Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Calibration of Precision Measuring Instruments
Uploaded by
elavarasanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Calibration of Precision Measuring Instruments
Uploaded by
elavarasanCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
CALIBRATION OF PRECISION MEASURING
INSTRUMENTS
Aim:
To study and calibrate the precision measuring instruments like Vernier caliper,
Micrometer, and Dial gauge.
Apparatus Required:
Surface plate, Vernier caliper, Micrometer, Dial gauge, and Slip gauges.
Specification:
Vernier caliper Range: L. C:
Micrometer Range: L. C:
Dial gauge Range: L. C:
STUDY:
1.) Vernier caliper:
The Vernier caliper has one L shaped frame with a fixed jaw on which Vernier scale is
attached. The principle of Vernier is that when two scale divisions slightly different in sizes can
be used to measure the length very accurately.
Least Count is the smallest length that can be measured accurately and is equal to the
difference between a main scale division and a Vernier scale division.
LEAST COUNT = 1 Main scale division 1 Vernier scale division
Uses:
It is used to measure the external diameter, the internal diameter and the length of the
given specimen.
2.) Micrometer:
The micrometer has an accurate screw having about 10 to 20 threads/cm and revolves in
a fixed nut. The end of the screw is one tip and the other is constructed by a stationary anvil.
LEAST COUNT = Pitch scale division / Number of threads
Pitch scale division = Distance moved / number of rotation
Uses:
Outside micrometer is used to measure the diameter of solid cylinder.
Inside micrometer is used to measure the internal diameters of hollow cylinders and
spheres.
3.) Dial gauge:
The dial gauge has got 2 hands. The short hand reads in mm. One complete
revolution of long hand reads one mm. The plunger of the dial gauge has to be placed on the
surface whose dimension has to be read.
Least Count = One division of the circular scale with long hand.
Uses:
It is used as a mechanical comparator.
4.) Slip gauges:
They are rectangular blocks hardened and carefully stabilized. The surfaces are highly
polished to enhance wringing. It is used as a reference standard for transferring the dimensions of
unit of length from primary standard. It is generally made up of high carbon, high chromium
hardened steel.
Uses:
These are accurate and used as comparator.
5.) Surface plate:
The foundation of all geometric accuracy and indeed of all dimensional measurement in
workshop is surface plate. It is a flat smooth surface sometimes with leveling screws at the
bottom.
Uses:
It is used as a base in all measurements.
PROCEDURE FOR CALIBRATION:
1.) The range of the instruments is noted down.
2.) Within that range, slip gauges are selected.
3.) The measuring instrument is placed on the surface plate and set for zero and the slip
gauges are placed one by one between the measuring points (jaws of the instruments.)
4.) The slip gauge (actual) readings and the corresponding (observed) readings in the
measuring instruments are noted down and tabulated.
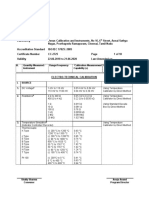
Slip Precision Measuring Instruments Reading (Observedl) in mm
Gauge Vernier Caliper Micro Meter Dial Gauge
S.No Reading
MSR VSR TR Error PSR HSR TR Error SHR LHR TR Error
(Actual)
(mm) (div) (mm) (mm) (mm) (div) (mm) (mm) (mm) (div) (mm) (mm)
In mm
1
2
.
.
10
Result:
The precision measuring instruments are studied and calibrated.
Calibration graphs are then drawn for all measuring instruments between
1.) Actual value and Observed value.
2.) Actual value and Absolute error.
