet
- Set7 06Document2 pagesSet7 06giyagirlsNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 12 Reaction Diagram & QuestionsDocument4 pagesChemistry 12 Reaction Diagram & QuestionschristinaNo ratings yet
- DupontDocument1 pageDupontchristinaNo ratings yet
- Tower SizingDocument1 pageTower SizingchristinaNo ratings yet
- H Xy Ethanol WaterDocument1 pageH Xy Ethanol WaterchristinaNo ratings yet
- The New Method: Inimum Iquid LowratesDocument9 pagesThe New Method: Inimum Iquid LowrateschristinaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Problem SetDocument1 pageChemical Problem SetchristinaNo ratings yet
- Bioreactor System QuizDocument2 pagesBioreactor System QuizchristinaNo ratings yet
- Figure 8.1-1 PDFDocument1 pageFigure 8.1-1 PDFchristinaNo ratings yet
- Pervaporation PDFDocument7 pagesPervaporation PDFbai tap hoa vo coNo ratings yet
- Metallurgical Extractions - SL - LLDocument37 pagesMetallurgical Extractions - SL - LLRoger RumbuNo ratings yet