Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Objectives For Lab 4
Uploaded by
joshy221196Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Objectives For Lab 4
Uploaded by
joshy221196Copyright:
Available Formats
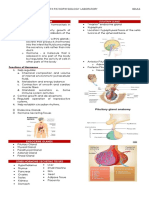
OBJECTIVES for Station #1
Parts & Components of Lower Airway
Identify on this Schematic Diagram:
Parts of the Lower Airway and their Components:
Conducting Portion of the Lower Airway:
* Larynx
* Trachea
* Right & Left Bronchi:
* Main or Principal or Primary Bronchi
* Lobar or Secondary Bronchi
* Segmental or Tertiary Bronchi
* Several successive divisions of tertiary
or segmental bronchi
* Terminal (smallest) bronchi
* Right and Left Bronchioles
* Regular Bronchioles
* Terminal Bronchioles
(End of Conducting
Portion)
Respiratory Portion of the Lower Airway:
* Respiratory Bronchioles
* Alveolar Ducts
* Atria or Vestibules of Alveolar Sacs
* Alveolar Sacs
* Individual Alveoli (End of Respiratory Portion)
OBJECTIVES for Station #2
Position of the Larynx, its Skeleton, Membranes & Ligaments
Identify:
Position of Larynx in Anterior Neck below Hyoid Bone (Vertebral levels of
Larynx: C4-C6). Its attachment to Hyoid bone by Thyrohyoid Membrane
and Lateral Thyrohyoid ligaments; and attachment to Trachea by
Cricotracheal Membrane
Hyoid bone (body, greater cornu or horn & lesser cornu or horn).
Attachments of following structures: Suprahyoid muscles: Stylohyoid,
Mylohyoid, Geniohyoid, Intermediate Tendon of Digastric muscle;
Infrahyoid muscles: Sternohyoid, Omohyoid, Thyrohyoid; Other
structures: Stylohyoid ligament, Thyrohyoid Membrane, Lateral
Thyrohyoid ligaments, Hyo-Epiglottic ligament.
Laryngeal Skeleton:
Thyroid cartilage: Superior cornu horn, Lamina, Superior tubercle,
Oblique line, Inferior tubercle, Inferior cornu horn, Laryngeal prominence
Cricoid cartilage: Lamina, Arch, Median ridge (on posterior midline),
Articular facets for Cricothyroid and Cricoarytenoid joints.
Epiglottis: Apex, Stalk, Lingual & Vestibular surfaces.
Arytenoid cartilage: Muscular process, Vocal process, Base, Apex, Articular
facets for Cricoarytenoid joints.
Corniculate cartilage & Cuneiform cartilage
Laryngeal Membranes & Ligaments:
Extrinsic: Thyrohyoid membrane, Median thyrohyoid ligament, Lateral
thyrohyoid ligament, Hyoepiglottic ligament, Cricotracheal membrane.
Intrinsic: Conus elasticus or Cricovocal membrane (just below true vocal
ligaments), Quadrangular membrane (just above false vocal ligaments),
Vocal ligament True vocal ligament (upper edge of Conus elasticus),
Vestibular ligament - False vocal ligament (lower edge of Quadrangular
membrane), Thyroepiglottic ligament (at the attachment of epiglottic
cartilage).
OBJECTIVES for Station #3
Laryngeal Cavity. Features of Mucous Membrane
Identify:
Laryngeal opening (aditus) and structures that bound it:
Epiglottis (anteriorly),
Aryepiglottic fold (laterally),
Interarytenoid fold (posteriorly)
It provides communication between the laryngeal vestibule and
laryngopharynx.
A small piriform fossa on each side of the Laryngeal Inlet
It is bounded: Medially - by the aryepiglottic fold, Laterally by the thyroid
cartilage and thyrohyoid membrane.
Subdivisions of Laryngeal Cavity:
Laryngeal Vestibule (extends from laryngeal opening to rima vestibularis)
2 Vestibular folds (false vocal folds). They cover lower edges of
quadrangular membrane: Vestibular ligaments.
Rima vestibularis (space between them)
Openings of 2 laryngeal ventricles (right & left)
Each opening is between Vestibular fold (above) and Vocal fold
(below) on corresponding side.