You might also like
- Experiment Measurement of Lengths, Heights, Diameters, Vernier CaliperDocument11 pagesExperiment Measurement of Lengths, Heights, Diameters, Vernier Caliperv sharvan kumar asst.prof(mech)No ratings yet
- Lab 2 MM322 Final ReportDocument8 pagesLab 2 MM322 Final ReportJnrNo ratings yet
- Micrometers Calipers Worksheet PDFDocument4 pagesMicrometers Calipers Worksheet PDFanon_404586944No ratings yet
- Route TrainingDocument14 pagesRoute Trainingjohn100% (1)
- Calibration of Precision Measuring InstrumentsDocument2 pagesCalibration of Precision Measuring Instrumentsabddul128No ratings yet
- Metrology Lab ManualDocument39 pagesMetrology Lab ManualNivedh Vijayakrishnan0% (1)
- ME2308 Lab ManualDocument28 pagesME2308 Lab ManualNishanth ShannmugamNo ratings yet
- MME-ME2308 EMM Lab ManualDocument29 pagesMME-ME2308 EMM Lab ManualRakesh Kumar100% (1)
- Metrology and Measurements Lab Manual: V Semester Mechanical Engineering Rajalakshmi Engineering CollegeDocument30 pagesMetrology and Measurements Lab Manual: V Semester Mechanical Engineering Rajalakshmi Engineering CollegeSanju JohnNo ratings yet
- Unit-Ii 3Document30 pagesUnit-Ii 3k.ghanemNo ratings yet
- Index: Ex. No Name of The Experiment Page No. Cycle IDocument29 pagesIndex: Ex. No Name of The Experiment Page No. Cycle Iprakashrs295No ratings yet
- MLR Institute of Technology - Lab Manual Engineering MetrologyDocument25 pagesMLR Institute of Technology - Lab Manual Engineering MetrologyVallik TadNo ratings yet
- Vernier CaliperDocument3 pagesVernier CaliperAndrew Crawford0% (1)
- Metrology Lab Manual NewDocument41 pagesMetrology Lab Manual Newg venkatesh100% (1)
- Study of Measuring Instruments and Gauges PDFDocument7 pagesStudy of Measuring Instruments and Gauges PDFRishabh HanseliaNo ratings yet
- MetrologyDocument157 pagesMetrologyVishwajit HegdeNo ratings yet
- ME2308 Lab ManualDocument28 pagesME2308 Lab Manualvenkateshyadav2116No ratings yet
- 1 Measuring Instruments and GaugesDocument59 pages1 Measuring Instruments and GaugesWbamlak AshebrNo ratings yet
- Metrology Lab ManualDocument35 pagesMetrology Lab ManualNo NameNo ratings yet
- Metrology and Surface Engineering Lab Manual: 3 Year B.Tech I-Semester Mechanical EngineeringDocument22 pagesMetrology and Surface Engineering Lab Manual: 3 Year B.Tech I-Semester Mechanical EngineeringKptt LogeswaranNo ratings yet
- Metrology Lab Exercise2Document87 pagesMetrology Lab Exercise2Hailu Yimer TeferaNo ratings yet
- ME8501 - Metrology and Measurements - Unit - IIDocument77 pagesME8501 - Metrology and Measurements - Unit - IIarunpdcNo ratings yet
- 1537326530linear & Angular MeasurementDocument49 pages1537326530linear & Angular MeasurementAl MamunNo ratings yet
- Linear Measurements: References: 1. Handbok of Dimensional Measurement 2. Http://fetweb - Ju.edu - Jo/staff/me/jyaminDocument70 pagesLinear Measurements: References: 1. Handbok of Dimensional Measurement 2. Http://fetweb - Ju.edu - Jo/staff/me/jyaminRodel VerzosaNo ratings yet
- Me TrologyDocument34 pagesMe Trologysiddharth thoratNo ratings yet
- University of North Carolina ManualDocument11 pagesUniversity of North Carolina ManualvysnktNo ratings yet
- METROLOGY AND QUALITY CONTROL LAB Manual PDFDocument28 pagesMETROLOGY AND QUALITY CONTROL LAB Manual PDFMuhammad zubeen100% (1)
- MMM Lab ManualDocument13 pagesMMM Lab ManualSangam PatilNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity No. 2Document4 pagesLaboratory Activity No. 2Me Being RandomNo ratings yet
- Vernier Calipers & MicrometrsDocument14 pagesVernier Calipers & Micrometrsفتى الجحيمNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual: Machining Processes and Metrology Lab (MEE211L)Document27 pagesLab Manual: Machining Processes and Metrology Lab (MEE211L)Agnivesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Me 2308 - Metrology & Measurements Lab: Infant Jesus College of Engineering and TechnologyDocument31 pagesMe 2308 - Metrology & Measurements Lab: Infant Jesus College of Engineering and TechnologyNeopoleanNo ratings yet
