Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Franck Condon Principle
Uploaded by
Samila Khewa33%(3)33% found this document useful (3 votes)
2K views9 pagesfrank condon principle
Original Title
Franck Condon Principle (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentfrank condon principle
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
33%(3)33% found this document useful (3 votes)
2K views9 pagesFranck Condon Principle
Uploaded by
Samila Khewafrank condon principle
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
Franck Condon Principle
Franck and Condon gave an explanation about the intensity
distribution of the vibrational progression of an electronic
transition.
The intensity distribution of a particular vibrational structure
progression in the electronic absorption spectrum or progression
in the electronic emission spectrum displays different kind of
pattern.
Let us first discuss the electronic absorption intensity
distribution. There are mainly three types of intensity distribution
seen in the experiments.
Case-1
As discussed a progression with v=0 , the v= 0 to v=0
transition, which is known as the vibration origin transition, is the
lowest in energy. This first band is seen to be very intense as
shown in the figure.
Further bands in v progression with v=0 progression appear
with very rapidly decreasing intensities.
This kind of intensity distribution is observed for the atmospheric
oxygen in the red part of the solar spectrum.
Case-2
In this case, the intensity of the bands in the v-progression with
v=0 at first increases with increasing in energy. The v = 0 to v =
0 transition band is not the intense one.
The intensities of the further bands increase slowly, the intensity
reaches to maximum and then decreases slowly with increasing .
This kind of pattern is shown in figure.
The electronic absorption of CO molecule shows this kind of
intensity pattern.
Case-3
In this case, a long progression is seen whose intensity rises
gradually and finally reaches a continuum.
Usually, in this type of pattern, the first observe band may not be
the v = 0 to v = 0 origin band.
The maximum intensity lies either at a very high v value as seen
in the iodine absorption spectrum possibly be even in the
continuum.
Franck-Condon principle :
These three different intensity distributions observed in the
experiments can be explained by Franck-Condon principle.
J. Franck in 1925 published a paper [Trans. Faraday Soc., Volume-
21, Year-1925, Page-536] to describe this phenomenon with
simple diagrammatical approach.
Later on, in 1928 Condon gave the wave mechanical formulation
on this idea [Physical Review, Volume-54, Year-1928, Page-858].
According to Franck:
The electron jump in a molecule takes place so rapidly in
comparison to the vibrational motion of the nuclei that
immediately afterwards the nuclei still have very nearly the same
relative position and velocity as before the jump.
Case-1 Case-2
Case-3
Problem: Isotope effect
The origin of v = 0 to v = 6 band in an
electronic transition observed in N14N14 is
located at 35600 cm-1. given that e = 1460
cm-1 and e =2360 cm-1 for N14N14 and based
on assumption that the harmonic
approximation is adequate, calculate e and
the position of the corresponding band origin
for N14N15.
Problem: Isotope effect
The dissociation energy of the H2 molecule is
4.46 eV while that of the D2 molecule is 4.52
eV. Find the zero-point energy of the H2
molecule.
You might also like
- Author Guidelines - Microwave and Optical Technology Letters - Wiley Online LibraryDocument32 pagesAuthor Guidelines - Microwave and Optical Technology Letters - Wiley Online Librarysoo kimNo ratings yet
- International Symposium on Selective Ion-Sensitive Electrodes: International Union of Pure and Applied ChemistryFrom EverandInternational Symposium on Selective Ion-Sensitive Electrodes: International Union of Pure and Applied ChemistryG. J. MoodyNo ratings yet
- Slide Uv VisDocument54 pagesSlide Uv VisElka Sushea IINo ratings yet
- Structure of Atom: Rutherford's Nuclear ModelDocument12 pagesStructure of Atom: Rutherford's Nuclear ModelGautham GrimaceNo ratings yet