2 Laryngeal Ventricles (right & left) on each side of the larynx
between vestibular and vocal folds. They extend from their
opening upward on each side between thyroid lamina &
quadrangular membrane
Supraglottic space space between two ventricles above glottis
Glottis
2 Vocal folds (true vocal folds). They cover upper edges of
Cricovocal membranes: Vocal ligaments & Vocalis muscles.
Rima glottidis or rima vocalis (space between vocal folds)
Infraglottic part of laryngeal cavity (space between glottis and
trachea)
Transition of infraglottic part of laryngeal cavity into trachea at the
level of C6 (lower border of Cricoid cartilage)
OBJECTIVES for Station #4
Laryngeal Muscles and their Actions
Identify:
Extrinsic muscles of the Larynx:
(These muscles move the larynx relative to the neck)
Sternothyroid m. It is between Manubrium Sterni & Oblique line of
Thyroid cartilage. It pulls Larynx downward. Nerve supply from branches
of Ansa Cervicalis (C2,3)
Thyrohyoid m. It is between Oblique line of Thyroid cartilage & Hyoid
bone. It pulls Larynx upward. Nerve supply from branches of (C1) through
Hypoglossal nerve (CNXII).
Inferior Constrictor of the Pharynx. Its Thyropharyngeus portion starts
from Oblique line of Thyroid cartilage and its Cricopharyngeus portion
starts from Arc of Cricoid cartilage, then two portions are attached to
Pharyngeal Raphe on posterior pharyngeal wall. Week elevator of Larynx.
Nerve supply from branches of Vagus (CNX).
Intrinsic muscles of the Larynx:
(These muscles move the laryngeal cartilages within the larynx)
Cricothyroid m. (between arch of arytenoid & lamina of thyroid
cartilages). It tilts thyroid cartilage forward & increases tension of vocal
folds. Nerve supply: external branch of superior laryngeal nerve (from
Vagus n.)
Muscles supplied by branches of Recurrent Laryngeal nerve (from Vagus n.):
Posterior cricoarytenoid m. (between muscular process of arytenoid &
lamina of cricoid cartilages). It abducts vocal folds, opens rima vocalis &
increases tension of vocal folds.
Lateral cricoarytenoid m. (between muscular process of arytenoid & arch
of cricoid cartilages). It adducts vocal folds & closes rima vocalis.
Thyroarytenoid m. (between thyroid & arytenoid cartilages). It narrows
laryngeal vestibule.
Vocalis m. (lowest part of Thyroarytenoid m. between front of thyroid
lamina & vocal process of arytenoid cartilage). Relaxes (reduces) tension
of vocal folds.
Transverse arytenoid m. & Oblique arytenoid m. between two arytenoid
cartilages. They approximate arytenoid cartilages, narrow laryngeal
vestibule & close rima vocalis.
Aryepiglottic m. & Thyroepiglottic m. Close laryngeal opening in deglutition.
OBJECTIVES for Station #5
Laryngeal Relations.
Identify:
Anterior relations:
Skin, superficial fascia, anterior jugular veins, deep & pretracheal fascias
Sternohyoid, Omohyoid, Sternothyroid & Thyrohyoid Muscles
Pyramidal lobe of thyroid gland (often absent)
Posterior relations:
Laryngopharynx and its walls
Piriform fossae (recesses)
Upper end of Esophagus (with its first constriction)
Retropharyngeal space
Cervical vertebrae C4 C6
Lateral relations:
Inferior pharyngeal constrictors
Branches of Recurrent laryngeal nerves
Upper poles of lobes of thyroid gland & superior parathyroid glands
Superior thyroid arteries and veins
External branches of superior laryngeal nerves
Carotid sheaths & Main neurovascular bundles of the neck:
Common carotid artery
Internal jugular vein
Vagus nerve (X CN)
Ansa cervicalis
Sternocleidomastoid muscles
OBJECTIVES for Station #6
Trachea & its Relations.