- Metrology-Lab-Manual 3 Year 1semDocument41 pagesMetrology-Lab-Manual 3 Year 1semBHARATH Chandra100% (1)
- Lab ManualDocument19 pagesLab ManualAjij Mujawar100% (1)
- BTM2133-Chapter 4 Measuring InstrumentsDocument61 pagesBTM2133-Chapter 4 Measuring InstrumentsAswaja3130% (1)
- Expt 1 - Calibration of Vernier CaliperDocument5 pagesExpt 1 - Calibration of Vernier Calipersathyadally100% (1)
- Metrology Lab Manual - BrijeshDocument23 pagesMetrology Lab Manual - BrijeshRohitGuptaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Measurement LaboratoryDocument24 pagesMechanical Measurement LaboratoryMahendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Final MM&M Lab ManualDocument66 pagesFinal MM&M Lab Manualchandrarao chNo ratings yet
- Metrology Uniit IIDocument53 pagesMetrology Uniit IIrramesh2k8712No ratings yet
- MQA Lab Manual 2018-2019Document27 pagesMQA Lab Manual 2018-2019poluri manicharanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Precision Measuring InstrumentDocument13 pagesChapter 3 Precision Measuring InstrumentAIDA SYAHIRAH BINTI SULAIMAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Vernier CaliperDocument13 pagesVernier CaliperAbdul AhadNo ratings yet
- Measuring Instruments LectureDocument35 pagesMeasuring Instruments LectureMAHESH SINGH100% (1)
- Linear & Angular MeasurementsDocument110 pagesLinear & Angular Measurementsavutu_kunduruNo ratings yet
- Linear & Angular Measurement: Course ContentsDocument26 pagesLinear & Angular Measurement: Course ContentsRamu VasaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02Document110 pagesLecture 02Getachew G/AmlakNo ratings yet
- Dimensional Measurements: Group 22 MembersDocument12 pagesDimensional Measurements: Group 22 MemberscfellowNo ratings yet
- Metrology: Nri Institute of TechnologyDocument55 pagesMetrology: Nri Institute of TechnologyKasijanto JantoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Metrology InstrumentsDocument17 pagesEngineering Metrology InstrumentsAnilChauvanNo ratings yet
- 2-Excercise EM 2023Document49 pages2-Excercise EM 2023aimy rouaneNo ratings yet
- Abestano PHY052 1 Activity 1 Measurement of LengthDocument10 pagesAbestano PHY052 1 Activity 1 Measurement of LengthLOREN MAE BULAYBULAYNo ratings yet
- ME 472 - Engineering Metrology and Quality Control: Linear and Angular MeasurementsDocument19 pagesME 472 - Engineering Metrology and Quality Control: Linear and Angular MeasurementsAtul GaurNo ratings yet
- Ensc 102L Lab ExperimentsDocument19 pagesEnsc 102L Lab ExperimentsgapuzsawalNo ratings yet
- Physics ExperimentDocument9 pagesPhysics ExperimentgapuzsawalNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Instruments For MeasurementDocument12 pagesMechanical Instruments For MeasurementLiviu AndreiNo ratings yet
- Lec 3 Precision Measuring Instrument PDFDocument20 pagesLec 3 Precision Measuring Instrument PDFUmair MalikNo ratings yet
- ME 472 - Engineering Metrology and Quality Control: Linear and Angular MeasurementsDocument19 pagesME 472 - Engineering Metrology and Quality Control: Linear and Angular MeasurementsAniket SankpalNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Mechanical and Materials EngineeringFrom EverandHandbook of Mechanical and Materials EngineeringRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Instrument Technology: Measurement of Pressure, Level, Flow and TemperatureFrom EverandInstrument Technology: Measurement of Pressure, Level, Flow and TemperatureRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Position Sensing: Angle and Distance Measurement for EngineersFrom EverandPosition Sensing: Angle and Distance Measurement for EngineersNo ratings yet
- Confined Space EntryDocument1 pageConfined Space EntryelavarasanNo ratings yet
- 1.tool Makers MicroscopeDocument7 pages1.tool Makers MicroscopeelavarasanNo ratings yet
