Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Resume: Title Sampling Technique Research Design Analysis (Non Parametric) Conclution
Uploaded by
Teguh S0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views1 pagedsdsf
Original Title
Irma Resume
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentdsdsf
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views1 pageResume: Title Sampling Technique Research Design Analysis (Non Parametric) Conclution
Uploaded by
Teguh Sdsdsf
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
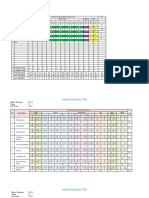
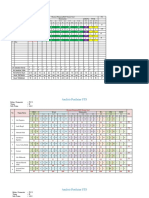
Resume
Title Sampling Technique Research Design Analysis (Non Parametric) Conclution
Experimental Non Parametric To check the data normality, Kruskal- Most samples demonstrated a In conclusion, aortic and
Study of Wallis tests have been conducted for nonlinear hyperelastic strain-stress pulmonary artery homografts
Anisotropic all the tissue sample stiffnesses response to UTT. Stiffness exhibit hyperelastic mechanical
Stress/Strain investigated. A value of = 0.05 is (measured by tangent modulus at characteristic with anisotropic
Relationships of taken as the significance level of the different strains) in all orientations effect. The calibrated Holzapfel-
Aortic and Kruskal-Wallis test. For all aortic and were compared and shown as Gasser constitutive model can
Pulmonary pulmonary artery homografts contour plots. For each vessel be applied in surgical preparation
Artery segments, probability distributions segment at all strain levels, stiffness and related simulation to predict
Homografts and are the same for anterior and posterior was not significantly different anisotropic biomechanical
Synthetic aspects, when comparing all among aspects and orientations. For behavior. The synthetic vascular
Vascular Grafts orientations for each region under synthetic grafts, stiffness was grafts are significantly stiffer than
true strain of 10%,20%, and 30% significantly different among homografts. The mechanical
(p>0.11 in all regions). For all Aortic orientations (p<0.042). Aorta is properties of SVG-GORE-TEX in
and pulmonary artery homografts significantly stiffer than pulmonary L orientation are comparable to
segments, probability distributions artery at 10% strain, comparing all those of the homografts, and
are the same for different orientations orientations, aspects, and regions this characteristic should be
(C, D and L), when comparing both (p=0.0001). Synthetic grafts are considered by surgeons when
aspects for each region under true significantly stiffer than aortic and performing reconstructive
strain of 10%, 20%, and 30% (p>0.10 pulmonary homografts at all strain cardiovascular surgery with this
in all regions). For SVG-GORE- levels (p<0.046). Aortic, pulmonary material. These differences
TEX, when comparing all the artery, and synthetic grafts exhibit between aortic and pulmonary
orientations, probability distributions hyperelastic biomechanical artery homografts and synthetic
are the same under true strain of 10% behavior with anisotropic effect. vascular grafts may play a role in
(p=0.051), but not the same under Differences in mechanical native neonatal tissue
true strain of 20% (p=0.027), and properties among vascular grafts behavior, ventricular/arterial
30% (p=0.027). For EVG-IMPRA, may affect native tissue behavior mechanical coupling, and risk of
when comparing all the orientations, and ventricular/arterial mechanical deformation due to abnormal
probability distributions are the same coupling, and increase the risk of hemodynamics of CHD.
under true strain of 10%, 20%, and deformation due to abnormal CHD
30% (p>0.10). hemodynamics.
