Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Design, Development and Characterization of Nanoemulsion Containing Rutin For Nose To Brain Delivery
Uploaded by
Sagar kishor savaleOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Design, Development and Characterization of Nanoemulsion Containing Rutin For Nose To Brain Delivery
Uploaded by
Sagar kishor savaleCopyright:
Available Formats
Design, Development and Characterization of Nanoemulsion Containing Rutin for Nose to Brain delivery
Mr. Sagar Kishor Savale (Department of Pharmaceutics)
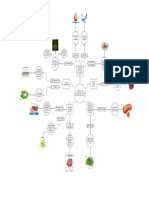
Introduction Optimized batch results
In the present investigation, Rutin-loaded Nanoemulsion(RU-NE) were prepared to enhancing CNS delivery for the
treatment of brain tumor. RU is highly lipophilic drug having a low oral bioavailability of 4%. RU-NE were prepared by
Spontaneous emulsification method with Ethyl Oleate, Tween 80 and Polyethylene glycol 400 as a Oil, surfactant and co-
surfactant respectively. Response surface methodology (RSM) using the central composite rotatable design (CCRD) model
was used. Three independent factors such as Oil concentration (X1), Surfactant Concentration (X2), Co-surfactant
concentration (X3) were used. Parameters investigated include dependant factors Droplet size, and Drug Content. RU-NE
were formulated and characterized by Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and Transmission electron microscopy
(TEM). The optimized RU-NE were transparent appearance, thermodynamically stable with average droplet size of 228.60
nm and % drug content of 94.77 %. The In vitro and ex vivo release studies of optimised NEs were conducted. Accelerated
stability studies showed that there was no significant change in the mean droplet size and % drug content after storage at Figure 3: In vitro drug release profile Figure 4: ex vivo drug release profile of
25 2C/60 5% RH for the period of three months, thus demonstrating a promising perspective for nose to brain of RU-NE (n=3, mean SD) RU-NE (n=3, mean SD)
delivery of poorly water-soluble RU. pH 6.4 simulated Formulation Iso propyl alc.
Methodology
1 Selection of drug delivery system, drug and excipients
Preformulation study
2 Figure 5: Histopathological Study On Sheep Nasal Mucosa
Experimental design by Central composite rotatable design
3
Accelerated stability studies
4 Formulation of NE by Spontaneous emulsification technique
Table 2: Stability study of RU-NE in terms of Droplet size, PDI and %
5 Characterization and evaluation of prepared RU-NE Drug content (mean SD, n=3)
Formulation of optimized batch Stability Test period
6
parameter
7 In vitro diffusion studies and In vitro Cytotoxicity studies 0 month 1 month 2 month 3 months
ex vivo study MDS (nm) 2280.027 229.6 1.80 229.4 0.03 230.1 0.013
8
PDI 0.189 0.89 0.197 1.83 0.195 0.92 0.262 1.045
9 Solid state characterization (TEM, DSC and IR) % DC 94.72 1.14 92.02 0.41 90.98 1.05 90.98 1.05
10 Accelerated stability studies Conclusion
Nose to Brain delivery In this Nano-drug delivery system, RU is successfully incorporated
Formulation Batches into NE by Spontaneous emulsification method with high drug
content due to its high lipophilicity. The RU-NE were formulated
Table 1: Formulation batches by CCRD-RSM design & Result Analysis using central composite response surface methodology by fitting
Sr. Con. Of oil Con. Of Con. Of Droplet Drug quadratic model to the response data. The results shows that drug
No (mcl) Surfactant (ml) Cosurfactant (ml) size Content
loaded Nanoemulsion for intranasal is very a promising approach for
delivering drug to CNS for the treatment of brain tumour.
(nm) (%)
1 200 1.00 7 239.47 90.08 Future Perspectives
2 200 1.00 9 228.60 94.77
Future studies of RU-NE should aim to address a number of challenges such
3 200 0.50 7 352.50 55.65
as Preclinical and clinical studies in relevant to animal models should be
4 200 0.50 9 250.15 88.90 Response surface plots by the Design
performed. Clinical Study in cancer infected patient Long- term toxicity
5 180 1.00 9 275.40 71.55 Expert software
6 180 1.00 7 316.69 58.00 studies should be carried out beyond proof- of-concept studies. Long-term
A)RSM showing the effect of the concentration of
7 180 0.50 7 412.58 43.96 total Oil & Smix on Droplet size storage stability is also requires for clinical application. After performing all
B)RSM showing the effect of the concentration of
8 180 0.50 9 300.01 60.61 these studies, in near future, RU-NE will Be the king of pharmaceutical
total Oil & Smix on Drug Content
market.
