Professional Documents
Culture Documents
V Const: 10.1.1 Batch Reactor
Uploaded by
christinaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
V Const: 10.1.1 Batch Reactor
Uploaded by
christinaCopyright:
Available Formats
The typical reactor types in which experiments are performed are:
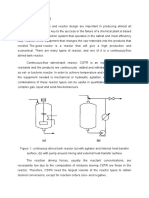
10.1.1 BATCH REACTOR
sampler
V = const
A typical batch reactor ( V = const ) is a vessel of constant volume (i.e., a flask, autoclave, etc.)
into which the reactants are charged at the beginning of the run. The reactor is equipped either with a
cooling/heating coil or jacket, or is well insulated, and can be run isothermally (or close to it) or
adiabatically. A mixer provides for vigorous agitation of the reaction system. The progress of reaction
can be monitored by taking samples of the reaction mixture in specified time intervals and analyzing
their composition, i.e. concentrations of certain components are observed as a function of time. In case
of gas phase reactions, which proceed with the change in the number of moles, the change of the overall
pressure in the system can be monitored in time and tied to reaction progress in case of single reactions.
Another type of batch reactor, which is infrequently used in practice to generate rate data but
which illustrates an important concept to be used later, is the constant pressure batch system where the
volume of the reaction mixture may change in time (i.e. in case of gas phase reactions which proceed
with the change in the total number of moles).
You might also like
- Abstract For CSTR Lab ReportDocument4 pagesAbstract For CSTR Lab ReportNabilah SyaheeraNo ratings yet
- Stirred Tank Reactors in SeriesDocument25 pagesStirred Tank Reactors in SeriesChristopher Emeka Ominyi100% (1)
- MixingDocument11 pagesMixingchristinaNo ratings yet
- Matric NumberDocument3 pagesMatric NumberchristinaNo ratings yet
- PFR Data AnalysisDocument46 pagesPFR Data AnalysisAkk KolNo ratings yet
- Cinética Química UDocument16 pagesCinética Química UJesus Manuel Yallerco VenegasNo ratings yet
- Reactors1 2Document4 pagesReactors1 2Mourad kharbachNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactorDocument5 pagesChemical Reactornevelle4667No ratings yet
- Chemical Processes and Industrial PlantsDocument12 pagesChemical Processes and Industrial Plantskevin mosconiNo ratings yet
- Course NotesDocument20 pagesCourse NotesMARIO ALBERTO LOPEZ MENDOZANo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactorDocument15 pagesChemical ReactorMithelesh KoulNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 - CSTRDocument22 pagesLab 1 - CSTRnur athilahNo ratings yet
- FullDocument33 pagesFullEja RotiKeju100% (2)
- Chemical Reactor2Document5 pagesChemical Reactor2Sohail AsgharNo ratings yet
- Mass Balance PDFDocument8 pagesMass Balance PDFssfoodtechNo ratings yet
- 3.0 Introduction and TheoryDocument3 pages3.0 Introduction and Theorynur effendy bin omarNo ratings yet
- CRE Lab ManualDocument19 pagesCRE Lab ManualMayursinh Solanki100% (1)
- Types of Reactor2Document4 pagesTypes of Reactor2Aleem AhmedNo ratings yet
- Assignment Reactor 1Document14 pagesAssignment Reactor 1DilaFirizqinaNo ratings yet
- Dynamics and Control of Recycle Systems. 2. Comparison Alternative Process DesignsDocument11 pagesDynamics and Control of Recycle Systems. 2. Comparison Alternative Process DesignsJean Pierre León BravoNo ratings yet
- First Page PDFDocument1 pageFirst Page PDFSpNo ratings yet
- Batch ReactorDocument4 pagesBatch ReactorHarini BugattiveyronNo ratings yet
- 1.1 AbstractDocument25 pages1.1 AbstractZati TarhiziNo ratings yet
- Batch ReactorDocument9 pagesBatch ReactorKy ChangNo ratings yet
- BNBBHBHBHJBJHDocument25 pagesBNBBHBHBHJBJHZati TarhiziNo ratings yet
- CSTR MurphyDocument24 pagesCSTR MurphyMurphy MofeNo ratings yet
- PFR ReactorDocument19 pagesPFR Reactorkhairi100% (1)
- Chemical ReactorDocument2 pagesChemical ReactorMagesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Plug Flow ReactorDocument16 pagesPlug Flow Reactormirdza94No ratings yet
- Types: Chemical ReactorDocument3 pagesTypes: Chemical ReactorVeni DwiNo ratings yet
- Overview of Chemical Reaction EngineeringDocument7 pagesOverview of Chemical Reaction EngineeringMuhammad kalimullahNo ratings yet
- Chapter One 1.1. BackgroundDocument16 pagesChapter One 1.1. Backgroundchisom100% (1)
- Stirred Tank ReactorDocument32 pagesStirred Tank ReactorChristopher Emeka Ominyi100% (1)
- Plug Flow Reactor ModelDocument4 pagesPlug Flow Reactor ModelMagesh kumarNo ratings yet
- CSTR 40LDocument11 pagesCSTR 40LSeiji Kyousei100% (1)