You might also like
- Resume: Title Sampling Technique Research Design Analysis (Non Parametric) ConclutionDocument1 pageResume: Title Sampling Technique Research Design Analysis (Non Parametric) ConclutionTeguh SNo ratings yet
- Sci Rep 2016Document12 pagesSci Rep 2016sagarsrinivasNo ratings yet
- Schiller Etal 2008Document28 pagesSchiller Etal 2008ramsis321No ratings yet
- 2011 Meyer Bertrand Boiron Deplano Stereoscopically Observed Deformations Compliant Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm ModelDocument8 pages2011 Meyer Bertrand Boiron Deplano Stereoscopically Observed Deformations Compliant Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm ModelmikibenezNo ratings yet
- JavierDocument15 pagesJavierapi-447863630No ratings yet
- Ursino and Cristalli - 1996 - A Mathematical Study of Some Biomechanical FactorsDocument18 pagesUrsino and Cristalli - 1996 - A Mathematical Study of Some Biomechanical FactorsKMBANo ratings yet
- JunctionLoss V3Document25 pagesJunctionLoss V3john-john castañedaNo ratings yet
- Computational Vascular Fluid-Structure Interaction: Methodology and Application To Cerebral AneurysmsDocument18 pagesComputational Vascular Fluid-Structure Interaction: Methodology and Application To Cerebral Aneurysmsanon_755488696No ratings yet
- Dissection Properties of The Human Aortic Media: An Experimental StudyDocument12 pagesDissection Properties of The Human Aortic Media: An Experimental StudyAditya TiwariNo ratings yet
- Elbow Loaded FEM and ExperimentDocument10 pagesElbow Loaded FEM and ExperimentmtwakadNo ratings yet
- 227 Full PDFDocument3 pages227 Full PDFanon_629352389No ratings yet
- Numerical Analysis of Multiphase Blood Flow Within Carotid Artery & Bifurcation Using Mixture Model TheoryDocument6 pagesNumerical Analysis of Multiphase Blood Flow Within Carotid Artery & Bifurcation Using Mixture Model Theorynitesh_n2840No ratings yet
- Haruguchi 2003Document9 pagesHaruguchi 2003Harish SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Good Way For Reconstruction ..Hemodynamics Model of Fluid-Solid Interaction in Internal Carotid Artery AneurysmsDocument14 pagesGood Way For Reconstruction ..Hemodynamics Model of Fluid-Solid Interaction in Internal Carotid Artery Aneurysmsanon_755488696No ratings yet
- Dupplex Scanning of The Peripheral Arteries: Correlation of The Peak Velocity Ratio With Angiographics Diameter ReductionDocument8 pagesDupplex Scanning of The Peripheral Arteries: Correlation of The Peak Velocity Ratio With Angiographics Diameter Reductionpaquidermo85No ratings yet
- Transfer Impedance of The Respiratory SystemDocument12 pagesTransfer Impedance of The Respiratory SystemLucie LecarpentierNo ratings yet
- Ali Kordzadeh, Yiannis PanayiotopolousDocument23 pagesAli Kordzadeh, Yiannis PanayiotopolousArHamNo ratings yet
- Frontiers in EndocrinoDocument14 pagesFrontiers in EndocrinofandepepeelmagoNo ratings yet
- J Jacc 2011 09 077Document13 pagesJ Jacc 2011 09 077cardioalmenaraNo ratings yet
- Aneurysm Geometry in Predicting The Risk of Rupture. A Review of The LiteratureDocument6 pagesAneurysm Geometry in Predicting The Risk of Rupture. A Review of The LiteratureAnand KumarNo ratings yet
- Preoperative Physiology, Imaging, andDocument13 pagesPreoperative Physiology, Imaging, andSiLfia SahrinNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 0021929094001743 MainDocument11 pages1 s2.0 0021929094001743 Mainmartin.dureux888No ratings yet
- Atlas c1Document5 pagesAtlas c1davorribicicNo ratings yet