- Current Topics in Amorphous Materials: Physics & TechnologyFrom EverandCurrent Topics in Amorphous Materials: Physics & TechnologyY. SakuraiRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Class Xii Physics Assignment 2 Unit 2Document2 pagesClass Xii Physics Assignment 2 Unit 2vishal110085No ratings yet
- Chapter11 PDFDocument8 pagesChapter11 PDFpapipoNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument8 pagesAtomic StructureHari GoldNo ratings yet
- Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry 609 (2007) 17-26Document10 pagesJournal of Electroanalytical Chemistry 609 (2007) 17-26Alex B-RomeroNo ratings yet
- Mott Schottky IntroDocument5 pagesMott Schottky Introacollord2603No ratings yet
- PhotoChemistry PDFDocument22 pagesPhotoChemistry PDFAnkitranjan GogoiNo ratings yet
- Band Theory of SolidsDocument22 pagesBand Theory of Solidsmunku05100% (1)
- Chemical Kinetics Classnotes-374 PDFDocument41 pagesChemical Kinetics Classnotes-374 PDFAshok ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Photo ChemistryDocument7 pagesPhoto Chemistrysowbhagyasuresh95No ratings yet
- 11 Chemistry Notes Ch02 Structure of AtomDocument18 pages11 Chemistry Notes Ch02 Structure of AtomSayantanBanerjee0% (1)
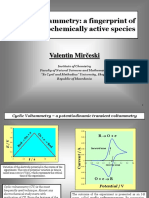
- Cyclic VoltammetryDocument26 pagesCyclic VoltammetryM Amjad MajeedNo ratings yet
- Energy Bands For Electrons in Crystals (Kittel Ch. 7)Document39 pagesEnergy Bands For Electrons in Crystals (Kittel Ch. 7)sabhanNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and Chemical BondingDocument4 pagesAtomic Structure and Chemical Bondinganshvishwakarma674100% (1)
- Liquid Drop Model and Bohr-Wheeler Theory of Nuclear FissionDocument6 pagesLiquid Drop Model and Bohr-Wheeler Theory of Nuclear FissionAmogh BorgaveNo ratings yet
- Minamata Disease: Mercury PoisoningDocument18 pagesMinamata Disease: Mercury PoisoningBijay Kumar MahatoNo ratings yet
- Electrical Properties of Semiconductors: Intrinsic vs ExtrinsicDocument2 pagesElectrical Properties of Semiconductors: Intrinsic vs ExtrinsicApril Wilson100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureDocument26 pagesChapter 4 Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureYash PlayNo ratings yet
- MCE enDocument192 pagesMCE enAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 8 (Chromatograms) Incl Answers - 73Document20 pagesTutorial 8 (Chromatograms) Incl Answers - 73Pedro0% (1)
- Uv Visiblespectroscopyppt 170925144657Document58 pagesUv Visiblespectroscopyppt 170925144657meenu sruthi priyaNo ratings yet
- Bohr's Model of the Atom and Its LimitationsDocument5 pagesBohr's Model of the Atom and Its LimitationsCRAZY FOOD LOVERSNo ratings yet
- Lebanese International University School of EngineeringDocument12 pagesLebanese International University School of EngineeringHassan RashedNo ratings yet
- Coordination CompoundDocument76 pagesCoordination Compoundashok pradhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 - Magnetic PropertiesDocument10 pagesChapter 15 - Magnetic PropertiesThành Phương TấnNo ratings yet
- ATOICV1 8 0 Electronic Spectra of Transition Metal ComplexesDocument136 pagesATOICV1 8 0 Electronic Spectra of Transition Metal ComplexesNITISH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Helium Neon LaserDocument10 pagesHelium Neon LaserSai SridharNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - DESHIDocument93 pagesModule 1 - DESHIRaghupatiNo ratings yet
- Advanced Organometallic Chemistry and Its Applications in Industry and Catalytic Reactions PDFDocument144 pagesAdvanced Organometallic Chemistry and Its Applications in Industry and Catalytic Reactions PDFdustinthewindNo ratings yet
- Density Functional Theory For BeginnersDocument2 pagesDensity Functional Theory For BeginnersSikander AzamNo ratings yet
- Solutions For Hydrogen AtomDocument41 pagesSolutions For Hydrogen AtomLohith HRNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistyDocument21 pagesElectrochemistyAagash PranavNo ratings yet
- Band Theory of SolidsDocument18 pagesBand Theory of SolidsSachi SinghNo ratings yet
- Theory Blackbody RadiationDocument116 pagesTheory Blackbody RadiationmibliotecaNo ratings yet
- 115 - Esr Spectros PDFDocument15 pages115 - Esr Spectros PDFShubhaNo ratings yet
- Module-2:: Metal Complexes and OrganometallicsDocument75 pagesModule-2:: Metal Complexes and OrganometallicsAshutosh100% (2)