- Dependence of The Kinetics of The Low-Temperature Water-Gas Shift Reaction On The Catalyst Oxygen Activity As Investigated by Wavefront AnalysisDocument12 pagesDependence of The Kinetics of The Low-Temperature Water-Gas Shift Reaction On The Catalyst Oxygen Activity As Investigated by Wavefront AnalysisAnonymous uCYIu1No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Chemical EngineeringDocument40 pagesLecture Notes Chemical Engineeringkrishnaswamy9No ratings yet
- Tutorial ReactorDocument4 pagesTutorial ReactorThinesh BoltNo ratings yet
- Plug Flow Reactor NotesDocument4 pagesPlug Flow Reactor Notesahmad pidotNo ratings yet
- Cstr-Experiment 2Document7 pagesCstr-Experiment 2Dhiyyah MardhiyyahNo ratings yet
- Liquid Phase ReactorDocument22 pagesLiquid Phase Reactorkrishy19s100% (2)
- CHPR5501 Adv. Reaction Eng. Part 1Document40 pagesCHPR5501 Adv. Reaction Eng. Part 1Elena TodorovskaNo ratings yet
- Flow ChemistryDocument6 pagesFlow Chemistryrr1819No ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Ideal Plug Flow Reactors Design: by Dr. Ramesh RedrouthuDocument25 pagesChapter 3: Ideal Plug Flow Reactors Design: by Dr. Ramesh RedrouthuTsega IsraelNo ratings yet
- P F RDocument4 pagesP F RMohamed Ragab MohamedNo ratings yet
- CRE - Solid Catalyzed ReactionDocument47 pagesCRE - Solid Catalyzed Reactionandono kusuma jatiNo ratings yet
- Batch Reactor: Optical High Precision Components by Hellma in The European Columbus Space LaboratoryDocument16 pagesBatch Reactor: Optical High Precision Components by Hellma in The European Columbus Space Laboratoryangelie_gubatanNo ratings yet
- Experimental Methods in Catalytic KineticsDocument13 pagesExperimental Methods in Catalytic Kineticsmarcos carrilloNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Process Design: Mody and Marchildon: Chapter 19 Chemical ReactionDocument11 pagesChemical Engineering Process Design: Mody and Marchildon: Chapter 19 Chemical ReactionMoro SalifuNo ratings yet
- Tubular Flow Reactor ReportDocument19 pagesTubular Flow Reactor ReportN Afiqah Razak100% (1)
- Tubular Flow Reactor Sample UiTM Lab ReportDocument20 pagesTubular Flow Reactor Sample UiTM Lab ReportNur AqilahNo ratings yet
- Types of ReactorsDocument5 pagesTypes of ReactorsPl ElectricalNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Methods of Analysis: Chapter 15 - 1Document9 pagesKinetic Methods of Analysis: Chapter 15 - 1natsdorfNo ratings yet
- Full ReportDocument27 pagesFull ReportmnizamarzukiNo ratings yet
- Kinetics of Homogeneous ReactionDocument56 pagesKinetics of Homogeneous ReactionSahel SahraeeNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Catalytic ProcessesDocument33 pagesSimulation of Catalytic ProcessesAkhi Sofi100% (4)
- Conservation of Mass Mass Flows Conservation Law MatterDocument8 pagesConservation of Mass Mass Flows Conservation Law MatterJef PerezNo ratings yet
- The Modeling of Chemical Reactors Chapter 7Document17 pagesThe Modeling of Chemical Reactors Chapter 7ManoakiNo ratings yet
- Batch and Semi-batch Reactors: Practical Guides in Chemical EngineeringFrom EverandBatch and Semi-batch Reactors: Practical Guides in Chemical EngineeringNo ratings yet
- An Introduction to the Neutron Kinetics of Nuclear Power Reactors: Nuclear Engineering DivisionFrom EverandAn Introduction to the Neutron Kinetics of Nuclear Power Reactors: Nuclear Engineering DivisionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Physico-Chemistry of Solid-Gas Interfaces: Concepts and Methodology for Gas Sensor DevelopmentFrom EverandPhysico-Chemistry of Solid-Gas Interfaces: Concepts and Methodology for Gas Sensor DevelopmentNo ratings yet
- Working Guide to Vapor-Liquid Phase Equilibria CalculationsFrom EverandWorking Guide to Vapor-Liquid Phase Equilibria CalculationsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Semi BatchDocument1 pageSemi BatchchristinaNo ratings yet
- Definition Problem: Metrohm, A.G. Dec 22, 2015Document1 pageDefinition Problem: Metrohm, A.G. Dec 22, 2015christinaNo ratings yet
- Definition of Separation Problem: Table 1. Molar Flowrate of Each Feed ComponentDocument1 pageDefinition of Separation Problem: Table 1. Molar Flowrate of Each Feed ComponentchristinaNo ratings yet
- Definition of Separation Problem: Table 1. Composition of Natural GasDocument1 pageDefinition of Separation Problem: Table 1. Composition of Natural GaschristinaNo ratings yet
- Key Separation EquipmentDocument1 pageKey Separation EquipmentchristinaNo ratings yet
- CHM PracticeDocument4 pagesCHM PracticechristinaNo ratings yet
- The New Method: Inimum Iquid LowratesDocument9 pagesThe New Method: Inimum Iquid LowrateschristinaNo ratings yet
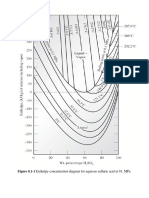
- Figure 8.1-1 PDFDocument1 pageFigure 8.1-1 PDFchristinaNo ratings yet