- Lesiones Carotídeas en Tándem: R. Merino-Sanz, J.J. Jiménez-Ruano, E. Rodríguez-Czaplycki, R. Gómez-MedialdeaDocument8 pagesLesiones Carotídeas en Tándem: R. Merino-Sanz, J.J. Jiménez-Ruano, E. Rodríguez-Czaplycki, R. Gómez-Medialdeabarmx911No ratings yet
- Cardiac Conductivity Values - A Challenge For Experimentalists?Document5 pagesCardiac Conductivity Values - A Challenge For Experimentalists?Hania O. AlmdNo ratings yet
- PIIS0007091217372124Document2 pagesPIIS0007091217372124Sangeeta TrivediNo ratings yet
- Hyrtl AnastomosisDocument6 pagesHyrtl AnastomosisMiguel SantosNo ratings yet
- Asimptomatik Aotrtic RegurgitasiDocument15 pagesAsimptomatik Aotrtic RegurgitasiSilvia AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- Anayiotos 2002Document10 pagesAnayiotos 2002Harish SubramanianNo ratings yet
- How Critical Is Fibrous Cap Thickness To Carotid Plaque Stability?Document6 pagesHow Critical Is Fibrous Cap Thickness To Carotid Plaque Stability?Arpit KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Ctangiographyincomplexupperextremity Reconstruction: Keywords: CT Angiography, Upper Extremity ReconstructionDocument5 pagesCtangiographyincomplexupperextremity Reconstruction: Keywords: CT Angiography, Upper Extremity ReconstructionIrinel BuscaNo ratings yet
- Arteriovenous Malformations of The Body and Extremities: Analysis of Therapeutic Outcomes andDocument12 pagesArteriovenous Malformations of The Body and Extremities: Analysis of Therapeutic Outcomes andClaudio SalazarNo ratings yet
- Degenerative Mitral Stenosis: Interpreting The Meaning of Mean GradientDocument3 pagesDegenerative Mitral Stenosis: Interpreting The Meaning of Mean GradientNasriNo ratings yet
- Antolič Et Al 2017 073 16739 l5 Transseptal Imaging of The Left Atrium With Cartosound Intracardiac UltrasoundDocument1 pageAntolič Et Al 2017 073 16739 l5 Transseptal Imaging of The Left Atrium With Cartosound Intracardiac UltrasoundAndrés AllaucaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Nasal Septal Deviation On Total Ethmoid Cell VolumeDocument5 pagesEffect of Nasal Septal Deviation On Total Ethmoid Cell VolumerioNo ratings yet
- Beat To Beat Interplay of Heart Rate Ventricular Depolarization and RepolarizationDocument10 pagesBeat To Beat Interplay of Heart Rate Ventricular Depolarization and RepolarizationLuis A Gil PantojaNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0741521495702881 MainDocument12 pages1 s2.0 S0741521495702881 MainRonald VillaNo ratings yet
- Jamaneurology Liang 2023 Oi 230009 1678913710.52029Document8 pagesJamaneurology Liang 2023 Oi 230009 1678913710.52029nazar shekhoNo ratings yet
- s10554 021 02418 6Document6 pagess10554 021 02418 6Sebastian ChandraNo ratings yet
- Trauma AORTICO-Radiol Clin N.A.2012Document19 pagesTrauma AORTICO-Radiol Clin N.A.2012Pepe pepe pepeNo ratings yet
- Emodinamik: Muhammad Yusuf Fathoni Yudhish ResiDocument23 pagesEmodinamik: Muhammad Yusuf Fathoni Yudhish Resiyusuf fathoniNo ratings yet
- Lee, Et Al. 2010 - Am Journ CardioDocument6 pagesLee, Et Al. 2010 - Am Journ CardioCARLOS SANTIAGO PEREZ RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0378603X14001053 MainDocument10 pages1 s2.0 S0378603X14001053 MainAdrian PachecoNo ratings yet
- 2005 - Different Approaches Measurement of Hemodynamic by Electrical Impedance Plethysmography MethodDocument2 pages2005 - Different Approaches Measurement of Hemodynamic by Electrical Impedance Plethysmography MethodsuknatsNo ratings yet
- AAA RepairDocument8 pagesAAA RepairKarthik ManiNo ratings yet
- Kam 2018Document11 pagesKam 2018JT DanielsNo ratings yet