Identify:
Location of Trachea in the root of the neck and superior mediastinum
Vertebral levels for upper (C6) & lower end (T5) of trachea
Tracheal tube (10-16 cm long) and its parts Cervical & Thoracic
Cricotracheal membrane (between cricoid & 1st tracheal cartilages
Tracheal C-shaped hyaline cartilages (16-20)
Annular ligaments (between cartilages)
Posterior (membranous) wall
Tracheal bifurcation (Vert. level: T4/5 or T5)
Carina trachealis (Vert. level: T4/5 or T5)
Tracheal relations (Cervical part):
Anterior: Isthmus of thyroid gland, Inferior thyroid veins, Thyroidea
ima artery, Sternothyroid & Sternohyoid muscles, Pretracheal fascia &
Pretracheal lymph nodes, Jugular venous arch; Posterior: Esophagus,
Branches of recurrent laryngeal nerves, Branches of inferior thyroid
artery; Lateral: Common carotid arteries, Lobes of thyroid gland,
Inferior thyroid arteries, Recurrent laryngeal nerves, Paratracheal
lymph nodes.
Tracheal relations (Thoracic part):
Anterior: Manubrium sterni, Thymic lobes
Brachiocephalic trunk, Left common carotid artery, Aortic arch, Deep
cardiac nerve plexus, Left brachiocephalic vein; Posterior: Esophagus;
Lateral: (Right side) - Pleura and right Vagus (CNX), Brachiocephalic
trunk;
Lateral: (Left side) - Left recurrent laryngeal nerve, Aortic arch, Left
common carotid & Subclavian Aa.
OBJECTIVES for Station #7
Bronchial Tree of the Right Lung.
Identify:
Thoracic part of Trachea and its bifurcation.
Bronchial Tree of the Right Lung:
Extrapulmonary bronchus and its principal characteristics:
Right Primary (1st Order, Main or Principal) bronchus
It is: Wider than the left one,
Shorter (about 2.5 cm. long),
More vertical in direction than the left.
It enters the right lung nearly opposite the fifth thoracic vertebra.
Intrapulmonary bronchi:
Superior lobar (secondary) bronchus and its branches:
Apical segmental (tertiary) bronchus (of superior lobe)
Anterior segmental (tertiary) bronchus (of superior lobe)
Posterior segmental (tertiary) bronchus (of superior lobe)
Intermediate bronchus (continuation of Primary bronchus)
Middle lobar (secondary) bronchus and its branches:
Medial segmental (tertiary) bronchus (of middle lobe)
Lateral segmental (tertiary) bronchus (of middle lobe)
Inferior lobar (secondary) bronchus and its branches:
Superior (apical) segmental (tertiary) bronchus (of inferior lobe)
Medial basal segmental (tertiary) bronchus (of inferior lobe)
Anterior basal segmental (tertiary) bronchus (of inferior lobe)
Lateral basal segmental (tertiary) bronchus (of inferior lobe)
Posterior basal segmental (tertiary) bronchus (of inferior lobe)
OBJECTIVES for Station #8
Bronchial Tree of the Left Lung.
Identify:
Thoracic part of Trachea and its bifurcation.
Bronchial Tree of the Left Lung:
Extrapulmonary bronchus and its principal characteristics:
Left Primary (1st Order, Main or Principal) bronchus
It is: Narrower than the right one,
Longer (about 5 cm. long),
More horizontal in direction than the right.
It enters the left lung nearly opposite the sixth thoracic vertebra.
Intrapulmonary bronchi:
Superior lobar (secondary) bronchus and its branches:
Apicoposterior segmental (tertiary) bronchus (of superior lobe)
Anterior segmental (tertiary) bronchus (of superior lobe)
Superior lingular segmental (tertiary) bronchus (of superior lobe)
Inferior lingular segmental (tertiary) bronchus (of superior lobe)
Inferior lobar (secondary) bronchus and its branches:
Superior (apical) segmental (tertiary) bronchus (of inferior lobe)
Anteromedial basal segmental (tertiary) bronchus (of
inferior lobe)
Lateral basal segmental (tertiary) bronchus (of inferior lobe)
Posterior basal segmental (tertiary) bronchus (of inferior lobe)
OBJECTIVES for Station #9
Respiratory Tree or Acinus, Respiratory Membrane.