Solid state characterization
A B
Reference
1. Sagar K. savale. 2015. A Review - Self Nanoemulsifying Drug Delivery
System (SNEDDS). International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical
and Nano Sciences, 4(6), pp.385-397.
2. Sagar Savale, et al. 2017. Nose to Brain: A versatile mode of drug
delivery system. Asian Journal of Biomaterial Research, 3(1), pp. 16-38.
Figure 1: DSC: A: Rutin , B: Physical Figure 2: TEM of RU-NE
mixture & C: Rutin NE Formulation
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- How To Boost Immune System Against Covid-19 InfectionsDocument18 pagesHow To Boost Immune System Against Covid-19 InfectionsSagar kishor savaleNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Corona Virus (Signs and Symptoms, Diagnosis, Basic Protective Measures Against The New Coronavirus, Drugs Used For Treatment)Document13 pagesCorona Virus (Signs and Symptoms, Diagnosis, Basic Protective Measures Against The New Coronavirus, Drugs Used For Treatment)Sagar kishor savaleNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- VitaminsDocument13 pagesVitaminsSagar kishor savaleNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Drug Release KineticsDocument51 pagesDrug Release KineticsSagar kishor savale80% (5)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Bulk and Tapped Density: A OverviewDocument5 pagesBulk and Tapped Density: A OverviewSagar kishor savaleNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Dissolution: How To Calculate Dissolution Calculation in Excel SheetDocument6 pagesDissolution: How To Calculate Dissolution Calculation in Excel SheetSagar kishor savaleNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- UV Spectrophotometric Method Development and Validation For Quantitative Estimation of MebendazoleDocument5 pagesUV Spectrophotometric Method Development and Validation For Quantitative Estimation of MebendazoleSagar kishor savaleNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Out of Specification (OOS) and Out of Trend (OOT) Analysis in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Investigations (MIR) : A OverviewDocument8 pagesOut of Specification (OOS) and Out of Trend (OOT) Analysis in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Investigations (MIR) : A OverviewSagar kishor savale100% (2)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Arc Reactor TechnologyDocument7 pagesArc Reactor TechnologySagar kishor savale100% (1)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- In Process Quality Control Tests (IPQC) For Parenteral or Sterile Dosage FormsDocument26 pagesIn Process Quality Control Tests (IPQC) For Parenteral or Sterile Dosage FormsSagar kishor savale100% (1)
- Dissolution How To Calculate Dissolution Calculation in Excel Sheet PDFDocument6 pagesDissolution How To Calculate Dissolution Calculation in Excel Sheet PDFSagar kishor savaleNo ratings yet
- Dissolution How To Calculate Dissolution Calculation in Excel Sheet PDFDocument6 pagesDissolution How To Calculate Dissolution Calculation in Excel Sheet PDFSagar kishor savaleNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Dissolution How To Calculate Dissolution Calculation in Excel Sheet PDFDocument6 pagesDissolution How To Calculate Dissolution Calculation in Excel Sheet PDFSagar kishor savaleNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Dissolution How To Calculate Dissolution Calculation in Excel Sheet PDFDocument6 pagesDissolution How To Calculate Dissolution Calculation in Excel Sheet PDFSagar kishor savaleNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Elements and Their Atomic WeightsDocument2 pagesElements and Their Atomic WeightsSagar kishor savaleNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Gefitinib Anti-Cancer AgentDocument8 pagesGefitinib Anti-Cancer AgentSagar kishor savaleNo ratings yet
- In-Vivo Brain-Distribution Study in RatsDocument12 pagesIn-Vivo Brain-Distribution Study in RatsSagar kishor savaleNo ratings yet
- In Process Quality Control Tests (IPQC) For Solid Dosage FromDocument28 pagesIn Process Quality Control Tests (IPQC) For Solid Dosage FromSagar kishor savale75% (8)
- Diffusion: How To Calculate Diffusion Calculation in Excel SheetDocument6 pagesDiffusion: How To Calculate Diffusion Calculation in Excel SheetSagar kishor savale100% (1)
- Curcumin Anti-Cancer AgentDocument26 pagesCurcumin Anti-Cancer AgentSagar kishor savaleNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- In Silico SoftwaresDocument11 pagesIn Silico SoftwaresSagar kishor savaleNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Tara GumDocument6 pagesTara GumSagar kishor savaleNo ratings yet