- Quantifying Scaphoid Malalignment Based Upon Height-to-Length Ratios Obtained by 3-Dimensional Computed TomographyDocument7 pagesQuantifying Scaphoid Malalignment Based Upon Height-to-Length Ratios Obtained by 3-Dimensional Computed TomographyLUIS SALVADOR FLORESNo ratings yet
- Stress Analysis of The Aortic Valve Using Finite Element Modelling SoftwareDocument9 pagesStress Analysis of The Aortic Valve Using Finite Element Modelling SoftwareMarco LaudisioNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis of Carpal Tunnel SyndromeDocument11 pagesDiagnosis of Carpal Tunnel SyndromeMrAppleNo ratings yet
- Bioengineering 07 00090Document15 pagesBioengineering 07 00090Peter BennetNo ratings yet
- Great Vessel and Coronary Artery Anatomy in Transposition and Other Coronary AnomaliesDocument7 pagesGreat Vessel and Coronary Artery Anatomy in Transposition and Other Coronary AnomaliesguleriamunishNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Dural Venous Sinuses and Con Uence of Sinuses Via MRI Venography: Anatomy, Anatomic Variations, and The Classification of VariationsDocument7 pagesEvaluation of Dural Venous Sinuses and Con Uence of Sinuses Via MRI Venography: Anatomy, Anatomic Variations, and The Classification of VariationsYulita MustikasariNo ratings yet
- Pedroso 2003Document13 pagesPedroso 2003Harish SubramanianNo ratings yet
- CFD and PTV Steady Flow Investigation in An Anatomically Accurate Abdominal Aortic AneurysmDocument15 pagesCFD and PTV Steady Flow Investigation in An Anatomically Accurate Abdominal Aortic Aneurysmrehena mojammelNo ratings yet
- PIIS0003497509012442Document5 pagesPIIS0003497509012442Tri RachmadijantoNo ratings yet
- Experimental Methods: 164 B. R. Thoomukuntla Et AlDocument4 pagesExperimental Methods: 164 B. R. Thoomukuntla Et AlMauricioArdilaNo ratings yet
- Boundary Conditions by Schwarz-Christoffel Mapping in Anatomically Accurate HemodynamicsDocument17 pagesBoundary Conditions by Schwarz-Christoffel Mapping in Anatomically Accurate HemodynamicsRaviTeja DuggineniNo ratings yet
- Latar Belakang Epidemologi Tujuan Metode Hasil Simpulan ReferensiDocument2 pagesLatar Belakang Epidemologi Tujuan Metode Hasil Simpulan ReferensiTeguh SNo ratings yet
- Thank You PDFDocument1 pageThank You PDFTeguh SNo ratings yet
- COntoh 2Document2 pagesCOntoh 2Teguh SNo ratings yet
- Analisis Penilaian HarianDocument12 pagesAnalisis Penilaian HarianTeguh SNo ratings yet
- Example Sentence S-P-ODocument1 pageExample Sentence S-P-OTeguh SNo ratings yet
- Explore: NotesDocument15 pagesExplore: NotesTeguh SNo ratings yet
- Analisis Penilaian Harian Tema: Sub TemaDocument5 pagesAnalisis Penilaian Harian Tema: Sub TemaTeguh SNo ratings yet
- Analisis Uts Tema 2Document5 pagesAnalisis Uts Tema 2Teguh SNo ratings yet
- Resume: Title Sampling Technique Research Design Analysis (Multivariate) ConclutionDocument1 pageResume: Title Sampling Technique Research Design Analysis (Multivariate) ConclutionTeguh SNo ratings yet
- Gambaran Status Gizi Balita Di Posyandu RT 5 RW V Perumahan Villa Tembalang Bulusan, Tembalang, SemarangDocument7 pagesGambaran Status Gizi Balita Di Posyandu RT 5 RW V Perumahan Villa Tembalang Bulusan, Tembalang, SemarangTeguh SNo ratings yet
- Analisis Dan Perancangan Sistem Informasi: Brav Deva BernadhiDocument8 pagesAnalisis Dan Perancangan Sistem Informasi: Brav Deva BernadhiTeguh SNo ratings yet
- Latar Belakang Epidemologi Tujuan Metode Hasil Simpulan ReferensiDocument2 pagesLatar Belakang Epidemologi Tujuan Metode Hasil Simpulan ReferensiTeguh SNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Lower Limb FinalDocument52 pagesIntroduction To Lower Limb FinalRafique Ahmed100% (3)
- 553 1 NLSC Sample 24 GuideDocument6 pages553 1 NLSC Sample 24 Guidekenethwaiswa77No ratings yet
- Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus (Includes: Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus, Autosomal Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus, X-Linked)Document18 pagesNephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus (Includes: Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus, Autosomal Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus, X-Linked)ironNo ratings yet
- Good BooksDocument16 pagesGood BooksFbihansip bancel100% (1)
- Post-Transcriptional ModificationDocument20 pagesPost-Transcriptional ModificationZain YaqoobNo ratings yet
- Oral Physio Slides - 5.mastication Dynamics of OcclusionDocument48 pagesOral Physio Slides - 5.mastication Dynamics of OcclusionMuhammadHafizZainudinNo ratings yet
- Talley & O'Connor Quiz SampleDocument5 pagesTalley & O'Connor Quiz SamplefilchibuffNo ratings yet
- Background Results: DR Aditya Bhat, DR, Amit Misri Department of Paediatric Cardiology, Medanta-The Medicity, GurgaonDocument1 pageBackground Results: DR Aditya Bhat, DR, Amit Misri Department of Paediatric Cardiology, Medanta-The Medicity, GurgaonADNo ratings yet
- Listening 2Document19 pagesListening 2Angelica BagosNo ratings yet
- Abdominal DistensionDocument10 pagesAbdominal DistensionMorad ImadNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Endocrine SystemDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Endocrine Systemjonelllantero032No ratings yet
- COVID ProlongadoDocument22 pagesCOVID ProlongadoSMIBA MedicinaNo ratings yet
- Organic AcidsDocument25 pagesOrganic Acidssatti_indianNo ratings yet
- Management of Severe Hyperkalemia PDFDocument6 pagesManagement of Severe Hyperkalemia PDFCarlos Navarro YslaNo ratings yet
- Hema 2 - Prelim Topic 1-Intro To HemostasisDocument4 pagesHema 2 - Prelim Topic 1-Intro To HemostasisLowenstein JenzenNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument7 pagesEndocrine SystemSolita PorteriaNo ratings yet
- English IIDocument107 pagesEnglish IIlauroNo ratings yet
- Argaud Et Al. - 2018 - Facial Emotion Recognition in Parkinson's Disease A Review and New HypothesesDocument14 pagesArgaud Et Al. - 2018 - Facial Emotion Recognition in Parkinson's Disease A Review and New HypothesesAleja ToPaNo ratings yet
- 4 PerceptionDocument44 pages4 PerceptionSanjeev KumarNo ratings yet
- Basic of Cardiovascular and Respiratory SystemDocument59 pagesBasic of Cardiovascular and Respiratory SystemMonika ChaikumarnNo ratings yet
- Scientific Posts: Csir-National Botanical Research InstituteDocument10 pagesScientific Posts: Csir-National Botanical Research InstituteYogesh KapilNo ratings yet
- 1ST Proff MBBS Papers (2021-11)Document66 pages1ST Proff MBBS Papers (2021-11)drbishalchowdhury13No ratings yet
- EOT2 BiologyDocument21 pagesEOT2 BiologyKasumi SatoNo ratings yet
- HPLC 09 2014Document29 pagesHPLC 09 2014api-243480627No ratings yet
- ISC Class 11 Bio Specimen PaperDocument6 pagesISC Class 11 Bio Specimen PaperparamNo ratings yet
- Davis's NCLEX-RN® Success 3E (2012) - MEMORY AIDS - IMPORTANTDocument4 pagesDavis's NCLEX-RN® Success 3E (2012) - MEMORY AIDS - IMPORTANTMaria Isabel Medina MesaNo ratings yet
- Materi HE GinjalDocument61 pagesMateri HE GinjalYafi Dyah C.INo ratings yet
- Рецептор ба түүний төрлүүдDocument9 pagesРецептор ба түүний төрлүүдАРСАЙNo ratings yet
- (McCauley-Bush, Pamela) Ergonomics Foundational (Book4You) PDFDocument347 pages(McCauley-Bush, Pamela) Ergonomics Foundational (Book4You) PDFmikiNo ratings yet
- Common Diseases of NewbornDocument162 pagesCommon Diseases of NewbornMichelle ThereseNo ratings yet