Identify:
Structures of Respiratory Tree or Acinus:
Respiratory bronchiole (with single alveoli)
Alveolar duct
Alveolar Atrium (Vestibule)
Alveolar sac
Alveoli
Air-blood barriers (respiratory membranes)
Alveolar capillary network (plexus)
Lobular branches of segmental artery & Intralobular tributaries of
Interlobular veins (contain oxygenated blood).
Respiratory Membrane or Air-Blood Barrier and its layers
(Components (from alveolar air to blood):
Layer of surfactant
Type I pneumocyte (alveolocyte) of alveolar wall
Fused basal laminae of two epithelial cells (Type I
pneumocyte and endotheliocyte of the wall of adjacent
blood capillary)
Endotheliocyte of the wall of adjacent blood capillary
OBJECTIVES for Station #10
Nerve Supply to the Lower Respiratory Tract.
Identify Nerve Supply to the:
Larynx:
Parasympathetic component branches from Vagus (CNX): Superior
Laryngeal nerve and its branches - Internal Laryngeal nerve (sensory
above vocal folds, and autonomic) and External Laryngeal nerve
(motor to cricothyroid muscle); Recurrent Laryngeal nerve and its
terminal branch Inferior Laryngeal nerve (sensory below vocal
folds, autonomic, and motor to laryngeal muscles, except cricothyroid
muscle).
Sympathetic component Laryngopharyngeal (medial) branches from
Superior Cervical Sympathetic Ganglion, Thyroid branches from
Middle Cervical Sympathetic Ganglion they form plexus on Inferior
Thyroid artery and distributed with its branches.
Trachea:
Parasympathetic component branches from Vagus (CNX): tracheal
branches from Recurrent Laryngeal nerves and direct tracheal
branches from both Vagi.
Sympathetic component Tracheal branches from Middle and Inferior
Cervical Sympathetic Ganglia and tracheal (medial) branches from
upper 5 Thoracic Sympathetic Ganglia.
Bronchi & Bronchioles:
Parasympathetic component Branches of Vagus (CNX) form Anterior
& Posterior pulmonary plexuses on primary bronchi from which
bronchial branches (nerves) are distributed along bronchial and
respiratory trees.
Sympathetic component (medial) branches from upper 5 Thoracic
Sympathetic Ganglia contribute to Anterior & Posterior pulmonary
plexuses on primary bronchi from which bronchial branches are
distributed along bronchial and respiratory trees.
OBJECTIVES for Station #11
Blood Supply to the Lower Respiratory Tract.
Identify:
Laryngeal Blood Vessels:
Superior Laryngeal Artery, which branches from Superior Thyroid Artery
near its bifurcation from External Carotid Artery. Superior Laryngeal Vein,
which drains into Superior Thyroid Vein, opening into Internal Jugular Vein.
Inferior Laryngeal Artery, which branches from Inferior Thyroid Artery
(branch of Thyrocervical Trunk of Subclavian Artery). Inferior Laryngeal
Vein which drains into Middle Thyroid Vein, opening into Internal Jugular
Vein, & Inferior Thyroid Vein, opening into Left Brachiocephalic vein.
Tracheal Blood Vessels:
Cervical part of Trachea is supplied by Tracheal branches of Inferior Thyroid
Artery, while its thoracic part is supplied by Tracheal branches of Bronchial
Arteries.
Veins accompany arteries and drain in Inferior Thyroid Venous Plexus.
Bronchial Blood Vessels:
Bronchial Arteries are derived from Descending Thoracic Aorta directly or
indirectly. Right Bronchial Artery is usually a branch of the Third Posterior
Intercostal Artery, whilst there are normally 2 Left Bronchial Arteries
(upper and lower) which branch separately from Descending Thoracic
Aorta. Bronchial Arteries accompany bronchial tree and they supply the
bronchial wall as far as the respiratory bronchioles.
Bronchial Veins are arranged into two systems. Deep Bronchial Veins
commence as Intrapulmonary Bronchiolar Plexuses, communicating
with Pulmonary Veins and eventually joining a single trunk which ends
in a main Pulmonary Vein. Superficial Bronchial Veins drain
extrapulmonary bronchi, visceral pleura and hilar lymph nodes; they
also communicate with the Pulmonary Veins and end on right in
Azygos vein and on left in Left Superior Intercostal or Accessory
Hemiazygos Veins. The main bronchial arteries and veins run on the
dorsal aspect of the extrapulmonary bronchi.