- UNIT IV NMR Mass - WatermarkDocument23 pagesUNIT IV NMR Mass - WatermarkvickyNo ratings yet
- Engineering Physics 2 Unit-3Document82 pagesEngineering Physics 2 Unit-3Sriram JNo ratings yet
- Spectroscopy-I Electronic Spectroscopy of AtomDocument45 pagesSpectroscopy-I Electronic Spectroscopy of Atomucuplup100% (1)
- Class:12 Physics Assignment 3 Topic: Dual Nature of Matter and RadiationDocument2 pagesClass:12 Physics Assignment 3 Topic: Dual Nature of Matter and RadiationAkshat RawatNo ratings yet
- UV-Vis Spectroscopy Components & Beer-Lambert LawDocument2 pagesUV-Vis Spectroscopy Components & Beer-Lambert LawJohn BobNo ratings yet
- Naming of Ionic CompoundsDocument24 pagesNaming of Ionic CompoundsDr. Ghulam Fareed100% (1)
- Free Radicals &carbocationsDocument13 pagesFree Radicals &carbocationsOmkar Kumar JhaNo ratings yet
- Radioactive Decay - WikipediaDocument22 pagesRadioactive Decay - WikipediaSaksham100% (1)
- Max Diem - Quantum Mechanical Foundations of Molecular Spectroscopy-WILEY VCH (2021)Document458 pagesMax Diem - Quantum Mechanical Foundations of Molecular Spectroscopy-WILEY VCH (2021)Vinayak SavarkarNo ratings yet
- Transport Properties of The Gas (Physical Chemistry 2)Document29 pagesTransport Properties of The Gas (Physical Chemistry 2)Adilla Rizka YonitaNo ratings yet
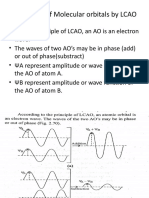
- Formation of Molecular Orbitals by LCAODocument14 pagesFormation of Molecular Orbitals by LCAOAMAN SINGHNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 4 PDFDocument64 pagesChapter - 4 PDFLily SelwinNo ratings yet
- Instrumental AnalysisDocument43 pagesInstrumental AnalysisGab Trinilla100% (1)
- Chapter 8: Band Theory of Solids Concept of Free Electron Theory: Hour 1Document25 pagesChapter 8: Band Theory of Solids Concept of Free Electron Theory: Hour 1Vivek kapoorNo ratings yet
- SPECTRAL CALCULATION OF ORGEL AND TANABE-SUGANO DIAGRAMSDocument18 pagesSPECTRAL CALCULATION OF ORGEL AND TANABE-SUGANO DIAGRAMSTiwari VishalNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Physics - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument15 pagesUnit 1 - Physics - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inMayank SharmaNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab Manual 2016 17 PDFDocument49 pagesPhysics Lab Manual 2016 17 PDFAYUSH ANANDNo ratings yet
- Von Seggern, David Henry - CRC Standard Curves and Surfaces With Mathematica - (2016)Document460 pagesVon Seggern, David Henry - CRC Standard Curves and Surfaces With Mathematica - (2016)N. AndradeNo ratings yet
- Calculus Worksheet CH 3 - Derivatives Test ReviesDocument2 pagesCalculus Worksheet CH 3 - Derivatives Test ReviesAdamNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Concepts of MechanicsDocument3 pagesFundamental Concepts of Mechanicskamilbisma50% (2)
- Comment On "A Generalized Helmholtz Theorem For Time-Varying Vector Fields," by Artice M. DavisDocument3 pagesComment On "A Generalized Helmholtz Theorem For Time-Varying Vector Fields," by Artice M. Davisfersoto07No ratings yet
- Engineering Physics - Unit 1Document68 pagesEngineering Physics - Unit 1Affan FarukiNo ratings yet
- Math P4 Past Paper QuestionsDocument17 pagesMath P4 Past Paper QuestionsShubangi PareshNo ratings yet
- 1463486214physical ChemistryDocument4 pages1463486214physical ChemistryShilp ShahNo ratings yet
- Optimal Jan24 Assignment 3Document4 pagesOptimal Jan24 Assignment 3Harish MokashiNo ratings yet
- Dirac's Wonderful EquationDocument2 pagesDirac's Wonderful Equation¡KyoNo ratings yet
- 4-SCATTERING MATRIX-15-Jul-2019Material - I - 15-Jul-2019 - 7 - SparametersDocument12 pages4-SCATTERING MATRIX-15-Jul-2019Material - I - 15-Jul-2019 - 7 - Sparametersabhignan routhuNo ratings yet
- PhysicmarsDocument97 pagesPhysicmarsNoé GsstNo ratings yet
- Example of CLT 6.6 PDFDocument11 pagesExample of CLT 6.6 PDFDanielle WatsonNo ratings yet
- Partial Derivative ExamplesDocument3 pagesPartial Derivative ExamplesTayyab HusaainNo ratings yet
- DNA of The GodsDocument150 pagesDNA of The Godsrobertofigueira100% (2)
- 15-9 5th Ed B&J Rotating BarDocument3 pages15-9 5th Ed B&J Rotating BarEduardo MuccioloNo ratings yet