- ActuatorsDocument3 pagesActuatorselavarasanNo ratings yet
- To Measure Gear Parameter by Gear Tooth VernierDocument3 pagesTo Measure Gear Parameter by Gear Tooth VernierelavarasanNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3Document3 pagesExperiment 3elavarasanNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Dimensions of A Given Specimen Using Slip Gauge AimDocument1 pageMeasurement of Dimensions of A Given Specimen Using Slip Gauge AimelavarasanNo ratings yet
- To Measure The Angles of Given Specimen Using Bevel ProtractorDocument3 pagesTo Measure The Angles of Given Specimen Using Bevel ProtractorelavarasanNo ratings yet
- Part B (2) 1.4.15Document229 pagesPart B (2) 1.4.15elavarasanNo ratings yet
- Metrology Lab ManualDocument21 pagesMetrology Lab ManualelavarasanNo ratings yet
- Sl. Quantity Measured / Instrument Range/Frequency Calibration Measurement Capability ( ) RemarksDocument26 pagesSl. Quantity Measured / Instrument Range/Frequency Calibration Measurement Capability ( ) RemarksBALAJINo ratings yet
- 112.scope Location 1 CC-2725Document10 pages112.scope Location 1 CC-2725Ravichandran DNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Lab EquipmentDocument23 pagesLesson 2 Lab EquipmentMarvin De JonggoyNo ratings yet
- Industrial InstrumentationDocument2 pagesIndustrial InstrumentationAbhijeeth BabuNo ratings yet
- 212MM212MMCH95Document26 pages212MM212MMCH95Diana Carolina Beltran PeñaNo ratings yet
- Lab Equipment Crossword Puzzle ANSWER KEYDocument2 pagesLab Equipment Crossword Puzzle ANSWER KEYDarla Milagros Choque EstradaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 MicrosDocument8 pagesModule 1 MicrosmagwiNo ratings yet
- TS 0071Document1 pageTS 0071Coop StElzearNo ratings yet
- Anemometer, Humidity Light Meter, Thermometer: Model: LM-8000Document2 pagesAnemometer, Humidity Light Meter, Thermometer: Model: LM-8000Mihwan SataralNo ratings yet
- CCR Equipment ListDocument1 pageCCR Equipment Listbehzad parsiNo ratings yet
- اجهزة قياس الضغطDocument3 pagesاجهزة قياس الضغطmarran almarranyNo ratings yet
- MM322 LabDocument8 pagesMM322 LabJnrNo ratings yet
- Vernier CaliperDocument10 pagesVernier CaliperIMade Adi WiadnyanaNo ratings yet
- Pitot-Static System Quiz Answer KeyDocument2 pagesPitot-Static System Quiz Answer KeyArchaios Drakos100% (1)
- WorldwideCheckList PDFDocument790 pagesWorldwideCheckList PDFTHSNo ratings yet
- Store Requisition (SR) : Approval SubjectDocument3 pagesStore Requisition (SR) : Approval SubjectDagim atnafuNo ratings yet
- Mechanical MeasurementsDocument3 pagesMechanical MeasurementsneerubandaNo ratings yet
- Syll Ei8452 Industrial InstrumentationDocument7 pagesSyll Ei8452 Industrial InstrumentationLokesh GopinathNo ratings yet
- Me2304 - Engineering Metrology and Measurements Question Bank For Regulation 2008Document29 pagesMe2304 - Engineering Metrology and Measurements Question Bank For Regulation 2008Ashok Kumar Rajendran75% (4)
- ASN TemplateDocument430 pagesASN TemplateMahbub UzzamanNo ratings yet
- SBRP - Rnav Esmiv 1d - Astob 1d - Haste 1d - Nilsu 1d - Pir 1d - Repax 1d - Tenik 1d Rwy 36 - Sid - 20230420Document1 pageSBRP - Rnav Esmiv 1d - Astob 1d - Haste 1d - Nilsu 1d - Pir 1d - Repax 1d - Tenik 1d Rwy 36 - Sid - 20230420Luiz Paulo MazzuccaNo ratings yet
- Eim Quiz TesterDocument3 pagesEim Quiz Testerbernie evaristo bacsaNo ratings yet
- Kuliah Sistem Pembangkit Tenaga IDocument24 pagesKuliah Sistem Pembangkit Tenaga ISurya FrederickNo ratings yet
- Kewrkmia PDF 1706372569Document22 pagesKewrkmia PDF 1706372569bielpwkNo ratings yet
- Instrument Calibration SheetDocument1 pageInstrument Calibration SheetirfanNo ratings yet
- Tle Reviewer Pt. 4Document4 pagesTle Reviewer Pt. 4Anonymous lnq6NlgaMNo ratings yet
- AnaumDocument22 pagesAnaumAsghar AliNo ratings yet
- Microscopes in LabsDocument31 pagesMicroscopes in LabsGabscoline BurellNo ratings yet