OBJECTIVES for Station #12
Lymphatic Drainage from the Lower Respiratory Tract.
Identify:
Lymphatic drainage from Larynx:
Laryngeal lymphatic vessels form superior and inferior groups; their
division being at the level of the vocal fold. Superior Lymph Vessels
pierce the thyrohyoid membrane to accompany the superior laryngeal
blood vessels, ending in the Superior Deep Cervical Lymph Nodes.
Inferior Lymph Vessels pass between the cricoid cartilage and the first
tracheal ring to the Inferior Deep Cervical Lymph Nodes, or pierce the
cricovocal membrane to reach the Pretracheal and Prelaryngeal
nodes.
Lymphatic drainage from Trachea:
A dense network of Lymph Vessels exists in Tracheal wall. Its Cervical
part drains to Pretracheal and Paratracheal Lymph Nodes, or directly
to Inferior Deep Cervical Lymph Nodes. Its Thoracic part drains to
Pretracheal and Paratracheal Lymph Nodes. Their efferent lymph
vessels unite with efferents from Parasternal and Brachiocephalic
nodes to form Bronchomediastinal trunks.
Lymphatic drainage from Bronchi:
In large Lobar Bronchi their efferent lymph vessels drain into
Bronchopulmonary (Hilar) nodes. Efferent lymph vessels from Main
Bronchi drain into Superior & Inferior Tracheobronchial nodes and to
Paratracheal nodes, from which Bronchomediastinal trunks originate.
OBJECTIVES for Station #13
Radiologic Anatomy of the Lower Respiratory Tract.
X-Rays of the Head & Neck and the Chest.
Identify on Radiological Images of the Neck & Thorax:
Larynx:
Epiglottis, Thyroid cartilage, Cricoid cartilage, Arytenoid cartilage,
Aryepiglottic fold, Laryngeal vestibule, Vestibular fold, Rima
vestibularis, Laryngeal ventricle, Vocal fold, Rima vocalis, Infraglottic
part of laryngeal cavity.
Trachea:
its Cervical & Thoracic parts, Tracheal Bifurcation, Primary bronchi
(right & left).
Other structures: Hyoid bone, Root of the tongue, Vallecula,
Oropharynx, Laryngopharynx, Oesophagus, Numbers of Cervical &
Thoracic vertebrae, Numbers of ribs, Sternocleidomastoid muscle,
Common carotid Artery, Internal Jugular Vein.
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- CMJ Journal Dec 2012Document74 pagesCMJ Journal Dec 2012joshy221196No ratings yet
- Stardust For StuffDocument1 pageStardust For Stuffjoshy221196No ratings yet
- ERPC LeafletDocument4 pagesERPC Leafletjoshy221196No ratings yet
- What Is Needed: If You Change Things Other Than Those Written Here With Godmode9 You May Brick Your SystemDocument2 pagesWhat Is Needed: If You Change Things Other Than Those Written Here With Godmode9 You May Brick Your Systemjoshy221196No ratings yet
- Gonorrhea and SyphilisDocument55 pagesGonorrhea and Syphilisjoshy221196No ratings yet
- MDSC 3311 PBL 1 (Without Group)Document5 pagesMDSC 3311 PBL 1 (Without Group)joshy221196No ratings yet
- Abdominal ExamDocument7 pagesAbdominal Examjoshy221196No ratings yet
- PECH 2001 Final Exam Key PointsDocument6 pagesPECH 2001 Final Exam Key Pointsjoshy221196No ratings yet
- MBJ PBL 5 BrainstormDocument2 pagesMBJ PBL 5 Brainstormjoshy221196No ratings yet
- Mbbs PBL BibleDocument76 pagesMbbs PBL Biblejoshy2211960% (1)
- MBJ PBL 5 BrainstormDocument2 pagesMBJ PBL 5 Brainstormjoshy221196No ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- HEMATOPOIESISDocument50 pagesHEMATOPOIESISGalih Maygananda Putra87% (23)