- Calculations in Micro Gram Per Milliliter and Nano Gram Per MilliliterDocument8 pagesCalculations in Micro Gram Per Milliliter and Nano Gram Per MilliliterSagar kishor savaleNo ratings yet
- Glass Making TheoryDocument14 pagesGlass Making TheorySK SHAHNAWAZNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Diverter Valve Wam BrochureDocument4 pagesDiverter Valve Wam BrochureEzequiel Guillermo Trejo NavasNo ratings yet
- Nhat Huy FillerDocument7 pagesNhat Huy FillerLê NhungNo ratings yet
- Kolorsafe Liquid Acid Neutralizer - SDS - NA - 012115 - FINALDocument8 pagesKolorsafe Liquid Acid Neutralizer - SDS - NA - 012115 - FINALJUAN FELIPE ORTIZ PARRANo ratings yet
- Metal DetectorDocument7 pagesMetal DetectorAlexNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Behaviour and Design of Structural Steel PinsDocument28 pagesBehaviour and Design of Structural Steel PinsJoão BarrigóNo ratings yet
- Biology Cells Graphic OrganizerDocument1 pageBiology Cells Graphic OrganizerMaci StackhouseNo ratings yet
- Cooling Towers: Key Design Factors and Operation PrinciplesDocument8 pagesCooling Towers: Key Design Factors and Operation PrinciplesMade PutraNo ratings yet
- Test Report: Noida Testing Laboratories, Noida G T - 20, SECTOR - 117, NOIDA, G. B. NAGAR, U.P., 201 316Document1 pageTest Report: Noida Testing Laboratories, Noida G T - 20, SECTOR - 117, NOIDA, G. B. NAGAR, U.P., 201 316Kushal Sharma0% (1)
- 13 - Chapter 3Document32 pages13 - Chapter 3Wahab Al-QaisiNo ratings yet
- Composite Fish Culture PDFDocument2 pagesComposite Fish Culture PDFHanumant JagtapNo ratings yet
- Turbine Desk OperatorDocument3 pagesTurbine Desk Operatortajshah283No ratings yet
- E. Steam Power Plant - Pe - ExamDocument4 pagesE. Steam Power Plant - Pe - ExamallovidNo ratings yet
- Lighting and AcousticsDocument18 pagesLighting and Acousticsmahira bhatiaNo ratings yet
- Newman Projections (Acyclic - 01)Document3 pagesNewman Projections (Acyclic - 01)Muhammad AliNo ratings yet
- MSDS Mindray M-30 LyseDocument2 pagesMSDS Mindray M-30 LyseSandra HubayaNo ratings yet
- Astm B495 10 2017Document1 pageAstm B495 10 2017shokhul lutfiNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- BC34.1 E9 Determination of Acid Value of FatsDocument3 pagesBC34.1 E9 Determination of Acid Value of FatsGlenn Vincent Tumimbang96% (26)
- Tds 071 Rev 05 Residhere Am 140 SDocument1 pageTds 071 Rev 05 Residhere Am 140 Sاحمد عدنانNo ratings yet
- Practical 3 Amylase Activity in Germinating Barley: (347 Words)Document4 pagesPractical 3 Amylase Activity in Germinating Barley: (347 Words)Carynl LeeNo ratings yet
- Chemical CarcinogenesisDocument24 pagesChemical CarcinogenesisKavitha S DineshNo ratings yet
- Avoid Costly Materials mistakes-CEDocument23 pagesAvoid Costly Materials mistakes-CEManish542No ratings yet
- Manufacture of The Ceramic Tiles and Sanitary: Produced By: Framed byDocument21 pagesManufacture of The Ceramic Tiles and Sanitary: Produced By: Framed byAmina CHAHBOUNINo ratings yet
- Building electricity vocabularyDocument9 pagesBuilding electricity vocabularyChan PhakkdeyNo ratings yet
- Cells and BatteriesDocument3 pagesCells and BatteriesmelissaNo ratings yet
- Types of SewerDocument14 pagesTypes of SewerAmbalal DhongadiNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Revision NotesDocument2 pagesClass 8 Science Chapter 1 Revision NotesShwetabh Aman SinhaNo ratings yet
- Juventas New Catalogue PDFDocument6 pagesJuventas New Catalogue PDFboona mNo ratings yet
- S&T Roofing Solutions Product Guide Mar2018-DP1 0Document12 pagesS&T Roofing Solutions Product Guide Mar2018-DP1 0sattar12345No ratings yet
- Rucofin GWG 200: Composition UsesDocument2 pagesRucofin GWG 200: Composition UsesConsultora2No ratings yet
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Stuff Matters: Exploring the Marvelous Materials That Shape Our Man-Made WorldFrom EverandStuff Matters: Exploring the Marvelous Materials That Shape Our Man-Made WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (289)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)
- Guidelines for Asset Integrity ManagementFrom EverandGuidelines for Asset Integrity ManagementRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction in the Science of Everyday LifeFrom EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction in the Science of Everyday LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)