- CAPE Mathematics Workshop Problem SolvingDocument49 pagesCAPE Mathematics Workshop Problem SolvingGabrielle MorganNo ratings yet
- Quantum Physics Time Travel Paradoxes Grandfather EffectDocument10 pagesQuantum Physics Time Travel Paradoxes Grandfather EffectKevin S. DeckerNo ratings yet
- 1 Vectors, Components, Operation On Vectors, Unit VectorsDocument26 pages1 Vectors, Components, Operation On Vectors, Unit VectorsklNo ratings yet
- Laplace EquationDocument3 pagesLaplace EquationGaber GhaneemNo ratings yet
- Particle Swarm Optimization With Particles Having Quantum BehaviDocument7 pagesParticle Swarm Optimization With Particles Having Quantum BehaviPedro StellaNo ratings yet
- Adv Eng Mater - 2022 - Faisal - Thermal Spray Coatings For Electromagnetic Wave Absorption and Interference Shielding A - DDocument49 pagesAdv Eng Mater - 2022 - Faisal - Thermal Spray Coatings For Electromagnetic Wave Absorption and Interference Shielding A - DdvdiepvcgNo ratings yet
- Special MatricesDocument7 pagesSpecial MatricesPrabhakar DasNo ratings yet
- Modified WKB Approximation For Fowler-Nordheim Tunneling Phenomenon in Nano-Structure Based SemiconductorsDocument18 pagesModified WKB Approximation For Fowler-Nordheim Tunneling Phenomenon in Nano-Structure Based Semiconductorsmaheshwarivikas1982No ratings yet
- HTTPSCDN - Savemyexams.co - Ukuploads201806June 2017 2PR Rms IGCSE Edexcel Physics PDFDocument12 pagesHTTPSCDN - Savemyexams.co - Ukuploads201806June 2017 2PR Rms IGCSE Edexcel Physics PDFLeman KasapNo ratings yet
- Vectors in Two Dimensions: What Is A Vector?Document13 pagesVectors in Two Dimensions: What Is A Vector?Lazarus MukwekweNo ratings yet
- Symmetry Operations and Point GroupDocument13 pagesSymmetry Operations and Point GroupRahul AroraNo ratings yet
- Laplace TableDocument2 pagesLaplace TableDavid VangNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Matrices and DeterminantsDocument43 pagesLesson 1 - Matrices and Determinantsgaryart111No ratings yet
- Chapter 11: Radiation: 11.1 Dipole Radiation 11.1.1 What Is Radiation? 11.1.2 Electric Dipole RadiationDocument4 pagesChapter 11: Radiation: 11.1 Dipole Radiation 11.1.1 What Is Radiation? 11.1.2 Electric Dipole RadiationMadhumika ThammaliNo ratings yet
- What Is A Wave? Forward vs. Backward Propagating Waves The One-Dimensional Wave EquationDocument22 pagesWhat Is A Wave? Forward vs. Backward Propagating Waves The One-Dimensional Wave EquationEster DanielNo ratings yet
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- The Fabric of Civilization: How Textiles Made the WorldFrom EverandThe Fabric of Civilization: How Textiles Made the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (57)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- Algorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsFrom EverandAlgorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (722)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (33)
- Sully: The Untold Story Behind the Miracle on the HudsonFrom EverandSully: The Untold Story Behind the Miracle on the HudsonRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (103)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (41)
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondFrom EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlFrom EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (57)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- To Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceFrom EverandTo Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (51)
- Hero Found: The Greatest POW Escape of the Vietnam WarFrom EverandHero Found: The Greatest POW Escape of the Vietnam WarRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (19)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Brain Rules (Updated and Expanded): 12 Principles for Surviving and Thriving at Work, Home, and SchoolFrom EverandBrain Rules (Updated and Expanded): 12 Principles for Surviving and Thriving at Work, Home, and SchoolRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (702)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (397)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (811)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindFrom EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (93)