- EsplenomegaliaDocument24 pagesEsplenomegaliaJhonatan Efraín López CarbajalNo ratings yet
- Congenital Hypothyroidism From MedscapeDocument11 pagesCongenital Hypothyroidism From MedscapeAgustin IskandarNo ratings yet
- The BodyDocument4 pagesThe BodySheila G. DolipasNo ratings yet
- Assessment of NewbornDocument33 pagesAssessment of Newbornmehta shivaniNo ratings yet
- Human Embryonic DevelopmentDocument8 pagesHuman Embryonic DevelopmentGargi BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Essensial Hypertension Pathogenesis and PathophsiologyDocument22 pagesEssensial Hypertension Pathogenesis and PathophsiologyAmeliana KamaludinNo ratings yet
- Embryology of The Head and NeckDocument18 pagesEmbryology of The Head and NeckDr-Firas Nayf Al-ThawabiaNo ratings yet
- Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation Concept MapDocument3 pagesDisseminated Intravascular Coagulation Concept MapphoebjaetanNo ratings yet
- Pathanatomy Full MCQ SDocument47 pagesPathanatomy Full MCQ SAbhishek RaoNo ratings yet
- Protection, Support and Locomotion HandoutDocument11 pagesProtection, Support and Locomotion HandoutLeslie Samuel0% (1)
- Part Ii Medulla SpinalisDocument46 pagesPart Ii Medulla SpinalisSuardimanAchoNo ratings yet
- Sanathana Sai Sanjeevini: ...... Healing FragrancesDocument25 pagesSanathana Sai Sanjeevini: ...... Healing Fragrancesamane72No ratings yet
- Practice QuestionDocument6 pagesPractice QuestionPAVITHRAN PadmanabhanNo ratings yet
- CH 2 Quiz Results CPC AAPCDocument3 pagesCH 2 Quiz Results CPC AAPCBrenda MedinaNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Worksheet PDFDocument2 pagesNervous System Worksheet PDFMaryechu100% (2)
- Obstructive JaundiceDocument54 pagesObstructive JaundiceJenine Ezra M. Conol50% (2)
- Sanjeevini Combination Sheet For SSC 9 Blood Pressure LowDocument1 pageSanjeevini Combination Sheet For SSC 9 Blood Pressure LowEduardoNo ratings yet
- Blood Vessel and Their FunctionDocument2 pagesBlood Vessel and Their FunctionSiti Zanirah ArifinNo ratings yet
- 05 Organ System Functions ActivityDocument6 pages05 Organ System Functions ActivityEdmund Dantes100% (1)
- Blood Supply of Long BonesDocument4 pagesBlood Supply of Long BonesmainehoonaNo ratings yet
- A Dancing Patient: Dr. Ahmed Al MontasirDocument33 pagesA Dancing Patient: Dr. Ahmed Al MontasirMontasir AhmedNo ratings yet
- Science - A Closer Look - The Human Body GR K-2 PDFDocument86 pagesScience - A Closer Look - The Human Body GR K-2 PDFlevNo ratings yet
- Cerebellopontine Angle Tumors: Guide:Dr Suchitra Dashjohn Speaker: DR Madhusmita BeheraDocument20 pagesCerebellopontine Angle Tumors: Guide:Dr Suchitra Dashjohn Speaker: DR Madhusmita Beheraasish753905No ratings yet
- Case MyelitisDocument34 pagesCase Myelitisyolanda nurlizaNo ratings yet
- Physiology of PregnancyDocument2 pagesPhysiology of PregnancyjamiegemNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System NotesDocument6 pagesEndocrine System NotesHannah Grace CorveraNo ratings yet
- ROSELA, ERLAINE MARIE Blood-LabDocument4 pagesROSELA, ERLAINE MARIE Blood-LabPadoNo ratings yet
- Ijavol 5no 3sep-Dec20161Document161 pagesIjavol 5no 3sep-Dec20161Ayesha JadoonNo ratings yet
- Evoluºia I Tratamentul În Sindromul Hemolitic-Uremic La CopilDocument6 pagesEvoluºia I Tratamentul În Sindromul Hemolitic-Uremic La CopilAntonia GenesNo ratings yet